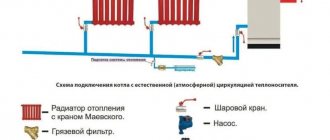
Any user of forumhouse.ru knows that water and heat are the life support of any home, because the comfort of living outside the city directly depends on this.
So, in this article we will look at the main aspects of providing your home with water and heat, namely:
- Where does the choice of a water supply and heating system begin, and what are the requirements for the boiler room?
- What are the required components of a modern water supply system for a private home?
- What is the essence of water treatment?
- Which pipes are best used for water supply and heating systems;
- How to choose a boiler and fuel;
- What are the main types of heating systems?
If there is no water in the tap
Without what can a house not be called a full-fledged home?
Without water and electricity. If only the power grids of your locality can be a constant source of electricity, then water can be obtained literally from under your feet: you just need to drill a well or dig a well.
Structure of aquifers and depth of water intake
What elements should the heating and water supply scheme of a house contain to supply water from a well or borehole?
Scheme with hydraulic accumulator
Scheme of autonomous water supply with water supplied from a well
It includes:
Pump. It can be superficial or submersible.
The first type of pumps is easier to repair and maintain, but can only provide water supply if the depth of the well or well is no more than 7-8 meters: the theoretical maximum height of the water column with a pressure difference of one atmosphere is 10 meters, and the difference between the pump volute and the suction pipe is noticeable less atmosphere. Submersible pumps, in turn, can provide pressure of tens and even hundreds of meters;
The serial connection of several working chambers of a well pump provides a huge output pressure
- Automatic pump control, including a power control relay and a pressure sensor. The task of automation is to supply power to the pump when there is a critical drop in pressure in the water supply system and turn it off when the specified maximum pressure level is reached;
- A check valve that prevents water under pressure from draining into a well or well;
- Hydraulic accumulator. It serves as a reservoir for pumped out water, compensating for its peak flow and allowing the pump to avoid turning on every time the tap in the house is opened.
Autonomous water supply system with surface pump and hydraulic accumulator
Scheme with storage capacity
Heating and water supply systems for country houses use storage tanks in two cases:
- When the centralized supply of cold water is intermittent or on schedule. The container allows you to create a supply of water for several days;
- During prolonged power outages. The advantage of this scheme lies in its relative energy independence (having pumped water into the storage tank, the pump can remain idle for days).
A large enough container can provide water to a home for several days.
In the simplest version, water supply with a storage tank is implemented as follows:
- The pump is equipped with a float valve that turns on the power relay when the water level drops and turns it off when the upper threshold level in the tank is reached;
- The local water supply is connected directly to the storage tank in its lower part through a ball valve, which allows you to turn off the water supply without draining the tank.
Free-flow water supply with storage tank
This scheme has several disadvantages:
- The pressure in the cold water supply system is limited by the height of the storage tank above the point of water collection. Meanwhile, many plumbing fixtures and some household appliances operate only at an excess pressure of 0.3 atmospheres or higher. You don’t have to look far for examples: all automatic washing machines and dishwashers, as well as instantaneous electric water heaters, fall into this category;
Storage tank in the attic of a private house
- For obvious reasons, the tank can only be placed in a heated room. Otherwise, in the absence of water supply, the water will simply freeze;
- The storage tank will become overgrown with lime deposits and will need periodic cleaning;
- With a large storage tank, the load on the floor beams will become a serious problem. The calculated maximum load on wooden beams is only 400 kg/m2. Meanwhile, the volume of the storage tank can be measured in cubic meters, which subtly hints at a weight of several tons.
The weight of a tank filled with water can reach several tons, which is obviously a lot for a wooden floor.
Is it possible to do without shut-off valves on the water supply?
Definitely not possible. To shut off the water in an emergency or in case of plumbing repairs, shut-off valves at the pipe entry into the house are necessary. It is installed in front of the water meter, if the water supply is drawn from a centralized main, or in front of the hydraulic accumulator, if from a well. In addition, it is recommended to install shut-off valves on the risers going to the upper floors - then when replacing the mixer at the top, you will not have to “dehydrate” the entire house.
