Thanks to heated floors, you can significantly increase the level of comfort in the room. Heated floors in a private house or apartment are an excellent opportunity to get an evenly heated, cozy room. The most affordable and effective is a water-heated system, which consists of polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes arranged according to a special pattern. Such a system makes it possible to reduce the cost of heating a room with conventional equipment (for example, electric heat radiators), looks aesthetically pleasing and is safe. How to lay a heated floor with water coolant with your own hands, read below.
Range of application and circuit features
Each project requires an individual calculation of the foundation depending on the characteristics of the soil, the weight of the house, the ratio of the building area to the length of the perimeter, the characteristics of the climatic zone and other factors.
To generalize as much as possible, the Finnish foundation of the design considered can be recommended for use in all climatic zones of the Russian Federation for all categories of soil with an approximate load of 1 - 3 tons per linear meter of MZLF.
The specified range of loads corresponds to most projects of frame houses with 1 - 2 storeys and one-story cottages without limiting the type of their construction. However, adapting UFF to heavier houses is not a problem: changing the design in this case occurs by increasing the cross-sections of the cushion and base of the strip foundation.
Typical design of MZLF - shallow strip foundation
In economic terms, the scheme is only suitable for buildings without basements.
Among the advantages of UFF are:
- An elegant and simple solution to frost protection
- High energy efficiency indicators, only slightly inferior to a scheme such as an insulated Swedish stove (USP).
- Good adaptability to changes in projects in terms of loads, base height, sequence of individual stages, maintainability of laid communications.
- The ability to carry out work with little effort and little money, taking significant breaks in time (for example, you can do without formwork, and it is permissible to work on heating installations and cast the floor slab after the roof has been installed).
- The option adapts better to the slopes of the site than USHP.
- The scheme can be used at high groundwater levels
The (largely conditional) disadvantages of this type of foundation are associated with insufficient energy efficiency in relation to the “passive house” concept and a significant amount of excavation work. The cost of the cycle when implementing schemes close to Omatalo technology is 100 - 120 $/m² of construction plan.
The option is more expensive than the standard zero cycle. However, if you take into account the insulation and wiring of communications, the Finnish scheme is a little cheaper.
A technical and economic comparison with USHP gives the following results: with a plinth height of 80 cm and above, the option is 10% - 15% more expensive than an insulated Swedish stove. The height of the plinth significantly affects costs, since it is directly proportional to the volume of backfill materials delivered to the site.
It should be noted that replacing extruded polystyrene foam with polystyrene foam (while maintaining the thickness of the heat-insulating layer) does not significantly reduce the cost of the project (the total amount is reduced by no more than 2% - 3%). If we assume the same level of energy efficiency, taking into account moisture absorption, then insulating the floor with PSB-S slabs is more expensive than using EPS.
Transcript
2 REASONS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BOILER AND CHP SYSTEM IN FINLAND? The need for effective use Shortage of finance for combustible fuels after the Second World War Solid fuels must be imported, as they are not available in the country. Competition in the heating market has become the main driver. > High efficiency has become a necessity. Strong municipalities High council tax (20%) Public buildings are good customers Residents' cooperatives are good customers, not apartment owners State. property (streets, parks) is also involved in the development of boiler plants > The participation of municipalities is crucial
3 WOULD YOU LIKE TO HAVE THE BEST HEATING SYSTEM IN THE WORLD? Minimum heat losses Minimum water changes Maximum reliability Efficient network Efficient production Three quarters of heat is produced in thermal power plants High productivity Widespread use of renewable sources Low emissions Sustainable environment Financial sustainability Low heat tariffs High profits High share of thermal power plants No subsidies 3
4 Highly efficient and reliable district heating systems in Finland The heating system is available to the consumer 99.98% of the time per year (maintenance takes 2 hours per year, including scheduled work) The probability of failure is 0.1 damage/km (compared to 1-2 damage/km in countries with transition economies) Prevention is part of maintenance, which minimizes the risk of failures The operating efficiency of heat supply systems (efficiency) is 91% (in some cities 94%) The frequency of water addition is once a year The minimum service life of heat pipes is 50 years (with the possibility of operation up to 100 years or more) 4
5 WOULD YOU LIKE TO HAVE A DISTRICT HEATING AND COOLING SYSTEM WITH EXCELLENT EFFICIENCY? Key performance indicator Finland (200 companies on average) Transition countries Heat loss 6-9% 15-40% Water level replenishment frequency / year Reliability 99.98% 99% or lower Share of CHP in the heating system 74% 30-60% Generation efficiency 93% 70-90% Share of renewable energy sources in production 40% 0-10% Personnel productivity (GW/person) Turnover profitability, % 10-20% Low or negative 5
13 Construction of level substations Prefabricated compact substations, already tested in factories Minimum 2 heat exchangers per substation Hot water temperature 55 C The substation is operated all year round The substation belongs to the client, but requires the approval of the network owner In the picture above: installation in Heibei Province, China In the picture on the right: substation for private use (50 kw), Helsinki
14 Features of centralized heating supply Heat production Heat production Fuel Fuel in Heat distribution Heat distribution All clients are provided with level substations Consumption is calculated on the basis of meters, since the 1950s. Heat production companies always operate on a commercial basis. The lowest heat prices and the highest company profits in Europe.
