The basis of any heating is a boiler. Whether the house will be warm depends on how correctly its parameters are selected. In order for the parameters to be correct, it is necessary to calculate the boiler power. These are not the most complex calculations - at the third grade level, you will only need a calculator and some data on your possessions. You can handle everything yourself, with your own hands.
There are several ways to calculate the power of a heating boiler
Which boiler to choose for a private house of 100 sq. m?
It is believed that for every 1 square meter of area of a well-insulated room, 1 kW of thermal power of the heat generator is required. This means that for 100 square meters of area you need a boiler with a power of 10 kW.
Interesting materials:
Is it possible to have sweets on a healthy diet? Can acrylic paints be mixed? Is it possible to look at photos of the dead? Is it possible to demolish a load-bearing wall? Is it possible to deregister a car through MFC? Is it possible to remove the tile without damaging it? Is it possible to collect chaga? Can Aramis Stilton be saved? Is it possible to sleep on one side? Is it possible to place an oven under the hob?
Heating a house with electricity
Nowadays, home heating with electricity is becoming increasingly popular. Most often, this method is used in places where there is no central gas pipeline.
Despite the fact that electricity is still more expensive than gas, knowing the specifics of installing equipment for electric heating at home can save you a lot of money.
Let's try to calculate the energy consumption for heating a 100 m² house using a specific example.
Before you start installing your heating
Practice shows that such an alternative source of home heating is the future.
Before installing such a heating system in your home, you need to decide:
- which method is most suitable for you,
- how much money are you willing to spend on this venture in order to be able to save later,
- how powerful the source of electricity is in the building.
It is these factors that should influence the choice of a home heating system.
Case Study
Let's give a practical example of electricity consumption for heating a 100 m² house.
The efficiency of an electric boiler is basically 100%. For 1 kW of heat energy, 1.03 kW of electricity is consumed.- Let’s take, for example, the electricity tariff for heating a house is 4 rubles.
- The heat consumption coefficient for heating 10 m² is equal to 1 kW, for this example 10 kW of heat per area of 100 m².
- The average daily energy consumption rate is 1 kW/hour, which means: 10 kW x 24 hours = 240 kW.
- We take the uninterrupted operation of the boiler as a basis, that is, we calculate the maximum per month: 240 x 30 = 7200 kW.
Total, monthly calculation: 7200 kW x 4 rubles = 28,800 rubles.
These are maximum calculations taking into account the constant operation of the boiler, which does not happen in practice. After all, having heated the house to a certain point, it turns off and does not work, and accordingly there is no energy consumption. Therefore, the resulting value can be safely divided by 2 = 14,400 rubles/month.
Types of boilers
To heat a private home, single-phase and three-phase boilers are most often used.
Their choice is a responsible matter, since your energy costs depend on it. After installing boiler equipment, the load on power lines increases significantly. Therefore, first of all, you need to contact the company that supplies electricity in your area and find out the maximum current strength.
When calculating kilowatts of energy, take into account the presence of working electrical appliances in the house.
Single-phase electric boiler for home heating
A single-phase boiler operates from a 220 V network. It is easy to connect, because the boiler power is in the range of 6 - 12 kW, so they are most suitable for installation in a house of no more than 100 m².
The characteristics of a single-phase boiler are as follows:
- works like any simple electrical device;
- 220V network required;
- installation without permits.
Go to catalog>>
Three-phase electric boiler for heating a private house.
Such a boiler has more power than a single-phase one, so it can be installed in houses larger than 100 m².
To operate the boiler, a 380 V network is required.
Characteristics of a three-phase boiler:
- power. For 10 m² you need 1 kW + 10-20% (as a reserve);
- operation from three phases 380 V, an increase in the current supply power in the room is required;
- For installation, you need to take permission from the energy sales office in order to increase the power used and install the boiler.
Go to catalog>>
Calculation by room volume
In this case, the main indicator is thermal energy equal to 41 W per 1 m³. This is also a standard value. True, in rooms with double-glazed windows, a value equal to 34 W is used.
22x2.6x41/145=16.17 – round up, resulting in 16 sections.
Pay attention to one very subtle nuance. Manufacturers, indicating the heat transfer value in the product data sheet, take it into account according to the maximum parameter
In other words, they believe that the hot water temperature in the system will be at its maximum. In life this is not always true. Therefore, we strongly recommend rounding the final result up.
Manufacturers, when indicating the heat transfer value in the product data sheet, take it into account according to the maximum parameter. In other words, they believe that the hot water temperature in the system will be at its maximum. In life this is not always true. Therefore, we strongly recommend rounding the final result up.
And if the power of the section is determined by the manufacturer in a certain range (a fork is installed between two indicators), then choose a lower indicator for calculations.
