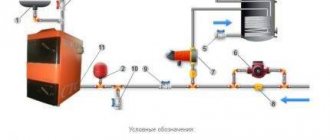
After the initial filling of the heating circuit, sooner or later, due to various reasons, the coolant level inevitably decreases. To avoid emergency shutdown of equipment during the cold season, timely replenishment of the heating system is required. Let's look at what this procedure is, what types of heating systems there are and what are the features of the coolant circulation in them, what types of coolant are used and what requirements are imposed on them, what are the main reasons for the decrease in coolant level in the system, what are the features of the make-up procedure for open and closed systems.
Charging diagram for a heating system with natural coolant circulation Source kotle.ru
Heating system - principle of operation, types, features of coolant circulation
An autonomous heating system is a complex of interacting equipment - a boiler, pipelines, heating devices and control devices. The principle of its operation is based on the transfer of heat from the unit through the coolant to the heating circuit, consisting of pipes, radiators and other heat receivers. As the liquid passes through the system, it gives off heat to the environment, and, already cooled, returns to the unit through the return line. Next, the coolant is heated to the required temperature and again starts in a circle.
There are 2 main types of heating systems:
- Natural or open.
The movement of coolant in the system is carried out under the influence of natural laws of nature. According to them, heated and therefore less dense water always tends to rise upward, while cooled and more dense water always tends to settle down. In this scheme, the boiler is located at the lowest point, and the expansion tank, through which the heating system is filled, is at the highest.
Construction of the simplest open-type heating system Source otoplenie-gid.ru
The operating principle of the system boils down to the following algorithm:
- The water is heated in the boiler heat exchanger.
- Upon reaching the set temperature and decreasing density, it rushes to the upper region of the heating circuit - it begins to flow through the pipes into the radiators.
- Having given off heat in the batteries, it cools, becomes denser and sinks down.
- Then it flows through the return line, mounted at a slight slope to the boiler.
- Finally, the cooled water enters the heat exchanger, is heated and re-entered through a direct line into the batteries.
A special open container is located at the highest point of this system. Through it, primary filling, level control and, if necessary, replenishment with coolant are carried out. In addition, the expansion tank serves as an internal pressure equalizer. So, if, when heated, the water heats up excessively and increases in volume, then it will simply go into this container, and will not expand or rupture the pipes.
An open tank at the top of the system compensates for the expansion of the coolant Source tinkoffjournal.ru
The main advantage of an open system is energy independence, ease of installation and operation. The deficiency is associated with low efficiency. The heating will only work in a small area, since the farther the battery is located from the unit, the less heat it will receive.
- Forced or closed.
The coolant in the system is introduced into the heating circuit under the pressure of a special circulation pump. Thanks to this, heated water reaches its destination faster and loses less heat along the way - regardless of the distance to the battery. Unlike the above, this system does not have direct contact with the surrounding air. The expansion of the coolant in it is controlled by a special closed membrane tank, divided in the middle by a rubber partition into two chambers - air and for coolant.
To pump water into a forced autonomous heating system, a private house must have a water supply system whose pressure is slightly higher than the internal pressure in the heating circuit. Replenishment is carried out through a special module or simply a check valve installed at the lowest point of the system.
Schematic representation of a forced closed heating system Source inside-lighting.ru
On a note! In addition to purely closed or open heating systems, there are hybrid options. An example is schemes with natural circulation, equipped with a pump to increase flow, reduce inertia and increase efficiency during periods of extreme cold.
Make-up - heating network
Feeding heating networks with a mixture of boiler blowdown water and water softened using the sedimentation method (without phosphate softening) is not allowed due to the risk of silting of the heating network with the products of the additional softening reaction.
The heating network is fed with softened, deaerated water, the quality of which meets the quality requirements for network and make-up water for hot water boilers, depending on the type of heat source and heat supply system.
Heating networks must be fed continuously using booster pumps or directly from feeder tanks. The number of make-up pumps must be at least two, one of them is a reserve one.
The heating network must be fed continuously in order to maintain a given pressure on the suction side of the network pumps during the operating mode of the heating networks and when the network pumps are stopped.
