Central heating systems of multi-storey communal buildings and individual residential buildings have not only significant design differences, but also different physical characteristics of the coolant used. When designing intra-house heating networks, the main design criterion is the pressure in the heating system, the parameters of which have a significant impact on the correct functioning of the entire heating system.
In individual residential buildings, autonomous systems are used for heating, which include various equipment; when independently filling the circuit with a coolant, it is important to maintain the correct pressure parameters. Monitoring and adjusting pressure within specified limits during operation of the heating system will ensure the longevity of its operation, optimize the consumption of thermal resources, and increase the efficiency of heat exchange devices.
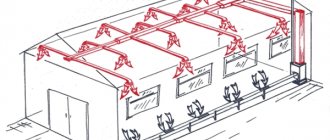
Rice. 1 Heating equipment in the house - appearance
Optimal pressure values for private houses
In a system without liquid coolant, the pressure is normal for the atmosphere - 0.1 MPa or 1 Bar.
The overall indicator is formed based on the following components:
- Hydrostatic pressure - created by the coolant and when the boiler is not working, is formed by the pressure of the water column. In an open system, a special reservoir is mounted at the top - an expansion tank. Based on its filling level, the height of the heating circuit will be measured.
- Dynamic pressure - created in closed networks by a pump for circulation and convection (heating and cooling directly affect the volume of water). Such indicators often differ in places where pipes of different diameters are connected, the location of shut-off valves and many other points.
General values affect the rate of circulation of the energy carrier in the pipes, direct heat exchange in different parts of the heating circuit, and also with increasing pressure, the efficiency of the heating network increases, because the resistance in the system decreases.
Stable operating pressure and optimal, according to the accompanying technical documentation, indicators for the equipment make it possible to reduce heat loss and guarantee that remote areas of the house receive energy with almost the same temperature indicators as during heating in the boiler.
Theoretically, any value is possible for it, as long as it can withstand heating equipment with boilers and radiators. There is a completely reasonable and justified interest in the issue of working pressure.
These are the maximum indicators that can be viewed in the technical documentation of the equipment. According to established standards, for a private home the optimal pressure is up to 3 Bar, although individual units have a lower limit.
Materials
- The pressure a polypropylene pipe can withstand is always indicated by the manufacturer in its labeling. Marking PN20 (typical for pipes without reinforcement) indicates a working pressure of 20 atmospheres, PN25 (standard for pipes reinforced with fiber and aluminum) - 25 kgf/cm2;
- The temperature of the coolant influences the pressure polypropylene pipes are designed for. Manufacturers always indicate operating pressure at a temperature of 20C. When heated to a maximum of 90 - 95C, the maximum operating pressure decreases to 7 - 9 atmospheres. The service life is also reduced: already at 80 degrees, polypropylene will last not 50, but not more than 25 years;
- All polypropylene fittings are without reinforcement and are designed for a working pressure of 25 atmospheres;
- What pressure can a metal-plastic pipe (with cross-linked polyethylene shells and an aluminum core) withstand? Manufacturers guarantee 10 - 16 atmospheres. The breaking pressure is usually not less than 25. From a practical point of view, metal-plastic can be installed in central heating systems only on the connections to the radiators after the shut-off valves, which make it possible to shut off the water in case of leaks;
- The pressure at which a polyethylene pipe can operate is determined by the ratio of its diameter to the wall thickness (this parameter is called SDR) and the type of polyethylene. Low-pressure polyethylene PE100 is noticeably stronger than high-pressure polyethylene PE32: for example, with the same diameter and wall thickness (SDR21), the first pipe can operate at a pressure of 8 kgf/cm2, and the second - only 2.5;
SDR is the ratio of outside diameter to wall thickness.
- The lower the SDR, the higher the tensile strength
; - There is an inverse relationship between pressure and pipe diameter with constant wall thickness. The larger the diameter, the larger the area of its internal surface, and if so, the greater the force with which the internal environment presses on them. Accordingly, at a constant operating pressure, the wall thickness, depending on the diameter of the pipe, decreases or increases;
- The most reliable and easy-to-install material for central heating systems is corrugated stainless pipe. Due to the corrugation, it absorbs water hammer and withstands the freezing of water in it without destruction. With a stated operating pressure of 10 - 15 atmospheres, the destruction pressure, according to the Lavita company, is 210 kgf/cm2;
Corrugated stainless steel is an ideal material for central heating systems.
- For steel pipes with welded joints, the strength calculation takes into account the strength coefficient of the weld. It is taken equal to 0.6 - 0.8. If a VGP pipe can withstand a pressure of 200 atmospheres without destruction, the design for the finished circuit includes a maximum of 120 - 160;
- All water and gas pipes are electric welded. Accordingly, during defrosting and the accompanying increase in pressure, they tear along the longitudinal seam. After welding a seam using electric arc welding, the strength of the pipe almost does not decrease;
- Central heating systems should be equipped with steel registers or bimetallic radiators. The strength of any system is equal to the strength of its weakest link: is there any point in using pipes that can withstand 150 atmospheres if the radiator collapses at 16?
- The champion in strength among bimetallic ones is Rifar Monolit of domestic production. A working pressure of 50 atmospheres and a destructive pressure of 100 are stated for it.
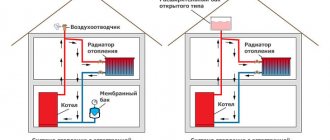
Closed and open types of heating circuit
Before making any calculations, you need to figure out which system is installed and what the main differences are. So, the main thing is the presence of an expansion tank (helps to collect excess liquid) in an open heating network and the tightness of the system in a closed one.
The membrane inside the vessel in the last type of heating system divides it into 2 compartments. One is filled with air, and the other is connected to a common line. This design allows you to remove excess liquid as its volume increases during heating. And when the water cools and decreases in volume, it will help make up for the shortage.