Solid propellant
How to heat a house if there is no gas in your village?
The holder of an honorable second place in terms of cheapness of heating is a solid fuel boiler. Traditional boilers of this type have a fairly high rated thermal power and allow it to be regulated in a way as ancient as the world - by limiting the access of oxygen (in other words, by a covered ash pan, which at the same time serves as an ash pit door).
Construction of a solid fuel boiler
Technological progress has made very minor changes to the design of a traditional heating device: the only difference is that in modern boiler models, the ash door is controlled via a chain by a mechanical thermostat.
Traditional solid fuel stove with mechanical thermostat
Restricting the access of oxygen to the firebox has one negative consequence - incomplete combustion of fuel. Gaseous products of combustion of wood or coal contain many volatile hydrocarbons. When the boiler vent is closed, your money literally flies down the drain.
So-called pyrolysis (or gas generator) boilers and furnaces do not have this drawback.
Gas generator from Viessmann
The combustion process of solid fuel is divided into two stages:
- Initially, it smolders in the firebox with limited access to oxygen. The products of incomplete combustion are carbon monoxide and those same volatile hydrocarbons;
- Then, in a separate chamber, atmospheric air is mixed with the products of incomplete combustion. They burn, giving up their heat to the heat exchanger and at the same time supporting the smoldering process of firewood or pellets in the primary firebox.
Electric heating
Electric boilers provide the most expensive heat for a home, and costs gradually increase as tariffs rise. On this wave, many manufacturers offer so-called economical boilers, which allow you to reduce heating costs by 20...50 (insert the desired number from the last advertisement you saw).
Electrode electric boilers are offered by manufacturers as an economical solution
Debunking myths
First and most importantly: any direct heating device (that is, converting electricity directly into heat due to the interaction of charged particles with the structure of the conductor) has an efficiency tending to 100%. This statement directly follows from the law of conservation of energy: the electric boiler does not produce any other types of energy except heat.
The law of conservation of energy was formulated more than two centuries ago and has not been challenged by anyone
Want to argue?
Let's think about it:
- The boiler does not perform mechanical work (that is, it does not move any mass against the gravity vector);
- It emits predominantly in the IR spectrum. Thermal radiation contributes to the same heating of the room;
- Minor losses due to currents induced in nearby electrical conductors, again, are ultimately converted into heat - the conductors have non-zero resistance.
Losses can only occur at the stage of transferring thermal energy to the coolant. Their level is determined not by the type of boiler, be it a heating element, electrode or induction, but by the quality of the thermal insulation of the body. However, all heat loss when placing heating equipment in a heated room is again spent on heating the surrounding air.
The heat dissipated by the boiler helps heat the house
Step number four: don't believe the advertising. Economical electric boilers are a myth on which manufacturers and sellers make money.
Heat pumps
The author has already talked about the design and operating principle of heat pumps in one of the related articles.
In short: they use electricity not to heat the coolant or air in the house, but to pump thermal energy from the heated to a lower temperature environment - soil, water or air. This is made possible by transforming the phase state of the refrigerant and changing its pressure.
The principle of operation of the HP: the device pumps heat into the house from its low-potential sources
A heat pump is a heating device that competes on equal terms in terms of cheapness of heating with solid fuel boilers, and is breathing down the neck of gas boilers. For every kilowatt of electrical power, a heat pump emits from 2.5 to 7 kilowatts of heat.
Several specific features of heat pumps:
- The ratio of effective thermal power to consumed electrical power decreases as the temperature difference between the external and internal heat exchangers increases;
Change in energy efficiency of air heat pump depending on air temperature
- As a result, the higher the temperature of the low-potential heat source, the cheaper the heating costs. In particular, geothermal (working according to the ground-water or ground-air circuit) HP are more profitable than air ones - simply because the soil temperature at the depth of the collector is higher than the winter air temperature;
Annual dynamics of soil temperature on the surface and at a depth of up to 10 meters
- For the same reason, with heat pumps it is beneficial to use low-temperature heating devices that heat up to 45 degrees Celsius or less.
The low temperature of the coolant is compensated by the increased size of the radiators.
Step number five: when heating the house with electricity, investments in a heat pump will quickly pay off. Monthly savings compared to direct heating devices will be 150-600% depending on the type of heat pump.
Warm floor
The transition from convection heating (that is, radiators, registers, convectors, etc.) to in-floor heating also helps reduce heating costs. In particular, a cable or film electric heated floor is more profitable than an electric boiler with batteries.
Electric underfloor heating is significantly more profitable than an electric boiler with heating radiators
Excuse me, but just a few paragraphs above we stated that the efficiency of all direct heating devices is the same!