21 Why Finnish district heating and cooling system? The coldest country in Europe provides the world's best district heating-cooling and thermal power system! Finland's geographical position between east and west provides unique understanding and decision-making for different climate conditions. A network of specialists provides comprehensive service! Finnish companies offer innovative ideas and proven services. Many years of experience in the use of various energy sources allows us to promote also renewable energy sources Providers of reliable solutions. Finland has been recommended as a reliable partner. Through clear planning we can provide a certified final product that meets legal and consumer requirements. The system is unique know-how in Finland! District heating and cooling is a profitable business! 21
Video on the topic: the process of installing the Finnish foundation UFF
The construction of any house begins with laying the foundation. Its strength, stability, quality of materials and work performed affect the service life of the entire structure. Among the modern methods of constructing foundations for a house, the Finnish slab foundation option is very popular.
This technology was invented in Germany, but it is called Finnish because... it is widespread in Norway, Sweden, and Finland. And, in terms of its capabilities, it is excellent for the Russian climate.
Stove in the house
To understand why Finnish houses are so warm, you need to know how houses are built in Finland. They are framed and modular, and most often they are made of wood. Even the supporting beams are made of wood.
This does not mean that throughout the country there are only wooden houses. They are decorated with other materials to make them look like modern homes. Most often, Finns heat themselves with wood. Most often, the stove is made of soapstone. It is also called soapstone and it retains heat very well.
The uniqueness of these stoves is that the material quickly absorbs heat and gradually releases it to the room. Despite the fact that it is a stone, it does not cool quickly, but gradually. This material is used for the construction of saunas, it is involved in the decoration of walls and floors.
Some Finnish factories even use it for dishes. The Finnish stove is very similar to the Russian one. You can not only throw firewood in it to warm the room, but also for baking bread.
Unlike Russian stoves, there are several large factories in Finland that produce Finnish stove heating. Over the many years of work, a defect has never been detected. The most famous manufacturer is Tukikivi. The stoves of this company are widely known in Russia. The high cost prevents Russians from purchasing such equipment, although everyone understands that there is nothing good to expect from a cheap product.
Step-by-step technology for arranging a Finnish slab foundation
- Work is being carried out to prepare and clear the construction site, and ring drainage is installed (if necessary).
To do this, first, using a level, it is necessary to calculate the height difference between the extreme points of the surface where the house will be located. This provides a more accurate construction project and selects the point relative to which the surface will be leveled;
- The future foundation is marked using pegs that are driven in around the perimeter of the construction site and a fishing line stretched between them;
- The soil layer is removed;
Advice! The removed layer of soil can then be used to create a garden.
Attention! When building on soil with a high groundwater level, a drainage system is installed at the initial stage of construction.
Advice! If a circular drainage system is nevertheless provided, then each layer of the slab (gravel, sand) is laid with a layer of geotextile.
The result is an even slab of relatively small thickness with good strength and excellent thermal performance. The floor does not directly touch the slab, thanks to the insulation layer. All communication systems are laid in the screed, including the heating system, which can be laid in the floor throughout the entire area of the living space.
