For a private home or country cottage, with the onset of cold weather, the problem of heating becomes urgent. Thanks to technological progress, today it is possible to create an autonomous heating system in your home using heating boilers and other related equipment. Coal, wood, and electricity can be used as fuel, but natural gas is still the most accessible and cheapest. This aspect is the main reason that today many citizens are trying to use gas to heat their homes. Properly designed autonomous gas heating of a private home will allow you not only to save your own money, but also to calmly await the onset of cold weather.
Despite the fact that today not all regions of our country are covered by a network of main gas pipelines for household gas, there are other, no less convenient ways to heat residential buildings with gas.
Short instructions
Installation diagram of a parapet type gas boiler.
Technical documents that contain characteristics of the area and a plan for supplying gas from the central pipe are drawn up and carried out by licensed organizations. Usually these are technical specialists of the gas campaign.
All installation of gas connection equipment (water heaters, boiler, meter, pipes) is done by a team of installers.
Conclude an agreement for gas supply from the central pipe and an agreement for the installation of equipment. These are completely different jobs, and they are carried out according to different estimates.
The room where you plan to install gas equipment must have ventilation, a window, lighting and a concrete floor. If you want to install the entire set in the kitchen, then you will have to drill holes in the doors and make ventilation near the gas installations.
After installation is completed, you need to conclude a contract for the maintenance of gas equipment. Call an employee from the gas control department and draw up a report on putting equipment and gas meters into operation.
Article on the topic: Patchwork pillows: patchwork technique, sewing patterns, photos, do-it-yourself patchwork style, pillowcase ideas, decorative sofa pillows, video
Take the commissioning act and enter into an agreement with the customer service department of the gas campaign for the supply of gas and payment for it at the meter.
Installation
Installation of an autonomous gas heating system begins with approval of the project and collection of documents. The gas supplier approves the project and makes the necessary adjustments. Only after this the installation of the system begins.
Requirements for boiler installation:
- Ceilings from 2.5m high;
- Unobstructed access to the boiler;
- Fire resistance of room walls – from 45 minutes;
- Availability of gas analyzing instruments;
- Boilers up to 60 kW can be installed everywhere except residential premises and bathrooms;
- Double-circuit units cannot be installed in the kitchen;
- Equipment from 150 kW are installed only on the basement or first floor.
It is recommended to install the system and install the boiler only with professional teams. Heating connection is carried out by certified specialists.
Gas autonomous heating device diagrams and their features
Gas autonomous heating device diagrams
There are only two fundamentally different schemes for organizing autonomous heating. They differ in the type of heating devices that run on gas:
- gas boilers;
- gas convectors.
Gas autonomous heating in its first version uses a gas-fired boiler to heat the coolant.
Next, the coolant circulating in the system naturally (gravitational circulation) or forcibly, through the use of pumps, distributes the resulting heat across all heating devices in the system (radiators, underfloor heating systems, etc.).
Currently, several options for such heating systems are being implemented. The choice directly depends on what kind of gas boiler you purchased.
To be more precise, depending on the developer’s needs, the required boiler design is selected, taking into account exactly how you want to see gas autonomous heating in an apartment or in a private house.
All gas boilers on the market are divided into:
- Single-circuit boilers. Intended only for organizing heating of the home. The main requirement for the system is constant volumes of coolant contained in it;
- A double-circuit gas boiler for autonomous heating has an additional circuit that allows you to heat water used for household needs.
Technically, this is implemented either in the form of a storage tank, with an installed thermostat and a separate burner, or a flow-through heater with plates.
Instantaneous heaters are used quite rarely, since it is difficult to regulate the temperature of the water flowing from the tap. In this embodiment, the gas boiler is already an element of not only the CO (heating system) and the SW (water supply system).
The second indicator by which autonomous gas heating systems are divided is what kind of gas is used in them. The nomenclature of the basic elements of the heating circuit depends on this.
There are also only two options:
- Use of natural gas supplied through a centralized gas pipeline;
- Use of liquefied gas.
