Formula for calculating Gcal for heating
Note!
People often encounter the problem of converting calories into kilowatts, which is explained by the use of a unit of measurement in many specialized manuals, which is called “C” in the international system. > Of course, such a problem will be completely eliminated if there is a hot water meter in the living room, since it is in this device that there are already pre-set readings that display the heat received. By multiplying these results by the established tariff, it is possible to obtain the final parameter of the heat consumed.
Convert Gcal to kW/hour
Thermal energy can be measured in various units, but in official documentation from housing and communal services it is calculated in Gcal. Therefore, it is worth knowing how to convert other units to gigacalories.
The easiest way to do this is when the relationships between these quantities are known. For example, it is worth considering watts (W), in which the energy output of most boilers or heaters is measured.
Before considering the conversion to this Gcal value, it is worth remembering that, like a calorie, a watt is small. Therefore, kW (1 kilowatt equals 1000 watts) or mW (1 megawatt equals 1000,000 watts) are more often used.
In addition, it is important to remember that power is measured in W (kW, mW), but kW/h (kilowatt-hours) is used to calculate the amount of electricity consumed/produced. In this regard, it is not the conversion of gigacalories to kilowatts that is considered, but the conversion of Gcal to kWh.
How to do this? In order not to suffer with formulas, it is worth remembering the “magic” number 1163. This is exactly how many kilowatts of energy must be spent in an hour to get one gigacalorie. In practice, when converting from one unit of measurement to another, you simply need to multiply the number of Gcal by 1163.
For example, let's convert into kW/hour 0.05 Gcal required to heat one cubic meter of water by 50 °C. It turns out: 0.05 x 1163 = 58.15 kW/hour. These calculations will especially help those who are thinking about changing gas heating to more environmentally friendly and economical electric heating.
If we are talking about huge volumes, we can convert it not into kilowatts, but into megawatts. In this case, you need to multiply not by 1163, but by 1.163, since 1 mW = 1000 kW. Or simply divide the result obtained in kilowatts by a thousand.
New Rule 354 formulas introduced by Decree 1708
New formulas for calculating heating dated 12/28/2021 No. 1708 came into force . This resolution introduced amendments to Rule 354 , which changed the formulas for calculating the cost of heating in apartment buildings.
In 2021, the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation (CC RF) twice considered cases related to the procedure for calculating fees for utility heating services. By Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated July 10, 2021 No. 30-P, the Federal Assembly and the Government of the Russian Federation are entrusted with the obligation “guided by the requirements of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the legal positions of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation based on them, expressed in this Resolution, to make the necessary changes to the current legal regulation , including providing for a procedure for determining the payment for utility services for heating in apartment buildings that are equipped with a collective (community) heat energy meter and in which not all premises are equipped with individual heat energy meters, taking into account the readings of the latter"
, and by Resolution No. 46-P dated December 20, 2021, the Constitutional Court decided “
The Government of the Russian Federation must, guided by the requirements of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the legal positions of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation based on them, expressed in this Resolution, immediately make the necessary changes to the current legal regulation , including providing for a procedure for determining the payment for utility services for heating in apartment buildings, individual residential premises in which have been transferred to individual apartment sources of thermal energy, bearing in mind the validity of imposing on the owners and users of such residential premises - provided that the regulatory requirements the procedure for restructuring the intra-apartment heating system in force at the time of its implementation was observed - only the costs associated with the consumption of thermal energy for the purpose of maintaining common property in an apartment building
.
In accordance with the above Resolutions of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, on December 28, 2021, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted Resolution 1708, which introduced significant amendments to the Rules for the provision of utility services regarding the procedure for calculating the cost of heating .
