Following a failure of pressure in the heating system comes a problem - the quality of heating the premises in the house decreases. You can, of course, set up the heating once and for a long time, but this period will not be indefinitely long. One day, the normal pressure in the heating system will change, and significantly.
We will tell you how to keep the physical parameters of the coolant under control. Here you will learn how to ensure a stable speed of movement of heated water through the pipeline to the devices. You will understand how to obtain and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
The article proposed for consideration describes in detail the reasons for the pressure drop in closed and open systems. Effective balancing methods are given. The information presented for review is supplemented with diagrams, step-by-step instructions, photos and video tutorials.
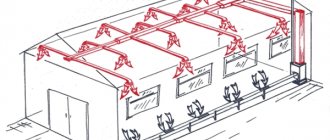
Pressure in an open heating system
Unlike a closed thermal circuit, a properly constructed open heating system does not require balancing over years of operation - it is self-regulating. Boiler operation and static pressure ensure constant circulation of water in the system.
The density of the heated water following the supply riser is lower than the density of the cooled coolant. Hot water tends to occupy the highest possible point of the circuit, and cooled water tends to be at its very bottom.
The pressure required for water circulation is achieved by the pressure in the supply riser or by a booster pump (+)
The pressure developed by the water column in the supply riser promotes the circulation of the coolant and compensates for the resistance present in the circuit pipeline. It is caused by the friction of water on the inner surface of the pipes, as well as local resistance (turns and branches of the pipeline, boiler, fittings).
By the way, pipes of increased diameter are used to assemble an open heating system precisely to reduce friction.
To understand how to increase pressure in an open heating system, you must first understand the principle of achieving circulation pressure in the thermal circuit.
Its formula:
Rts = h • (ro-rg),
Where:
- Рc – circulation pressure;
- h – vertical distance between the centers of the boiler and the lower heating radiator;
- рг – density of the heated coolant;
- ro – density of the cooled coolant.
The static pressure will be higher if the distance between the central axes of the boiler and the battery closest to it is as significant as possible. Accordingly, the intensity of coolant circulation will be higher.
To achieve the maximum possible pressure in the heating circuit, it is necessary to lower the boiler as low as possible - into the basement.
The closer the radiator is to the boiler on the supply circuit, the better it warms up. Regulators allow you to distribute heat between all radiators of the heating system
The second reason for the drop in pressure in an open heating system is related to its self-regulation. When the heating temperature of the coolant changes, the intensity of its flow changes. By increasing the heating of water for the heating circuit on cold winter days, owners sharply reduce its density.
However, when passing through heating radiators, water gives off heat to the room atmosphere, and its density increases. And according to the formula presented above, a high difference in the densities of hot and chilled water helps to increase the circulation pressure.
The more the coolant is heated and the colder it is in the rooms of the house, the higher the pressure in the system will be. However, after the atmosphere of the premises warms up and the heat transfer from the radiators decreases, the pressure in the open system will drop - the difference between the supply and return water temperatures will decrease.
Balancing a double-circuit open heating system
Gravity heating systems are made with one or more circuits. In this case, the horizontal length of each looped pipeline should not exceed 30 m.
But to achieve optimal pressure and pressure in an open system with natural coolant movement, it is better to make the pipelines even shorter - less than 25 m. Then it will be easier for water to deal with hydraulic resistance. In a circuit with several rings, in addition to limiting the length, the condition for heating radiators must be observed - the number of sections in all rings must be approximately equal.
Lack of pressure in an open double-circuit thermal system occurs due to design errors or contamination of the pipeline (+)
Balancing of the horizontal rings included in the vertical circuit is required at the design stage of the heating system. If the hydraulic resistance of any ring turns out to be higher than that of the others, the static pressure in it will not be enough and the pressure will practically stop.
To maintain the required pressure in a double-circuit heating system, it is necessary to reduce the cross-section of the pipes approaching the radiators. You can also install valves in front of the radiators that perform thermoregulation (manual or automatic).
You can balance an open-type dual-circuit system:
- Manually. We start the heating system, then measure the temperature of the atmosphere of each heated room. Where it is higher, we screw the valve, where it is lower, we unscrew it. To adjust the thermal balance, you will have to perform temperature measurements and adjust the valves several times;
- Using thermostatic valves. Balancing occurs almost independently; you just need to set the desired temperature in each room on the valve handles. Each such device will control the supply of coolant to the radiator itself, increasing or decreasing the supply of coolant.
