What are there
Classification of heating devices is carried out according to the following criteria:
- Coolant type. Can be liquid or gaseous.
- Material of manufacture.
- Specifications. This refers to dimensions, power, installation features and the presence of adjustable heating.
When choosing the best option, you need to take into account the characteristics of the heating system of the house and operating conditions. In this case, the entire list of requirements and standards relating to heating devices must be observed. Along with the power of the products, the specifics of their installation are of great importance. In the absence of a gas supply and the possibility of installing water heating, there is still an option with electric heaters.
Heated towel rail in the apartment.
We recommend reading the article How to choose a heated towel rail
There is the following division of heated towel rails according to the heat source: electric, water, combined. According to the material used in production: steel, copper, brass.
Advantages:
Huge selection of shapes and colors Good working pressure (up to 16 bar)
Flaws:
If you use a water heated towel rail during a lack of water supply, it will not function
Water heating system design
Water heating is the most common method of heating buildings. This explains the presence on sale of a significant variety of types of heating devices for water circuits. The reasons lie in the good level of efficiency of these products, as well as reasonable costs for purchase, installation and maintenance. The designs of these heating devices are very similar to each other. The core of each of them is a cavity: hot water circulates through it, heating the surface of the battery. Next, the convection process comes into play, transmitting heat to the entire room.
Radiators for water heating systems can be made from the following materials:
- Cast iron.
- Become.
- Aluminum.
- Combinations of materials (so-called “bimetallic batteries”).
Each of these types of heating devices has its own specifics. In each specific case, it is necessary to take into account the area of the heated room, installation features, quality and type of coolant used (for example, in some cases antifreeze is used). To regulate the battery power, it is possible to extend or detach sections. It is advisable that the length of one radiator does not exceed 1.5-2 meters.
Types of heating devices
Convection-radiator type device - aluminum
The design and efficiency of the heater determines the methods of heat transfer. This is the main classification of devices.
- Convective - transfer at least 75% of heat by convection - jets. Example – convectors, finned tubes. The source, usually a heating element, heats the air, it is transmitted into the room, and surfaces, furniture and people are heated by the warm air masses. The devices can be very efficient due to the speed at which the air warms up, but they consume a lot of electricity.
- Convective-radiative - transfer from 50 to 75% of heat by convective method. These are most traditional heaters: radiators, floor heaters, smooth tube heaters.
- Radiation – 50% of heat is radiation. This includes IR heaters, ceiling and panel devices. The heater generates infrared radiation, in this case the surfaces, objects and people in the room are heated first, and only then the air. Eliminating air from the heat transfer chain reduces heating costs.
Convective-radiation heaters are most often installed. The devices have high efficiency, are cheap and practical.
By coolant type
The heating system uses different types of coolant - antifreeze, water, mineral oil.
A traditional heating system implements the following scheme. The heat source is a boiler - gas, electric, door fuel. It heats a certain volume of coolant, which enters the system and gives off heat through the surface of pipes and heating devices.
The coolant must meet many requirements: absorb and release a sufficient amount of heat, not cause corrosion, and heat up to the required temperature.
- Water is the only option for central heating. The reason is the large distances between the heat source and the consumer. Replacing with any other option increases the price of heating tenfold.
- Steam is the so-called dry steam. Used in vacuum-steam systems, in low and high pressure systems. Plus - the room warms up 3 times faster, there is no risk of pipes freezing. The disadvantage is high fuel consumption.
- Antifreeze - “anti-freeze”. Glycerin solution, ethylene glycol solution, propylene glycol and others. Liquids prevent freezing even in pipes with the smallest diameter. It is recommended to pour antifreeze into a water heated floor. During circulation, the coolant acts as a lubricant, which increases the service life of pipes and radiators. The disadvantage is the need to select antifreeze to the type of boiler.
- Transformer or mineral oil is the coolant in oil heaters. This is a viscous, heat-intensive liquid that can transfer heat to the air in the room for a long time.
You can select a coolant and the corresponding heating device only when organizing an autonomous heating system.
According to technical characteristics
Ceramic heaters are resistant to corrosion, so they work longer without breakdowns.
To assess the efficiency of a particular model, it is necessary to analyze the technical indicators.
- Heat transfer is the main criterion. For this reason, a radiation apparatus is better than a convective apparatus. Cast iron radiators have the highest thermal inertia, while aluminum radiators transfer heat best.
- Working surface - it is important to consider the total area of the battery, and not the number of sections. The dimensions of the heater are calculated taking into account the volume of the room.
- Corrosion resistance – ceramic heaters are the most resistant. Of the metal models, the best are aluminum.