9
Modeling the optimal contour geometry
For one private house, several closed water circuits can be designed that will heat different rooms. They can differ significantly from each other in the type of wiring.
When designing, first of all, they take into account the operability of the system, as well as optimal geometry from the point of view of minimizing costs, ease of installation and the ability to fit heating elements into the design of the premises.
Natural and forced water circulation
Heating of the coolant for heating the house occurs in one or more devices located indoors. These can be stoves, fireplaces, as well as gas, electric or solid fuel boilers.
Water pressure in the circuit is ensured either through the use of circulation pumps or by arranging the geometry of the system to create conditions for natural circulation.
Also, the source of hot water can be a centralized heating system for several houses. In case of low pressure, it is possible to connect circulation pumps to create additional pressure and increase the speed of fluid movement through the pipes.
Installing a circulation pump creates sufficient pressure in the system, making it possible to use wiring options that cannot be used with natural circulation
When choosing an option with natural circulation of coolant or low pressure in pipes with centralized heating, you must carefully consider the possibility of maximizing the use of physical laws that allow you to start and maintain fluid movement.
A mandatory element of the wiring in this case is the acceleration manifold. It is a vertical pipe through which hot water rises, then is distributed among heating appliances and, having lost its initial temperature, flows down.
Due to different densities, a difference in hydrostatic pressure between the hot and cold columns of liquid occurs, which is the driving force for water circulation.
Vertical and horizontal wiring
Hot water can be supplied to radiators in different ways. The wiring is conventionally divided into vertical and horizontal, according to the position of the pipes (risers) supplying water directly to the heating radiators.
In modern houses, horizontal rather than vertical heating distribution is more often used. The reason is that the layout of radiators on different floors rarely coincides
Vertical circuits with top supply of hot water make maximum use of the difference in hydrostatic pressure between the warm and cold segments of the circuit, so they are almost always used with natural circulation, as well as with low pressure in the system.
In addition, such circuits are operational in case of emergency shutdown of the pump, which may occur due to its breakdown or lack of electricity.
Bottom supply wiring is practically not used for heating with natural circulation. If there is good pressure in the system, its use is justified, since such a scheme has two significant advantages relative to the alternative option.
Advantages of the scheme:
- smaller total length of pipes used;
- there is no need to run the pipe through the attic or technological niches under the ceiling of the second floor.
The horizontal heating distribution scheme is used for one-story private houses. If the building has two or more floors, then it is often used in cases where vertical risers are undesirable from a design standpoint.
Horizontal pipes supplying and discharging water can be organically integrated into the interior of the premises, as well as hidden under the floor or in niches located at floor level.
Sewerage
Sewage, as well as heating and hot water supply to the house are part of a single engineering support aimed at creating optimal living conditions. The function of the sewer system is to remove accumulated sewage from it.
Waste disposal
Wastewater can be discharged either through a centralized village sewer system or to a local septic tank. In the latter case, it must be equipped with filtration and disinfection subsystems.
As in water supply systems, sewer pipes outside the cottage are laid below the freezing point so that sewage safely reaches the septic tank and does not freeze in winter. If you have to make a lot of turns, it is recommended to install inspection wells. In the case where the wastewater is discharged above the level of the supply to the toilet, a salolift is installed.
Pipes
The sewer network is free-flowing, so nowadays the lines are almost always made of plastic. Pipes for indoor use have a thinner wall thickness and are made of gray plastic. Their diameter is 50 or 100 mm. External sewerage requires the presence of orange pipes with thicker walls; their cross-section is calculated at the design stage. Internal sewer pipes can be soundproofed.
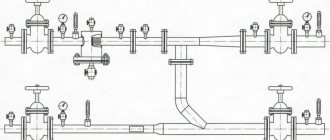
What you need to know about collectors?
This design ensures a uniform supply of liquid to several simultaneously switched on water taps while maintaining the required pressure. When selecting equipment, you should remember that there are manifolds for distributing cold and hot water.