Depending on the load, the depth and location of the stiffeners may vary. The heavier the building is planned to be built, the more rigid the structure is assumed at the stage of laying the foundation.
Law of 2 E: how houses are heated in Finland This is Finland
In Northern European Finland, spending on heating is a visible part of any family's expenses. However, in their concern for saving money, Finns do not agree to forget about the environment. The sun, air and earth are good friends of the modern inhabitant of the country of Suomi.
“Even a cold summer is warmer than a mild winter,” a Finnish proverb noted long ago. And even in a mild winter, each house using Finnish technology - be it a high-rise building in a big city, a separate country house or a cottage on a lake - consumes many kilowatt-hours of energy.
The stove still provides heat
Photovoltaic batteries make energy even in Finland. Photo: Niko Nurmi/Tekes
The owner of his home has the opportunity to significantly reduce his own costs. It is much more difficult for the inhabitants of high-rise buildings: they are “hostages” of the central (in Finnish, more precisely: remote) heating supply. What and how the house is heated is sometimes unknown to them, and it is difficult to influence this. Here are lighting and multiple home appliances - they are in your hands: there is intense competition between electrical energy manufacturers. You can go to a specialized website, compare prices and choose a good one. Those who are very reckless in the pursuit of savings change electric companies every year.
About a hundred years ago, the only way to heat your home was with stoves of various designs, and even today, in virtually any new cottage, the fireplace occupies its main place. However, the fireplace now plays a secondary role: it alone cannot heat large houses.
Until quite recently, the best friend of a Finnish homeowner could be called a boiler that was heated with fuel oil. Uncomfortable, uneconomical and unecological, it is not yet forgiven: and at the moment, 20% of the Finnish housing stock is heated in this way. But it’s becoming less and less common to own houses, and never new ones – paying extra cash and spoiling the external environment is absolutely not in Finnish customs. Nowadays in Finland the law of two “Es” rules – economy plus ecology.
Geothermal heating pump draws energy from the ground
Very often, a new house using Finnish technology draws energy, like the mythological Antaeus, from the earth. Because in Finnish conditions at a depth of 200 meters the temperature can reach +10 degrees. Finnish rocks are like huge heating devices: they accumulate heat in the summer and release it during the winter. Tubes are placed in the ground through which 40% ethyl alcohol moves.
A special device is installed in the house: something like a reverse refrigerator with a computer built inside. Naturally, it is expensive, but it is reimbursed in 5-7 years and makes it possible to save 30 percent of electrical energy and more. It is not surprising that such enviable figures also seduce the owners of old houses, and they undertake to remodel their own houses.
Finns are warmed by sun and air
Heating pump in a private apartment in Espoo, Finland. Photo: Sari Gustafsson/Lehtikuva
The Finns even made the surrounding air work for them - just imagine a refrigerator turned inside out, where the cool part is outside, and the heating system with a circulating specialized substance is indoors. In frosts down to -25? this works great: after spending 1 kW of electrical energy on the job, the heating pump will produce up to 2 or even 5 kW of heat.
Such a “warm” refrigerator, or rather, an air conditioning device, is effective for small houses - no more than 120 meters of living area. But for small houses this is a real godsend: there is no need to drill the ground and install expensive equipment: all costs are no more than 2000–3000 euros.
Text: Tatiana Derkach and Vladislav Bykov, October 2012
Calculation of materials for the foundation Finnish slab
When calculating, the following parameters should be taken into account:
- Ground water level;
- The general condition of the soil on the site being built;
- Temperature and climate conditions;
- Number of floors of the future building;
- Exact plan for the location of the walls (for connecting communications).
Advice! This type of foundation involves many preliminary stages and a large preparatory work front. And since concrete is poured at once, it is better to trust the professionals.
A Finnish slab foundation is chosen if:
- Construction is required as soon as possible;
- Construction is carried out on difficult terrain;
- Presence of high groundwater levels;
- Construction will be carried out on soil with strong freezing;
- A durable and strong foundation structure for the house is necessary;
- This implies the installation of a floor heating system;
- The project requires the creation of a high building plinth;
- It is not possible to dig a deep pit;
- High energy efficiency required;
- There is no need to install a subfloor.
