What should the temperature of the tap water be?
Let's find out. Our topic today is the temperature of the water in the hot water tap and in the heating radiators. We will find out what the temperature should be in accordance with the current regulatory documentation, and in what cases it can deviate significantly from normal values. Let's get started.
Heating standards for apartment buildings heated centrally
These norms are the most “ancient”.
They were calculated at a time when they did not save on fuel for heating the coolant, the batteries were hot. But houses were built mainly from materials that were “cold” in terms of heat-saving qualities, that is, from concrete panels. Times have changed, but the norms remain the same. According to the current GOST R 52617-2000, the air temperature in residential premises should not be lower than 18°C (for corner rooms - at least 20°C). At the same time, the organization that supplies thermal energy has the right to reduce the air temperature at night (0-5 hours) by no more than 3°C. Heating standards are set separately for different rooms of the apartment: for example, in the bathroom it should be at least 25°C, and in the corridor - at least 16°C.
Society has been fighting for a long time, and at times not unsuccessfully, to change the procedure for determining heating standards, tying them not to the air temperature in the premises, but to the average temperature of the coolant. This indicator is much more objective for consumers, although it is unprofitable for the heat energy supplier. Judge for yourself: the temperature in residential premises often depends not only on the operating system, but on the nature of a person’s life activity and living conditions.
For example, the thermal conductivity of brick is much lower than that of concrete, so in a brick house at the same temperature you will have to spend less thermal energy. In rooms such as the kitchen, the process of cooking food does not generate much less heat than from radiators.
Much also depends on the design features of the heating devices themselves. For example, panel heating systems will have a higher heat transfer rate than cast iron radiators at the same air temperature. Thus, heating standards tied to air temperature are not entirely fair. This method takes into account the outside air temperature below 8°C. If such a value is recorded for three days in a row, the heat generating organization must unconditionally supply heat to consumers.
For the middle zone, the calculated values of the coolant temperature depending on the external air temperature have the following values (for the convenience of using these values using household thermometers, temperature indicators are rounded):
Outside air temperature, °C
Temperature of network water in the supply pipeline, °C
Using the table above, you can easily determine the water temperature in a panel heating system (or any other) by using a regular thermometer at the time of draining part of the coolant from the system. For the forward branch, use the data in columns 5 and 6, and for the return branch, use the data in column 7. Note that the first three columns establish the release temperature of the water, that is, without taking into account losses in the transmission main pipelines.
If the actual coolant temperature does not correspond to the standard temperature, this is the basis for a proportional reduction in the payment for the central heating services provided.
There is also an option to install heat meters, but it only works when all apartments in the building are served by a centralized heating system. In addition, such meters are subject to annual mandatory inspection.
How climate zones affect air temperature
The main factor that is taken into account when calculating the temperature schedule is presented in the form of the calculated temperature in winter. When calculating heating, the outside air temperature is taken from a special table for climatic zones.
The coolant temperature table should be drawn up so that its maximum value satisfies the SNiP temperature in residential premises. For example, we use the following data:
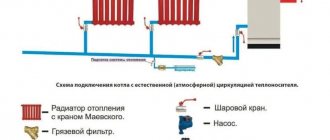
- Radiators are used as heating devices, which supply coolant from bottom to top.
- The type of apartment heating is two-pipe, equipped with parking pipe distribution.
- The calculated values of the outside air temperature are -15 degrees.
In this case we receive the following information:
- Heating will be started when the average daily temperature does not exceed +10 degrees for 3-5 days. The coolant supply will be carried out at a value of 30 degrees, and the return will be equal to 25 degrees.
- When the temperature drops to 0 degrees, the coolant value increases to 57 degrees, and the return flow will be 46 degrees.
- At -15, water will be supplied at a temperature of 95 degrees, and the return will be 70 degrees.
This is interesting! When determining the average daily temperature, information is taken from both daytime thermometer readings and nighttime measurements.
Heating system temperature graph
In this form, the water flow changes, but its temperature remains constant.
Qualitative. The temperature of the liquid changes, but its flow does not change.
In our systems, the second regulation option is used, that is, qualitative.
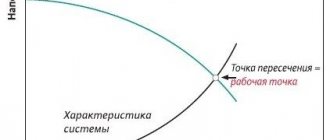
There is a direct relationship between two temperatures: the coolant and the environment. And the calculation is carried out in such a way as to ensure the heat in the room is 18 degrees and above. Hence, we can say that the temperature graph of the source is a broken curve. The change in its directions depends on temperature differences (coolant and outside air).
The dependency schedule may vary. A specific diagram has a dependency on:
- Technical and economic indicators.
- Climate.
- CHP or boiler room equipment.
High coolant values provide the consumer with great thermal energy.
Below is an example of a diagram, where T1 is the temperature of the coolant, Tnv is the outside air: A diagram of the returned coolant is also used.
What does it depend on?
