One of the main expenses of the family budget is paying for public heating or purchasing fuel to heat the house. Every reasonable owner probably thinks about real and effective ways to reduce these costs. But they can be reduced literally to a minimum using alternative energy sources. What are they and how are they used? Agree, it's worth finding out.
You will learn everything about how to arrange alternative heating for a private home from the article we presented. With our help, you can easily decide on the most suitable option for you. A detailed description of the operating principles of “green energy” schemes will provide an opportunity to decide which technological method is best to use to generate heat.
The article describes in detail the types of free energy sources and provides methods for generating heat for use in everyday life. To help independent home craftsmen and zealous owners of country estates, photo collections, diagrams and very useful video instructions are included.
Heat pumps
Heat pumps are a very real alternative to traditional heat generators and boilers.
The operating principle of this energy-saving system is somewhat reminiscent of an air conditioner, which transfers heat from indoors to outdoors. A heat pump transfers heat from the ground into a heated room and transfers cold back.
When a heat pump operates, energy is not spent on generating heat, but solely on moving it.
Heat pump operation diagram. Click to enlarge.
The functionality of this system makes it possible to obtain approximately 4.5 kW of thermal energy, spending only 1 kW of electrical energy on its transportation.
Heat pumps are highly efficient, reliable and cost-effective. Alternative heating of the described type has only one significant drawback - the decision to install it should be made only at the zero construction cycle.
This requirement is dictated by the large volume of excavation work.
Solar collectors
Despite the fact that heating a country house with solar panels is almost impossible in harsh climates, it is impossible not to consider this type of alternative source of energy and heat.
The greatest efficiency can be achieved only with intense solar radiation - only in this case the temperature in the premises will be as comfortable as possible.
Varieties
Solar systems for heating the coolant (in our case it is a water-glycol solution) can be divided into passive and active.
The first ones are combined into one so-called “water heater”, which is located on the roof. The coolant reservoir is located above the collector level, and cold water is supplied to the tank from below.
Scheme of operation of a flat solar collector. Click to enlarge.
The latter have a structural difference from passive solar heating systems: the solar collectors themselves are placed on the roof of the house, and the coolant reservoir is located in the house.
The coolant is water, circulates in the heating system using a pump.
Most often, solar collectors are used for household needs - heating water in storage tanks.
But in this case, in winter you will have to drain all the water from the tank to avoid freezing.
There are two different types of solar collectors: flat plate and vacuum (tube).
A flat-plate collector is a solar absorber with glazing on the top, having a layer of foil-coated thermal insulation on the inside.
Diagram of the operation of a pipe manifold. Click to enlarge.
The absorber is a flat sheet of metal connected to a piping system.
It “collects” solar heat, transferring it to the coolant. The glass should not reflect glare - to achieve maximum effect from light energy.
A tube collector differs from a flat one only in the presence of vacuum glass pipes collected in one bundle.
An absorber made of a sheet of steel is inserted into each tube - it can be rotated inside to even out the sunlight.
Tube solar collectors are more expensive to install and maintain, but they provide a greater effect than flat ones due to longer retention of solar heat.
Both types of heating systems are mounted on the roof of the house - in the inclined part.
Recently, manufacturers have been offering so-called “solar” roofs, in which solar panels are already installed, but this option has not become widespread due to the leakage of the roof covering.
Ventilation
The use of ventilation as a source of heating, at least, sounds interesting, because the purpose of ventilation is to remove from the premises air that contains dust, oxygen deficiency and the presence of unpleasant odors. But some of the heat is also removed with the air. How can this be used? You can also install a heating element into the ventilation system (in its supply part) with your own hands to supply heated air to the house.
The greatest efficiency is in the supply and exhaust ventilation system, with forced circulation and heat recovery.
The systems use warm exhaust air to preheat cold, supply air. The best efficiency and equipment utilization rates are achieved by regulating the air flow according to its actual need.