Replenishment of heating networks, therefore, is the process of replenishing losses or disassembling water from heat pipelines or heat consumer systems.
Blowdown water from steam boilers and steam converters is often used to feed heating networks. In cases where the above-mentioned purge lines are directly connected to the return line of the heating installation, they are usually equipped with check valves.
To feed heating networks, as well as evaporators and steam converters, it is allowed to use part of the washing water of anion exchange filters, as well as H - cationized water after the breakthrough of N3 prl, provided that it is decarbonized and neutralized.
To feed heating networks, as well as evaporators and steam converters, it is allowed to use part of the washing water of anion exchange filters, as well as H - cationized water after breakthrough Ma, provided that it is decarbonized and neutralized.
To feed heating networks, deaerated water (natural or softened by soda-lime, cation exchange or other method) or water with stabilized hardness should be used.
It is allowed to replenish the heating network with boiler blowdown water or a mixture of it with cationized water. To protect the heating network from corrosion, the make-up water must be alkaline and must be sulfated (chapter). To save the reagent (sodium sulfite), the heated water should be sulfated.
Water for feeding heating networks with open water supply must have a carbonate hardness of no more than 700 mcg-eq/kg, and must also meet sanitary standards for drinking water. To obtain water of the specified quality, tap water is used, treated according to the following scheme: H - cationization in the starvation mode of cation exchanger regeneration - buffer cationization - decarbonization. The introduction of buffer cationization into the scheme serves to smooth out fluctuations in alkalinity and eliminate acidity if it appears in the filtrate after H - cation exchange filters.
The installation for replenishing heating networks must ensure their replenishment with chemically purified deaerated water in operating mode and emergency replenishment with untreated water from domestic or industrial water supply systems.
Water for feeding heating networks must meet the following requirements: residual hardness 0 8, oxygen content 0 1 mg/l; There should be no sludge in the make-up water.
Water for feeding heating networks with direct water supply must also meet sanitary standards for drinking water.
The installation for replenishing heating networks must ensure their replenishment with chemically purified deaerated water in operating mode and emergency replenishment.
Types of coolants and requirements for them
In autonomous heating systems for a private home, the following types of liquid coolants are used:
- Water.
This is the most common type of coolant, which has the following advantages:
- Minimum price.
- Availability.
- Maximum heat capacity (ability to transfer heat).
- Low viscosity, which means the least load on the circulation pump.
- Low corrosiveness - only in the presence of dissolved oxygen.
- Ecological cleanliness.
- Small expansion coefficient - no more than 0.03%.
Water is the most common and accessible coolant for most heating systems Source eurosantehnik.ru
The disadvantages of using water as a coolant are manifested in corrosion activity on unprotected steel parts of the system, as well as high crystallization temperatures. Therefore, if the house is left in cold weather long enough to cool the premises to 00C, then the water will need to be drained. Otherwise, under the force of expansion, freezing water will rupture pipes, batteries and heat exchanger.
- Antifreeze.
It is an antifreeze for radiators of cars operated in cold weather. Recently, they have preferred to fill autonomous heating systems of only closed types - due to the high toxicity of the vapors, they are not used for open circuits. It is marked with numbers - 65, 40 or 30 - which means the freezing mark of the liquid at a temperature below zero.
It is characterized by the following number of features:
- Average market price.
- The heat capacity is average, but lower than that of water.
- High viscosity - which characterizes a high load on the pump.
- Almost complete absence of corrosive activity.
- Toxicity - due to the ethylene glycol included in the composition.
- The expansion coefficient is up to 0.05% - almost 2 times higher than that of water.
Antifreeze contains harmful ethylene glycol, so it can only be used in closed systems Source otoplenie-gid.ru
Unlike water, antifreeze does not cause corrosion, but this is not always a good thing. So, for example, if a heating circuit becomes depressurized, fluid will begin to leak, while water and other corrosive liquids will quickly “heal” the leakage points by forming rust.
- Propylene glycol.