Upon completion of the work, finishing work can begin.
Construction of a house begins with the installation of the foundation. The quality of its execution, stability and strength will affect the service life of the structure. It is important to choose the right type of foundation for your home. Among its many types, the Finnish slab foundation is popular.
The Finnish stove was invented by Finnish engineers. The resulting slabs are of relatively small thickness. They are characterized by durability and good thermal performance. This type of foundation is recommended for use in buildings where it is planned to install a heated floor system. This system is widespread in Finland, Sweden, and Norway. In these countries, frame-type houses are often built; this foundation can be used not only for frame houses.
The Finnish stove is considered a variation of the Swedish stove and has some differences. It is adapted to the climatic conditions of Russia and was developed taking into account the individual needs of developers in this region. This type of slab differs from the Swedish one in the presence of additional stiffening ribs around the perimeter, as well as in the peculiarities of laying insulation.
The Finnish slab is laid over the entire area of the building, and the pressure on the ground is significantly reduced. The design is a complete platform for the home. Heavily heaving soils, which are characterized by the rise of the base when the soil freezes, are not dangerous for such a foundation. Thanks to the peculiarities of its construction, the load on it from the soil is reduced to almost a minimum.
Stiffening ribs allow you to increase the height of the section in places where large loads are expected. The location of the stiffeners depends on the structure. For example, the larger the size of the building, the more rigid the structure must be made.
To summarize what a Finnish slab is: it is a type of foundation installed on various types of soil for the construction of a house in which it is planned to install a heated floor system. This foundation can be used to construct a building without a heated floor system. The external walls of the future building are supported by additional stiffening ribs. Insulation is laid on top of the slab, after which a screed is made.
The insulation protects the heat from the floor from dissipating, since the floor does not directly touch the slab. The screed is made after the underfloor heating system and sewer pipe system are installed. Therefore, it is recommended to make such a foundation for a building where the construction of heated floors is provided. This creates a flat floor with a heating system.
The slab has a relatively small thickness, which allows it to be used in places where there is a high groundwater level. However, when building a foundation, it is necessary to create a drainage system. Most often, it is recommended to create a circular drainage and a sand cushion, and these layers should be separated by geotextiles. However, with low groundwater levels, such drainage may not be suitable. Since to install this foundation there is no need to prepare a very deep pit, therefore all preparation work for pouring this foundation is reduced to a minimum.
System installation
The construction of a water floor using logs based on Finnish technology requires a standard installation algorithm, regardless of the materials used in the work, be it gypsum plasterboard, gypsum fiber board (V) or other slabs.
evrazForumHouse Member
Similar technologies, where pipes or heating cables are sealed with a solution in the grooves of gypsum plasterboard and covered with a top layer of gypsum plasterboard, are painted by many manufacturers of underfloor heating systems.
Water-heated floor on joists in a wooden house.
On FORUMHOUSE you can read detailed instructions for installing a subfloor yourself.
Insulation
The system should transfer heat upward, and not pass it into the ceiling, which will lead to increased heating of the medium and a decrease in efficiency. A vapor barrier is laid between the joists, a layer of insulation (mineral wool, EPS) is placed on top, covered with a layer of vapor barrier. Insulation will protect both the wood and the insulation from condensation, provided that it is not just plastic film. Under a regular film, condensation will form in even larger quantities.
Base
When installing the system, the optimal distance between the logs should be observed - 60 cm; in this case, there is no need to create additional sheathing to distribute the load, and the sheets form a monolithic structure. The sheets are attached to the joists with self-tapping screws.
Highway
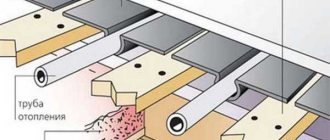
The size and diameter of the pipe depends on the area of the room, heat loss, and the power of the equipment used to heat the coolant. The most popular range is 16-20 mm in diameter. The pipe pitch is also individual in each specific case, but on average it is 100 mm, more often at the edges. The pipe is secured with special metal or plastic brackets or self-made clamps.
Warm water floors, wooden floors.