Heat pumps
In this case, the fuel and energy resources can be water-water or brine-water pairs.
"Water-water"
The principle of operation of such heating is as follows: water taken from an earthen well is pumped through a heat pump, and with its thermal energy it supplies heat to the house. The waste water is discharged into the ground.
In order for this scheme to work flawlessly for a house with an area of up to 80 m2, the owner of the house will need to drill at least two water intake and drainage wells, the depth of which is 50 m or more.
"Brine-water"
The principle diagram of heating with a heat pump with brine-water fuel is somewhat different: the thermal energy of the fuel is a solution placed in U-shaped pipes.
Schematic diagram of the operation of a heat pump. Click to enlarge.
The pipes must be placed in a drilled well at a depth of at least 150 m, or a heat exchanger must be constructed from the pipes, which will be located at a depth of 5 m and below. This will be needed in order to reduce temperature differences at different times of the year.
Both the number of wells and their size will be determined on the basis of 50 W/mp, i.e., 50 W of thermal energy can be obtained from each linear meter of one well. In the case of installing a heat exchanger, the calculation is slightly different - 40 W/m2 of the heat exchanger area, taking into account the interpipe distance of up to 800 mm.
The leader in the amount of capital investment for heating a private house with a heat pump has a longer payback period, but the costs of operating and maintaining the equipment will be minimal compared to other types of heating systems.
Waste oils
Another type can be called alternative energy sources such as waste oils.
And, although this type of fuel and energy resource is not renewable and is often disposed of - collected, stored, transported, processed - many manufacturers of home heating boilers use waste oils as fuel (in the production of multi-fuel boilers).
Why oils? Because their caloric content exceeds the caloric content of other types of fuel - diesel fuel, coal, wood. Disadvantages: the need for a special storage container to store reserve stock; alternative fuel must be of proper quality.
Advantages of using heat pumps
Saving. If you compare the costs of heating using a heat pump with the costs of gas equipment, you will get an impressive amount with a difference in favor of pumps. And all because alternative sources in the heating system are the thermal energy of water and earth.
Safe work. Regarding the explosion and fire hazard of heating equipment running on gas, an electric heat pump for heating a house is a completely harmless device! This also includes the ease of operation of the equipment.
Versatility of use. A heat pump can work both for heating and cooling rooms (something akin to the operation of split systems in “hot-cold” modes).
Full automation of work. Unlike solid fuel boilers, heat pumps do not require constant loading of fuel, and they do not require constant monitoring, inspection, or cleaning.
And the heat pump does not require a connection to the main gas pipeline - this is autonomous heating of a country house, which is provided by a simple connection to the power supply network.
conclusions
Heating without gas is possible. Some heat sources serve as a complete replacement for a gas boiler, while others can only be used as a supplement. For convenience, let's combine everything into a table:
| Alternative to gas | Addition |
| Ground source heat pump Solid fuel boiler Pellet boiler | Fireplace with water circuit Air fireplace Pellet fireplace Solar collectors Inverter air conditioners Air source heat pump Electric boilers |
There are other alternative ways to heat a building that are not included in the list: stoves, boilers, electric boilers and other heating devices.
And, of course, it is important to remember that installing other heat sources is not the only way to save gas and reduce dependence on it. It is necessary to work to improve the overall energy efficiency of the building: identify and eliminate all heat leaks, use heat more efficiently and minimize heat loss in the building
Heat pumps
The most universal alternative heating for a private home is the installation of heat pumps. They work on the well-known principle of a refrigerator, taking heat from a colder body and releasing it in the heating system.
The circuit is complex at first glance and consists of three devices: an evaporator, a heat exchanger and a compressor. There are a huge number of options for implementing heat pumps, but the most popular are:
The cheapest implementation option is air-to-air. In essence, it resembles a classic split system, but electricity is spent only on pumping heat from the street into the house, and not on heating air masses. This helps save money while keeping your home perfectly warm throughout the year.
