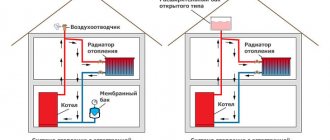
Many country property owners complain about pressure drops in autonomous heating systems in a private home. This problem may be intermittent and occur without any reason. To eliminate a malfunction, it must be identified, and only after that the “healing of the system” begins. Good constant pressure is observed in a properly designed circuit with a circulation pump and a properly located sealed tank.
All elements of the heating system are located according to the following diagram. The boiler is installed first. Pipelines and radiators depart from this unit, then an expansion tank and a circulation pump are installed. Please note that the membrane tank can be installed at any point in the system. The optimal location for installing the pump is considered to be the pipe gap between the boiler and the tank.
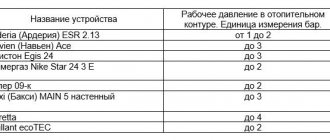
Important! Not everyone knows what pressure should be in a closed heating system. Normal values are considered to be 1.5…2 atmospheres.
Leaks inside the boiler
The second type of leaks is leaks inside the boiler. There are units inside boilers that can leak water. Such problems, as a rule, can always be noticed. Components where leakage may occur include:
- Auto air valve;
- Explosion valve;
- Three way valve;
- Expansion tank.
The first component where a leak may occur is the auto-air valve. It sits on top of the pump and has a small cap from which drops of water can escape along with the air that is formed in the heating system. These drops can dry out, however this happens in rare cases, usually they start to come out of the boiler.
The problem with the auto air valve is very common. This happens if the auto air valve is not inspected, it is not cleaned or changed in a timely manner.
The second leakage point is the explosion valve. Some people pipe the blast valves through the wall to the outside to avoid flooding the kitchen or other room under the boiler depending on where the boiler is placed.
This is usually recommended by the workers who installed the boiler. They recommend running the pipe down the drain or through a wall to the street. It often happens that pressure escapes through this explosion valve. The explosion valve was once triggered, a grain of sand or something else got in there, and now water is slowly oozing from it.
To check the explosion valve for leaks, you need to grab the tube that comes from it with your hand. If the tube is warm or hot within a meter or so, then the problem is most likely in the explosion valve. In this case, you should dismantle the tube and check visually whether water is dripping or not.
The third possible hydraulic leakage unit is a three-way valve. This valve switches between heating and hot water supply. It often happens that similar nodes that are responsible for switching fail. This indicates that the servo is broken. In this case, water will flow out and the pressure will drop.
The fourth leakage point may be the expansion tank. There is no air in this tank. It has a membrane, thanks to which air is pumped in one direction, and pressure from the heating system flows into the other.
If the expansion tank fails, then there is no compensation in it - the water is pressed completely against the expansion tank. When the temperature at the boiler drops, the heating system cools down, and the pressure, which was, for example, 1.5 Bar, drops to almost zero or to the value at which the boiler can no longer turn on. Typically this value is 0.5 Bar.
These are all the main reasons why pressure in the heating system may drop. Of course, there are other reasons that can lead to this problem.
To identify the cause of the pressure drop in the heating system as soon as possible, you should contact a specialist. Thanks to their qualifications, experience and knowledge in the field of design and proper installation of heating systems, they will be able to quickly find the cause and eliminate the malfunction.
Location of expansion tanks
There are several options for expansion tanks depending on their location in the system.
- Built-in closed - all modern boiler models are already equipped with expansion tanks. Their volume directly depends on the size and performance of the boiler. The greater the expected load on the tank, the larger the displacement of its expander.
- External open - usually used under conditions of natural gravitational circulation of fluid in the system. It is an open container installed at the top point. The liquid displaced from the pipes rises up along with the air, and goes back into the system under the influence of natural atmospheric pressure and gravitational force.
Optimal value for a private house or cottage
Any boiler operates at certain system settings, in particular, it is necessary to correctly calculate the water pressure. This value is influenced by the number of floors of the building, the type of system, the number of radiators and the total length of the pipes. Usually for a private house the pressure level is 1.5-2 atm, but for a five-story apartment building this value is 2-4 atm, and for a ten-story building it is 5-7 atm. For higher buildings, the pressure level is 7-10 atm, the maximum value is achieved in heating mains, here it is 12 atm.