In the latter case, there are two nuances of storing its reserves and, accordingly, certain differences in the necessary equipment.
Liquefied gas is stored in a gas holder, the capacity of which can be quite large. Or standard liquefied gas cylinders are used.
Efficiency of gas boilers
The efficiency of the boiler and autonomous heating system depends primarily on the temperature of the exhaust gases: the lower it is, the more economical the autonomous heating is.
The most economical are condensing boilers with an exhaust temperature that is equal to the temperature of the liquid returned from the heating system (about 30°C). In second place are fan boilers, where the exhaust is heated to the temperature of the liquid supplied to the system (about 55°C). The exhaust temperature of atmospheric boilers is 110°C.
The experience of the AvtonomGaz company shows that clients with condensing boilers spend half as much on heating per square meter as clients with traditional atmospheric boilers. As a result, the condensing boiler pays for itself in a single heating season.
Fireplace for gas heating at home
In terms of equipment costs, gas fireplaces are comparable to their electric or wood-burning counterparts. But gas fuel is much cheaper.
And, unlike firewood, gas heating using a fireplace in a country house means there are no problems with ash. Plus, you don’t have to constantly monitor the operation of the firebox and worry about chopping logs.
Fireplaces that convert gas into thermal energy are used in heating systems because... are not equipped with the devices necessary to service two circuits
According to the type of installation, gas fireplaces are:
- wall;
- island;
- built-in
In terms of their general design and internal contents (burners, automation, design of combustion chambers), they completely replicate gas boilers. In both cases, the technology for connecting to networks is identical. Differences exist only in the principle of heating the premises.
According to the principle of connecting and organizing the heating system, gas fireplaces are similar to floor-standing heating boilers
A hot water boiler is initially designed to heat water, and a regular fireplace is designed to convect air from the body and front screen, behind which fuel combustion occurs.
Turnkey cost
List of brigade works:
- Checking the premises. Inspection and measurements of premises, consultation and recommendations.
- Design. Determining the needs of owners and drawing up technical requirements, selection of equipment, its configuration, power.
- Purchase of equipment. Coordination and delivery.
- System installation. Installation of working equipment and piping according to technical standards.
System testing and first start-up. Testing, inspection, adjustment of operating mode, consultation with owners.
Approximate minimum cost for a house area of 100 square meters. m will be 260 thousand rubles, for an area of 200 - from 350 thousand and so on. This takes into account average prices for equipment.
Multi-level floor
To zone the space, craftsmen install floors at different levels. They advise installing a podium to separate the kitchen and dining room. This option is considered one of the most practical because, among other things, the owners have additional free space where they can hide something. It is convenient to use boxes or crates for this. Wicker baskets will look good. But such space can remain free.
However, such a design should not be made if there are small children in the family, since the podium can become an obstacle for him. In addition, various floor coverings can be used.
They will zone the space between the living room and the kitchen and protect the podium from damage. For example, tiles are laid in the kitchen area, and laminate flooring in the dining room. The main thing is to choose colors and textures and combine the finishes correctly.
Condensing gas boilers
Condensing boilers have the same advantages and disadvantages as fan boilers, but are much more economical. Real savings from using a condensing boiler are more than 15%.
Their main drawback is their relatively high price. They are one and a half times more expensive than fan boilers. However, significantly lower gas consumption makes the high price of condensing boilers justified, especially for consumers using liquefied gas.
Since the condensate formed in the combustion products is discharged into the sewer system, a condensate icicle does not form at the end of the pipe.
How to make gas heating for a private house with your own hands
Do-it-yourself installation of autonomous heating is quite within the capabilities of a person who has skills in such work
Various installation schemes are examined in detail, attention is paid to individual details
You can do all the work on installing a home heating system yourself, except:
- connecting the home heating system to the gas network;
- designing gas heating at home.
Insertion and design are performed only by specialized licensed organizations.