Laying
The space between the contours of the pipes is filled with segments cut from sheets; there should be grooves around the pipes for filling with glue. The optimal groove size is 3 pipe diameters, this is enough for maximum heat removal. The segments are screwed with self-tapping screws, in increments of 10–15 cm; the length of the fasteners should be sufficient for fixation in the joists.
Filling
To fill the grooves, tile adhesive is most often used; a cement-sand mixture can be used, but when mixing, it is necessary to use plasticizers. To increase adhesion and ensure that the finishing layer of the “pie” is more firmly connected to the intermediate layer, it is recommended that after filling the seams with pipes, go over the entire surface with the adhesive mixture “to tear off”. This is advice from a user under the nickname Vitaon, he professionally installs such systems and shared his trick with the forum members.
VitaonForumHouse Member
Before the finishing layer, the surface consists of alternating strips of dry plasterboard and ditches filled with adhesive. Immediately before gluing, it is necessary to cover the entire surface with putty, a wide spatula and a thin layer of glue - you will get a homogeneous base. Apply glue on top under the final layer. With this method, adhesion increases many times over.
Finish floor
A water floor over wooden joists allows you to use almost any decorative covering in a private home; only cheap linoleum is a contraindication - it will have a noticeable “smell” when constantly heated. The best option is ceramic tiles or laminate flooring. In the case of laminate, there is no backing underneath it due to its thermal insulation properties.
Design Features
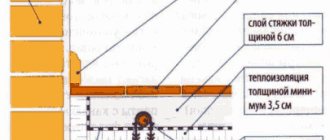
The design is a cold circuit. The insulation must be laid on the foundation slab, and the thickness of the insulation must be at least 150 mm. When using insulation, the warm floor on the first floor does not touch the cold contour of the base slab. The heated floor is laid in a reinforced screed, which should be 80 mm.
A special feature of this foundation is its quick installation, since the slab is poured in one sitting. However, the cost of this design is higher than other types. When arranging this foundation, it is necessary to use a reinforced screed. The insulated Finnish stove is suitable for the construction of almost any house. These can also be frame-type houses.
You can choose the type of Finnish slab for the foundation in the following cases:
- if you need a foundation for a house that needs to be built quickly;
- if a durable foundation is needed;
- if a heated floor system is installed in the house;
- if the building will be erected on soil with severe freezing.
Warm floor on a wooden base
A more affordable way to install a water-heated floor on a wooden base is to install it using a plank method. The main advantage of this option is that the base does not need to be disassembled to install the system: the heated floor is laid out on a used base.
Related article: Interior of a one-room apartment: how to fit everything into 35 square meters (43 photos)
To lay a warm water floor on a wooden base, you should purchase special metal products into which pipes are inserted
It is recommended to disassemble the floor only if it makes squeaks when walking or sag.
Before laying, it is necessary to calculate the required length and pitch of the pipes. To do this, you can use either the services of a specialist or an online calculator.
The optimal pitch between pipes for our climate is 150-200 mm. It is better to choose pipes for the system with a diameter of 1.6-1.7 cm, corrugated.
The simplest installation method is a snake. After the calculations have been made, you will need to mark the floor, starting from the walls and moving towards the center of the room. The heating pipes and chipboard guides will be laid according to the markings.
The guides should be placed so that there is space between them for the pipes plus 1 cm.
The guides can be attached to the subfloor using self-tapping screws or nails. In this case, as in the previous case, the guides must have rounded ends for turning the pipes. To increase heat transfer, you can wrap heating pipes in foil.
Before laying down the plywood and finishing coat, you should turn on the heating and check the circuit for leaks.
Builders advise choosing materials that do not contain formaldehyde for flooring.
Advantages and disadvantages
This foundation has its pros and cons of use, like any other type of foundation.
There are the following advantages of the Finnish stove:
- possibility of creating a high base;
- a small amount of excavation work is required, since a deep pit is not needed under the Finnish slab;
- high energy efficiency;
- no subfloor installation required;
- the ability to install a heated floor system;
- can be installed on difficult terrain;
- suitable for installations with high groundwater levels;
- Possibility of finishing after installation is complete.
