A winter greenhouse is a useful structure for a plot of land that allows you to grow garden crops all year round. It is used both for personal needs and for growing fruit plants for sale.
The most versatile material for constructing greenhouses is polycarbonate. It is this that allows the use of the latest construction technologies, design developments and technical equipment for greenhouses.
Polycarbonate retains heat well and allows enough sunlight to pass through. Source plodogorod.com
Types of winter greenhouses
According to the type of construction, a winter greenhouse can be of two types:
- conditionally capital, this is a structure that can be dismantled at any time;
- capital, such a structure cannot be dismantled. Built on a foundation.
According to the types of greenhouse roofs, there are:
- thermos (recessed). The main part of the greenhouse is located underground, which provides heat in the greenhouse;
- arched Very convenient for growing plants in the ground;
- gable, promotes growing plants in boxes;
- single-pitched, very convenient if attached to the house.
Features of installation of warm greenhouses
Depending on the purpose of the greenhouse, the method of its heating, the level of illumination and other technical characteristics are selected. Winter greenhouse structures are buildings on a foundation that can withstand strong gusts of wind and snow loads.
First, you need to decide on the place where the winter greenhouse with heating will be installed with your own hands. It could be a hillock or a hill. If the terrain is flat, then it is advisable to create an earthen embankment. This method contributes to additional heating of the greenhouse building due to the sun.
It is advisable to allocate an area for a vestibule within the building area. It will create a transition zone and cold air will not penetrate to the planted plants.
Heating and lighting of a winter greenhouse
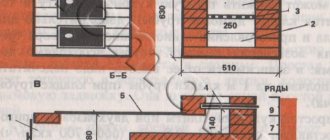
The winter greenhouse must have heating. It can be: stove, electric, water. Stove heating (using a stove) or biofuel heating (straw, hay, manure, grass, fallen leaves) is perfect for a small greenhouse.
The process of heating with biofuel begins with digging a trench around the perimeter of the greenhouse, into which it is laid, and then covered with soil. For greenhouses with an area of more than 20 sq.m. It is better to use water heating using metal pipes or electric heating using electric heaters.
For normal plant growth, sufficient lighting is required for 12-15 hours a day.
The range of light should be 400-700 nanometers. Lighting below 380 nanometers, which is ultraviolet and above 780 nanometers, infrared, will have a negative effect on vegetable crops.
The light source in the greenhouse can be:
- incandescent lamps. An outdated option for greenhouse lighting due to low efficiency;
- mercury lamps emit enough light and are affordable;
- sodium lamps, the most effective option for flowering plants, but expensive;
- halogen lamps are very effective, but short-lived when exposed to water;
- luminescent, durable and inexpensive illuminators, but with low light output;
- LED lamps are the best option for lighting greenhouses, since they consume little energy and provide the necessary amount of light for plant growth.
Useful tips from Krovelson
- For temporary heating, you can use a bucket of hot coals. It is installed on a brick inside the greenhouse, which is also a good conductor of heat and retains it for a long time. There is another “grandmother’s” method - a kerosene lamp between two bricks, covered with a metal bucket.
- When choosing a greenhouse, the future owner must clearly understand its purpose: what crops will be grown there, how the greenhouse will be used (all year round or only during the summer season). It is necessary to decide on the area and location of the beds inside in order to achieve a more effective use of the greenhouse.
- Before installation, it is important to understand whether additional communications will be carried out inside. If the structure is planned to be made solid, then all work on installing heating, watering, and ventilation must be carried out in a timely manner in order to avoid future alterations.
- The design of the greenhouse must be suitable for the local climate. In regions with heavy precipitation (snow), pitched greenhouses are most often installed so that snow does not accumulate on the roof, but simply comes off it without consequences, without creating stress on the frame and preventing deformation.
- We are always ready to help clients and choose the optimal solution, advise on the choice of materials, and find an option that fits the required budget. We have high-quality products from the manufacturer and modern types of structures that will serve their owners for a long period and will not require repair work.
Material for winter greenhouse
There are no problems with the choice of material for a winter growing greenhouse these days. This could be: wood, PVC pipes, polycarbonate, old window frames. As a rule, the frame is made of wood or metal.
Wood is a more affordable material, but less durable. The metal is strong and durable, able to withstand any load of the greenhouse covering.