There is no contradiction here. With equal energy consumption, the heating film will give off the same amount of heat as a heating element boiler; however, this heat will be distributed differently in the heated volume. The temperature will be highest at the floor level, and the lowest at the ceiling.
Air temperature during underfloor heating
What is the result?
As a result, while maintaining subjective comfort, we will be able to reduce the average temperature in the room, thereby reducing heat leakage through the building envelope. The savings will be inversely proportional to the outside temperature: say, at +10 outside, a decrease in the average temperature in the room by 4 degrees (from 22 to 18 ° C) will result in a 50 percent reduction in costs ((22-10)/(18-10)= 1.5), and at -10 - only 14 percent ((22 - -10)/(18 - -10) = 1.14).
Traditional and condensing gas boilers
A typical gas boiler operates with a return temperature of at least 55°C. A further decrease in temperature threatens the condensation of aggressive gas combustion products on the heat exchanger, which will entail a significant reduction in its service life.
However, let's remember one subtlety: when natural gas (mostly consisting of methane) is burned, mainly water and carbon dioxide are formed. Acids (primarily carbonic acid) are contained in combustion products in fairly small quantities. And when water vapor condenses, it releases a fairly large amount of thermal energy.
A condensing gas boiler uses the so-called higher calorific value, which includes the energy of gas oxidation and the energy of condensation of combustion products on a separate corrosion-resistant heat exchanger - an economizer. Its efficiency is 11-12% higher than that of a traditional gas boiler.
Scheme of operation of a condensing boiler
Comparison of the efficiency of gas boilers of different generations
Low return temperature may seem like an obstacle to the operation of a water heating system.
However, this is an imaginary problem that has two very simple solutions:
- Using underfloor heating , which we will pay attention to a little later;
Installation of water heated floor
- Increasing the number of radiator sections . When using aluminum heating devices, it will not result in large expenses and will quickly pay off in savings on gas.
Step number two: if your house is gasified, your choice is a condensing boiler.
In what units is energy measured?
It is measured in joules, calories and watts.
Historically, physicists count work, energy, and the amount of heat in joules. Heating engineers calculate heat for heating a home in calories, while electricians and power engineers calculate energy in watts. Calories are heat flow because this energy is counted over a certain time.
It is very important to understand that energy can be spent in different ways: it can be quickly, or it can be slowly.
The heat meter counts the gigacalories of thermal energy spent per month, and the electric meter counts the watts of electrical energy spent per month. But not just watts, but kilowatts (kW) spent in one hour (kW/hour).
Comparison of heat sources
To begin with, let's compare different heat sources according to the most important indicator - the cost of a unit of thermal energy, kilowatt-hour.
- Mains gas, including metering - 50-80 kopecks;
- Dry firewood - 1 ruble 30 kopecks;
- Pellets (granulated wood processing waste) - 1 ruble 50 kopecks;
Pellets are an inexpensive fuel with a high calorific value
- Coal - 1 ruble 70 kopecks;
- Gas from a gas tank - 2 rubles 40 kopecks;
Gas tank installation
- Gas from cylinders - 3 rubles 20 kopecks;
- Diesel fuel - 4 rubles;
- Electricity when using direct heating (boilers, oil heaters, convectors, fan heaters) - 5 rubles.
Please note: the specific price may vary depending on local market conditions and utility rates, but the price ratio has remained unchanged for many years.
So, step number one: if you have the opportunity to gasify your house, do not neglect this opportunity. The investment will quickly pay off.
Turbocharged (with forced removal of combustion products) gas boiler
What is energy and how is it different from heat?
Heat, or the amount of heat, is part of the internal energy of a body that spontaneously, without external influence, moves from bodies that are more heated to bodies that are less heated through thermal conductivity or radiation (due to electromagnetic radiation).
Thermal conduction can occur through a solid body and due to convection currents. Thus, we have three ways of heat transfer:
- radiant;
- on a solid body;
- convection.
The most effective method of heat transfer is radiant, since it is possible to achieve a maximum temperature gradient between cooled and heated bodies, up to several thousand degrees and, accordingly, high heat transfer rates.
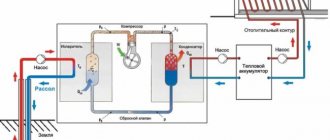
Electric heating costs with a two-tariff meter and a heat accumulator.
Let's say we installed a large tank of water in the basement of our house and heat it during the night tariff period. And during the day, during the period of the daily tariff, we use the stored heat to compensate for the heat loss of our building. In fairness, it should be noted that such a system will only work if there is sufficient electrical power supplied. After all, this heat accumulator needs to be heated in a very short time. So, heating costs will be:
150*5*24*0.92 = 16560 rubles