The temperature curve depends on two quantities: outside air and coolant. Frosty weather leads to an increase in coolant temperature. When designing a central source, the size of the equipment, building and pipe size are taken into account.
The temperature leaving the boiler room is 90 degrees, so that at minus 23°C, the apartments are warm and have a value of 22°C. Then the return water returns to 70 degrees. Such standards correspond to normal and comfortable living in the house.
Analysis and adjustment of operating modes is carried out using a temperature diagram. For example, the return of liquid with an elevated temperature will indicate high coolant costs. Underestimated data will be considered a consumption deficit.
Previously, for 10-story buildings, a scheme with calculated data of 95-70°C was introduced. The buildings above had their own chart of 105-70°C. Modern new buildings may have a different layout, at the discretion of the designer. More often, there are diagrams of 90-70°C, and maybe 80-60°C.
Temperature chart 95-70:
Temperature chart 95-70
Minimum temperatures
First, you should pay attention to this point: there is not a single document that would determine the standards for heating batteries. There are documents that regulate the temperature of the coolant and the temperature in the apartment
Why is this so? This can be explained by the different thermal conductivity of the materials used to produce heating batteries, as well as the design features of different models.
Cast iron, steel, copper and aluminum (they are most often used to make radiators) have different thermal conductivities. This means that batteries made from these materials heat up and release heat differently. That is, provided that the coolant temperature at the inlet is 100 °C, the cast iron radiator will not heat up to such a temperature. A copper device can (among the above 4 materials, copper conducts heat the best).
It would be possible to set heating standards for radiators for a specific type of material. However, the situation is complicated by manufacturers who use various tricks when developing radiator shapes. as well as improving the heat transfer of an individual product. Therefore, it is very difficult to develop universal temperature standards for water batteries.
It is also worth adding that batteries with 5 and 11 sections heated to the same temperature create different heat flows. Therefore, the room will warm up differently. Of course, this is said to understand the idea. In practice, when planning a water heating system, the optimal dimensions and required power of the heating battery for each room are always calculated. Therefore, if the entire heating system operates correctly, the battery, which has a sensor and thermostat, will give off the required amount of heat.
From the above it follows that it is best to measure the temperature of the coolant and check whether the resulting indicator corresponds to the norm. This can be done in different ways. Some of them include measuring the temperature of the radiator, and using correction values depending on the material used to make the heating device.
The minimum temperature of the coolant is +30 °C (this is according to the Decree of the State Construction Committee dated September 27, 2003 No. 170). Such water must circulate through a system in which the coolant moves in a “bottom-down” pattern when the outside temperature is +10 °C.
If it is 0 °C outside the window, go to radiators with a sensor. as well as a device for adjusting the heating, water must flow no colder than +57 ° C. It is clear that the battery can heat up almost to this temperature. The above-mentioned document has a whole table that indicates the normal temperature of the coolant at the inlet and outlet depending on the weather and the method of supplying heated water.
Types of charts
Depending on the purpose of the heating network, the implementation methods differ. The first option is a normal heating schedule. It represents constructions for networks that operate only for space heating and are centrally regulated.
The increased schedule is calculated for heating networks that provide heating and hot water supply. It is built for closed systems and shows the total load on the hot water supply system.
The adjusted schedule is also intended for networks operating for both heating and heating. This takes into account heat losses as the coolant passes through the pipes to the consumer.
What should the battery temperature be during the heating season?
d) for supply and circulation pipelines of hot water supply networks:
- pressure - based on the highest pressure in the supply pipeline when pumps are operating, taking into account the terrain;
- temperature - in accordance with
SNiP 2.04.01.
Clause 16.9 - Chapter 16 Heating points When calculating the heating surface of water heat exchangers for hot water supply and heating systems, the water temperature in the supply pipeline of the heating network should be taken equal to the temperature at the break point of the water temperature graph or the minimum water temperature if there is no break in the temperature graph, and for heating systems - also the water temperature corresponding to the calculated outside air temperature for heating design. The larger of the obtained heating surface values should be taken as the calculated value.
At the supply it is from 95 to 105 °C, and at the return - 70 °C. Optimal values in an individual heating system H2_2 Autonomous heating helps to avoid many problems that arise with a centralized network, and the optimal temperature of the coolant can be adjusted according to the season. In the case of individual heating, the concept of standards includes the heat transfer of a heating device per unit area of the room where this device is located.
The thermal regime in this situation is ensured by the design features of heating devices
It is important to ensure that the coolant in the network does not cool below 70 °C. 80 °C is considered optimal
With a gas boiler, it is easier to control heating, because manufacturers limit the ability to heat the coolant to 90 °C. Using sensors to regulate the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be adjusted.
CHP and heating networks: what is the relationship
The purpose of thermal power plants and heating networks is to heat the coolant to a certain value, and then transport it to the place of consumption. It is important to take into account the losses on the heating main, the length of which is usually 10 kilometers. Despite the fact that all water supply pipes are thermally insulated, it is almost impossible to avoid heat losses.