Work order
The operating principle of water heating is as follows: water heated by a gas boiler circulates naturally or forcedly through pipelines, giving off heat to the premises. The optimal heating scheme for a two-story private house includes a system with heated floors on the first floor and radiator heating on the second floor. Coolant circulation can be natural (gravity flow) or forced (circulation pump).
Let's consider the procedure for installing autonomous gas heating using the example of a 2-story building:
- installation of a boiler in the boiler room on the first floor;
- installation of a safety group, expansion tank, circulation pump
- installation of a pumping and mixing unit for heated floors to circulate the coolant at the required temperature;
- installation of a manifold for heated floors;
- laying heated floors (specifications of materials and work procedures can be found on the Internet);
- installation of radiators and connecting them to the collector in all rooms of the second floor;
- Upon completion of the complete heating installation, the heated floor is poured with concrete.
Heating schemes for a private house with a gas boiler can be of two types:
1. Single-circuit heating circuit for a private house with a gas boiler (closed, designed only for heating premises)
2. Double-circuit circuit using a special boiler (simultaneously heating and heating tap water)
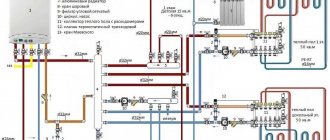
Autonomous heating wiring diagrams
Heating distribution from a gas boiler is based on several standard heating schemes, which differ in the type of circulation of the coolant (usually water) and in the methods of piping. There are the following types of heating installation:
- Single-pipe heating distribution, in which the pipes are looped and the radiators are arranged in series. The coolant leaving the boiler passes through each radiator in turn. The temperature of the coolant decreases as it moves. It is primitive and imperfect, since the coolant temperature drops towards the end of the cycle.
- The Leningradka system with dedicated bypass radiators is intermediate and eliminates some of the problems of a single-pipe scheme;
- Improved Leningradka system with shut-off and balancing valves;
- Two-pipe wiring consists of supply and return pipes running parallel to each other. Allows the coolant spent in the radiator to be returned to the boiler for heating. The coolant is supplied to the radiator according to this scheme without heat loss.
- Radial (collector) wiring distributes the collected coolant among individual radiators. The scheme is complex and rarely used.
Heating schemes for a 2-story private house can be as follows:
1. Open type heating system
The expansion tank is an open container with an inlet pipe connected to the supply riser. It is installed at the highest point of the heating system - the coolant does not overflow outside, and the expansion tank additionally acts as an air vent.
Scheme of autonomous gas heating of open type
2. Closed heating system
The system is equipped with a sealed expansion tank, divided by an elastic membrane into water and air chambers. With thermal expansion, excess coolant enters the water chamber of the tank. The pressure in the air chamber increases, and as the temperature decreases, the coolant returns to the pipelines. The tank can be installed at any point, but it is usually mounted next to the boiler on the return pipe. A pressure relief valve is installed.
Scheme with natural and forced recirculation, which are used for heating a two-story private house
Composition of the autonomous system
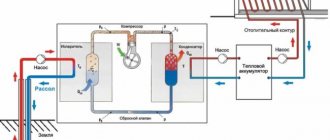
Typically such systems consist of pipes, batteries and a heat source. As a heat source, autonomous gas heating of a country house includes a boiler that burns gas and heats the coolant (usually water).
The coolant, moving naturally or forcibly (using pumps) through a system of pipes and batteries, transfers heat to the room, heating it.
To monitor the safety of the system, it is necessary to use gas analyzing devices.
Gas heating schemes for a house
We will talk about water heating using gas. You should immediately decide on the type of coolant circulation. It can be natural (such systems are also called gravitational) or forced (with a mandatory pump).