Antifreeze liquids based on propylene glycol are produced on an industrial scale specifically for autonomous heating systems.
Main operational features:
- Low heat capacity. In its pure form, it is almost 2 times lower than that of water. However, when diluted with water, the indicator increases to an acceptable level.
- High viscosity, which creates additional load on pumping equipment.
- Expansion coefficient – no more than 0.05%.
- Harmlessness.
- Lack of corrosive activity due to additives.
Although propylene glycol is the most expensive on the list of antifreezes under consideration, its popularity is high due to its absolute harmlessness. In purified form, it is added to both cosmetics and confectionery products.
Propylene glycol is the best antifreeze option for the heating system of a private home Source santehexpress.ru
- Brine.
The product is a solution of simple salts - common table salt, calcium chloride and some others. It is used as a budget alternative - to fill the heating system in a private home instead of water. The higher the salt concentration, the lower the freezing point of brine.
Features of operation:
- The lowest cost is based on the price of the amount of salts used.
- Sufficient heat capacity - 2/3 of that for water.
- Minimum viscosity.
- Expansion coefficient – 0.03%.
- No toxicity.
The main disadvantages manifest themselves in the form of low fluid mobility with a high concentration of salts and high corrosion activity on the walls of the metal elements of the system.
Metal elements rust quite quickly when in contact with salts Source vyborradiatora.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in engineering systems (heating, water supply, sewerage and others) and related work
Selection requirements
The liquid poured into the heating system as a coolant must meet the following series of requirements:
- High specific heat capacity.
The parameter characterizes the amount of thermal energy that must be supplied to 1 kg of a substance to raise its temperature by 10C. For heating fluids, this figure should be as large as possible. Ordinary water has the highest indicator among other liquids poured into the circuit.
- Operating temperature range.
Each individual coolant has its own characteristic operating temperature spectrum. Violation of these conditions leads either to equipment damage or to irreversible loss of coolant properties.
For example, when water freezes, it expands and ruptures the pipes or radiators in which it is located. On the other hand, organic coolants, when heated above 1000C, decompose into individual components, forever losing their original characteristics.
Any industrially produced coolant has a strictly specified operating temperature range Source sdvor.com
- Corrosivity.
The chemical activity of the coolant can lead to rusting of the metal parts of the circuit. The problem can be solved with inhibitory additives. For this reason, many coolants include special additives.
However, the problem most often manifests itself when the coolant is in constant contact with oxygen, and is practically absent when dissolved gases are removed from it.
This is especially true for ordinary water - after it is saturated with air bubbles at the point of contact - the expansion tank - it more actively corrodes steel pipes, radiators and other elements. Therefore, only closed-type heating systems are allowed to be filled with any type of coolant. In addition, they are most often equipped with plastic pipes that are inert to corrosion.
- Viscosity.
The viscosity index determines the degree of internal friction, and, consequently, fluidity. This in turn affects the pumping speed. Therefore, the greater its value, the more energy will be required to move the coolant through the system.
The promotion of viscous coolant is facilitated by the installation of powerful circulation pumps Source zaggo.ru
Water has the standard of minimum viscosity. All other coolants used in autonomous heating circuits have a higher value, and therefore worse fluidity characteristics.
- Lubricity.
Modern heating systems include a number of equipment in which the coolant additionally acts as a lubricant. This is not only a circulation pump, but also make-up and emergency shutdown valves, a thermostat, protocol sensors, pressure sensors, etc. Therefore, it is also necessary to select the liquid based on its lubricity in accordance with the specific type of system.
- Safety for others.
The substance used as a coolant in domestic heating systems must be completely safe for others. It should not be used in a vapor state, as if it ruptures due to the high temperature, it can cause burns.
Also, antifreeze should not be toxic, as, for example, compositions with ethylene glycol have. Therefore, for a number of reasons, domestic heating systems are most often filled with water.
The design of the heating system of a private house does not exclude contact of the coolant with household members, so it should not include toxic components Source klimatlab.com
- Chemical activity.