For radiators that operate at different heights and at quite a decent distance from the boiler, constant pressure adjustment is required. In this case, special regulators are used to reduce it, and pumps to increase it. But the regulator must always be in good working order, otherwise sharp fluctuations and drops in coolant temperature will be observed in certain areas. The system must be adjusted so that the shut-off valves are never completely closed.
Air lock as a cause of pressure increase in closed systems
When operating a closed system, it is not uncommon for the pressure to increase, which may be accompanied by a decrease in the overall coolant temperature and blocking of the boiler. All this leads to imbalance in the operation of the circuit and failure of its individual elements.
Why does the pressure increase in the system or is there a sharp increase in it? Typically, in closed heating circuits using gas equipment or other types of boilers, such changes occur due to airing. Air locks are a fairly common cause of pressure drop. Typically, the presence of such problems is determined in the following cases:
- equipment breakdown;
- incorrect system startup;
- automation malfunctions;
- presence of cracks in the boiler heat exchanger.
There are several reasons for such system failures:
- the contour is filled from the top point;
- upon startup, there is a very rapid filling of water in the system;
- Mayevsky valves or air vents are faulty;
- the heating radiators were not vented after their repair;
- The impeller of the circulation pump is loose, that is, air pumping occurs with disturbances.
Relieving pressure in the heating system and filling it with water from the bottom with the taps open to bleed air will help solve the problem. The filling itself should be slow, the work ends when water begins to flow from the top point of the circuit. In addition, after installing the heating system and before starting its operation, it is recommended to treat the air drain valves with ordinary soap foam. This allows you to detect air leaks and prevent the formation of air jams in time.
Water heating system design
The method of heating a house using a liquid coolant (water, or water-based antifreeze) today is one of the most thorough and reliable schemes: water is heated in a boiler, transferred to heating radiators, transfers thermal energy to the air space in the house and completes the cycle by returning into the boiler.
The owner of a private house most often uses natural gas to power the boiler, but can also use wood, coal or kerosene. The design of the heating circuit consists of key components - boiler, pipes, heating radiators - and auxiliary components - expansion tank, hydraulic pump, thermostats, valves.
Low water pressure in the boiler what to do
If no leaks are found in the radiators, then the reason why the pressure is lost lies in the boiler. Why does this happen and how to increase (gain, pump up, increase) blood pressure? If you frequently pump up water and the boiler does not hold pressure, there is a possibility that microcracks have formed in the heat exchanger. When the boiler heats up, the cracks increase and leakage occurs. The intervention of a specialist is urgently required, or you can eliminate the fistula yourself.
Soldering the heat exchanger The reason for the appearance of microcracks is wear of the heat exchanger, frequent washing with reagents, poor quality of the metal from which it is made, water hammer with a sharp increase in pressure in the line. They usually happen after accidents in water mains. Places where there are microcracks can be identified by the scale layer. If removing the heat exchanger is easy, you can try to solder them. Bithermal heat exchangers are almost impossible to repair due to their design features; they will have to be replaced. The pressure in the boiler does not rise (gain) when the feed tap is flowing. If the pressure in the line is higher than the pressure in the boiler, the liquid through the make-up valve increases the pressure in the boiler to a critical point, and a discharge occurs through the safety valve. As a result of this, the pressure decreases, the water from the heating system presses the liquid in the water supply and heating system. Close the tap, check the tightness of its connection or replace it if it is faulty. The pressure turns off (falls) to 0 if the three-way valve malfunctions. Large pieces of scale or rust may get into the valve and obstruct flow; clean the valve. A problem with the expansion tank can cause pressure changes. When heated, the volume of water in the system increases, this excess enters the expansion tank. There is a rubber membrane inside the tank. The space between the outer wall and the tank membrane is filled with gas. Excess liquid fills the membrane and the pressure in the heating system is released. Gas equalizes excess pressure. After the temperature drops, the liquid enters the system again. This does not happen when there is a gas leak. The reason for the expansion tank not working properly is a worn nipple that needs to be replaced. Worse, when the membrane breaks, you will have to change the tank itself.
Sectional view of the expansion tank. To pump air into the expansion tank, you can use a car pump. How to add (apply, pump up) pressure in the expansion tank?
Best answers
amateur:
You must have a vent, an air vent. Put a hose on it so as not to get it wet, and quietly open the tap and try to relieve the pressure. (this is my opinion, but it’s better to call a specialist.)