Gravity systems require the installation of large-diameter rubles, that is, there is a lot of coolant in the system. The second point is that due to the fact that the coolant moves through the pipes at a low speed, the heating efficiency is not very high. Distant radiators in long branches can be cold. It's about the shortcomings. There are many of them, but there is one big advantage - systems with natural circulation do not depend on electricity
This is important in those regions where the power is often turned off
Scheme of a natural circulation system
Now a little about forced circulation systems. They are more efficient - the coolant moves at a given speed, delivering heat to all corners of the system. The presence of a pump allows the use of pipes of small diameters. This means that there is not much coolant in the system and it warms up quickly. In general, they provide a greater level of comfort, but have a serious drawback - they require electricity to operate, meaning they require backup power. If the light is rarely turned off, it is enough to install an uninterruptible power supply with several batteries. They can ensure the boiler operates for tens of hours. If the lights are turned off often and for a long time, you will also have to build a generator into the system. In any case, these are additional costs and considerable ones.
There are also combined systems - they are designed as gravity, but have a built-in circulation pump. This solution can be called ideal from a practicality point of view: as long as there is light, the heating works as forced heating, as soon as the power supply is lost, everything works as a gravitational system. In general, a good option, except that the pipes will be large and too visible.
Wiring method
There are three types of systems - single-pipe, double-pipe and beam. In single-pipe radiators, they are connected in series to one pipe. This wiring method is economical - fewer pipes are required, but it is difficult to compensate for it - it is difficult to achieve the same heat transfer from radiators. The thing is that the coolant enters the first radiator in the branch hot - straight from the boiler. It passes through it, cools a little, goes to the next one, cools a little more. So throughout the entire thread.
Scheme of a single-pipe gas heating system for a private house
It turns out that the coolant that reaches the last radiator is much colder than the first one. The only way out is to take this phenomenon into account when designing the system and increase the number of sections in the radiator as it moves away from the boiler. But the last radiators will still remain the coldest.
You can more or less easily balance the system shown in the photo above. It contains thermostats on each radiator - devices that allow you to change the amount of coolant passing through the radiator. In order not to “crush” the circulation in the entire system, a bypass is placed under each radiator - a jumper along which coolant flows that did not go through the radiator.
In a two-pipe system, radiators are connected in parallel - to the supply and return pipelines. In this system, the pipe consumption is much greater, since two threads are pulled at the same time. But in this case, each heating device is supplied with a coolant with the same temperature, due to which the heat transfer from the radiators will be the same (if the same batteries are installed).
Example of a two-pipe circuit
In this scheme, you can also install thermostats, but this does not require bypasses - only the flow to one radiator is regulated. So despite the higher pipe consumption, two-pipe systems are more popular.
The beam wiring method is the most expensive in terms of the number of tubes. In them, each radiator has a separate supply and return pipe. It connects to a collector - a device with one input and several outputs. In this case, adjustment is possible both on the manifold and on the radiator using a thermostat.
Radial heating wiring diagram
Gas heating of a private house made according to this scheme will be the most reliable: if one of the pipelines is damaged, all the others will work. Therefore, this method is often chosen if pipes are hidden in a screed.
conclusions
There are many schemes for installing and distributing heating in a private house - it is impossible to consider all options within the framework of one article. The choice of an economical heating system for a private house depends on many components, including the number of floors, area and architectural layout of the house in plan. When designing home heating, specialists should set the task of offering not just the cheapest and most economical heating - the chosen scheme should also heat the house as efficiently as possible, and its maintenance should be quick and inexpensive. Below you will find a detailed video on how to install gas heating in a private house with your own hands.
Equipment for autonomous gasification at home
Equipment for autonomous gasification
The “heart” that any autonomous gas heating system has is the boiler, the designs of which are divided into:
- number of circuits - one or two;
- according to the principle of heat selection:
- Convective: the coolant receives only the heat generated during gas combustion;
- Condensing: additionally receives heat taken from combustion products due to their condensation on an economizer, which in this case represents an additional heat exchanger.
Gas heating boilers
Convective gas boilers, which are equipped with certain autonomous heating schemes, have a rather serious problem.
It consists in the formation of condensate on their heat exchangers, which, in addition to water, contains acids.
The simplest and most effective way to avoid this is the high temperature of the heat exchanger, which can only be achieved in cases where the coolant temperature in the “return” is + 60 degrees or higher.
This means that only wall-mounted radiators, registers and convectors can work with such a boiler.