The efficiency of the systems is very high. For 1 kW of electricity you can get up to 6-7 kW of heat. Modern inverters work great even at temperatures of -25 degrees and below.
“Air-water” is one of the common implementations of a heat pump, in which the role of a heat exchanger is played by a large-area coil installed in an open area. Additionally, it can be blown by a fan, causing the water inside to cool.
Such installations are characterized by a more affordable cost and simple installation. But they are capable of operating with high efficiency only at temperatures from +7 to +15 degrees. When the bar drops to a negative level, efficiency drops.
The most universal implementation of a heat pump is “ground-water”. It does not depend on the climate zone, since a layer of soil that does not freeze throughout the year is available everywhere.
In this scheme, the pipes are immersed into the ground to a depth where the temperature is maintained at 7-10 degrees throughout the year. Collectors can be located vertically or horizontally. In the first case, it is necessary to drill several very deep wells, in the second, to lay the coil at a certain depth.
The disadvantage is obvious. complex installation work that will require high financial investments. Before deciding to take such a step, you should calculate the economic benefits. In areas with short, warm winters, it is worth considering other options for alternative heating of private houses. Another limitation is that a large free area is required - up to several tens of square meters. m.
The implementation of a water-to-water heat pump is practically no different from the previous one, however, the collector pipes are laid in groundwater, which does not freeze throughout the year, or in a nearby body of water. It is cheaper due to the following advantages:
- Maximum well drilling depth – 15 m
- You can get by with 1-2 submersible pumps
Biofuel boilers
If there is no desire and opportunity to equip a complex system consisting of pipes in the ground, solar modules on the roof, you can replace the classic boiler with a model that runs on biological fuel. They require:
It is recommended to install such installations in conjunction with the previously discussed alternative sources. In situations where one of the heating devices does not work, you can use the second one.
When deciding on the installation and subsequent operation of alternative sources of thermal energy, it is necessary to answer the question: how quickly will they pay for themselves? Of course, the systems considered have advantages, including:
- The cost of energy produced is less than using traditional sources
- High efficiency
However, you should be aware of the high initial material costs, which can reach tens of thousands of dollars. The installation of such installations cannot be called simple, so the work is entrusted exclusively to a professional team that can provide a guarantee on the result.
Alternative heating of a private home is becoming in demand, which is becoming more profitable against the backdrop of rising prices for traditional sources of thermal energy. However, before you start converting your current heating system, you need to calculate everything by considering each of the proposed options.
It is also not recommended to abandon the traditional boiler. It must be left and in certain situations, when alternative heating does not fulfill its functions, it will remain possible to warm your home and not freeze
Life in a private house
It is much more diverse and colorful than in a city apartment.
Most people, realizing all the advantages of their own building, strive with all their might to exchange stuffy rooms for the freedom of a private plot. And even if it is only the summer season at the dacha, and not a permanent place of residence, the owners are trying to put all the best into the house. Communications and centralized gas supply are not always available to independent buildings.
Radiators and heating pipes
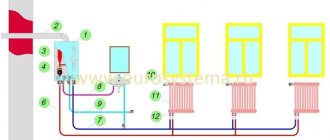
In addition to modern heating boilers, pipes and radiators are no less important components. They are necessary for the efficient transfer of thermal energy to the air in the room. During the design of the system, it is necessary to solve two problems - to reduce heat losses when transporting coolant through pipes and to improve the heat transfer of batteries.
Any modern heating radiators must not only have good heat transfer performance, but also a design that is convenient for repair and maintenance. The same applies to pipelines. Their installation should not be difficult. Ideally, the installation can be carried out by the home owner himself without the use of expensive equipment.
Modern heating radiators
Design of heating radiators
To increase heat transfer, aluminum is increasingly being used as the main material for batteries. It has good thermal conductivity, and casting or welding technology can be used to obtain the desired shape.