When the coolant moves from a thermal power plant or simply a boiler house to the consumer (apartment building), a certain percentage of water cooling is observed. To ensure the supply of coolant to the consumer at the required standardized value, it is required to be supplied from the boiler room in the maximum heated state. However, it is impossible to increase the temperature above 100 degrees, since it is limited by the boiling point. However, it can be shifted towards increasing the temperature value by increasing the pressure in the heating system.
The pressure in the pipes according to the standard is 7-8 atmospheres, however, when the coolant is supplied, a loss of pressure also occurs. However, despite the pressure loss, a value of 7-8 atmospheres allows for efficient operation of the heating system even in 16-story buildings.
This is interesting! The pressure in the heating system of 7-8 atmospheres is not dangerous for the network itself. All structural elements remain operational in normal mode.
Taking into account the reserve of the upper temperature threshold, its value is 150 degrees. The minimum supply temperature at sub-zero temperatures outside the window is not below 9 degrees. The return temperature is usually 70 degrees.
Temperature measurement techniques
- An ordinary household thermometer on the surface of a heating device.
- A device designed to measure temperature in a non-contact manner. Such a meter is called -.
- Alcohol thermometer.
- A special electrical device.
If you take measurements with an ordinary thermometer, you will need to add a few more degrees to the readings.
The most accurate readings can be obtained using an infrared device - a pyrometer. Its error is no more than 0.5 degrees.
To regularly monitor temperature, use only the safest device - an alcohol thermometer.
For these purposes, it is attached to the radiator using tape and wrapped in thermal insulation material.
How to use the electric version of the thermometer?
You need to take a wire with a thermocouple and attach it to the heating device. This is how the indicators are taken.
If a commission comes to your apartment to measure the temperature of the batteries, they must have a certified device.
You have the right to demand from a representative of the inspecting organization documents confirming that the equipment has passed state verification.
Very serious requirements are placed on the heating system.
The process of delivering hot coolant using circulation pumps (the rules for installation in the heating system are written here) to a residential building and distributing it evenly throughout all apartments is not an easy task.
This issue must be approached responsibly and with an understanding of all technological subtleties.
In order for the heating system to work efficiently, all its elements must function harmoniously.
This applies to all pipes and batteries. in each of the apartments of a multi-storey building.
Therefore, when replacing radiators (read how to install heating radiators in a private house in this article), you need to take into account the features and subtleties of the heating main.
If this is not done, some apartments will experience an excess of heat, while bad times will come for the residents of other apartments (they will have cold radiators).
How can we optimize the heating of urban homes?
Answer: by introducing the following standards:
The safety regulations state that the temperature of the working liquid substance in the heating main must be 20 degrees less than the temperature of self-igniting materials.
For residential multi-apartment buildings, the coolant limit has established standards - 65 - 115 degrees Celsius (this takes into account seasonality);
if the water, for some reason, overheats and reaches the reading of 105 degrees, emergency measures must be taken to prevent it from boiling;
The standard limit for water circulating through batteries is 75 degrees. In case this indicator is exceeded, a restrictive structure must be installed on the battery (about methods of heating distribution in a private house is written here);
in regions located in the middle latitudes of our country, the heating season, as a rule, begins on the fifteenth of October and ends on the fifteenth of April.
In some cases, these standards may be changed.
Service providers should rely on the average daily outdoor temperature.
Additional influencing factors
The coolant temperatures themselves are also directly influenced by such equally significant factors as:
- A decrease in temperatures outside, which entails a similar decrease indoors;
- Wind speed - the higher it is, the greater the heat loss through the front door and windows;
- The tightness of walls and joints (installation of metal-plastic windows and insulation of facades significantly affects heat retention).
There have been some changes in building codes recently.
For this reason, construction companies often carry out thermal insulation work not only on the facades of apartment buildings, but also in the basements, foundations, roofs, and roofing. Accordingly, the cost of such construction projects increases. It is important to know that insulation costs are quite significant, but on the other hand, this is a guarantee of heat savings and reduced heating costs. For their part, construction companies understand that the costs they incurred for insulating facilities will be fully and soon recouped. This is also beneficial for owners, since utility bills are very high, and if you pay, it is really for the heat received and stored, and not for its loss due to insufficient insulation of the premises.
Temperature of heating radiators in the apartment: standards
Apartment heating standards determine the specific value of a sufficient indicator for residential and non-residential premises, with permissible deviations from their indicators.
They are developed more simply than for work premises, since those living in the housing exhibit low and, at the same time, stable activity:
- For residential premises, the air temperature is from 20 to 22 degrees Celsius, while acceptable limits are considered to be from 18 to 24 degrees;
- If we take corner rooms, then the indicator should not be less than twenty degrees, since such rooms are more susceptible than others to low external temperatures and winds;
What temperature should the apartment be during the heating season?
What to do if the radiators in the apartment are cold, read here.