The coolant components must not interact with the heating circuit components. For example, if the heating system of a double-circuit boiler with steel radiators is filled with ethylene glycol, then the internal zinc coating of the batteries will quickly become thinner.
Moreover, heating the coolant to standard 80-900C will lead to the loss of its basic properties - the fluidity will become higher than that of water. Over time, this will inevitably lead to leaks of various connections with seals based on rubber, paronite and other polymers.
Recommendation! In most cases, water is used to charge the heating circuit. However, if the use of antifreeze cannot be avoided, for example, when the house is periodically left for a long time without heating during cold periods, then the choice is recommended to be made in favor of products based on propylene glycol. At the same time, it is better to purchase products from well-known lines with technical documentation confirming the quality.
The use of antifreeze will help avoid freezing and rupture of pipes and radiators if the house is left without heating in cold weather Source santehplus72.ru
Make-up control
In a small-volume heating system, pressure level differences, as well as a decrease in the total amount of coolant, can usually be compensated by means of membrane tanks.
It is for this reason that adding liquid to the system is a relatively rare occurrence.
Simplification of the design involves manually turning on the pumping equipment, as well as opening and closing the make-up line. In this case, monitoring the pressure level must be systematic.
Controlled heating is more complex, but extremely efficient. It is in the automatic mode that a direct refusal to work on the “direct action” principle is assumed. There is no need to regulate the operation of the source of all generated thermal energy, or to add or subtract the resources used. This option is based on the use of a control module.
Thus, the automatic control mode is based on selecting the most comfortable temperature conditions and is more convenient, and also allows for significant savings in energy consumption.
The Italian brand of heating boilers “Beretta” has earned popularity in our country. Beretta gas boiler - types of equipment and an overview of popular models.
How to calculate heat loss at home and why it is needed, you will find out here.
The piping diagram for a solid fuel boiler is presented at the link. We will also talk about the importance of proper strapping.
Reasons for reducing coolant volume
A decrease in the level in heating systems of a private house occurs due to the following number of reasons:
- Leak. Often the coolant begins to flow at the joints. It most often appears immediately after the crimping process. Therefore, they can be detected and eliminated immediately. However, there are also hidden, old leaks. It is quite difficult to identify them, due to the fact that they are located in concrete floor or wall screeds. To detect such an accident, it is often necessary to use a thermal imager. The only way to avoid this is to make all joints in an open, serviceable area.
- Exceeding operating parameters of a critical level. For example, if the coolant suddenly overheats, its pressure will increase sharply and exceed the permissible level for the equipment. As a result, the emergency valve will operate, which, in contrast to the replenishment module, will independently begin to eject liquid from the heating system until the internal pressure returns to normal.
Triggering of the emergency valve leads to the release of part of the coolant from the system Source stroy-podskazka.ru
How to fill the heating system in an apartment building
Scheme of water heating with associated movement of water: 1 – boiler; 2 – main riser; 3 – expansion tank; 4 – air collector; 5 – supply risers; 6 – return risers; 7 – return line; 8 – expansion pipe; 9 – pump; 10 – direction of pipe slope.
The water valve located in the house should be closed, and the water discharge on the coolant supply pipeline is gradually opened. At this time, the discharge on the return line is blocked. Then you need to very slowly open the valve on the return line until it is completely open
Caution must be exercised because if the high-pressure water supply of a general heating system is suddenly opened, this can lead to sudden changes in pressure, causing water hammer. The shock can be so powerful that one will be enough to break the system in the most vulnerable places
It will take some time for the heating system to fill. Reset should be monitored continuously. When water flows without any admixture of air bubbles, and this can be understood by the cessation of the characteristic hissing sound, close the discharge valve. Now it’s time to open the water supply valve to a specific room. At the final stage, all that remains is to bleed the air from all heating circuits. This method of filling the system with water is provided for.
A system with top piping looks much easier to use
In this case, you should simultaneously, with the same caution, open both dampers at once, while the discharge should be closed. To bleed air, go up to the attic of the building and open the air valves provided by the design
Features of recharge
Heating systems of open and closed types primarily differ in the features of coolant circulation. In the first case, it moves by gravity, in the second, under pressure created by the pump. Therefore, the recharge methods for both cases will be different. Let's look at them in more detail.