But you need to keep in mind that aluminum is very sensitive to water. Modern cast iron heating radiators do not have this drawback, although they have lower energy intensity. To solve this problem, a new battery design was developed in which the water channels are made of steel or copper pipes.
These modern heating pipes are practically not subject to corrosion, having minimal dimensions and wall thickness. The latter is necessary for efficient thermal transfer of energy from hot water to aluminum. Modern heating radiators have several advantages, which are as follows:
- Long service life - up to 40 years. However, it depends on operating conditions and timely cleaning of the system;
- Possibility of choosing a connection method – top, bottom or side;
- The package may include a Mayevsky faucet and a thermostat.
In most cases, models of modern cast iron heating radiators are designed to be designer. They have classic shapes, some of them are made in a floor version with elements of artistic forging.
The efficiency of a heating radiator depends on correct installation and connection method. This must be taken into account when installing the system.
Modern heating pipes
Polymer pipes for heating
The choice of modern heating pipes largely depends on the material they are made of. Currently, polymer lines made of polypropylene or cross-linked polyethylene are most often used. They have an additional reinforcing layer of aluminum foil or fiberglass.
However, they have one significant drawback - a relatively low temperature threshold of up to +90°C. This entails a large temperature expansion and, as a result, damage to the pipeline. An alternative to polymer pipes can be products made from other materials:
- Copper. From a functional point of view, copper pipes meet all the requirements for a heating system. They are easy to install and practically do not change shape even at extremely high coolant temperatures. Even when water freezes, the walls of copper lines will expand without damage. Disadvantage: high cost;
- Stainless steel. It does not rust, its inner surface has a minimum roughness coefficient. Disadvantages include cost and labor-intensive installation.
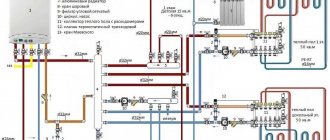
How to choose the optimal equipment for modern heating? To do this, it is necessary to use an integrated approach - make the correct calculation of the system and, according to the data obtained, select a boiler, pipes and radiators with the appropriate performance characteristics.
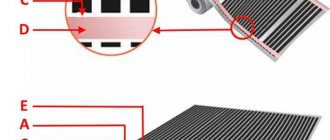
The video shows an example of modern home heating using a heated floor system:
Adjustment mechanism
Thermostatic mixing valve
A thermostatic mixing valve is also used in radiator-type heating schemes, but convective air circulation (even with balanced ventilation and careful insulation) still leaves the lower layers as the coldest part of the room.
The source of thermal energy can be either a central heating plant or an autonomous boiler. In any case, boilers operate effectively in stable modes and will not provide smooth adjustment of coolant flow in each individual room.
For this purpose, special fittings with selected operating parameters and a specific type of design are included in the system. Installing a mixing valve for underfloor heating gives the following stabilizing result in normalizing the temperature in the house:
Mixing valves perform the task of combining a high-temperature heating circuit with a low-temperature underfloor heating distribution, since the recommended temperature in the pipes under the floor is 40°C, and for the water leaving the boiler 70 - 90°C.
Work principles
If the coolant is too hot, a cold stream is mixed into the water
The three-way valve for heated floors performs its function in the following order:
- the hot coolant from the boiler is directed to the distribution manifold, from which it diverges through the loops of the underfloor heating system;
- a thermo-mixing valve is installed along the path of movement, reacting to the heating temperature of the water;
- when the flow temperature exceeds the set value on the regulator, the latter opens a passage for mixing cooled water from the return pipeline;
- in the tee, two converging flows are mixed and the coolant of the desired temperature is released into the system;
- When balance is achieved, the change in the internal sections of the valve stops.
The valve body is made of brass and consists of 3 channels converging to the adjustment mechanism. The use of 3 different methods of mixing water flows distinguishes 3 types of three-way valve designs.