- The kitchen is a work space where, in most cases, there is a heat source - an electric or gas oven. The temperature in this room should be between 19-21 degrees. Acceptable is from 18 to 26 degrees;
- The optimal temperature for toilets is 19-21 degrees. The limit values range from 18 to 26. One way or another, bathrooms are not among the coolest rooms;
- The bathroom is a hot room because it has a fairly high level of humidity. The minimum temperature here ranges from 18 to 24 degrees. The permissible maximum is 26 degrees. But still, at another 20 degrees, the comfort of using this room decreases;
- For non-residential premises, the temperature is calculated based on the frequency of their operation. In corridors, the acceptable temperature level is 18-20 degrees, however, 16 is also acceptable. For storerooms, the air temperature should be 16-18 degrees. Permissible limits are 12 and 22 degrees.
Since the need for heat during sleep is somewhat reduced, according to GOST, it is allowed to lower the temperature level in residential premises to 3 degrees from 00.00 to 05.00 in the morning. Such a decrease in the norm will not be considered a violation.
What are the requirements for the heating system?
The heating process in a multi-storey building is based on the results of many engineering calculations, sometimes they are not so successful.
The complexity of the process lies not in the delivery of heated water to the facility (building), but in its uniform distribution throughout all apartments, under the conditions of ensuring standard temperature indicators and optimal humidity in the apartments.
How effective such a system will be directly depends on the coherence of all its elements, including pipes and radiators in each apartment.
For this reason, replacing radiator batteries without taking into account the features of the heating system can lead to extremely undesirable consequences: one of the apartments may experience a shortage of heat, while another will have an excess of it.
It is through the establishment of standards that optimization of heating of city apartments is achieved:
- Safety requirements determine that the temperature of the coolant in the heating system should be 20 degrees less than the temperature of materials that tend to spontaneously ignite. For multi-apartment residential buildings, the standard coolant temperature should be in the range from 65 to 115 degrees, taking into account the season;
- When water overheats to 105 degrees, measures must be taken to prevent the liquid from boiling;
- The standard limit for the temperature of water flowing through heating radiators is 75 degrees. If this value is exceeded, the battery must have a restrictive design;
- The heating season in mid-latitudes begins in mid-October and ends in mid-April. In reality, service providers must initiate the start of heating from the moment when an average daily temperature of no higher than 8 degrees is recorded for five consecutive days.
Changes in heating design
Replacement of existing heating devices in an apartment is carried out with the obligatory approval of the management company. Unauthorized changes in the elements of warming radiation can disrupt the thermal and hydraulic balance of the structure.
When the heating season begins, changes in temperature conditions in other apartments and areas will be recorded. A technical inspection of the premises will reveal unauthorized changes in the types of heating devices, their quantity and size. The chain is inevitable: conflict - court - fine.
Therefore, the situation is resolved like this:
- if non-old ones are replaced with new radiators of the same size, then this is done without additional approvals; the only thing you need to contact the management company for is to turn off the riser during repairs;
- if new products differ significantly from those installed during construction, then it is useful to interact with the management company.
Water temperature in the boiler and heating pipes
After performing the above calculation, it is necessary to adapt the heating temperature table for the boiler and pipes. During heat supply operation, emergency situations should not occur, a common cause of which is a violation of the temperature schedule.
The normal water temperature in central heating radiators can be up to +90°C. This is strictly monitored at the stage of coolant preparation, its transportation and distribution to residential apartments.
The situation with autonomous heat supply is much more complicated. In this case, control depends entirely on the owner of the house
It is important to ensure that there is no excess temperature of the water in the heating pipes that goes beyond the established schedule. This may affect the safety of the system.
If the water temperature in the heating system of a private home exceeds the norm, the following situations may occur:
- Damage to pipelines. This is especially true for polymer lines, where the maximum heating can be +85°C. That is why the normal temperature of heating pipes in an apartment is usually +70°C. Otherwise, deformation of the line may occur and a gust may occur;
- Excessive air heating. If the temperature of the heating radiators in the apartment provokes an increase in the degree of air heating above +27°C, this is outside the normal limits;
- Reduced service life of heating components. This applies to both radiators and pipes. Over time, the maximum water temperature in the heating system will lead to breakdown.
Also, a violation of the water temperature schedule in the autonomous heating system provokes the formation of air jams. This occurs due to the transition of the coolant from liquid to gaseous state. Additionally, this affects the formation of corrosion on the surface of the metal components of the system. That is why it is necessary to accurately calculate what temperature should be in the heat supply batteries, taking into account their material of manufacture.
Most often, a violation of the thermal operating conditions is observed in solid fuel boilers. This is due to the problem of adjusting their power. When a critical temperature level in the heating pipes is reached, it is difficult to quickly reduce the boiler power.