To make the device body, brass or stainless steel is used; there are devices made of impact-resistant plastic that can withstand heating to temperatures of more than 100°C. Metal products are attached to pipelines using threaded bushings. To connect plastic pipelines, manifolds with compression transition elements or with special bushings (fittings) are used that allow plastic pipes to be soldered.
When selecting a collector, you should take into account the number of outputs intended for switching external equipment. Standard products provide up to 6 channels, but manufacturers allow 2-3 collector modules to be connected in series. For coupling, couplings are provided at the nodes; the method of connection depends on the design features of the collector. If switching of the additional unit is not required, the collector is closed with an end cap.
Recommendations for the buyer
Basic recommendations for selecting a collector:
- Before purchasing a collector, you should decide on the type of material of the water pipes. It is recommended to use products made of polymers (for example, cross-linked polyethylene) that are not destroyed by water and do not have threaded connections.
- During the installation process, it is necessary to provide for the installation of a tap for the side lines. There are manifold blocks with integrated valves; the installer needs to connect the pipes and the manifold itself to the central riser. Please note that if the locking mechanism is damaged, the entire manifold block will need to be replaced. When using brass or stainless steel products, the taps must be installed separately.
- A block of additional devices is installed in front of the manifold (for example, meters, filters or a check valve).
How to connect a house to a centralized water supply?
In most cases, cottage communities are connected to a centralized network or have their own well, so it will not be difficult to supply water to the house on a general basis. If there is a need to connect directly to the central main line, then you should contact the local Vodokanal service for technical conditions for such a connection. In accordance with this document, you need to prepare a design for the cottage water supply system (connection point, pipe laying diagram, etc.) and coordinate it with the same service, after which you can make an insertion with shut-off valves into the pipeline and pull the pipes to the house.
6
Equipment and materials
Many people wonder how to make plumbing with their own hands. This is quite within the capabilities of anyone who has a desire to understand its structure.
The selection of equipment is carried out after determining the source. To connect to the central water supply, pipes and shut-off taps are sufficient. It is advisable to install a well at the connection point, but you can do without it. This is determined by the technical conditions issued by the water utility.
In the case of an autonomous option, the water supply scheme becomes significantly more complicated. Various equipment will be required for lifting and cleaning.
Pump equipment
A submersible or surface pump is used to supply water. Surface pumps are much cheaper than submersible pumps and can be purchased immediately with a hydraulic accumulator; this installation is called a pumping station. They are easy to maintain, and the well casing can be of small diameter, sufficient for the passage of a water intake hose with a filter tip.
Pumping stations are suitable for drawing water from surface sources. They are also installed if the pressure in the central water supply is very low and does not suit the consumer.
If the depth to the surface of the water in the well (well) is more than 5 meters, then the choice clearly remains with a submersible (deep) pump.
When choosing a pump, take into account:
- height of water rise (pressure) from the depth of the pump to the highest point of water collection in the house;
- required hourly flow rate (liter/min.), taking into account the number of users;
- pump diameter, taking into account the diameter of the well casing:
- pump type: vibration, vortex, borehole, centrifugal (the last 3 pumps are a type of centrifugal).
Vibration pumps are inexpensive, but they are not recommended for use in wells, due to the vibration created in the environment; they are only suitable for wells. The most reliable choice is a vortex pump. It has the lowest requirements for water purity.
Important: in each specific case, taking into account the type of well, water purity, and lifting depth, the right choice can only be made by a specialist with experience in operating pumps in a given area.
Hydraulic accumulator
For every electric motor, the hardest moment is starting up. Increased currents by 7 times, low torque, starting under load, all this significantly reduces its service life. To prevent the pump from starting frequently, due to a glass of water, a minute of hand washing, flushing the toilet, leaks in the network and other little things, a hydraulic accumulator must be installed.
And the larger the tank volume, the better for the pump. As well as for users, in case of a power outage
Its installation is mandatory, and its good condition is very important.