Three way thermostat
The thermostat mixes hot and cold flow
The set temperature is maintained by a three-way thermostatic valve, which automatically mixes the hot liquid flow from the heater and cooled water from the return pipeline. The need for quantitative changes in flows is determined by the thermostat settings.
This product can be used in underfloor heating systems (especially complex configurations), on radiator wiring and in the internal hot water supply circuit.
Automatic change in the temperature of the outgoing coolant protects a person from elevated temperatures in the event of a pipe rupture. If for some reason the flow of cold water stops, the valve will automatically close the flow of hot pressure from the boiler. The temperature-sensitive unit responds to the amount of heating and, accordingly, changes the cross-section of the inlet holes, achieving the required balance.
The layout of the thermostatic valve for a heated floor looks like this:
A pressure throttle is a device that provides fluid pressure regardless of the pressure difference at the inlet and outlet. Paired with a thermal head for a heated floor, it stabilizes the operation of all system circuits when incoming conditions change.
3-way thermostatic valve
The operation of this valve is not as complicated as a thermostat. Only the incoming hot media is regulated. For more information about the operation of three-way valves, watch this video:
To analyze changes in temperature indicators, the kit includes a thermal head for heated floors, which acts as an executive body based on a signal from an external sensor.
Ground-to-water heat pumps
These devices are the most versatile alternative sources of heating for suburban households in terms of dependence on the climate zone.
The principle of their operation is based on the fact that even at a depth of several tens of meters in permafrost areas, the soil temperature exceeds zero degrees.
Heat exchangers designed to extract heat from the ground are probes that are immersed in special wells. It requires the laying of pipelines, the length of which exceeds several dozen meters, and in addition to the high price of the pump, the cost of its installation itself is quite high. Thus, drilling one well costs approximately several thousand rubles per linear meter, but more than one is needed. In addition, you still need to install a pump and immerse probes in the well.
It will cost a little less to install a ground-water pump with a horizontally located collector. Heat exchangers are immersed in trenches below the freezing level. The disadvantage of such heating is the large area required to install a heat pump. The resulting heat is spent on heating water for domestic needs and transferring thermal energy to heating devices.
Renewable natural sources of thermal energy
However, there are systems and heat sources whose operating costs are significantly lower than in all the cases described above, including gas heating. We are talking about renewable natural sources of thermal energy:
- Wind energy.
- The warmth of the earth.
- Solar energy.
Wind energy
Wind power plants (WPPs) intended for individual use are mainly used to produce electrical energy to solve home energy supply problems.
The operating principle of these installations is based on the process of rotating the wheel using wind power with the subsequent generation of electrical energy.
Wind energy heating operation diagram. Click to enlarge.
The efficiency of using wind turbines increases significantly with the additional use of uninterruptible power supplies, helium batteries or additional photovoltaic panels.
The main disadvantage of wind turbines is that the use of wind energy at full capacity in our climatic conditions is possible only 70-110 days a year.
Warmth of the earth
Alternative heating in a private house can be done in the form of a heat pump, which collects low-temperature thermal energy from the ground, increases its thermal potential and transports it to the house’s heat supply system.
Heat pumps are environmentally safe, economical, and capable of utilizing almost any type of low-temperature heat.
Scheme for heating a house using earth energy. Click to enlarge.
The disadvantages of this option for installing heat supply systems (heating, hot water supply, air conditioning) include the relative complexity of installation and installation, which must be done when installing a zero cycle due to the large volume of excavation work.
Solar energy
The use of solar energy is one of the most promising areas, including in temperate climates. The operating principle of such systems is quite simple.
The principle of operation of solar panels. Click to enlarge.
Solar energy enters the solar collector, where it is converted into heat. The coolant ensures the transfer of thermal energy to heating systems, hot water supply or a battery, from where its final consumption is produced.
The main advantage of solar heating is that it is an almost “free” renewable energy source throughout the year.
Disadvantages include the initial costs of installing the system and the undesirability of using it in a private residential building as the main source of heat.