Final conclusions
There are two of them:
- If the hot water temperature is low or excessively high, do not hesitate to invite housing workers to draw up a report on violation of the procedure for providing utility services. Based on it, you can recalculate for hot water supply and pay less than your neighbors;
Commission inspection report on a complaint about low water temperature
- When independently replacing risers and connections for centralized heating and hot water supply, use only metal pipes - galvanized steel, copper or corrugated stainless steel. Modern polymer materials do not have sufficient heat resistance to withstand any prolonged overheating under force majeure circumstances.
Stainless steel pipes for apartment water supply
Adjustment features
The parameters of heating routes are the responsibility of the management of thermal power plants and heating networks. At the same time, housing office employees are responsible for the network parameters inside the building. Mostly, residents' complaints about the cold concern deviations to the lower side. Much less common are situations where measurements inside thermal units indicate an increased return temperature.
There are several ways to normalize system parameters that you can implement yourself:
- Reaming the nozzle. The problem of lowering the temperature of the liquid in the return can be solved by expanding the elevator nozzle. To do this, you need to close all the gates and valves on the elevator. After this, the module is removed, its nozzle is pulled out and drilled out 0.5-1 mm. After assembling the elevator, it is started to bleed air in the reverse order. It is recommended to replace the paronite seals on the flanges with rubber ones: they are made to the size of the flange from a car inner tube.
- Silence the suction. In extreme cases (during the onset of extremely low frosts), the nozzle can be completely removed. In this case, there is a danger that the suction will begin to act as a jumper: to prevent this, it is turned off. For this, a steel pancake with a thickness of 1 mm is used. This method is emergency, because this can cause a jump in battery temperature to +130 degrees.
- Difference control. A temporary way to solve the problem of temperature rise is to adjust the differential with an elevator valve. To do this, it is necessary to redirect the DHW to the supply pipe: the return pipe is equipped with a pressure gauge. The inlet valve of the return pipeline is completely closed. Next, you need to open the valve little by little, constantly checking your actions with the readings of the pressure gauge.
A simply closed valve can cause the circuit to stop and defrost. A reduction in the difference is achieved due to an increase in return pressure (0.2 atm/day). The temperature in the system must be checked every day: it must correspond to the heating temperature schedule.
Heat losses of the building
The initial data in this case will be:
- thickness of external walls;
- thermal conductivity of the material from which the enclosing structures are made (in most cases indicated by the manufacturer, denoted by the letter λ);
- surface area of the outer wall;
- climatic region of construction.
First of all, find the actual resistance of the wall to heat transfer. In a simplified version, it can be found as the quotient of the wall thickness and its thermal conductivity. If the outer structure consists of several layers, find the resistance of each of them separately and add the resulting values.
How does a heating regulator work?
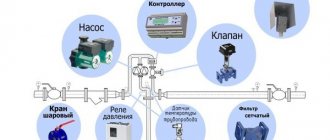
A regulator is a device that provides automatic control and adjustment of the temperature parameters of the coolant circulating in the heating system.
It consists of the following nodes and elements:
- Computing and switching unit;
- Actuator on the coolant supply line;
- An actuator for mixing water from the return line (sometimes a three-way valve is used and then they are combined);
- Boost pump on the “cold bypass” line (not always);
- Booster pump on the supply line;
- Shut-off fittings and valves;
- Coolant supply sensor;
- Return sensor;
- Outside air temperature sensor;
- Sensor (sensors in several places) room temperature;
The last two positions can be used either together or instead of each other, depending on how the heating schedule is set.
Now let's figure out how the control processes actually occur, how the regulator works.
Main elements of the temperature control system
The coolant temperature at the outlet of the heating system (return) depends on the volume of water passing through it, since the load is relatively constant. Therefore, the regulator, covering the water supply, increases the difference between the supply and return to the required value (sensors are embedded in these pipelines), to the required value.
If, on the contrary, it is necessary to increase the flow, then a booster pump is installed into the heating system, which is also controlled by the regulator. To lower the temperature of the incoming flow, the so-called “cold bypass” is used - part of the water circulated through the system is again sent to the inlet.
Thus, by redistributing flows depending on the data collected by the sensors, the regulator ensures a strict temperature schedule for the heating system.
One of the Vailant regulator block models
Often the heating controller is combined with a DHW controller using one computing unit. The hot water regulator is much simpler in terms of control and actuators. Using a sensor on the hot water supply line, the passage of coolant through the boiler is adjusted, and the stable 50 degrees required by the standard is ensured.
The need to perform constructions and calculations
A temperature schedule must be developed for each locality. It allows you to ensure the most competent operation of the heating system, namely:
- Bring heat losses during the supply of hot water to houses into line with the average daily outside air temperature.
- Prevent insufficient heating of rooms.
- Oblige thermal stations to supply consumers with services that meet technological conditions.
Such calculations are necessary both for large heating stations and for boiler houses in small towns. In this case, the result of calculations and constructions will be called a boiler room schedule.