Polycarbonate is considered the best cladding material due to its high light conductivity and thermal insulation. Glass can be used for greenhouses with a small area. It is not recommended to use film, as condensation collects under it and can freeze at low temperatures.
Landing
Preliminary preparation of the plant is necessary: the shoots of the seedling are shortened to 3-5 buds, cutting off weakened growths, the roots are trimmed and left in water with the addition of a biostimulant (for example, “Zircon”) for 24 hours. The soil at the planting site is prepared in advance by digging it up with humus and the necessary fertilizer complex.
When planting a young crop, ensure its correct location: the root collar is buried 10 cm into the soil. Upon completion of planting, the soil is well compacted, and the tree trunk circle is watered abundantly.
DIY winter greenhouse
The work of constructing a winter greenhouse with your own hands begins with pouring the foundation. To do this, you need to clear a place along it, and put pegs with ropes as markings. Both the outer contour of the foundation and the inner one should be marked.
Dig a trench half a meter deep, fill it with sand or sand with crushed stone, compact it and water it. Then put up the formwork, lay down the reinforced mesh, and fill it with cement mortar.
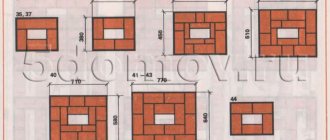
After a month, you can begin building the walls of the greenhouse. The walls of the greenhouse can be built from foam concrete blocks, for laying which you can use cement or specially designed glue.
Place a thin layer of cement mortar on the foundation and waterproofing (roofing material, bicrost, etc.) on top. The first row of blocks must be laid on cement. Make the roof single or gable.
An inexpensive option for growing cucumbers, herbs and other vegetables in a winter greenhouse is a greenhouse made of PVC pipes covered with plastic film. Thanks to the flexibility of the pipes, the frame of the greenhouse can be made of any type (arched, gable, lean-to, dome).
Mark the boundaries of the future greenhouse with boards, on the outside of which place reinforcement 15-20 centimeters long above the ground. Install the ends of the pipes onto the reinforcement pins.
To ensure the strength of the arched structure, another PVC pipe is tied under the pipes that create the arch (with a tie wire or a clamp). The film can be attached to the pipes with special clamps.
Typical technology for constructing such a building
So, how to build a winter greenhouse and what to pay attention to during work? Just like the summer one - except that a foundation will be needed. And then, as soon as the installation of the greenhouse is completed, you can begin installing the heating. So, polycarbonate greenhouses running on biofuel are considered the most reliable in this regard - this is the most ideal option for a summer residence. After all, technical heating has its limits, and it is not so cheap. But for a structure that stands right next to the house, it is quite suitable, because it can be connected to a communal heating system. So, in order to determine the correct heating wiring, it is necessary to take into account the following formula: the amount of heat demand = the temperature difference between the thermal conductivity coefficient and the glazing area. And calculating this value is just the first step.
Now you need to select heating devices. Aluminum convectors are considered one of the best, they evenly distribute heat throughout the greenhouse.
The next step is to prepare the soil. Its optimal composition is a layer of sand + a layer of turf soil + a layer of humus. To treat such soil, you need to prepare a mixture of a teaspoon of urea and one teaspoon of superphosphate - this way all pests will be destroyed in winter.
So, as soon as all the elements of the heat accumulator are laid at the bottom of the pit and its ventilation pipes are installed, everything needs to be covered with PVC film on top. This is necessary to ensure that the soil does not get into the heat accumulator and eventually clog it. On the other hand, such a coating helps create good conditions in the greenhouse for the accumulation of humus.
As a result, both the bottom and walls of high beds should be covered with PVC film. You need to “shoot” it against the walls with a regular construction stapler, and in those places where the film will be “pierced” by pipes, small cuts should be made. After which the soil can be backfilled into the greenhouse: infertile soil is placed on the path, where tiles will later be laid, but the beds are filled with a top, turf layer. By the way, pieces of turf need to be laid with their roots facing up, so that plant debris does not germinate. But even before pouring soil into the beds, it is important to fence off their inner walls and tighten them every meter with strong eight-millimeter wire - otherwise the soil will simply burst apart the walls. And in order to prevent the wire from rotting, it is advisable to wrap it in advance with plastic insulating tape and put a plastic pipe on it.