Afterword
In this article, we rather briefly examined the heating of a private residential building, an alternative to gas. We hope that after reading it you will be able to choose the most optimal heating source for you or give preference to a combination of the schemes described above.
Solar systems
Solar energy can be used to heat residential premises in two ways:
- by converting it into electricity, which will then be used by heating equipment;
- for heating liquid coolant circulating naturally or using a pump through convectors or radiators.
The simplest alternative home heating can be created with your own hands using a solar heating collector, a circulation pump and batteries.
The peculiarity of the use of solar systems is that even in the southern regions, where there are many sunny days a year, no one has canceled cloudy weather and night time. For this reason, we can conclude that they are not suitable as round-the-clock sources of thermal energy. The following options for implementing this type of heat supply are possible:
- A solar heating collector for heating a house operates in parallel with an electric heater. The temperature of the coolant is controlled using special sensors. If the degree of heating drops below a certain value, heating continues with heating elements.
Wind generator assembly and connection
The second most popular source of alternative energy is wind. Homemade wind generators allow you to provide your home with heat at minimal cost.
First stage. Choose the appropriate type of structure and its power. Beginners are recommended to choose the most popular vertical wind generators. Select power individually. Increasing the power of a wind generator is achieved by increasing the size of the impeller and adding additional blades.
However, remember that the more powerful the device, the more difficult its balancing will be. The best option for self-production is a windmill with an impeller with a diameter of about 2 m and 4-6 blades.
Second phase. Make a foundation for a wind generator. A basic three-point base is enough. Determine the depth and area of the structure individually, taking into account the characteristics of the soil and the climate at the construction site.
Install the mast no earlier than the base has completely hardened, i.e. in about 1.5-2 weeks. Instead of a foundation, you can use guy wires. This is an even simpler option for installing a mast. Dig a small pit approximately 50-60 cm deep, install the wind generator mast in it and securely fasten the structure using ordinary guy wires.
Third stage. Make the blades. At home, a metal barrel is perfect for this.
You need to divide the container into equal parts in an amount equal to the number of selected blades. Make marks first, it is important that the blades have exactly the same size. Cut out the blades of the future wind generator. The grinder will help you with this
If you don’t have a grinder, you can get by with scissors for cutting metal.
Fourth stage. Secure the workpiece to the generator with bolts, and then bend the blades. Many parameters of the wind generator’s operation depend on how far the blades are bent. It is impossible to give any specific recommendations in this regard. You can only determine the appropriate angle through experience.
Fifth stage. Connect the electrical wires to the generator and connect the system elements into a circuit. Fix the generator on the windmill mast, then connect the wires to the mast and connect the generator and battery to the circuit. Apply the load using wires. At this point the wind generator is ready. You can connect it to a water heating system using the same storage tanks.
If you wish, you can assemble and install several windmills if one device is not enough to fully provide your home with heat.
Thus, the use of alternative energy is a very promising area that definitely deserves attention. Now you too can feel part of the modern world and save significantly on heating costs by assembling a simple wind or solar installation. Follow the instructions and everything will work out.
How to save money on the implementation of “green energy”?
Having analyzed the financial component of alternative types of heating, one can come to a disappointing conclusion - significant funds will be required at the initial stage.
After 3-7 years, depending on the chosen heating method, significant savings will become noticeable thanks to the energy-independent system.
It is profitable and convenient to use combined sources of alternative heating. To do this, you can choose the most optimal combination for your home.
You can save money by using and installing alternative heat generation units. Many home craftsmen are very enthusiastic about creating their own analogs to factory-made alternative energy conversion devices.
So, it is quite simple and inexpensive to assemble a solar installation from a hose, which will serve as an additional source of water heating.
Small windmills are successfully assembled at home using improvised materials. Also, well-read farmers living in rural areas are constructing installations for converting biological waste of plant and animal origin into biogas.