The volume of the hydraulic accumulator for water supply is determined by a special calculation. Simplified, you can select by pump output per minute, if the pump was selected taking into account the number of users. The result obtained is the minimum volume. If space allows for a larger tank, consider going a couple sizes larger. Each manufacturer has its own tank size. This row serves as an example, the volume is indicated in liters: 8, 10, 12, 18, 25, 30, 35, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100 and more.
It must be borne in mind that the useful volume of the tank, that is, the volume of water that it will give up when the power is turned off, is only 1/3 of its volume. This is provided that the air chamber has a free pressure of 0.2 bar lower than the pump shutdown pressure. Owners pump air above this value, therefore, the tank will give even less.
Storage tanks for water
Essentially, this is the same hydraulic accumulator, only much larger in size. If the hydraulic accumulator serves to protect the pump from frequent starts, then the accumulator tank also serves to create a reserve supply of water. But do not delude yourself, a tank of 500 liters will be able to release no more than 225 liters of useful water, with the correct pressure in the air chamber.
Therefore, it is easier and cheaper to install a simple tank of the required volume, but you will have to take water from it in a bucket. It can be installed in the attic, but the pressure will not be enough, and in winter you will need to take care to ensure that the water does not freeze.
Tip: by installing a system for automatically replenishing the storage tank, you can ensure uninterrupted water supply to your home.
Construction of an individual well
Scheme of constructing a well “on sand”
On the lands near Moscow, in order to reach the aquifer, wells with a depth of no more than 30 m (“on sand”) are often constructed. The work is carried out using a self-propelled unit. A steel or plastic casing pipe is placed into the drilled hole, the diameter of which is determined based on the need for water. For example, for a house with 4–6 water points and a water flow rate of 1.5–2 m³/h, a pipe with a diameter of 115–133 mm is sufficient.
A mesh or gravel filter (or a combination of both) is placed at the bottom of the pipe and a submersible pump is lowered into the well. The system is equipped with a hydraulic accumulator (expansion tank) and a pressure switch.
In the case of a large cottage with a daily water consumption of 3–4 m³/h, it is advisable to drill an artesian well with a depth of 40 m and equip it with a caisson with a pumping complex. A permit is required to drill such a well and a tax is charged for its use.
7
Two-pipe heating
A two-pipe heating system requires connecting each radiator to pipelines that are responsible for the flow of heated coolant and the removal of coolant. The main positive aspect of this design is the ability to adjust the temperature of individual heating elements.
Vertical scheme
When implementing such a project, several wiring options are provided:
- Lower two-pipe distribution - the main heating unit, which supplies coolant to the heating elements, is located in the basement or above the floor level of the lower floor. Riser pipes in a multi-storey building are diverted from the main pipe, the presence of which ensures the flow of working fluid to the radiators. Subsequently, the cooled liquid moves in the opposite direction through the outlet pipes.
- Upper two-pipe distribution - involves supplying coolant from the main heat generator directly to the attic of the house. Passing through the heating radiators, the heated working fluid returns from the upper distribution through the corresponding risers.
In order to remove air that accumulates during operation, it is recommended to supplement the two-pipe system with a special expansion tank. Installing the tank yourself allows you to ensure high pressure levels when moving coolant, which helps to increase heating efficiency.
Horizontal scheme
This option is the most common when installing two-pipe heating.
Functionality is ensured by forced circulation of coolant. There are the following options for implementing such a scheme:
- Dead end. It is characterized by relatively low consumption of materials when installing heating. The obvious negative point here is the impressive length of the system circuit, which is laid in a wide circle from the main heating unit. Compliance with such a requirement complicates the regulation of the temperature of individual heating elements.
- Along the way. Allows you to make correction of the coolant temperature in individual radiators more convenient due to the equal length of the circulation circuits. At the same time, the implementation of such a project requires the use of a significant number of pipes.