Heating radiator temperature in the apartment: normal
Minimum indicator
It happens that even when the heating is turned on, there is still not enough heat in the apartment. This happens if the standard temperature of the heating radiators in the apartment does not correspond to the real one. As a rule, this happens for several reasons, the most popular of which is airiness in the system. To eliminate it, you can call a specialist or handle it yourself using a Mayevsky crane.
If the culprit is the unsuitability of batteries or pipes, then you cannot do without specialists. In any case, the period when the heating system was not working and the temperature of the radiators in the apartment did not meet the standards according to GOST standards should not be paid by the consumer.
Unfortunately, there is no minimum standard for the temperature of heating radiators in an apartment, so you have to navigate by the air temperature in the room. What heating temperature should be in the apartment? Heating standards for an apartment in an apartment building should vary from +16 to +25 degrees.
In order to document that the temperature of the heating pipes in the apartment does not correspond to the norm, you need to invite a representative of the organization that provides heat to the house.
Why do temperature fluctuations occur?
The reasons for temperature changes are determined by the following factors:
- When weather conditions change, heat loss automatically changes. When cold weather sets in, to ensure an optimal microclimate in apartment buildings it is necessary to expend more thermal energy than during warming. The level of heat loss consumed is calculated by the “delta” value, which is the difference between the street and indoors.
- The constancy of the heat flow from the batteries is ensured by a stable temperature of the coolant. As soon as the temperature decreases, apartment radiators will become increasingly warmer. This phenomenon is facilitated by an increase in the “delta” between the coolant and the air in the room.
The increase in coolant losses must be carried out in parallel with the decrease in air temperature outside the window. The colder it is outside, the higher the temperature of the water in the heating pipes should be. To facilitate the calculation processes, a corresponding table has been adopted.
Heat supply of a multi-storey building
Heating distribution unit for an apartment building
Heating distribution in a multi-storey building is important for the operational parameters of the system. However, in addition to this, the characteristics of the heat supply should be taken into account. An important one is the method of supplying hot water - centralized or autonomous
An important one is the method of supplying hot water - centralized or autonomous.
In most cases, a connection is made to the central heating system. This allows you to reduce the current costs in the estimate for heating a multi-storey building. But in practice the level of quality of such services remains extremely low. Therefore, if there is a choice, preference is given to autonomous heating of a multi-storey building.
Autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
In modern multi-storey residential buildings, it is possible to organize an independent heat supply system. It can be of two types - apartment-based or communal. In the first case, the autonomous heating system of a multi-storey building is carried out in each apartment separately. To do this, make independent piping and install a boiler (most often a gas one). A common house installation involves the installation of a boiler room, which has special requirements.
The principle of its organization is no different from a similar scheme for a private country house. However, there are a number of important points to consider:
- Installation of several heating boilers. One or more of them must perform a duplicate function. If one boiler fails, another must replace it;
- Installation of a two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building, as the most efficient;
- Drawing up a schedule for scheduled repairs and maintenance work. This is especially true for heating heating equipment and safety groups.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the heating scheme of a particular multi-storey building, it is necessary to organize an apartment-by-apartment heat metering system. To do this, energy meters must be installed on each incoming pipe from the central riser. That is why the Leningrad heating system of a multi-storey building is not suitable for reducing operating costs.
Centralized heating of a multi-storey building
Elevator unit diagram
How can the heating distribution in an apartment building change when it is connected to a central heating supply? The main element of this system is the elevator unit, which performs the functions of normalizing coolant parameters to acceptable values.
The total length of the central heating mains is quite large. Therefore, at the heating point, such coolant parameters are created so that heat losses are minimal. To do this, increase the pressure to 20 atm. which leads to an increase in the temperature of hot water to +120°C. However, given the characteristics of the heating system in an apartment building, supplying hot water with such characteristics to consumers is not permitted. To normalize the parameters of the coolant, an elevator unit is installed.
It can be calculated for both a two-pipe and a single-pipe heating system in a multi-storey building. Its main functions are:
- Reducing pressure using an elevator. A special cone valve regulates the volume of coolant flow into the distribution system;
- Reducing the temperature level to +90-85°C. A mixing unit for hot and cooled water is designed for this purpose;
- Filtration of coolant and reduction of oxygen content.
In addition, the elevator unit performs the main balancing of the single-pipe heating system in the house. For this purpose, it is equipped with shut-off and control valves, which automatically or semi-automatically regulate pressure and temperature.
You also need to take into account that the estimate for centralized heating of a multi-story building will differ from autonomous heating. The table shows the comparative characteristics of these systems.