Homemade wind generators are quite functional. But to assemble them you will need to make preliminary calculations, purchase consumables, and spend your time
In the future it is used for the needs of the farm. Depending on the size of the waste digestion tank and the area of a private house, it is possible to completely provide the farm with biogas to satisfy all needs.
Types of alternative heating systems
An alternative to gas heating is, as a rule, automated heat supply systems that use modern technologies and the latest developments in practice.
These systems are an ideal solution for owners of private and country houses, especially those located at a distance from places where the gas pipeline network is laid.
Alternative heating can have the following types:
- Diesel.
- Electric.
- Solid fuel (coal, briquettes, firewood, etc.).
- Natural renewable sources (wind energy, earth's heat, solar energy, etc.).
Which of the above options is most optimal for use in a private country house? To answer this question, consider the advantages and disadvantages of each of them from the point of view of efficiency and economy.
Use of diesel fuel
One of the main advantages of using diesel fuel for heating a private home is the relatively low cost of installing a thermal installation that produces thermal energy.
Any other types of heating, the principle of which is based on the combustion of fuel with the subsequent release of heat, require much higher installation costs than boilers running on liquid fuel.
The main disadvantages of this system include the high cost of operation and the need for regular maintenance and monitoring of the system.
Electric heating
Electric heating is a good alternative to gas heating in a country or private residential building.
This system is characterized by ease of installation and operation, a high level of automation, ensuring reliable and high-quality operation of the entire system.
Electric heating can be adjusted for each room individually. Click to enlarge.
In addition, heating systems operating on electricity are characterized by an almost maximum efficiency value (about 100%).
The list of numerous advantages can be supplemented by the small overall dimensions of heating systems and the ability to install them in almost any room.
Electric heating can be adjusted for each room individually.
The disadvantages of the system include the high cost of electrical energy, the dependence of stable operation on the availability of current and the quality of the electrical network.
Use of solid fuels
The most balanced alternative to gas heating is boilers running on solid fuels.
These devices combine the relatively high availability of solid fuel, low installation cost and fairly high efficiency (efficiency can reach 85% - 95%).
The performance of solid fuel boilers is ensured by their periodic “refueling”, which must be done manually 3-4 times a day.
The structural reliability of these boilers should also be noted. The main disadvantages of a heating system using solid fuel are related to the need to prepare, dry and organize the storage of firewood (coal, briquettes, etc.).
Heat gains from welding transformers.
Welding transformers can be placed in the room where welding work is carried out and outside this room. All electrical power supplied to transformers is converted into heat.
If welding work is carried out in the same room where the transformers are installed, the heat generation from them will be:
Qtr. = 1000 ∑Nset × Codn × Kzagr × Kisp × Kt, W
where: ∑Nset - the total installed power of transformers, in kW - is accepted according to the passport); Kodn - the simultaneity coefficient is accepted in the range of 0.5 ÷ 1 - with several units of installed equipment, some of them may not work; Kzagr - load factor in fractions of a unit accepted within the range of 0.5 ÷ 0.8 or as specified by electrician-technologists; Kisp - power utilization factor in fractions of a unit, accepted within the range 0.7 ÷ 0.9; Kt - coefficient taking into account the amount of heat supplied to the air in the room from processed parts that are in the room for a limited time.
This coefficient can be determined by calculating the heat input from cooling materials.
Qcooling = C × G ( tmat. - tv ), kJ
C is the specific heat capacity of the material of the cooling product, kJ/(kg × ºС); G is the mass of the cooling product, kg; tmat. — initial temperature of the product material, ºС; tв — initial air temperature in the room, ºС.
If welding transformers are located outside the room where welding work is carried out, heat input into the welding work room is determined by the formula:
Qmechan.arr. = 1000 ∑(ζ × Nset) Codn × Kzagr × Kisp × Kt, W
where: ζ is the efficiency of transformers in fractions of unity - taken according to the catalog or passport of the transformer.