- Ray. It assumes radial distribution of the coolant, which is accompanied by maximum consumption of consumables. An obvious advantage is the possibility of hidden installation of the pipeline system in the thickness of concrete. This allows you to maintain the visual appeal of heated rooms.
Technology
How to properly assemble water supply and heating in a country house or in a house from the materials you have? Let's look at the installation of some components of these systems.
Connection with fitting
The welded connection of a polypropylene pipe with a fitting is performed as follows:
- A pipe with aluminum reinforcement is stripped of foil using a shaver or trimmer (depending on the location of the reinforcing layer). Stripping will prevent contact of the foil with water, its electrochemical corrosion and delamination of the pipe with the accompanying loss of strength;
Cleaning reinforcement with a shaver
- A nozzle of the appropriate size is attached to the heating element of the soldering iron;
- The soldering iron heats up to operating temperature (260 degrees);
- The socket of the fitting and the pipe are combined with the nozzle and melted by it;
- Then the parts are removed from the nozzle, combined with each other in a translational motion and fixed until the molten polymer sets.
Soldering connection steps
The duration of heating and setting of the polymer depends linearly on the diameter of the pipe
Connecting the radiator to the radiator plug
In modern aluminum radiators, an annular silicone gasket is responsible for sealing this connection. To prevent it from getting wrinkled, you can apply a little liquid soap or silicone grease to the cut of the heater manifold.
The photo shows a plug for an aluminum radiator with an o-ring gasket
Threaded connection
Sealing of threads is carried out:
- Sealant thread (Tangit Unilok and its analogues);
Tangit Unilok: convenient, fast, reliable
- Plumbing flax with silicone sealant. Silicone will prevent rotting of organic fiber upon contact with water and condensate, as well as its burning out when heated;
- Linen with any quick-drying paint. It will perform the same functions as the sealant.
Tip: To avoid getting your hands dirty, apply a little sealant or paint to the threads before winding the flax, and to the flax itself after it is wound. The winding will be evenly saturated as the thread is tightened.
Apply sealant, then wrap flax
Common connection options
If you decide to install a single-pipe system, you will have to choose between two types:
- simple circuit without regulation;
- "Leningradka" with the ability to turn off individual radiators.
In terms of control method, the first option is clearly inferior to the second; its only advantage is its budget cost.
Installation of a simple single-pipe system of horizontal or vertical type is simple and reliable, but temperature control in the network is impossible (+)
Installing the Leningradka will cost a little more, since in addition to the pipes you need to purchase a set of shut-off valves. Using bypasses and valves, you can reduce/increase the amount of coolant supplied to the radiator.
Diagram of the Leningradka device: using shut-off valves, you can temporarily turn off individual unnecessary radiators without changing the functional qualities of the entire system as a whole (+)
"Leningradka" is recognized by professional heating engineers as the best option for a single-pipe system for a 2-story residential building.
Complete set and installation of equipment
- circulation pump;
- gas or electric boiler (power depends on the size of the house, characteristics of the coolant, etc.);
- expansion tank;
- pipes 20 mm and 25 mm;
- adapters, gaskets, plugs;
- set of radiators;
- Mayevsky cranes.
Along with steel pipes, polymer or metal-plastic pipes can be used, with the latter being preferred.
In heating circuits with closed expansion tanks, air is bled using automatic bleeders equipped with shut-off valves and floats, or Mayevsky valves supplying each radiator
First, they find a suitable place for the boiler and install it, then assemble the pipeline leading to the radiators. Tees are fixed in places of radiator branches and bypasses. The pump is installed on the return line, next to the inlet to the boiler, and connected to the power supply.
The installation location of an open expansion tank is the highest point of the system; a closed one can be mounted in any convenient place, for example, in a boiler room. Radiators are suspended from the walls using special fasteners and equipped with plugs and taps.
How to safely lay communications in a wooden house?
Pipelines should be fixed to wooden walls and ceilings using fasteners designed to prevent their deformation and damage when the building settles. Compensation gaps left where pipes pass through the roof, walls or partitions serve the same purpose.