- Resistance to pressure - convectors are the most resistant, since they do not have such a load. The best radiators are cast iron and bimetallic.
- Easy to maintain - convectors and aluminum panels only need to be wiped periodically. Cast iron and steel must be painted.
- Service life – cast iron batteries last the longest – 50 years. Bimetallic ones last 30–40 years. Steel ones are the least durable - no more than 10–15 years.
Thermal characteristics are not the only parameter of choice. Radiators must meet the requirements of the selected heating system.
Cast iron batteries
The cast iron type of heating devices is one of the most common options for completing domestic centralized systems. It was preferred to other varieties mainly because of its low cost. Subsequently, devices of this type began to be gradually replaced by devices with a higher heat transfer coefficient (for cast iron batteries it is only 40%). Currently, old-style systems are mainly equipped with cast iron radiators. As for modern interiors, you can find designer cast iron models in them.
The strengths of heating devices include a significant surface area through which energy is transferred from the coolant to the surrounding space. Another noticeable advantage is the durability of cast iron batteries: they can last 50 years or more without problems. There are also disadvantages, and there are many of them. Firstly, the coolant is used in very large volumes (up to 1.5 liters for each section). The cast iron heats up slowly, so you have to wait until, after turning on the boiler, heat begins to flow into the rooms. Repairing such batteries is not easy, and in order to minimize the likelihood of breakdowns, they have to be cleaned every 2-3 years. Installation work is complicated by the large weight of the radiators.
General information
Some people ask this question: what should you first pay attention to when choosing steel heating radiators? The range of steel heating devices today is very diverse. On the one hand, there is plenty to choose from, but on the other hand, a large selection can cause a feeling of confusion
Steel radiators, first of all, may differ by manufacturer. They may also vary in color, size, price range, size or design features. Today, steel radiators are a completely worthy replacement for cast iron radiators, which were the leader in popularity not so long ago.
Steel radiator design
It is not recommended to install steel heating radiators in rooms where there is a high level of humidity, so they are not suitable for a bathroom. Today, steel heating devices can be seen not only in private homes, but also in shops, offices, and country cottages. This is due to their low cost, and at the same time, beautiful and stylish design.
The cost of steel heating radiators primarily depends on their power ratings and size. Sometimes some steel radiators with similar parameters are more expensive than others, only because of the more popular brand. Therefore, think about whether it is worth paying the extra money. Of course, domestic devices will cost slightly less than those produced in Europe. But in terms of size and operating parameters, they may not differ or may differ, but not significantly.
Classification and sizes of steel radiators
In order to choose the most suitable radiator, you need to take into account the following nuances:
- More uniform heating of the entire room depends on how deep and low the heating device is located.
- It is necessary that the radiator be equipped with an element such as a Mayevsky valve, as this will make it possible to bleed excess air from the system. It is also advisable that the radiator be equipped with water interruption taps. Unforeseen emergency situations may arise, and such cranes will come in handy.
- If a heating radiator is installed under a window, then its width should be no less than 50-70% of the width of the window opening.
- To make the heating radiator more practical, you can choose a model that is equipped with a thermostat. Such an element can be either manual or automatic.
Requirements for installing a heating radiator
Bimetallic batteries
The strength of bimetallic structures are special convection panels that increase the quality of air circulation. In addition, devices of this type can be equipped with special regulators, with the help of which you can increase or decrease the coolant flow. Installation work in its simplicity resembles the installation of aluminum radiators. Each section has a power of 180 W, providing heating of 1.5 m2 of area.
In some cases, the use of water-type heating devices encounters serious difficulties. For example, bimetallic radiators cannot be installed in systems where antifreeze is used as a coolant. These non-freezing liquids, which protect pipes from freezing, can have a destructive effect on the inside of batteries. You should also take into account the high cost of this heating option.
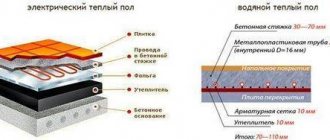
Electric types of heaters
In cases where problems arise with the organization of water heating, it is customary to use electric heaters. They are also available in several varieties, differing from each other in power and method of heat transfer. The most significant disadvantage of household heating devices of this kind is the high cost of electricity consumed. In this case, it is often necessary to lay new wiring designed for increased loads. If the total power of all electric heaters exceeds 12 kW, technical standards provide for the organization of a network with a voltage of 380 V.
Equipment power calculations
The indoor temperature depends on the following factors:
- air temperature outside the building;
- the thickness of the walls of the house and the quality of its individual elements;
- heat capacity of the materials from which the house is built.