Calculation methods
The price for heating is calculated in the following ways:
- if there is no communal meter, according to consumption standards, according to formulas 1, 2, 3, 4;
- if the apartment building has a common building metering apparatus, but none of its premises has individual meters - according to formulas 7, 11;
- if the apartment building is equipped with a common building meter, and one or more of its premises (but not all) has an individual meter - according to formulas 7, 11;
- in an apartment building, in which a common house accounting apparatus is installed, and all premises are equipped with individual devices, according to formulas 10, 11;
- in a private house in which an individual meter is installed - according to formulas 11, 12;
- in an apartment building with a common building meter, despite the fact that more than half of the premises have heat energy distributors - according to formulas 7, 11, and is also adjusted once a year according to formula 5. Homeowners at a general meeting can appoint more frequent adjustments. In the event of equipment breakdown or violation of the integrity of seals, the premises are treated as if they do not have switchgear.
The volume of consumed heat energy when paying for heating during the heating season, if the apartment building is equipped with a common house meter and an open system (natural circulation) is used, is calculated according to the following system: the volume of consumed heat energy is equal to the difference between the volume of consumed heat energy according to the data of the common house meter and the product of the volume of heat energy used for hot water supply. The volume of heat energy for hot water is calculated according to the standard heat energy consumption for hot water supply, and the volume of hot water used by the apartment building for general house needs.
If metering devices for heating and hot water in an apartment building are installed separately, and the calculation is carried out during the heating season, then the price for heating is calculated according to the standard scheme.
When paying for heat energy during the heating season, the amount of heat energy calculated according to the readings of individual metering devices is used only for those periods for which the meter readings were transmitted by consumers. When paying for heat energy evenly throughout the year, the readings of individual metering devices are used when adjusting the readings for the past year.
If an individual heating meter was installed earlier than three months ago, then the payment for heat energy is calculated based on the standards in the same case, but if the apartment building has a common building meter, then the payment is calculated according to the rules for houses with common building meters.
If, during the verification of previously submitted information about the readings of individual metering devices, inaccuracies or malfunctions in the operation of the devices were discovered (including violations of the integrity of the seals), the verification contractor must provide the consumer with a recalculation of the cost of services, as a result of which an additional charge will be made or the overpaid funds will be written off due to subsequent periods.
Methodology for calculating thermal energy for heating
Please note that this option includes only the actual volumes of energy consumed and if your house is equipped with a centralized hot water supply, then the amount of heat spent on hot water supply needs is not taken into account. The same applies to non-residential premises: if they are not in the house, then they will not be included in the calculation.
- 0.025 Gcal – standard indicator of heat consumption per 1 m² of living space;
- 100 m² – the sum of the area of premises intended for general house needs;
- 70 m² – total area of the apartment;
- 7,000 m² – total area (all residential and non-residential premises).
We recommend reading: When is a grace day in Zhukovsky city park
What is a Gigacalorie and how many calories are in it?
The concept of Gigacalories is most often found in documents in the field of thermal power engineering. This value can be found in receipts, notices, payments for heating and hot water.
It means the same thing as a calorie, but in a larger volume, as evidenced by the prefix “Giga”. Gcal determines that the original value has been multiplied by 109. In simple terms: 1 Gigacalorie contains 1 billion calories.
Like the calorie, the Gigacalorie does not belong to the metric system of physical quantities.
The table below shows an example comparison of values:
| Console | Number of calories |
| kcal (kilocalorie) | 1 000 |
| Mcal (megacalorie) | 1 000 000 |
| Gcal (gigacalorie) | 1 000 000 000 |
The need to use Gcal is due to the fact that when heating the volume of water needed for heating and household needs of the population, even 1 residential building releases a colossal amount of energy. Writing numbers denoting it in documents in calorie format is too long and inconvenient.
A value such as a gigacalorie can be found in payment documents for heating
You can imagine how much energy is spent during the heating season on an industrial scale: when heating 1 block, district, city, country.
How to calculate heating payments
S.o. = Pl x N x T, where
- S.o. – the amount of payment indicated on the receipt;
- Pl is the area of the apartment to which heat is supplied;
- N – standard heat consumption, calculated using the formula given above;
- T – tariff for consumed utility service. This value is individual for each region. For Moscow, for example, it can be 1,800 rubles per Gcal, and in Novosibirsk – 1,300 rubles per Gcal.
- The house does not have a common meter installed, and fees are charged only during the heating season.
- The house is not equipped with a common meter, and fees are charged all year round.