Table of coolant temperature versus outside air temperature
In order to calculate the optimal temperature regime, you need to take into account the characteristics of heating devices - batteries and radiators. The most important thing is to calculate their specific power, it will be expressed in W/cm2. This will most directly affect the transfer of heat from heated water to the heated air in the room
It is important to take into account their surface power and the resistance coefficient available at window openings and external walls
After all the values are taken into account, you need to calculate the difference between the temperature in two pipes - at the entrance to the house and at the exit from it. The higher the value in the inlet pipe, the higher the value in the return pipe. Accordingly, indoor heating will increase under these values.
| Weather outside, C | at the entrance to the building, C | Return pipe, C |
| +10 | 30 | 25 |
| +5 | 44 | 37 |
| 57 | 46 | |
| -5 | 70 | 54 |
| -10 | 83 | 62 |
| -15 | 95 | 70 |
Proper use of coolant involves attempts by house residents to reduce the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet pipes. This could be construction work to insulate a wall from the outside or thermal insulation of external heat supply pipes, insulation of floors above a cold garage or basement, insulation of the inside of a house, or several works performed simultaneously.
Heating in the radiator must also comply with the standards. In central heating systems it usually varies from 70 C to 90 C depending on the outside air temperature
It is important to consider that in corner rooms the temperature cannot be less than 20 C, although in other rooms of the apartment a decrease to 18 C is allowed. If the temperature outside drops to -30 C, then the heating in the rooms should rise by 2 C
The temperature in the remaining rooms should also increase, provided that it may be different in rooms for different purposes. If there is a child in the room, then it can vary from 18 C to 23 C. In storerooms and corridors, heating can vary from 12 C to 18 C.
How to write a complaint to the management organization
If the hot water temperature schedule is violated constantly and regularly, then residents can write a collective or individual complaint against the management company that transports hot water. For a complaint to have legal force, it must be drawn up in a legally competent manner, citing facts and arguments. Any notary or lawyer can provide assistance in drawing up such a document.
The header of the document must contain the correct name of the organization against which the complaint is being made and the name of the responsible manager (if known to the complainant) to whom the document is addressed. Below are the personal details of the applicant: last name, first name, patronymic, address where the applicant is registered, contact information for subsequent communication regarding the application.
General complaint form:
- Document title;
- A statement that the temperature schedule is violated when providing residents with hot water according to the application form in accordance with Federal Law No. 195 under Article 7.23;
- The statement itself contains a description and essence of the complaint. It is necessary to write in the document that independent and control measurements of the hot water temperature were carried out with information from the previously drawn up report: date of measurement, personal data of the employee who carries out the control measurement of hot water temperature, temperature parameters;
- The complaint should end with a requirement to eliminate violations in the DHW supply or eliminate violations of the DHW temperature regime. In addition, you can oblige the company to inform you about the implementation of relevant work;
- At the end of the written complaint, the date of its preparation is indicated and the signature of the applicant is affixed. The complaint must be submitted and registered in 2 copies. The document is sent to the management organization by registered mail with notification, or is independently delivered by the applicant to the company’s office.
Complaint form to the housing and communal services management company
The second copy of the complaint, which remains with the applicant, must contain a mark on the acceptance of the document, and it must also indicate the date of receipt of the application and bear the seal of the management organization. The response to the complaint must be received no later than 30 working days.
Welcome to the real world
Let's look at the main scenarios in which the temperature of the hot water supply or heating may be noticeably higher or lower than normal.
Dead-end DHW system
In-house hot water supply systems can be divided into two main categories:
- Dead-end. Water is supplied through a single bottling into the risers, which are plugged on the top floor, and moves through the bottlings and risers only during its disassembly through the mixers in the apartments. This category includes DHW systems of buildings built before the early 1980s;
- Circulating. Two hot water dispensers are connected to each other by groups of risers connected by jumpers on the upper floors. Hot water continuously circulates through them; circulation is ensured by the pressure difference between the lines of the heating main, the difference on the throttling washer or the pump.
Two dispenses in the hot water circulation system
In the diagram, the jumpers between the risers are highlighted in blue.
In the absence of water supply in a dead-end system, the water in the pipes will inevitably cool down. Its cooling rate can be reduced by thermal insulation of the filling; however, thermal insulation is often damaged during repair work and is not always restored upon completion.
From a practical point of view, this feature of a dead-end system has two consequences:
- In the morning (after several hours of no water supply), water at room temperature is drained through an open hot water tap for several minutes;
Before heating water in a dead-end hot water system, it has to be drained for a long time
- Even with intensive water withdrawal, the water temperature decreases noticeably due to heat loss at the bottling, risers and connections. If the distance from the water collection point to the heating unit is large, it is possible that the water on the way to the mixer will be cooled from the maximum permissible +75°C to 55°C and below.
No difference in the route
Immediately after the end of the heating season, heat supply organizations usually reduce to a minimum, or even to zero, the difference between the supply and return of the heating network. Thus, they artificially stop the operation of heating systems, reducing their own costs.
After the end of the heating season, the difference between the lines of the heating network is reduced to a minimum
In the absence of a differential, the circulation of hot water in buildings with elevators (read - with the selection of hot water from the heating network) is impossible. Moreover, a huge volume of network water in heating mains is renewed only through water withdrawal. This is why the hot water temperature in summer often drops to 45-50 degrees and even lower.