When calculating your home's heating needs, you need to take into account all factors, including heat loss through windows and doors, walls and floors with ceilings. Special standards required in the calculation process must be applied taking into account the climatic conditions of the area in which the residential property is located and the degree of existing thermal insulation.
The general meaning of the calculation is to calculate the total heat losses corresponding to the minimum air temperature in your region in order to purchase equipment that can more than compensate for these losses
The greatest heat loss occurs through the outer walls of the house. As the temperature difference between inside and outside the building increases, heat loss also increases.
If we take into account the material from which the external walls were built and the thickness of these walls, then for an external air temperature of – 30°C, the heat loss will be different and amount to:
- brick with internal plaster - 89 W/m² (2.5 bricks), 104 W/m² (2 bricks);
- chopped with internal lining (250 mm) - 70 W/m²;
- from timber with internal lining - 89 W/m² (180 mm), 101 W/m² (100 mm);
- frame with expanded clay inside (200 mm) – 71 W/m²;
- foam concrete with internal plaster (200 mm) – 105 W/m².
However, heat loss occurs not only through external walls, but also through other enclosing structures.
At the same – 30°С they will be for:
- wooden attic floors - 35 W/m²;
- wooden basement floors – 26 W/m²;
- double wooden doors without insulation – 234 W/m²;
- windows with double frame made of wood – 135 W/m².
To calculate the total heat loss of a building, you need to calculate the area of all enclosing structures in square meters, multiply by the standard heat loss by type of structure, taking into account the materials from which they are made, and summarize the results.
The calculation should be made based on the minimum seasonal temperature of a particular area. Heat losses through the walls are calculated separately, because it is necessary to take into account the area of glazing and doorways.
Losses through floors without hatches into the attic or underground are calculated for the entire area as for single structural elements.
The heating boiler is chosen taking into account the fact that its power should be enough to compensate for heat loss with a 20-30 percent margin.
On our website there is a block of articles devoted to the calculation of water heating, we recommend that you read:
- Hydraulic calculation of a heating system using a specific example
- Calculation of water heating: formulas, rules, examples of implementation
- Thermal calculation of a heating system: how to correctly calculate the load on the system
Oil radiators
The principle of convection is also used in the operation of oil electric heaters. A special oil is poured inside the device to be heated by a heating element. To regulate heating, a thermostat is often used, turning off the power when the desired temperature is reached. Oil-based devices have high inertia. This manifests itself in the slow heating of the device and the same slow cooling after the power supply is cut off.
The surface temperature is usually heated to 110–150 degrees, which ensures compliance with safety regulations. Such a device must not be installed close to flammable surfaces. Oil radiators are equipped with convenient adjustment of heating intensity, designed for 2–4 operating modes. Keeping in mind the power of one section (150–250 kW), choosing the optimal model for heating a specific room is not at all difficult. The maximum power of such a device is limited to 4.5 kW.
Infrared heating
The choice of infrared heating devices brings the following dividends:
- Energy savings of up to 30% when compared with conventional electrical appliances.
- Oxygen in the air does not burn.
- The room heats up in a matter of minutes.
Infrared devices are classified according to the method of wave transmission. In new heating devices, radiation is transmitted into the surrounding space thanks to resistor conductors installed on a special film. The power of warm mats can reach 800 W/m2. Film heaters are convenient because they can be used to create heated floors.
As for carbon emitters, the waves are emitted in spirals from a sealed transparent bulb. The power of such devices is in the range of 0.7-4.0 kW. The power of carbon heaters is an order of magnitude higher, which requires more stringent fire safety measures.
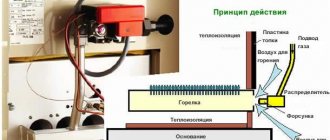
Gas heating
In order to save money, you can use gas heaters. Their simplest variety is a gas convector, which is connected to a main gas pipeline or a liquefied propane cylinder. The burner of the device is completely protected from contact with the surrounding atmosphere: in this case, a special tube is used to supply oxygen, which is led outside through a hole in the wall. These devices are characterized by high power (at least 8 kW) and low cost of operation. Among the weaknesses of gas heaters are the mandatory registration with regulatory agencies, the need for effective ventilation and the need for regular cleaning of nozzles.
Gas convector
Heating in such a heating device occurs due to the combustion of gas, where combustion products are discharged through the chimney pipe. The cost of such convectors may vary depending on their specifications. With this type of heating you can set different temperatures in different rooms. The efficiency may be higher than that of boilers, but in principle the same. The disadvantages include the following: There are no different capacities, it does not heat the water, you can only heat one room. Such convectors are suitable for heating cottages and garages due to the possibility of being powered by a gas cylinder.