In-floor convectors and underfloor heating systems are completely out of the question, as they will burn your feet rather than warm them.
For condensing boilers, the low temperature of their heat exchangers (and return), on the contrary, is comfortable.
Therefore, it is quite simple to understand that a boiler of this type is installed in the house by the radiators mounted under the windows and the presence of warm water floors.
Gas convectors
Convectors, during operation, do not require intermediate coolants. They transfer heat from their heat exchangers directly to the air of the room they heat.
Combustion products are discharged outside the house through the core of a coaxial pipe passing through the outer wall. At the same time, through the shell of the specified pipe, clean air is taken in and supplied to the combustion zone.
Heating using convectors has the following specific features:
- Installation does not require wiring of intra-house pipes or allocating a room for a boiler room.
- If the room is isolated, then a separate convector will have to be installed in it. And this automatically entails the need to install a separate gas cylinder in each room, or to install gas supplies throughout the house.
- If the gas heating system uses convectors, then the heat in the rooms of the house is distributed extremely irrationally (it is very hot under the ceiling, quite cold at the floor level).
- Gas convectors are easy to install and run yourself.
This option is most often preferred in cases where it is necessary to install such a system in a private house, if there is no possibility of connecting to the main gas pipeline.
What are the requirements for a room when heating with gas?
Autonomous heating requires compliance with standards for the premises where equipment should be installed and pipelines installed. Let us briefly summarize these requirements.
Boiler room
A separate room in which a gas heating boiler and other auxiliary equipment are installed. It is prohibited to install gas equipment in living rooms. Boiler room requirements:
- area of at least 6 m² (based on at least 4 sq. m per boiler), volume of at least 15 m³, ceiling height of at least 2.2 m;
- the presence of at least one window with an area of 0.5 m²;
- supply of fresh air through an opening in the door or from the street;
- free access to equipment for maintenance;
- gas, electricity, water supply. Electrical network: single-phase current, nominal, 220 V, 20 A, grounding, circuit breaker;
- communication characteristics must comply with regulatory requirements;
- sewerage for disposal of emergency drains and chimney condensate;
- plastered walls, finishing with flammable materials is prohibited;
- flat floor made of non-combustible materials;
- door with a width of at least 0.8 m.
Requirements for the ventilation and chimney of the boiler room can be found in detail in SNB 4.03.01-98, taking into account the changes in edition No. 8, introduced from 2008-03-01.
Furnace
A built-in or attached room for the installation of usually up to two gas heating boilers of up to 100 kW each. Any floor, including basement, basement, attic. The combustion chamber can be a separate building that meets certain requirements that apply to equipment with an open combustion chamber. If the combustion chamber is closed (which is typical for almost all modern boilers), then there are no restrictions in the combustion room.
Minimum combustion volume depending on equipment power:
- up to 30 kW - 7.5 m3;
- up to 60 kW - 13.5 m3;
- up to 200 kW - 15 m3.
Dimensions of the combustion room:
- height not less than 2.2 m;
- the width of the passage between the most protruding point of the equipment and the opposite wall must be at least 1 m;
- the minimum perimeter of the room and area can be determined by volume and height.
Supply and exhaust ventilation in the furnace room must be provided:
- a window with an area of 0.25 sq.m to the street;
- hood to an adjacent room with a grille at the bottom of the wall or door with an area of 0.02 sq.m.
Stove assembly
It’s worth noting right away that choosing equipment powered by sawdust only makes sense if such fuel is available or the opportunity to purchase it. If this condition is met, then all that remains is to assemble the structure - and assembling a sawdust stove with your own hands is quite simple.
The set of materials required to assemble the stove is as follows:
- A piece of pipe with a wall thickness of about 1 cm and a diameter of 40 cm;
- Large container (barrel, large can, pipe or gas cylinder);
- Pipe with a diameter of 7.6 cm for arranging a blower;
- Sheet metal with a thickness of 1 cm for the furnace lid;
- A metal pipe with a diameter of about 10 cm for installing a chimney.