If the construction of a winter greenhouse was not intended for cucumbers, and there will not be such strong humidity in it, it is better to make the frame for it wooden. It can be impregnated with a good antiseptic, and it will serve for quite a long time. Wood is a much more technologically advanced material; it is much easier to screw and attach something to it than to a metal frame.29
Winter greenhouse made of polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is considered an ideal material for winter greenhouses. Its advantages are that it:
- not subject to damage;
- has a presentable appearance;
- suitable for any frame due to its low weight;
- has high light conductivity;
- easy to install;
- withstands heavy loads and temperature changes.
To build a polycarbonate greenhouse, you need a foundation, which can be either strip or timber, or stone or brick. For the frame it is better to use metal profiles, pipes and corners.
The first row of pipes is fixed to the foundation using anchor bolts. Vertical posts can be secured in the same way or welded. Next, secure the horizontal (under the roof) pipes in the same way and make a roof.
Polycarbonate sheets must be cut to fit the frame. You need to start installing them from the bottom of the greenhouse from the corner. On the inside of the greenhouse, the joints must be insulated using sealants or other means.
Criterias of choice
In principle, heating a greenhouse is possible using a variety of stoves and heaters, as long as the power generated allows creating the desired temperature in a certain area. But if we talk not about the “principle”, but about the practical use of certain solutions, we need to think about completely different things. Thus, the best heating system designs will be useless if their dimensions do not allow the use of a particular device in a particular room. The power of devices varies not only according to area, but also according to material - it has long been known that heat loss through polyethylene is higher than through polycarbonate.
The next important criterion is the amount of costs, and one should take into account both the costs of the components, their installation, and subsequent use. Some types of heaters are completely impractical in small greenhouses, others are installed at a minimal price, but during operation they consume a large amount of fuel or energy.
Steam heating is justified if it is possible to connect the greenhouse to the heating system of the house. It is advisable to insulate the pipes properly, and you will have to create a significant reserve of boiler power. It is undesirable to use such a system when the distance from the home to the greenhouse is more than 10 m. An autonomous steam heater can be installed in the greenhouse itself, water circulation is provided by special pumps.
In early spring, it is recommended to use solid fuel boilers and stoves, as they resist frost well. Boilers are better than stoves because they do not require frequent additions of fuel and they are used very efficiently. Boilers operating on solid fuel cannot be placed directly in a greenhouse, so as not to dry out the air; in extreme cases, humidifiers must be placed nearby.
Geothermal greenhouse heating is only rarely practiced because heat pumps are expensive and very difficult to install. It is advisable to create a comprehensive heating system that simultaneously warms not only the greenhouse, but also the house
Important: heat pumps are needed for liquid soil heating systems; they are not capable of supplying water to radiators
Water circulates through them, at the same time it warms up quite strongly and enters a special line. Solar panels (or, in other words, photovoltaic panels) are not suitable for heating greenhouses, since they are designed to generate electricity. It is advisable to use, along with collectors, gas boilers, furnaces, heat pumps and other heating means to protect against darkness.
Thermal tape is used quite often in greenhouses. The composition is a glass thread, supplemented with a thermostat. Inside there are eight nichrome wires surrounded by waterproof rubber. The device operates stably only in the temperature range from 15 to 20 degrees, which allows you to consume current only as needed. Each part of the plant is heated equally; the only alternative that can achieve the same effect is heating with manure. But tape is better because it helps warm up the greenhouse in almost any weather, not just in the warm months.
The tape prevents the death of plants during sudden frosts.
Quite often, a lamp or even a series of lamps are used for heating purposes. Infrared heating of this type is directed from top to bottom and effectively affects the entire plant, and also warms up the soil layer. According to research, such systems increase germination by 30-40%.
A simple greenhouse for greenery
To create a small greenhouse for greenery or seedlings, you need to put together a wooden box using self-tapping screws and corners. Next, make a greenhouse lid from the boards; you can use plastic film or glass as a covering material.
Attach the lid to the base box with metal hinges. If the greenhouse is large, you can make several covers. The main thing is to treat the wooden parts with an antiseptic.
When is a heater needed?
The presence of a heater helps to achieve earlier germination, harvesting ahead of schedule and in a shorter period. Sometimes such a device is installed in ordinary
greenhouses in regions with rather short summers or very changeable weather.
They are recommended to be used in the spring to allow early sowing of seeds or seedlings. In summer, the technique is used if the air temperature in the region can drop to critical levels. In autumn, especially at night, when frosts begin. In winter - if there is not enough power of the general heating system.