This type of foundation is excellent for constructing buildings on difficult types of soil. This can be land with deep soil freezing, sandy, swampy and heaving soils.
- relatively expensive design;
- Installation of a Finnish slab can take up to 2 weeks, depending on the characteristics of the soil and the speed of completion of the main work.
What is the difference between Finnish heating and Russian
The Finnish heating system is distinguished by the fact that it does not have a coolant. This eliminates the worry about pipes. The heat is accumulated by the stove itself, and this heat is enough to provide a large room, even several floors. These functions are beyond the capabilities of any boiler. Only a Russian solid fuel boiler can compete with it, but you need to constantly add firewood to it, and this is inconvenient.
Russians most often heat their homes with gas or electricity. Both of these methods are very expensive and people have to pay about 100 euros during the winter month just to keep their house warm. People who live on land sometimes install wood-burning stoves, but in this case the residents even have to get up in the middle of the night to add wood to the firebox. It is not comfortable.
In Russian villages, electricity costs less than in the city. Therefore, those people who do not want to spend money on a wood stove buy electric boilers. In any case, the Finnish heating method is becoming more and more popular every year. Since there is demand, then maybe there will be more offers, and prices will drop a little so that a Russian person, even with a small income, can install such heating.
Heat-intensive Finnish stoves are the main source of heat in Finland. The house is heated when there is a need for it. Remember that a warm home can only be ensured by high-quality stove heating.
Materials
There are many ways to protect the interior of a house from the cold, but first of all you need to insulate the floor and roof, since it is through these structural elements that the main heat loss occurs. Only when these structures are well protected from the cold does it make sense to insulate a wooden house from the inside or outside.
It is advisable to insulate the floors of the second and subsequent floors if they are installed on concrete floors.
For insulation, various materials with a low thermal conductivity coefficient are used:
- polystyrene foam or penoplex;
- polyurethane foam;
- mineral or glass wool;
- penofol;
- wood sawdust.
Each of them has its own advantages, and in most cases the choice depends on the availability of a particular material and the personal preferences of the homeowner. The thickness of the heat insulator depends on the climate in which the wooden house is located, on its location in relation to the ground level, as well as on the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Thermoplastics
Polystyrene foam and penoplex are very similar materials. They are produced by foaming plastic masses, sometimes introducing additional additives that prevent decomposition and make them unattractive to rodents. Both of these materials have a very low thermal conductivity.
Note! For comparison: in terms of thermal efficiency, 5 cm thick foam is equivalent to 75 cm thick brickwork.
It is convenient to use such materials, as they are produced in the form of sheets of various thicknesses. Transporting them to the construction site is not a hassle. They are very light and durable. You can cut polystyrene foam or penoplex with a regular stationery knife. When insulating the surface, they can be used to seal the resulting gaps at the joints with ordinary polyurethane foam. Adhesion with insulation is very good.
Polyurethane foam is a material that is more commonly seen in everyday life as foam mats. Such mats are not used in construction, and polyurethane foam is applied to the surface by spraying. Later, during the process of hardening and polymerization, it foams and hardens. As a result, polyurethane foam forms a durable, waterproof, airtight, warm coat for building structures.
Mineral wool
Various construction wools have been used as insulation for a very long time. Currently, glass wool, mineral or basalt wool are most often used.
In appearance and production technology, they are very similar to each other, differing from each other only in the raw materials used. To obtain them, raw materials are heated, melted using special equipment, and then drawn into threads. Later, when these fibers harden, looms that vaguely resemble weaving machines knit a bulky mass of low density from them.
Such insulation is produced in the form of rectangular mats of various thicknesses or in the form of rolls.
Penofol
Penofol refers to thin plates or sheets of polyethylene foam. Their thickness can be from 3 mm to 10 mm. In terms of thermal insulation qualities, this material is comparable to foam plastic or penoplex, but it is more convenient to work with due to the fact that it is flexible. Penofol is produced and supplied for sale and to construction sites in rolls 0.5 meters and 1 meter wide.
The insulation is produced in three versions - foil on one side, on both sides, or foil on one side and with an adhesive layer applied on the other. The latter option is most preferable to use, since installation of such insulation takes very little time. It is enough to cut out the required blank from the sheet and, having separated the protective film from the adhesive layer, apply it to the wooden surface and press briefly.