Electrical wiring in wooden houses can be laid in both open and hidden ways. The option of wiring over the walls (in plastic boxes or corrugated sleeves) is safer, but is not always acceptable from the point of view of interior design. In the second case, wires are allowed to be enclosed only in metal pipes and ducts, which are laid inside walls and ceilings.
5
Two-pipe heating system for a 2-story house
Truly comfortable living conditions can only be achieved by installing a two-pipe heating system. Its design allows you to regulate the temperature in individual rooms and save energy resources.
How does a two-way circuit work?
Unlike a single-pipe circuit, a two-pipe circuit consists of a pair of lines with different purposes: one of them supplies coolant, the second returns it back. The radiators are connected not in series order, but in parallel. One circuit, with heated coolant, extends from the riser to the radiators of both floors, the second is mounted to the boiler outlet and is also distributed to both floors.
Radiators are equipped with thermostatic valves that allow you to set a comfortable temperature. If desired, you can reduce the heating intensity partially or completely block the flow of water into the device.
Some devices are fundamentally embedded in the return line, for example, a membrane tank that regulates pressure, a circulation pump and a safety valve are traditionally installed in front of the boiler
In modern 2-story houses, two-pipe structures are used, since they are much more efficient than single-pipe ones:
- reduce pressure loss;
- do not require a powerful pump;
- keep the coolant temperature the same for each radiator;
- allow you to use many different thermal devices within one system (for example, radiators, convectors and “warm floors”);
- make it possible to repair and replace parts without compromising overall functionality.
The main disadvantage is the difficulty of self-installation - during assembly, consultation and supervision of professionals is required.
Successful solutions for installing a two-pipe system
There are many incarnations of various schemes, but when drawing up a project you should start from individual requirements.
The simplest diagram for arranging a heating system in a 2-story house. It is characterized by the following points: 2 circuits for heating and hot water production, liquid coolant, forced circulation (+)
A number of universal schemes are suitable for providing heat to houses of various sizes and number of floors.
Detailed diagram of two-pipe wiring for a one-story house with a fully equipped basement. The problem of thermal insulation of the floor in the basement was solved by connecting a water-based “warm floor” system
If you install additional equipment, such as a membrane tank, the capabilities of the heating system will expand.
A and B – two variants of the wiring device, upper and lower type. Additional equipment: expansion tank, Mayevsky taps, overhead line (+)
The following diagram combines the three most popular wiring diagrams.
Level 1 – dead-end wiring with parallel installation of both circuits; Level 2 – counter wiring, characterized by two-way radiator connection; 3 – collector wiring with improved balancing
All of the above schemes are suitable for heating a 2-story building.
Boiler room maintenance cost
Technical (service) maintenance of the boiler room
| Name of works | Volume | Price |
| Service contract for floor-standing boiler (gas, diesel) up to 60 kW | with 1st scheduled departure | from 14 000 ₽ |
| Service contract for floor-standing boiler (gas, diesel) from 60 to 170 kW | with 1st scheduled departure | from 20 000 ₽ |
| Service contract for floor-standing boiler (gas, diesel) up to 60 kW | with 2 scheduled trips | from 22 000 ₽ |
| Service contract for floor-standing boiler (gas, diesel) from 60 to 170 kW | with 2 scheduled trips | from 30 000 ₽ |
| Service contract for wall-mounted gas boiler | with 1st scheduled departure | from 10 000 ₽ |
| Service contract for wall-mounted gas boiler | with 2 scheduled trips | from 15 000 ₽ |
| The exact cost is calculated after check-out | engineer |
Attention. This cost is a preliminary estimate; these prices should only be used as approximate prices. The exact cost of the work is calculated after an engineer visits the work site, its complexity, and quantity.