- The expansion tank is installed at the top of the heating circuit, for example in an attic or other special room at a height, connected to the heating system riser, and on the other side to a drain that protects in case of overflow.
- To create an open-type network with a pressure of 1 Bar, the tank must be installed at a height of 10 m from the minimum. For an average power of 3 Bar (usually standard boilers) you will need a height of more than 30 m.
- This is precisely the reason for the more frequent choice of open-type heating systems for low-rise buildings. The operating pressure in them in rare cases is higher than the usual hydrostatic pressure even when heated, which means that it is not necessary to install additional fuses other than the equipped drain.
Remember, normal operation of an open-type system is ensured by installing the boiler at the lowest level of the heating circuit and the tank at the highest.
The pressure in a closed system is much more affected by changes in water temperature and safety valves must be installed. Usually for a two-story building they set it at 2.5 atm. In a small house the limit of 1.5-2 atm is maintained.
Electrical installation
Work on installing the floor begins after the subfloor is completed.
To do this, the soil is cleaned to a depth of up to half a meter, a layer of sand and crushed stone is poured in and concrete is poured. Electric floor heating does not require a high screed, but its optimal height is 10 centimeters. Do-it-yourself work is performed in the following order:
- Laying waterproofing. Groundwater should not get onto the cable. To do this, use roofing felt or thick film.
- Creating a thermal insulation layer to prevent heat from escaping into the ground. It is not recommended to use foil as an insulator.
- Laying reinforced mesh and fixing it.
- Laying the cable and tying it to the sheathing. Calculate the required cable length in advance. Choose a solid wire, without solders. Heating mats can replace the wire.
- Installation of temperature sensors, especially in the area near the machine, where it is necessary to maintain a certain temperature.
- Connecting the cable to a separate panel and test switching on.
- If everything works properly, a layer of screed is poured over the grate, allowed to dry, and the finished floor is installed.
The system does not require special maintenance.
Why monitor pressure while heating your home?
The difference in pressure when water is supplied and when it moves in the opposite direction reflects how efficiently a particular system operates.
A small one indicates that the coolant successfully passes through the pipes and the rooms receive the proper amount of energy, and an increase in this difference with a large difference signals an increase in the resistance of the area, a reduced flow rate and excessive cooling.
- How fast will be the water flow and heat exchange between objects in different parts of the system, possible heat losses, and the efficiency of the network directly reflects the total pressure indicator.
- Maintaining it is essential for the efficient operation of the heating circuit throughout the building. The stability of the values will reduce heat loss and ensure rapid distribution of the coolant to all corners of the house, practically matching the temperature obtained during heating.
Large differences in a long heating supply line, where there are many radiators with thermostatic valves, can be regulated using automatic limiters.
It is necessary to create excess pressure in closed systems for:
- Ensuring forced movement of liquid in pipes;
- Monitoring the condition of the network using a pressure gauge in order to replenish or repair it in a timely manner;
- Under pressure, faster heating occurs.
Homeowners are interested in the second item from this list - the device’s measurement readings, so that it is clear how serviceable and efficient the entire heating circuit structure is.
Installation recommendations
In order to carry out all repair or adjustment procedures, the pressure heating system must be correctly assembled; the main conditions for proper installation are:
- The mandatory presence of a safety group of fittings above the boiler, consisting of a pressure gauge, an automatic air vent and a drain valve. These devices are required for setting up, de-airing and protecting the boiler from excess pressure.
- The presence of Mayevsky taps on all radiator heat exchangers, intended for their de-airing, and thermostats.
- The presence of an air vent at the highest point of the circuit.
- The presence of a bypass in a parallel branch with the electric pump, allowing its removal for the purpose of repair and maintenance work without draining the coolant.
- Installing an electric circulation pump, preferably with three speeds, allows you to optimally adjust the desired speed of movement of the coolant.
- The presence of coarse filters and periodic flushing of the circuit are also necessary. This allows you to extend the service life of all components of the system and will avoid many troubles associated with clogging of channels and fittings of plumbing fittings with salt deposits and other dirt.
Rice. 8 Boiler equipment safety group - installation example and appearance
Maintaining the nominal pressure in a closed-type heating system is one of the important conditions for its normal functioning; there is a pressure gauge in the circuit to monitor the readings. Any deviations from the nominal values outside the operating range mean some kind of malfunction; to eliminate them, there are a number of methods on how to increase the pressure in the heating system or, conversely, reduce its performance.
Causes of pressure drop in the heating system
Jumps after the start of the heating season 2-3 weeks later require careful inspection to identify possible problem areas. Pressure loss can be caused by contamination, small cracks, extensive wear, possible defects of the equipment manufacturer, as well as a defect in the expansion tank.
Among the common reasons:
- A leak. It is necessary to check the threaded connections; perhaps there is too little sealant, or the welding technology for polypropylene pipes was violated;
- Air. After starting the system for constant heating, it needs to adapt. At first, such a decrease in pressure is the norm, but it can be adjusted by replenishing the coolant, it will increase to the required level
- New aluminum batteries. Contact of radiators with water will initiate the oxidation reaction. It will end after the entire area has been oxidized and the situation will stabilize.
Having identified strong pressure drops, it is worth consulting with a specialist, because the reasons can be different. The engineer will diagnose the heating system, check how well and accurately the pressure gauges, air vents, and fuses work.
Modern heating equipment is equipped with special sensors that respond not just to a pressure surge, but to changes in the temperature of the energy carrier.
Any problems in the operation of heating in a private household not only bring discomfort and costs for repairing equipment, but often people can be injured or the building itself can be damaged. It is important to be attentive to the system and competent during control.