- A common metering device is installed on the house; payments are made during the heating period.
- The house is equipped with a common meter, fees are charged throughout the year.
- The house has a common metering device; in addition, there are meters in all rooms: apartments and non-residential areas.
Why do we pay for heat supply in EPD in summer?
The Unified Payment Document (UPD) contains accounts for various sectors of the housing sector, including utility costs for the use of heat in the summer. Tenants justifiably have a question: why do I pay for heat supply in the summer, while the heating season is within autumn-spring.
The legislation of the Russian Federation allows for the collection of payments for heat supply in two ways:
- in equal monthly installments;
- only in winter.
Most often, management companies use the first method, since it allows the monthly payment amount to be “spread out” evenly. When accrued using the second method, the costs of the home budget during the heating season will increase significantly, and the rest of the time will not be charged.
You cannot blindly trust the amounts written on the receipt. If there are any doubts about the integrity of housing and communal services representatives, it is best to make independent simple calculations using a calculator using the above calculation methods. If a discrepancy is identified, contact the utility company with a request to issue an invoice again.
Formula for calculating Gcal for heating
What is Gcal? Gcal is a gigacalorie, that is, a measurement unit in which thermal energy is calculated. You can calculate Gcal yourself, but first study some information about thermal energy. Let us consider in the article general information about calculations, as well as the formula for calculating Gcal.
- Q – previous volume of thermal energy;
- V1 is the heat carrier flow rate parameter in the supply pipe. The heat source can be water vapor or ordinary water.
- V2 – volume of water flow in the outlet pipe;
- T1 – temperature in the coolant supply pipe;
- T2 – temperature at the pipe outlet;
- T – cold water temperature.
How to calculate heating bills for your apartment
Calculation methods changed several times, heating provided for general house needs appeared, which was calculated separately from heating provided in residential premises (apartments) and non-residential premises, but then, in 2022, heating again began to be calculated as a single utility service without splitting the fee.
Since 2022, when the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 6, 2022 No. 354 “On the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings” came into force, the procedure for calculating the amount of heating fees has undergone a number of changes.
Standard heating consumption per sq. m.
The calculation methods and examples presented below provide an explanation of the calculation of the heating fee for residential premises (apartments) located in apartment buildings with centralized systems for supplying thermal energy.
Be that as it may, heating standards are not observed, so consumers have every right to file a corresponding complaint and demand a recalculation of tariff plans. The choice of one or another calculation method depends on whether a heat meter is installed in the house or apartment. In the absence of a general house meter, tariffs are calculated according to standards, and those, as we have already found out, are determined by local authorities. This is done through a special decree, which also determines the payment schedule - whether you will pay all year round or exclusively during the heating season.
We recommend reading: Fire Door Kosgu 2022 310 Or 346
Metering devices for houses and apartments
A special device allows you to accurately calculate tariffs for water supply, electricity, gas and heat. Users are allowed to install a heat meter to record heat energy consumption. The device measures in Gcal/h, kW/h and kJ/h. Popular today.
Vane meters
The vane meter operates effectively at temperatures below 22 degrees.
The meter has the form of a mechanism with a perpendicular axis of rotation. The model is characterized by low sensitivity, which allows you to accurately measure heat costs. The regulators are suitable for rooms with good thermal insulation and temperatures of +26 degrees. The vane device, when adjusting the temperature up to +22 degrees, counts a minimum of Gcal.
Advantages:
- inexpensive cost;
- power supply from batteries;
- ease of use;
- accuracy of measurements.
Minuses:
- risk of breakdowns due to water hammer;
- rapid wear of the mechanism;
- increased pressure in the system;
- When the impeller jams, the water flow is not allowed to pass through.
Vane-type devices are suitable for taking readings when a small volume of water is used.
Devices with jump recorders
Electronic devices are more expensive, but they count gigacalories more accurately.
The pulse device takes readings remotely from 2-16 channels, so it is suitable for a private or apartment building. Data recording and transmission is carried out on an LCD monitor, via a plug-in interface, to a laptop or computer using a network cable, or via a GSM network.