It is especially important that the value of the total hydraulic resistance of the heating system (all rings in the circuits) does not exceed the value of the circulation pressure. Otherwise, warming up the coolant and attempting to balance the system will not improve circulation.
Circulation pump for open heating system
It happens that measures to balance the heating circuit of a gravity system have no effect. Not all causes of low pressure can be solved by adjustment - choosing the wrong pipe diameter cannot be corrected without a complete reconstruction of the circuit.
Then, in order to increase the pressure and improve the movement of water without significant modifications to the heating, a circulation pump or booster pumping device is installed in the system. The only thing that its installation will require is moving the expansion tank or replacing it with a membrane expansion tank (closed tank).
In case of a serious drop in pressure, not a circulation pump, but a more powerful booster pump is needed. However, booster pumps are not suitable for open heating systems, because develop significant dynamic pressure
The energy consumption of circulation pumps does not exceed 100 W. Therefore, there is no need to fear that it will push the coolant out of the circuit.
The volume of water in the heating system is more or less constant, provided that the filling of the open circuit is controlled. Therefore, no matter how much water the circulation pump pushes along the circuit in front of it, the same amount will flow into it from the return pipe.
By bringing the pressure in the thermal system to the required level, the pump will make it possible to lengthen it, reduce the diameter of the pipeline and achieve circuit balance with high hydraulic resistance.
The pressure rises and falls - the boiler does not work stably
From all of the above, it is clear that air comes out from the part of the expansion tank in which it should be or does not have sufficient pressure. And here the pandemonium begins with changes in the operation of the boiler. All this can manifest itself in different ways and depends on the pressure in the air chamber of the Republic of Belarus.
For convenience, we will divide these manifestations into different stages.
FIRST STAGE - The pressure in the boiler drops slowly, about once a week you have to top up the boiler, but there are no obvious leaks in the expander, and there are no obvious leaks in the heating system itself.
SECOND STAGE - On the boiler pressure gauge, the pressure is constantly “walking” In heating mode it rises, perhaps even above 3 Bar, until the relief valve is activated; in hot water mode, on the contrary, it drops to values less than 1 bar and then the boiler may begin to shut down, the protection is triggered .(If it has a pressure sensor)
THIRD STAGE - If there is absolutely no air left in the tank, then the pressure on the pressure gauge drops to zero in a very short time, sometimes in a minute.
There is only one way out for all options! It is necessary to again create the necessary pressure in the expansion tank of your boiler, in its air part.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. How to balance heating radiators in a home heating system. Let us remind you that without valves on each heating radiator it will not be possible to balance the system.
Video #2. Recommendations from a heating engineer for restoring operating pressure in closed-type heating circuits. The video also explains the procedure for pumping an expansion tank that has lost its “factory” gas:
A properly balanced heating system will perform its functions for several years. But one day the characteristics of the coolant will change or critical elements of the thermal circuit will fail. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly monitor coolant indicators using pressure gauges in order to promptly respond to pressure changes.
Please write comments if you have any questions about the topic of the article. We are waiting for your stories about your own experience in normalizing pressure in the heating circuit. We and site visitors are ready to discuss controversial issues in the block located under the text of the article.
How to pump up a boiler expansion tank
Diagram of boiler taps Ariston Class 24
A Fitting for draining water into the central heating circuit (CH)
B Connection for draining water into the hot water supply circuit (DHW)
C Connection for gas supply
D Connection for cold water supply
E Connection for supplying water from the central heating circuit
S Safety valve outlet
T Drain tap
F Filling tap
How to properly pump air into the expansion tank
We follow the specified order
- Turn off the boiler from the network.
- We turn off all the taps to the boiler, supply, return, and cold water input.
- Open the drain fitting in the boiler. (T - in the diagram) and completely drain the water. (Here is an article about how to drain water from the boiler) The pressure in the boiler should be zero!
- We connect the pump with a pressure gauge to the RB through the spool - the drain fitting is open.
- The pump needs to pump air into the tank until water stops flowing from the drain fitting. At this stage, the main goal is to empty the tank of water.
- We release the pumped air by monitoring the pressure with a pump pressure gauge, and if necessary, pump it up. The pressure in the expander should be within 1.1-1.3 bar. (See the passport for your boiler - often indicated)
- Close the drain plug.