Boiler room repair, diagnostics and prevention
| Name of works | Volume | Price |
| On-site inspection and diagnostics (without repair) | up to 50 km from MKAD | from 3,500 ₽ |
| On-site inspection and diagnostics (without repair) | from 50 to 100 km from MKAD | from 5,500 ₽ |
| Cleaning the burner (atmospheric) | power up to 60 kW | from 2,000 ₽ |
| Cleaning the burner (supercharged) | power up to 60 kW | from 3,500 ₽ |
| Cleaning the burner (atmospheric) | power from 60 to 170 kW | from 8,500 ₽ |
| Cleaning the boiler combustion chamber | power up to 60 kW | from 4,000 ₽ |
| Cleaning the boiler combustion chamber | power from 60 to 170 kW | from 6,000 ₽ |
| Checking and pumping up pressure in the expansion tank | without dismantling work | from 2,500 ₽ |
| Checking and pumping up pressure on the expansion tank | with dismantling and installation | from 4 500 ₽ |
| Refilling the heating system with a pump | system volume up to 200 liters | from 3 000 ₽ |
| Replacement of heating element, pump, heat exchanger, with coolant drain | for a unit | from 3 000 ₽ |
| Conversion of a gas boiler to liquefied gas | for a unit | from 3 000 ₽ |
| Burner settings | gas / diesel | from 2 500 ₽ |
| The exact cost is calculated after check-out | engineer |
Attention. This cost is a preliminary estimate; these prices should only be used as approximate prices. The exact cost of the work is calculated after an engineer visits the work site, its complexity, and quantity.
Possible problems
What problems may you encounter:
With instantaneous water heater
Each chosen method of providing a home with hot water has its own weaknesses.
Electric flow heaters often fail due to burnout of heating elements, which become covered with scale and cannot withstand the load.
The same applies to the heat exchanger - poor water quality clogs the coil or honeycomb, which leads to excess pressure, and possibly even rupture and leakage of the equipment.
Therefore, maintenance consists of organizing proper filtration of the hot water supply, replacing heating elements and ensuring correct connection from an electrical point of view.
High-power electrical appliances must be equipped with individual electrical protective equipment. As for geysers and boilers, they need periodic cleaning of excess combustion products.
With storage water heater
The main problems remain the same - the performance of the heating elements, the quality of the incoming water and electrical safety.
It is electrical safety that many users neglect, not realizing that this is not only protection against electric shock, but protection of the most expensive equipment.
All models of storage heating tanks are made of metal, which means that without proper grounding, they are subject to accelerated corrosion. If the tank leaks, then in most cases such equipment cannot be repaired
This is why it is so important to check the ground circuit
As for heating elements, in these models they are even more susceptible to burnout than in flow-through ones.
Everything you need to know about hot water is presented in this section of the site.
Selection of heating radiators
It is impossible to give recommendations for all occasions on the choice of radiators. You need to choose the type of radiator by assessing the capabilities of your budget, the volume of the room and its area, as well as the size and number of windows, and the type of boiler. An important point when choosing radiators is the furnishings and design of the room. Therefore, we will consider the parameters of radiators, which are selected individually, taking into account the specifics of the situation.
The types of radiators are as follows:
- Aluminum . These are usually cast structures, characterized by low weight, low cost and fast heating. The disadvantages include the not very original appearance and the rapid decrease in water temperature.
- Bimetallic . Such radiators are more resistant to hard water, are intended for a centralized system, although they can be used for a private home, and have a good design. The cost of bimetallic radiators is quite high. Additional sections can be added or removed.
- Steel . These are heat devices with great efficiency, beautiful to look at, have a long service life, and cost less than the options discussed above. They heat up quickly, but also quickly reduce their temperature. The main advantage is the small volume of water for heating, which saves electricity and gas.
- Cast iron . The main advantages are corrosion resistance, slow temperature decline, beautiful design and long service life. The negative factor was the heavy weight and cost.
Which ones to choose?
Since cast iron, aluminum and bimetallic radiators contain a large volume of water, they are not suitable for an electric boiler. In this case, it is better to purchase steel models. For gas boilers you can install any radiators. If you purchase a structure that quickly reduces the temperature, then the house must be well insulated. Otherwise, the consumption of electricity or gas will be high.