Open system
The basis for the functioning of an open heating system is the expansion tank located at the highest point. In most cases, it is installed under the ceiling or in the attic of the house. The procedure for recharging the heating system is carried out through it from the water supply. The coolant level in it should not fall below the set level, otherwise the circulation process will simply be interrupted. As well as rising to the edges so that the liquid begins to flow out, it should not either.
To optimize control, modern expansion tanks are designed and function as follows:
- A return and forward line is supplied to the installed expansion tank. The first is at the bottom level, the second is 100 mm higher.
The open heating system is recharged through an expansion tank Source mynovostroika.ru
- Hot water rises through a straight pipe, accumulates and goes into the heating circuit through the return line.
- A control-feed pipe cuts into the opposite wall of the tank. It is located 150 mm above the level of insertion of a straight line.
- An overflow pipe is installed 100 mm above the level of the control pipe. Its purpose is to automatically drain the coolant from the tank when it overflows - so that it does not overflow. Its outlet leads to a sewer or reservoir.
- Under normal conditions, the coolant level should be balanced between the control and overflow pipes.
- All tube outputs are assembled in the boiler room for better control and management.
- To make recharge, a water supply is connected to the control tube through a shut-off valve. As needed, the valve opens and water fills the expansion tank until it begins to flow out of the overflow tube. The watercourse is blocked.
- To check the level in the tank, the control tube periodically opens. If water flows out of it, the level is fine; if not, replenishment is required.
Often an expansion tank is installed under the roof of a house. Source ytimg.com
A more complex control mechanism includes a float mechanism that automatically monitors the level and, as necessary, adds coolant to the tank.
Closed system
In order to pump water or antifreeze into a closed heating system, a more sophisticated mechanism is required than simply opening a tap and supplying it from the water supply. Since the coolant circulates in a sealed circuit and is constantly under pressure of 0.5-3 bar. Modern boilers are equipped with pressure gauges for visual control by the user, as well as safety devices for automatic control of equipment operation.
The role of such a device in closed systems is performed by an emergency valve. If the pressure exceeds the norm, the coolant will be discharged into the sewer or a special tank. Moreover, if the pressure is below normal, the pressure sensors will also not allow the unit to start. To restore the pressure to normal levels, there are special replenishment modules.
Heating system recharge module with filters Source ytimg.com
Signs of lack of coolant
Water in the heating system circuit can decrease for various reasons. And this happens quite often. If the owners of the house have not yet bothered to install an automatic system for replenishing the heating network, you can determine the lack of coolant by the following signs:
- overheating of the supply water supply and cold radiators;
- gurgling water in the riser;
- frequent starts and stops of the gas boiler burner;
- overheating of the solid fuel boiler and activation of the safety valve.
overheating of the supply water supply and cold radiators;
gurgling water in the riser;
frequent starts and stops of the gas boiler burner;
overheating of the solid fuel boiler and activation of the safety valve.
A shortage of coolant in the circuit is especially dangerous if a TT boiler is used as the main heating equipment in the network. If there is not enough water in such a unit, it will boil. After its complete evaporation, a fire will definitely start in the boiler room. Unfortunately, such situations are far from uncommon.
Also, due to a lack of coolant in the heating system, pipes may melt, radiators may fail, etc. Therefore, it is imperative to monitor the pressure in the circuits of heating systems set for private houses (1.5-2 bar).
Video description
Video example of arranging automatic recharge of a heating system:
Another common problem is increased water hardness. It is formed by insoluble salts, which, when heated in the system, can form deposits in the form of scale and clog the coolant flow. To eliminate such consequences, the following methods are used:
- Chemical softening with reagents. Salts settle at the bottom of containers or settle in filters.
- Installations with ion exchange resins.
- Softener filters installed on household dishwashers and washing appliances.
- Reverse osmosis type filtration.