Boss Heat:
Anywhere in the heating system where there is a drain valve (Mayevsky tap, radiator drain, etc.), open and drain into a jar or bucket. It is most convenient to turn on the relief valve on a wall-mounted boiler.
Eliseikin:
Look for a drain valve... there must be one!
alexm66:
The boiler has a drain valve (usually from the bottom). It usually opens with a key - there is no flywheel on it. The instructions for the boiler indicate its location. In this case, it is advisable to stop the boiler.
So I say:
Before releasing the pressure, check that the valve on the expansion tank is open. If it is closed, open it, the pressure should drop. If it was open, bleed it from the battery in any convenient place. Under no circumstances should you bleed off the pressure from the boiler safety group yourself - if a speck gets under the valve seat, it can be very difficult to wash it off - this is how the valve drips.
Victor:
Install an expansion tank and forget about pressure surges.
L@rchik:
Bleed the air from the heating radiators, the pressure will immediately drop. Do not interfere with a well-functioning mechanism (boiler).
basic information
A modern house is a complex communications system; automation of units makes it possible to reduce interference in their operation to a minimum. Despite this, owners of heating systems face a number of problems. Experts identify five main reasons for pressure drop in a closed heating system: failure of the radiator; installation errors; discrepancy between the boiler power and the “native” pipeline; depressurization and leakage; interruptions/jumps in gas supply.
Exercising control
According to modern standards, models of heating devices are equipped with control sensors. Their task is to monitor the pressure level and, in case of surges, temporarily or completely block the operation of the unit and system. By displaying the error code on the boiler information display, the user can read the information in the instructions or find the answer on the manufacturer’s official website. The most well-known models of gas boilers support operation within 1.5–2 atm. Units of the Bosch, Ariston, Baxi brands, and a Navien boiler - all of them are produced with a forced fluid movement system and a pump, the pressure drop is controlled by a program.
Principle of operation
How does pressure work in gas boilers? Let us consider in detail the process of operation of the equipment. Turning on the unit starts the operation of the sensors, and from the first seconds the coolant temperature begins to be recorded. The outdoor thermostat, if provided with the model, is automatically activated, and you see how the arrow lights up and heating occurs. As the temperature increases, the pressure increases, the water heats up and expands. A safety valve is periodically turned on, which discharges excess into the sewer. Operation may malfunction if too much water goes down the drain - this leads to a drop in pressure. The boiler automatically turns off when the temperature set by the program is reached. What happens inside the expansion tank? It consists of two parts separated by a diaphragm. Excess liquid accumulates in one part, and nitrogen in the second. The coolant fills the tank as much as the difference between the nitrogen values and the system value is large. Having reached the temperature set by the program, nitrogen pushes water out of the tank by deforming the membrane - heating stops.
The main reasons for increased pressure
Most often, the reason why the pressure in the heating circuit increases in a closed heating system is equipment failure due to which the indicators either jump up or drop sharply down. But apart from this, the reasons also include the following:
- A sharp increase in coolant pressure due to blocked shut-off valves. An increase in pressure is observed in the system, after which the boiler is blocked and the system stops. To fix the problem, you need to check the fittings for leaks, open valves and taps to relieve pressure.
- The reason for the increase in pressure in the heating system may be contamination of the dirt filter. Rust particles, debris, sand and slag accumulate on the surface of such a filter. As a result, the pressure increases greatly in the area between the boiler and the filter. To eliminate the cause, it is necessary to regularly clean the filters, at least 3-4 times a year. Also, a good solution would be to replace conventional mud filters with magnetic or flush filters. They cost more, but their maintenance is much easier.
- The operating pressure of the system may increase due to a malfunction of the heating boiler automation. This is a manufacturing defect, incorrect system settings, or a breakdown of the control board. All these problems require boiler repair, which can only be carried out by a master.
- There are leaks in the make-up tap, that is, water will constantly penetrate into the general circuit, which causes a pressure surge. The repair is usually quite simple, you just need to replace the rubber gaskets. But if there is a defect, the crane or equipment should be completely replaced.
Why does the pressure drop in a double-circuit or conventional boiler? This situation most often occurs when the expansion tank breaks down or the air valve leaks. To fix the problem, you may need to repair or completely replace the tank.