Operating principle of an autonomous water supply system
The water supply system is one of the most important elements in home improvement. The essence of its work is the automated supply of the required volume of water, for which the user now only needs to start the equipment and then simply periodically monitor it.
An autonomous network independent of the central water supply must be properly designed and calculated in order for the house to be fully provided with water according to the needs of the owners. The system must be organized so that water flows freely to all water intake points.
For normal operation, the water supply system is equipped with devices and technical devices that provide automatic or partially automatic operation.
To automate the process, a hydraulic accumulator is used. It is used as a buffer tank for storing water and as a device for maintaining stable pressure.
The membrane tank has two compartments - for air and water, they are separated by a rubber membrane. When the container is filled with water, the air chamber is compressed more and more, causing the pressure to increase.
Autonomous water supply systems consist of internal and external parts. Includes pipeline branches of the same name, laid from the source of water intake to water collection points, fittings, plumbing, pump, storage tank or hydraulic accumulator
Reacting to an increase in pressure, the electric relay turns off the pump. As soon as one of the owners opens the tap, the pressure in the system begins to drop. The relay again reacts to a decrease in pressure and turns on the pump unit to replenish the consumed water.
The use of a hydraulic accumulator in a water supply system allows not only to automate the process of water intake and ensure its supply. The service life of pumping equipment is significantly extended due to the reduction of on/off cycles.
Water supply is the life support of a home. It depends on how comfortable a person will live in his home.
To select the correct system parameters, you must:
- Formulate requirements for the intensity and regularity of water supply. It is possible that in a small country house you can get by with a system with a regular storage tank and a minimum of plumbing fixtures.
- Determine possible sources, feasibility and cost of their construction, water quality.
- Select equipment and calculate options for laying utility networks.
A well-designed system requires professional installation and the use of high-quality components.
When should utility networks be laid?
The best option is when, in parallel with the architectural design, an engineering design of the building is also developed, which contains, in particular, diagrams for installing equipment and laying highways. Then, at the stage of constructing the frame of the house, communications will be installed without problems. If you are installing them in an already built house, you will have to make holes and channels in ready-made structures - foundations, floors, walls, which will result in additional labor and financial costs.
Engineering design of the first floor of the house
2
Advantages and disadvantages of water supply options
Central water supply
Advantages:
- Purified water complies with SanPiN
- Quality control
- No pump required
Flaws:
- High price
- Possible low pressure
Artesian well
Advantages:
- Low cost of water lifting
- Adjustable pressure
- No chemical contamination, no disinfection required
Flaws:
- Filtering required
- May require removal of metal salts
- Construction costs
Surface well, well
Advantages:
- Costs are lower than for an artesian well
- Adjustable pressure
Flaws:
- Filtering required
- Cleaning required
- Primary water is contaminated
- Possible presence of harmful chemicals
- Disinfection may be required
Surface reservoir (river, lake, pond), rainwater
Advantages:
Minimal costs if a body of water is nearby
Flaws:
- Water, highly polluted, with the presence of chemicals used in agriculture
- Use without filtration, purification and disinfection is hazardous to health.
- High costs for water treatment
The comparison shows in what order preference should be given to water supply options.
How to organize hot water through a heat exchanger?
To organize a hot water supply system, several types of heat exchange devices are used, but their essence boils down to one thing - to create a circuit that will transfer heat from a heating source (for example, the same furnace or boiler) to the water supply system. Therefore, it will be impossible to clearly describe the installation instructions; everything depends only on the selected type of device.
But the general approach for installing a heat exchanger will be as follows:
- Install the heat exchanger near or inside the selected heat source. This could be a boiler, a heating stove, a chimney, or a heating radiator.
- A cut is made on the cold water inlet pipe and a tee is installed. In the case of a DHW heat exchanger, only metal pipes can be used!
- Connect one of the pipes to the heat exchanger, and remove the second pipe from its outlet, which will become the source of hot water distribution.
There is a fundamental difference between cast iron, copper, steel and stainless steel heat exchangers that is worth considering.