Note! If the water hardness is not very high or medium, then the functionality of a closed heating system that operates without leaks will not be particularly affected. Insoluble salts will quickly be deposited in a thin layer on pipes and heat exchangers, but will not affect the efficiency of the system as a whole. Another thing is flow plate heat exchangers. Due to the large volume of water passing through them, deposits will only grow over time and eventually simply clog the entire lumen.
Installation features
The direction of the water must coincide with the direction of the arrow on the body of the device.
The valve is placed on the pipe so that the direction of the liquid coincides with the direction of the arrow. The filter plug is directed downward, and the adjustment screw must be accessible for use. The pressure gauge dial rotates to make it easy to read the values.
The winding material is used rationally so that excess does not fall into the lumen of the gearbox. Boiler feed in the form of a valve should not depend on main loads (compression, torsion, bending, vibration). For this purpose, additional supports or compensators are installed.
The mismatch between the axes of the pipelines should not be more than 3 mm for a length of 1 m. For longer lengths, 1 mm is added for each linear meter. The make-up circuit is connected to the pipeline near the expansion tank.
Video description
Video on how to top up a heating system:
Location of the make-up unit
It is best and easiest to recharge an open system from above - through the expansion tank. At the same time, it is still recommended to do the initial download from the lowest point. Since this will allow the bulk of the air to be displaced from the circuit.
In closed systems, pumping can be done from any point, since the coolant circulates through a sealed circuit. However, even in this case, there are special recommendations regarding the location of the point and the implementation of the recharge procedure itself:
- Modern models of wall-mounted and compact boilers are already equipped with special refueling and top-up points.
- For refilling, you must choose a place next to the drain valve at the lowest point of the system.
- The optimal location for the make-up unit is in the return pipeline next to the expansion tank. This will enable the system to immediately respond to an increase in pressure, and also eliminate water hammer.
Mechanical or automatic replenishment, which one to choose?
The make-up valve can be mechanically or automatically controlled. The first option is installed where small heating systems operate. In them, as a rule, any surges in the operating pressure of the coolant are regulated using membrane tanks. And the easiest way to compensate for the loss of water volume is to manually open the supply tap in a cold water supply. The main inconvenience of this option is the need for experience to perform the described operations, as well as the possession of certain technical knowledge and skills.
Note! In this case, you will have to independently control the pressure inside the closed heating system. An excessive increase in the volume of coolant can lead to an emergency situation
Automatic make-up valves are installed in large branched systems. They are often included in the heating boiler package, becoming part of its automation. Installation of such a device does not cause any particular difficulties. But its implementation makes the entire scheme volatile. And this must be taken into account when choosing one or another type of technical unit.
Operating principle of automatic valve
Auto make-up valve
The operating principle of the automatic valve is extremely simple. The operating parameters are pre-configured. Water losses are programmed in advance - the lowest pressure indicators are set. If the volume of coolant drops, say, by 10%, the valve is activated and starts the pump. The latter pumps the required volume of liquid from the cold water supply line. When replenishment occurs, the valve is activated again and shuts off the supply automatically.
The described device is easy to install. First, a measuring pressure gauge or any other electrical contact sensor is installed on the cold water supply line, which allows you to regulate the pressure in two directions. One of its groups is adjusted to lower operating pressure. This is where the intermediate relay or contactor is installed. When the volume of hot water drops inside a closed circuit, it turns on a mechanism that starts the suction pump. The second group turns off all these links when the water volumes are replenished. An electric valve—a valve with an electric motor—can be used as an actuator.
Note! When using an automatic make-up valve, the heating system independently controls the pressure and also independently calculates the compensating volume of water. This is the main advantage of this technical unit
When is it necessary to organize make-up using a bypass circuit?
Automatic recharge of systems and its efficiency
As a rule, all closed heating systems can function effectively only with high operating pressure of the coolant. But the deciding factor here is also the temperature of the hot water.
As it increases, the thermal expansion of some technical components increases. It can be compensated by installing an expanzomat - a hydraulic accumulator capable of accumulating hydraulic energy when there is an excess of it and releasing it when there is a shortage. It must be connected using a bypass circuit. Read how to do this here.