Sawdust
Sawdust has traditionally been used as insulation, since it was a by-product of any sawmill production, and its origin has always accompanied the production of lumber. For a very long time, sawdust was used to insulate wooden floors, falling asleep in layers between the joists.
A mass of sawdust, if it is not subject to getting wet, can lie in a closed space for years without caking. At the same time, the low density of such insulation is maintained, which provides excellent thermal insulation properties. The disadvantage of such insulation is that the sawdust cakes very quickly and even begins to rot, as soon as you wet them a little. To prevent rotting of sawdust and damage by various wood borers, they are treated with a solution of potassium permanganate or the sawdust is mixed with lime.
Preparing the base
To install a heating structure along joists, you will first need to prepare a base on which the layers of the heated floor “pie” will be laid in a certain sequence.
Preparation consists of the following steps:
Stage one. The base of the subfloor is leveled. If there are defects in the form of cracks and chips, they are eliminated. The surface should not have a large slope.
Stage two. After the base is prepared, a layer of waterproofing is placed on it. Today, the market offers a large selection of materials that provide reliable protection against moisture penetration. For waterproofing under heated floors, polyethylene film is suitable. The sheets are laid overlapping, and the joints are sealed with tape.
Laying the waterproofing layer
Stage three. At this stage, the installation of wooden logs is carried out.
Stage four. Thermal insulation material is laid between the laid joists.
Installation of heat insulator
Stage four. The heating system is installed using one of the methods below.
Complete solution
By definition, a foundation is a structure that transfers loads from a building to the ground. However, the Finnish foundation is always a comprehensive solution including:
- excavation;
- water supply and electricity supply to the house;
- reserve mortgages for communications;
- sewer line to the treatment plant;
- drainage system;
- storm drainage;
- protective grounding circuit;
- reinforced concrete load-bearing tape;
- plinth ready for finishing;
- waterproofing of load-bearing structures;
- protection of soil from freezing;
- radon protection system;
- floor insulation;
- house heating system - water heated floor;
- distribution of water supply pipes with hot water recirculation;
- routing of sewerage pipes with installation of drains;
- air intake line from the street for burning the fireplace;
- reinforced floor screed.
How to insulate the floor of a wooden house with your own hands
The most important is thermal insulation over a cold crawl space, basement or open space such as in a house with a pile foundation. Before starting work, the logs must be hemmed underneath with OSB, boards or other material that is resistant to moisture and temperature fluctuations.
Installation of a moisture-and-windproof membrane
It is clear that there is no wind in the basement, and there is no need to protect the insulation from blowing out. But such films have good vapor permeability. They freely allow water vapor to pass through themselves, which allows excess moisture to erode from the mineral wool.
Installation is carried out without strong tension. The panels are overlapped over the joists and hemming. Attached with a stapler. The film should be applied to the walls by 20-30 cm.
Laying mineral wool
The slabs are inserted between the joists at random. Do not compress too much, otherwise excessive compaction will cause rapid shrinkage. The cracks are filled with scraps of mineral wool, which makes the process virtually waste-free.
Important. You cannot walk on thermal insulation boards.
Installation of vapor barrier
The film is spread on the insulation with an overlap of 30 cm on the walls. The panels are laid overlapping and glued with tape so that moist air does not penetrate through the leaks. If communications pass through the floor, the exit points are carefully sealed.
Installation of the counter-lattice bar
This stage is not always present even in manufacturers’ technological maps, but if the subfloor is made of natural wood, it is advisable to install a counter-lattice.
The bars are packed onto the joists through a layer of vapor barrier. The minimum thickness is 25 mm. A ventilation gap is not needed if the subfloors are made of moisture-resistant materials.
Subfloor installation
Boards are attached to the counter-lattice, and sheet materials - OSB, DSP, plywood, etc. - are attached to the joists. When laying dry screed, a damper tape is laid along the walls. It not only compensates for temperature changes, but also improves sound insulation. By the way, many manufacturers recommend laying soundproofing materials at all joints of structures to reduce noise.