How is the equipment installed?
So, you have decided on the type of gas tank. What are the next steps?
The entire process of autonomous gasification consists of 7 stages:
- An engineer comes to the site to coordinate the details. At the same time, the specialist takes into account the conditions in which the system will operate;
- After this, the company delivers to the house the equipment necessary for supplying gas;
- The team is digging a pit and installing a concrete slab. The container should be buried in the ground to a certain depth, which must be calculated by specialists.;
- The gas tank is laid on a concrete slab, then workers must clearly fix the position of the tank;
- Then it is covered with mineral wool to prevent moisture from entering, and pipes leading into the house are connected to it;
- The pit is backfilled and compacted with earth;
- The system is being tested. After commissioning, the parties enter into a service agreement.
Installation nuances
The tank and pipes weigh a fair amount and are large in size. Therefore, it is worth considering the availability of access roads to the house. The equipment truck and crane must have sufficient space to unload and carry out all work.
Important: When laying pipes, you should take into account the depth of soil freezing in winter. It is usually about 1.5-2 m underground.
Furniture items
A few examples of furnishing a kitchen combined with a living room:
- 1. Sofa. It becomes an object that zones space. The sofa is placed with its back facing the place where food is prepared. In small rooms (less than 20 sq m) a corner is placed, which is placed against a wall installed perpendicular or parallel to the kitchen.
- 2. Set. According to designers, minimalist models without elaborate details look modern. The service, vases or glasses are placed on an open shelf. You can buy a fashionable display case for them. Furniture is placed near the wall. If the space is large (20 sq. m, 25 sq. m or 30 sq. m), then in the central part you can install an island, which also has sections for kitchen appliances.
- 3. Furniture set. The style should be combined with the design of both rooms. In small rooms, a compact table and chairs made of transparent material or painted in light colors look good. You can add a table with a round top to your living room interior. In spacious rooms, the kit is installed near the wall or in the central part. An elongated rectangular dining table would look good here.
Date: September 25, 2022
In what cases is its use unjustified?
First of all, it is inappropriate to use a non-volatile boiler in large houses with an area of over 150-160 m2, where it is almost impossible to organize normal natural coolant circulation. A more optimal solution would be to install a volatile boiler, a UPS and a generator (in most cases, a 1 kW generator is sufficient).
Also, installing a non-volatile gas boiler is not justified if the pressure in the gas main is low. Typically, residential line pressure is 50 millibars, but it may be lower in some areas or may temporarily decrease. The minimum pressure in the line required for the operation of non-volatile models is 13-15 mbar.
Application area
Autonomous gas heating of the house can be used for different types of housing.
Private houses
For private permanent residences, the use of an autonomous gas supply is especially effective, since the equipment requires supervision and periodic checks.
Dachas
For dachas visited on weekends, such heating is also suitable. The main thing is that a gas leak does not start or the exhaust fan does not turn off when the owner leaves for a week.
Apartments in low-rise buildings
This opportunity has appeared in new low-rise buildings. In this case, the cylinder has to be placed in a box outside, which in cold weather reduces the effectiveness of its use. The method is suitable for regions with mild climates.
The best known manufacturers and models: characteristics and prices
Teplodar Kupper OK 15
The most famous domestic combination boiler, burning coal, wood, pellets, natural gas (when installing a burner). It is distinguished by time-tested reliability at a low cost, successful design of the firebox, and ease of cleaning. Separately, it is worth noting the presence of blocks of heating elements with a power of 6 kW, with the help of which you can heat the coolant for a long time if the solid fuel burns out completely at night. The owners also note a rather nice stylish design and build quality.
However, there are also a sufficient number of disadvantages: a small loading hole and the firebox itself (firewood up to 35 cm), a steel heat exchanger, relatively low efficiency, high soot formation.
Cost: 19,900-21,200 rubles.