The scenario for which readings need to be measured is specified by the user. Ultrasonic devices can be connected to the water and gas supply system, are part of the ASKUE system, or can be combined with the “smart home” system.
Advantages:
- many options for public and private measurements;
- possibility of integration into several accounting systems;
- strength due to the absence of moving parts;
- beautiful appearance and compactness;
- protection from dust and moisture – the meter can be placed in the kitchen or outdoors;
- durable body;
- self-diagnosis functions for problems;
- extensive communication;
- execution with or without a removable computing unit;
- the period between inspections is 6 years, between replacements is 10 years.
Minuses:
- high price;
- communication capabilities depend on the specifics of the output;
- costs for the purchase of flow meters, pressure sensors, remote control modules for basic equipment.
For outdoor use, models with difference recorders with a moisture protection level of IP 68 are suitable.
Heating tariffs in Russia in 2022
The tariff for users connected to the heating network directly without intermediate energy conversion points is lower and amounts to 1806.89 rubles if the resource supplier is and 1773.19 rubles if the supplier is Mosenergo.
On average, Muscovites living in a standard two-room panel house today pay about 1,300 rubles. From mid-2021, the tariff is expected to increase, which should not exceed 4%; accordingly, the payment will increase by approximately 50 rubles. and will be about 1350 rubles.
How is the heating fee calculated according to the standard?
If payment for heat is calculated according to the old rules, and a common building meter is installed in the house, then the final figures in consumer receipts will depend on how much heat the apartment building consumed during the past year.
- The total amount of thermal energy consumed by the house is determined by the readings of the general house meter. Its installation allows you to avoid paying for heat lost along the way due to uninsulated heating mains and other problems of heating networks.
- Heated area of the consumer's apartment or non-residential premises.
- Total heated area of the building. All residential premises are taken into account, as well as entrances, attached shops connected to a common heating system, etc.
- The tariff for thermal energy established by law. Tariffs are determined by local authorities.
This is the ratio of Kal and Gcal to each other.
1 Cal 1 hectoCal= 100 Cal 1 kiloCal (kcal)= 1000 Cal 1 megaCal (Mcal)= 1000 kcal = 1000000 Cal 1 gigaCal (Gcal)= 1000 Mcal = 1000000 kcal = 1000000000 Cal
When they say or write on receipts, Gcal - we are talking about how much heat was supplied to you or will be supplied for the entire period - this could be a day, a month, a year, a heating season, etc. When they say or write Gcal/hour, this means how much heat they will release to you and me in one hour. If the calculation is for a month, then we multiply these ill-fated Gcal by the number of hours per day (24 if there were no interruptions in heat supply) and days per month (for example, 30), but also when we actually received heat.
Heating tariffs
The full cost of electricity is paid by citizens who do not have an electricity meter at home. It is important to know that the maximum consumption volumes do not depend on how many people are registered in the apartment (house), but are determined separately per subscriber.
If the house has a gas boiler, then the lowest preferential tariff for natural gas is provided for those citizens who have metering devices (meters), and in winter it is 0.1143 BYN. for 1 cubic meter of gas. In summer, this amount will already be 0.4114 rubles per m 3. Without a meter, if you have individual gas heating appliances, you will have to pay according to the square footage of your home - 0.4874 rubles during the heating period and 0.1827 Belarusian rubles. summer period for each m2 of area.
We calculate the consumption of an electric boiler
You can find out complete information on the selection, operation and maintenance of gas boilers from all manufacturers if you go.
One of the decisive questions in choosing this device is how much it will cost to heat a house with an electric boiler. After all, you can save on the cost of the device itself, and then pay huge bills. To prevent this from happening, consider the following table.
Difference in consumption of ion and heating element boilers.
We will give an example for an inverter and induction boiler, the area of the heating room is a house of 240 m2, with a standard ceiling height of 3 m, where there are good plastic windows, doors with good thermal insulation, the house itself is insulated.
And then, we will give a more specific example with numbers on how to calculate the consumption of an electric boiler, provided that your entire system is connected, the batteries are installed, in general, everything is ready for use. And let’s try to figure out whether a heating element electric boiler or an induction one is beneficial.