Video description
Video on how to install the make-up valve:
- If replenishment is carried out through the return, then the boiler must be turned off. Otherwise, cold coolant entering a heated heat exchanger can lead to thermal deformation of the latter. This is especially true for cast iron models.
- Automatic make-up for a floor-standing boiler with a cast-iron heat exchanger is best done through a direct manifold.
- If possible, it is better to make replenishment through a hydraulic arrow so that the cold coolant quickly mixes with the hot one and eliminates thermal shock for the heat exchanger.
- On condensing-type boilers, it is advisable to install the make-up in the return line - to increase the efficiency of the system.
- If there is indirect heating in the boiler system used for hot water supply to the house, it is allowed to supply heated water from it for replenishment through the return line.
Reference! Modern boiler models from official manufacturers are equipped with technical documentation, which includes important technical information. This is, first of all, a diagram of the correct piping indicating the location of the recharge unit.
How to connect to the heating system
With a closed circuit, there is not much difference where to connect the make-up pipeline - to the supply or return. We recommend using the classic proven method - the insertion point should be located on the return line next to the boiler, after the circulation pump and expansion tank. Causes:
- the unit is located in the combustion room, next to the equipment and instruments;
- pumping water into the return line is immediately reflected on the pressure gauge installed in the supply behind the boiler;
- the insert is located at the lowest point, the flow is distributed in 2 directions - into the boiler and radiators, the air is squeezed out evenly.
Classic scheme for inserting a recharge module
The piping of solid fuel units involves the installation of a condensation protection circuit with a three-way valve. You cannot make makeup in front of this valve - cold water will immediately close it and the boiler pressure gauge will begin to lag in readings. Cut inside the circuit, between the 3-way valve and the heat generator.
In a similar way, the make-up flows into the return line of the open system. The second option is to add coolant directly to the tank; the disadvantage of this method is to lay the supply pipe into the attic.
Briefly about the main thing
An autonomous heating system is based on the principle of transferring heat with a coolant heated in a heat exchanger to radiators, and then returning it through the return line in a cooled state to the boiler for reheating and restarting the system. There are open or natural systems and closed or forced ones. In the first, the coolant moves by gravity, in the second, under pressure using a pump.
They can use water, antifreeze, propylene glycol and brine as a coolant. Each liquid has its own characteristics and recommendations for use. When choosing a coolant, the following characteristics are considered:
- Specific heat.
- Operating temperature range.
- Viscosity.
- Corrosive activity.
- Lubricity.
- Chemical activity.
- Environmental safety.
A decrease in coolant level can occur due to reasons such as leakage, evaporation, losses from air vents and repair or maintenance of filters, reset by an emergency sensor. Feeding open and closed systems has its own characteristics and algorithm of actions. The open one is fed through an expansion tank located at the top point of the system, the closed one through the valve - from the bottom position, most often through the return line. At the same time, special requirements are imposed on the choice of location for installing the recharge unit.
Manual recharge scheme
The simplest option for filling the system is implemented in 90% of double-circuit wall-mounted boilers, where a cold water supply pipe is a priori connected. A manual valve is installed inside the housing, connecting this line with the heating return line. Often, a boiler feed tap is found on solid fuel heat generators with and without a water circuit (for example, heating units of the Czech brand Viadrus).
Reference. On some models of gas heaters equipped with a DHW heat exchanger (in particular, Beretta), instead of a manual tap, manufacturers install an automatic make-up valve with an electromagnetic drive. If the coolant pressure drops below 0.8 Bar, the boiler itself draws water to the required level.
In wall-mounted double-circuit heat generators, the make-up valve is located at the bottom, where the pipelines are connected
. To assemble a classic make-up unit suitable for any type of system, you will need the following parts:
- tee with side outlet DN 15-20, corresponding to the material of the heating main pipe - fitting for metal-plastic, polypropylene, and so on;
- poppet (spring) check valve;
- ball valve;
- couplings, fittings.