Viadrus Hercules U22 D-4
One of the best combined gas-wood boilers for heating a private home, also one of the most popular. The Czech model with a cast iron heat exchanger is characterized by ease of use and well-known durability, ensured by good alloys and build quality. The boiler has a fairly good efficiency of 80%, is absolutely omnivorous, has an optimal firebox size (firewood 40-45 cm long can be placed), and also has compact dimensions and a stylish appearance.
According to reviews from owners, when the draft valve is tightly closed, abundant soot formation is typical. The cast iron structure, depending on the power variation, weighs on average 250 kg, so a reinforced floor is required for installation, and at least 3 people for transportation. Also a relative disadvantage is the price of the Czech model.
Cost: 63,000-67,500 rubles.
Roda Brenner Classic BCR-04
Another practically standard Czech combi boiler with a cast iron heat exchanger and a technologically advanced, efficient and practical design. The body is separated by a layer of thermal insulation, which reduces heat loss through the boiler modules and keeps the body relatively cold. Everything is also distinguished by Czech reliability, practicality during operation and cleaning, and good efficiency.
According to installation experience and reviews from owners, no shortcomings or malfunctions were found over more than 6 years of operation. One can only note that the price is still high for the average Russian buyer.
Cost: 53,000-55,000 rubles.
HEPHAESTUS VPR KSTGV-20
Inexpensive and compact double-circuit combi boiler of domestic production. It has a good efficiency of 80%, achieved thanks to the excellent design of the heat exchanger. The primary heat exchanger is steel, but the secondary (for DHW) is made of copper. Almost always, the factory equipment includes a gas burner of the “BRAY” type with the well-known simple Italian SIT automatic system.
Please note that the maximum permissible operating pressure is only 1 bar. It is also worth noting that the model is quite rare on sale.
Cost: 23,500-26,400 rubles.
Karakan 20 TEGV
Another domestic dual-circuit model. It has the simplest possible design, is not demanding on fuel, has a large loading opening and firebox, as well as a block of heating elements installed from the factory.
However, the heat exchanger is made of steel, the efficiency is only 75%, the weight is 101 kg, and the maximum permissible operating pressure is 1 bar. There have been no service complaints over more than 5 years of operation.
Cost: 22,500-25,000 rubles.
Heating with coal or wood
Wood and coal share the same disadvantages. They require very frequent loading (so often that a large house may need a stoker), require regular ash cleaning, and their storage takes up a fair amount of space on the property. In addition, they also emit a strong odor.
Frequent downloads.
Firewood needs to be loaded into the heating system three to four times a day. This will take at least hours during the season. More than three working weeks of continuous physical labor, worked from bell to bell. It is not surprising that many people prefer to find a stoker. However, this in turn affects the price. Taking into account the payment for the stoker, heating a house of 100 square meters with firewood for a year will cost . This is more than the same amount for diesel fuel ( ) or electricity ( ).
Coal is not particularly better in this regard. It must be loaded into the heating system two to three times a day, that is, a little less often than firewood. As a result, the cost of time (and, accordingly, money if you have to pay the stoker) turns out to be slightly less than when using firewood, but the difference is insignificant: for heating a house of 100 square meters, taking into account the payment of the stoker.
In fairness, it should be noted that this problem has a partial solution. There are special boilers with a bunker into which coal is filled not several times a day, but only once every three to four days. This is a significant improvement over refueling every few hours, but compared to propane-butane or even diesel fuel it looks rather pale.
Warehouse space.
The peculiarity of firewood is the need for a large room for storage and drying. To avoid wasting up to 40% of energy on moisture evaporation, they must be dried for three years. A large room will take up part of the site that could otherwise be put to more useful use. Coal storage also requires a significant area.
Danger of poisoning.
An unpleasant odor is a constant companion of any type of solid fuel, but in this case we can talk about a threat not only to smell, but also to life. If the boiler room is located directly in the house, when using solid fuels, the danger of carbon monoxide poisoning cannot be completely eliminated.
Disadvantages of heating with wood or coal
- Very frequent downloads.
- The need to clean up the ash and pay for the stoker.
- Smell in the house and area.
- Part of the site is occupied by a warehouse.