Initial data:
Duration of operation is 10 hours, during the day it was heated to the set temperature and turned off. To begin with, we will calculate the invert one, and also take into account the fact that over time its efficiency decreases significantly.
The first year of heating will be the most efficient and least expensive. 24 (power)*10 (operating time)*30 (days per month)*7.2 (cost of electricity) = 19,450 rubles per month or 136 thousand rubles for 222 days.
In the 2nd year, energy consumption will increase by an average of 15%, the heating duration will increase by an hour and a half and, based on these data, the monthly amount is 22,400 rubles, and for the heating season you will have to pay 156,500 rubles for electricity.
In the 3rd operational year, the heating element “wears out” even more and losses will be up to 18%, and the operating time will increase by three hours compared to the first year. The energy consumption will be 24 kW, and the energy output will be 16 kW. However, with proper care, timely cleaning and necessary operational measures, these indicators can increase with less intensity.
Next, let's look at an example in numbers with an induction double-circuit boiler. All data is the same as in the first case. 20 (power)*240 (room area)*30 (calendar month)*2.7 (tariff)*10 (operation duration)=16,200 rub. per month, and for the entire season 113,402 rubles.
An undoubted advantage is the fact that the amount will remain unchanged in subsequent years, provided that the established tariff does not change and electricity consumption remains constant, unlike the first example. The efficiency does not decrease after the service life expires, since there is no scale formation.
If you were in doubt before, then from the calculations it becomes obvious that this boiler is more profitable.
Well, for comparison, let’s give an example of how much electricity a gas boiler consumes. To operate the pump, it needs 60 W, during ignition it consumes about 120 W, and if there is a closed combustion chamber for the fan to operate, another plus 30 W. In total, by adding up all the needs of a particular unit, you will get the total amount of energy consumption for gas equipment.
We independently calculate payments for heating in conditions with and without individual meters
Heating payments make up the lion's share of total utility costs. Find out from this article how heating fees are calculated according to the new 2022 rules and how the tariff is determined when meters are not installed. By being able to “read” your receipt, you will be aware of how much you are paying and for what. This will allow you to timely identify intentional or accidental errors in the calculations indicated on the receipts.
According to current legislation, in all houses where there is a technical possibility, communal meters must be installed. If they are absent, a multiplying factor is applied when calculating the heating fee. In 2022 it was 1.4, and from the beginning of 2022 it was increased to 1.6.
The cost of heating services per 1 sq. m in Gcal in 2022 in an apartment building
Heating charges vary from region to region. The maximum indicators (which, of course, are in demand) are set by the regional administration, as a rule, for every six months. Plus, the formulation “heating price per 1 kW per m²” is not correct - government authorities limit the cost of the gigacalorie itself consumed by a utility unit.
After all, a gigacalorie is an analogue of a unit of work (the same Joule or kilowatt-hour), simply having a larger scale for convenience. For example:
- 1 gigacalorie corresponds to 4,184,000,000.00 Joules (4.184 gJ);
- 1 gigacalorie corresponds to 1,162.22 kilowatt-hours (kWh).
It is convenient to account for heat in gigacalories due to the large scale of thermal energy consumption (heat has an extremely high energy density compared, for example, with the same mechanical work).
These standards vary greatly among different regions due to the fact that temperature climatic regimes also differ significantly between them (winter in the Stavropol region is one thing and quite another in Anadyr). In addition, even within the same region (subject of the Federation) there may be several types of standards, depending on the quality of the house for which this standard is applied.
If this is a wooden barracks built in the 50s of the last century, then it will require more energy to maintain a comfortable temperature environment than in more modern multi-story buildings.
The standard is set specifically for 1 m² of living space, that is, there is a link: the larger your apartment, the more you will have to pay for heat if standard coefficients apply, regardless of how effective the thermal insulation is in your home.
Understanding this, the state administration seeks to create conditions and stimulate the process of equipping all consumers with individual heat meters, that is, at a minimum, to install communal heat meters.