By the way: low DHW temperature affects the operation of the sewage system. Since relatively cold water is used for washing dishes, the grease washed away by it settles on the walls of the sewer pipes and forms plugs that impede the movement of drains. It is in the summer that most calls to housing organizations related to sewerage blockages in apartments occur.
Fat deposits in the sewer
DHW switching
In buildings with an open heat supply circuit, hot water is supplied to consumers directly from the heating main through connections into the supply and return lines of the elevator unit.
Elevator unit with hot water taps
In both dead-end and circulation systems, the hot water supply switches between lines depending on the temperature of the heating main.
In the circulation system, three switching schemes are possible:
- Supply and return. The scheme is used only in summer, outside the heating season;
- Serve-serve. This scheme is typical for the off-season, when the supply temperature does not exceed the cherished +75°C;
- When the supply temperature rises, the DHW switches to a return-return circuit. Switching is carried out manually, after the corresponding order of the organization - the heat supplier.
If the hot water supply is not switched to return for any reason (due to the mechanic’s forgetfulness, faulty shut-off valves, etc.), as the temperature of the heating main supply increases, the temperature of the hot water supplied to the house will also increase. Moreover, it can go far beyond the boundaries prescribed by SNiP 2.04.05-91. What will happen at a water temperature of about 150 degrees with pipes designed for 90 - I think there is no need to explain.
The result of overheating of a reinforced polypropylene pipe
Track temperature tests
Once a year, shortly before the end of the heating season, heating mains are tested for temperature. The tests involve the heating system, but the hot water supply must be turned off during the tests.
During the test, the supply temperature rises to the maximum values prescribed by the temperature schedule.
The tests are designed to identify areas of the heating network that require repair.
If you do not turn off the domestic hot water supply to your home, overheated water will again flow into the water supply system, retaining its liquid state only due to high pressure. The situation is complicated by the fact that tests begin in April-May, when the hot water supply is turned on from the supply pipeline.
Hot water supply is included from the supply
Deviations from the temperature chart
A decrease in heating supply temperature (and, accordingly, cold in apartments) may have the following reasons:
- Deviation of the thermal power plant or boiler house from the temperature schedule due to lack of fuel or other external factors;
- Repair work on the heating network section. During this time, the bypass lines of the heating main are activated, which means an increased load on them above the design load - and again, a decrease in the parameters of the coolant;
Winter heating main repair
- Incorrect elevator nozzle design. If its diameter is reduced, the temperature of the mixture of supply and return water entering the heating circuit will be lower than that provided for by the schedule.
In addition: the temperature of the mixture may be noticeably higher than the calculated one due to erosion of the nozzle by suspended particles. However, this situation is the exception rather than the rule: heat suppliers take control measurements in all elevator units several times during the winter to prevent excessive consumption of thermal energy.
Water jet elevator with nozzle removed
Elevator operation without nozzle
The last scenario is related to the operation of elevator units during extreme frosts.
Heating parameters and, accordingly, the nozzle diameter are calculated for the consumption of thermal energy during the average minimum cold weather. Simply put, the calculation uses the minimum temperature that has held for at least five days in recent years.
Temperature of the coldest five-day period in Russian cities (first column)
Meanwhile, every few years frosts can drop significantly below these values. Increased heat losses from the building mean cold in the apartments, a large number of complaints about the heating and... recalculation for heat, which for its suppliers is fraught with the loss of a significant part of the income.
In elevators with an adjustable nozzle, the problem is solved by adjusting it.
Adjustable nozzle adjusts according to heat demand
In other cases, it is often practiced to operate a water-jet elevator without a nozzle: it is removed, and the suction (pipe connecting the elevator to the heating return) is muffled with a steel pancake.
Elevator with nozzle removed
In this case, water flows directly into the heating circuit from the supply of the heating main, which has a maximum temperature in extreme cold (up to +150°C).
In addition: the same scheme is used when dismantling the nozzle to change its diameter (brewing or boring). A complete stop of the elevator in severe frosts is fraught with defrosting of the access heating.
In the photo - a defrosted radiator in the entrance
Parameters for calculating heating systems: radiators
Heating optimization is related to the thermal output of heating devices. Radiator batteries have an interval of 140-220 watts.
The second parameter for calculation can be found in SNiP; to heat 1 square area, 100 watts are required. This is a rounded value; rooms differ in the degree of insulation.
Types of radiators
Cast iron radiators
Cast iron batteries have proven themselves well. Reliable, have good thermal characteristics. They are inert, take a long time to heat up, but take longer to cool down.
The power of cast iron radiators is calculated by sections; the heat output of one section is 150 watts.
Aluminum radiators
Good heat dissipation up to 200 watts per section, they heat up quickly, but are not durable. They have poor contact with other metals and begin to deteriorate upon contact. Operating temperature - 70 °C
Steel radiators
Good heating, does not have power characteristics like aluminum or cast iron. The power is indicated in the product passport, depending on the size and design: 200W-10kW. Designed to operate at a coolant temperature of 70 °C.