- We open all the taps to the boiler - everything that was closed.
- We feed the boiler through the make-up tap (F) to a pressure of approximately 1.2-1.5 bar
- Let's start the boiler.
To pump air into the expansion tank, you can use any pump and pressure gauge. There is a car nipple there. I used an auto compressor. True, for this I had to drag the battery home. With an electric compressor, be careful to turn it off in time and not over-pump.
Before starting the boiler, it will not be superfluous to expel any air that has entered the system.
In Ariston class 24, to do this, press and hold for about 5 seconds. ESK button. The boiler will go into purge mode for 6 minutes, exit this mode on its own, or you can force it by pressing ESK again.
Preventing the formation of air jams
Preventative measures against the occurrence of air locks are as follows:
- Pay attention to the correct installation of pipes and connections of heating devices. Many problems are caused precisely by mistakes made at this initial stage.
- To prevent air locks, proper commissioning of the equipment is necessary, before which it is important to first check all components and connections.
- Before putting devices into operation, check them for functionality. Using a compressor, you need to apply a pressure level that is ¼ higher than its normal operating value. If it does not weaken within 30 minutes, then everything is in order and the system is ready for operation. If the pressure drops sharply, then leaks are possible, which should be promptly identified and repaired before starting operation.
Causes of problems
Let's take a closer look at what affects the level of pressure indicators in the system:
- installation height of a wall-mounted boiler, height and length of the pipe system/circuit;
- material of pipes and elements, as well as the effect of liquid on them;
- correctness and integrity of the design of main tracks.
The standards for monitoring pressure level indicators are slightly different in an autonomous heating system. You should pay attention to the model and technical parameters of the boiler, the pipeline network and pipe characteristics, installation locations and the number of floors in the building.
Why does it jump
During operation, the pressure inside the circuit constantly changes under the influence of a number of factors:
- Thermal expansion of the coolant when heated and a decrease in volume when cooled;
- Thermal deformation of pipes, radiators and boiler walls, as a result of which the actual volume of the heating circuit changes;
- Due to the presence of dissolved gases in the liquid and the release of gas in the form of bubbles and gas pockets;
- Locally in places where the bore diameter of pipes changes.
A liquid, by definition, is a practically incompressible medium, therefore any changes in the volume of water or the internal volume of the heating circuit lead to significant pressure surges.
In a closed volume, due to thermal expansion, the pressure of the liquid can sharply increase by an order of magnitude.
As it cools, water in the same closed volume reduces its volume, and the pressure drops sharply, causing boiling and the formation of gas pockets even at room temperature.
Optimal value for a private house or cottage
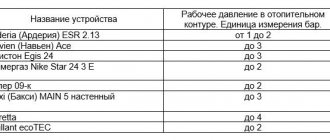
Any boiler operates at certain system settings, in particular, it is necessary to correctly calculate the water pressure. This value is influenced by the number of floors of the building, the type of system, the number of radiators and the total length of the pipes. Usually for a private house the pressure level is 1.5-2 atm, but for a five-story apartment building this value is 2-4 atm, and for a ten-story building it is 5-7 atm. For higher buildings, the pressure level is 7-10 atm, the maximum value is achieved in heating mains, here it is 12 atm.
For radiators that operate at different heights and at quite a decent distance from the boiler, constant pressure adjustment is required. In this case, special regulators are used to reduce it, and pumps to increase it. But the regulator must always be in good working order, otherwise sharp fluctuations and drops in coolant temperature will be observed in certain areas. The system must be adjusted so that the shut-off valves are never completely closed.
Make-up tap
A common cause of pressure drop is a malfunction of the make-up valve. Causes:
- Loose tap connections. When opened, water will constantly flow into the drain, causing a voltage drop;
- The additional make-up tap is open. This position of the shut-off valves causes constant fluctuations in coolant pressure.
To ensure heat supply and water heating in an individual residential building, owners most often install gas boilers with closed coolant circulation. To install and operate a gas boiler, it is necessary that a gas pipeline runs nearby. If there are no gas supply networks nearby, bottled liquefied petroleum gas can be used for heating.
The dual-circuit design allows you to increase the pressure of the working medium in the system circuit. A decrease in pressure contributes to problems during the operation of the heating system. Let's take a closer look at what the causes are and what methods can be used to eliminate this unpleasant problem.