However, there are a number of limitations:
- Now an individual metering device for an apartment (in houses built before 2012) is installed if there is a centralized supply from a single riser. If there are several pipes, then the installation of an IPU is considered physically impossible at this stage due to the need to install a large number of meters (for each battery), the high cost of the process and the complexity of accounting. Apartment buildings put into operation after 01/01/2012 (as a new building or after a major overhaul) are required by law to be equipped with individual and communal heat meters.
- Also, sometimes technical difficulties arise that make it impossible to install a common house metering device (CDMU).
In these cases, accounting is carried out in accordance with the standards. But if it is technically possible to install IPU and ODPU, and consumers still prefer to remain on the standard system of charging for heat supply, then penal increasing coefficients already begin to apply (you can learn how to decipher KPU, IPU and other abbreviations in the receipt for housing and communal services find out here).From 01/01/2017, this increasing coefficient is equal to 1.1 to the fee set by the heat supply organization. The very cost of 1 Gcal per 1 square meter in each region, of course, will be different.
New heating payment procedure
Let us remind you that Rules 354 amended Rules 307, according to which, from September 1, 2022, the provisions of Rules 307 in relation to all utilities with the exception of heating became invalid. Since Rules 354 provided for payment for heating utilities based on consumption (that is, exclusively during the heating period - either according to metering devices or according to consumption standards), and Rules 307 provided for payment for heating throughout the year in monthly equal payments, carried out once a year payment adjustments, the Government of the Russian Federation gave the constituent entities of the Russian Federation the right to decide on the choice of payment method for heating - either according to Rules 354 or according to Rules 307. At the same time, the existence of two options for heating payments was declared as temporary, established for a certain “transition period” necessary to abandon norms of Rules 307 and the establishment of the procedure for payment for heating provided for by Rules 354. The end date of such a “transition period” was set as December 31, 2022, after which a single and only procedure for payment for heating, regulated by Rules 354, .
We recommend reading: Dairy Kitchen Set for Children 6 to 12 Months in Klin
On June 30, 2022, the Russian Federation Regulation of May 23, 2021 N307 (hereinafter referred to as Rule 307) finally expired - the same resolution providing for payment of heating monthly in equal installments throughout the year. Now the procedure for calculating heating fees is determined exclusively by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 05/06/2021 N354 (hereinafter referred to as Rules 354). However, the norms of Rules 307 have not disappeared - it was on the last day of Rule 307 that the RF Regulation N603 of June 29, 2021 came into force, by which the procedure for calculating heating fees provided for by Rules 307 is included in Rules 354 as one of the options for calculating heating fees.
What is the consumption standard for heating utilities for the population in 2022?
The most important of all housing and communal services in our country, undoubtedly, is the heating of residential premises. In this situation, the standard refers to a heuristically determined amount of heat energy necessary to maintain comfortable temperatures in an apartment (or private house).
A house with a metering device is in a more advantageous position - here residents pay only for the heat actually used. Here the bill is issued strictly for gigacalories. In the Russian Federation, its cost differs and ranges from 1.5 thousand rubles to 2.5.
Procedure for calculating heating fees
The cold water component is the volume of cold water for hot water supply needs. Determined in the presence of individual metering devices - according to the readings of the hot water metering device, in the absence of an individual metering device - according to the standard - 3.5 m3 / person. per month.
The thermal energy component for hot water supply needs is determined based on the readings of a common house hot water meter. The amount of thermal energy recorded by a common house meter is distributed in proportion to the consumed volume of hot water.
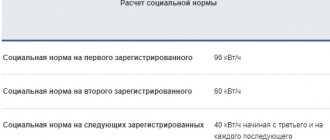
Norm Gcal Per 1 M2 When Calculating Heating Payments 2022
For consumers who do not have metering devices , the rate of consumption of utilities for heat supply is approved by the Resolution of the Akim of the Kostanay region dated September 5, 2022, No. 418 in the amount of 0.032 Gcal/m2 per month during the heating season.
Tariffs for services for the production, transmission, distribution and supply of thermal energy were approved by Order No. 265-OD of the Department of the Committee for the Regulation of Natural Monopolies, Protection of Competition and Consumer Rights, and from October 1, 2021 are :