The purpose of the check valve is to prevent water from the heating network from flowing back into the water supply system. If we are talking about pumping antifreeze using a pump, you cannot do without a valve. The fittings are installed in the order listed:
- The tee cuts into the heating return after the circulation pump.
- A check valve is connected to the outlet pipe of the tee.
- Next is a ball valve.
Advice. If there is no fine filter at the entrance of the water supply to a private house, it is advisable to provide one on the make-up line. The element will protect the heating system from the entry of fine sand and rust particles that accumulate on the check valve plate and in the seats of three-way valves.
The operating principle of the unit is simple: when the tap is opened, water from the centralized main flows into the heating pipelines, since its pressure is higher (4-8 Bar versus 0.8-2 Bar). The filling process of a closed system is monitored by a boiler or safety group pressure gauge. If you accidentally exceed the pressure, use the Mayevsky tap on the nearest radiator and bleed off excess water.
To control the amount of coolant in the expansion tank of an open heating network located in the attic of the house, the tank must be equipped with 2 additional tubes with a diameter of ½ inch:
- The control line, ending with a tap in the boiler room, cuts into the side wall at approximately half the height of the tank. By opening this valve, you can determine the presence of water in the tank without climbing into the attic.
During the replenishment process, air bubbles escape through the tank lid, the maximum level is monitored by the flow of water from the upper fitting through the pipe - The overflow tube is inserted 10 cm below the tank lid, the end is discharged into the sewer or simply onto the street under the roof overhang. Being in the furnace room and opening the feed tap, you should see this pipe; when water flows from there, filling stops.
Comment. If you are interested in calculating the minimum volume of the expansion tank, follow the dedicated link.
The circuit with a check valve and shut-off valve is also applicable for filling solar systems (solar collectors) and geothermal circuits of heat pumps with antifreeze. How to use the boiler make-up valve is described in the video:
Water volumes for various heating system elements
Water volume (liters) in the radiator section
| Radiator material/type | Dimensions*: height×width, mm | Volume, l |
| Aluminum | 600×80 | 0,450 |
| Bimetal | 600×80 | 0,250 |
| Modern cast iron battery (flat) | 580×75 | 1,000 |
| Old style cast iron battery () | 600×110 | 1,700 |
*IMPORTANT! The dimensions in the table are approximate.
In most models of modern manufacturers, they are ±20 mm in width; the height of heating radiators can vary from 200 to 1000 mm.
The volume of radiators with very different heights can be approximately calculated from this table using the rule of proportion: it is necessary to divide the volume by the height and then multiply by the height of the selected model. If the heating system is extended, then it is better to check the volume parameters with the manufacturer.
Volume of water in 1 linear meter of pipe
- ø15 (G ½") - 0.177 liters
- ø20 (G ¾") - 0.310 liters
- ø25 (G 1.0″) – 0.490 liters
- ø32 (G 1¼") - 0.800 liters
- ø40 (G 1½") - 1,250 liters
- ø50 (G 2.0″) – 1,960 liters
Also read the review of which pipes are best to choose.
The main dimensions of the internal diameters of pipes (a range of values from 14 to 54 mm are taken) that the consumer may encounter.
| Inner diameter, mm | Volume of liquid in 1 m of pipe running, l | Inner diameter, mm | Volume of liquid in 1 m of pipe running, l |
| 14 | 0,1539 | 30 | 0,7069 |
| 15 | 0,1767 | 32 | 0,8042 |
| 16 | 0,2011 | 34 | 0,9079 |
| 17 | 0,2270 | 36 | 1,0179 |
| 18 | 0,2545 | 38 | 1,1341 |
| 19 | 0,2835 | 40 | 1,2566 |
| 20 | 0,3142 | 42 | 1,3854 |
| 21 | 0,3464 | 44 | 1,5205 |
| 22 | 0,3801 | 46 | 1,6619 |
| 23 | 0,4155 | 48 | 1,8096 |
| 24 | 0,4524 | 50 | 1,9635 |
| 26 | 0,5309 | 52 | 2,1237 |
| 28 | 0,6158 | 54 | 2,2902 |