Design work on the creation of heating systems requires a clear understanding of the dimensions of heating elements, including radiators. Considering the significant diversity of the latter, such systematization is a truly important task. There are three large groups of radiator sizes:
- standard for the former USSR;
- low radiators;
- tall and non-standard.
Based on the type of materials, radiators are classified as follows:
- aluminum;
- cast iron;
- steel;
- bimetal
Non-standard radiator sizes
In addition to standard heating devices, radiators of other sizes are widely available on the market.
They are intended for use in atypical buildings or to give a room a special style. The following types and dimensions of radiators are distinguished:
Low or small heating radiators have a high heat transfer per unit surface area; they can be placed under low window sills or in buildings with stained glass. These include all heating devices with a center distance of less than 400 mm. Based on the material used, they can be either cast iron, aluminum or bimetallic.
Low horizontal cast iron heating radiators predominantly have section dimensions (W x D x H) of 93 x 140 x 388 mm, their heat output is 106 W at an operating pressure of 9 atm. Foreign manufacturers also produce more compact models with center distances of 200 and 350 mm. Bimetallic compact heating devices are available with a wide range of center distances, the width of such a section starts from 40 mm, the height is in the range of 150-450 mm. The depth compensates for the compactness of the remaining dimensions and is 180 mm. Thermal power varies from 80 to 140 watts at an operating pressure of 25-35 atmospheres.
Aluminum radiators have dimensions similar to bimetallic ones with connection distances from 150 to 400 mm in 500 mm increments, thermal power ranges from 50 to 160 W.
The normal operating pressure for them is 16 atmospheres, which can be increased to 24 atmospheres during pressure testing. It should be noted that such narrow horizontal bimetallic and aluminum heating radiators do not have water flow through the middle sections; they are heated only due to thermal conductivity from the collectors, while circulation is ensured by the outer flow section.
There are tall and narrow heating radiators, which are used in cases where there is a need for high heat transfer when, for various reasons, it is impossible to occupy a significant length of the wall. Cast iron high heating radiators are found only among products of foreign manufacturers; their section width is 76 mm. with a possible height of 661-954 mm, the depth of such devices reaches 203 mm. The working pressure is 10 atmospheres, and for the largest ones it cannot exceed 6 atmospheres. heat transfer, depending on the size, ranges from 270 to 433 watts.
Narrow bimetallic heating radiators are mainly designer designs with non-standard dimensions and are not intended for central heating systems; they are used in private houses with individual heating. As a rule, these are not sectional, but monolithic structures. If we take a section, then an example of its size could be (W x D x H) 80 x 95 x 880 mm. at a working pressure of 4 atmospheres. When crimping, it is not recommended to exceed this figure more than 6 atm.
For those who want to make the most efficient use of room space, flat heating radiators with a shallower depth are available on the market. Their choice is not as large as that of the above heating devices. Sold thin heating radiators can only be made of aluminum. Their depth starts from 52 mm with thermal power from 105 to 161 W. Flat radiators also include panel radiators, the depth of which is 60 mm.
Initial data for calculations
The calculation of the thermal power of the batteries is carried out for each room separately, depending on the number of external walls, windows and the presence of an entrance door from the street. To correctly calculate the heat transfer rates of heating radiators, answer 3 questions:
- How much heat is needed to heat a living room?
- What air temperature is planned to be maintained in a particular room.
- Average water temperature in the heating system of an apartment or private house.
Note. If a single-pipe wiring is installed in the cottage, you will have to make allowances for cooling of the coolant - add sections to the last radiators.
The answer to the first question - how to calculate the required amount of thermal energy in various ways - is given in a separate manual - calculating the load on the heating system. We present 2 simplified calculation methods: by area and volume of the room.
A common way is to measure the heated area and allocate 100 W of heat per square meter, otherwise - 1 kW per 10 m². We propose to clarify the methodology - take into account the number of light openings and external walls:
- for rooms with 1 window or entrance door and one external wall, leave 100 W of heat per square meter;
- corner room (2 external fences) with 1 window opening - count 120 W/m²;
- the same, 2 light openings – 130 W/m².
Important condition. The calculation gives more or less correct results for ceiling heights of up to 3 m; the building was built in the middle temperate climate. For the northern regions, an increasing coefficient of 1.5...2.0 is used, for the southern regions - a decreasing coefficient of 0.7-0.8.
Distribution of heat losses over the area of a one-story house
When the ceiling height is more than 3 meters (for example, a corridor with stairs in a two-story house), it is more correct to calculate heat consumption by cubic capacity:
- room with 1 window (external door) and a single external wall – 35 W/m³;
- the room is surrounded by other rooms, has no windows, or is located on the sunny side - 35 W/m³;
- corner room with 1 window opening – 40 W/m³;
- the same, with two windows – 45 W/m³.
The second question is easier to answer: a comfortable temperature for living is in the range of 20…23 °C. Heating the air more strongly is uneconomical; heating the air less is cold. The average value for calculations is plus 22 degrees.
The optimal operating mode of the boiler involves heating the coolant to 60-70 °C. The exception is warm or too cold days, when the water temperature has to be reduced or, conversely, increased. The number of such days is small, so the average design temperature of the system is assumed to be +65 °C.
In rooms with high ceilings we calculate heat consumption by volume
Dimensions of standard radiators
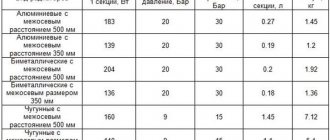
Depending on the material from which the radiators are made, their dimensions also differ. The most common standard sizes of heating devices are considered as basic, refer to the center distance of 500 mm and are:
- The standard dimensions of cast iron heating radiators according to the specification are for one section (width x depth x height) 93 x 140 x 588 mm. In various modifications, the depth can also be 85, 90 and 110 mm, and the width – 108 mm. For exotic cast iron radiators in “retro” style, the standard sizes are even more varied. It is not difficult to determine the dimensions of the heating device assembled from them - 10 mm of the thickness of the paronite gasket is added to each section. Also, if the radiator is installed in a niche or in cramped conditions, you should take into account the length of the mandatory installed flush valve. The heat output of one section is about 160 W. with a difference in room air temperature and coolant temperature of 70 C, the maximum permissible operating pressure in the system is 9 atmospheres.
- The standard dimensions of bimetallic heating radiators (width x depth x height), due to the wide range and significant number of manufacturers, are as follows: 80-82 x 75-100 x 550-580 mm. The average heat flow from a section of such a device is about 160-200 W; due to the presence of a steel core in the design, the operating pressure in the system can reach 25-30 atm. and during pressure testing, pressure testing up to 35-50 atmospheres is possible.
- Aluminum horizontal heating radiators, even with the same dimensions, can differ significantly in technical parameters. The standard dimensions of their sections are (W x D x H) 80 x 80-100 x 575-585 mm. The heat transfer of a section of this type of heating device depends on the fins and the depth of the structure, being in the range of 180-200 watts at a maximum operating pressure of the system of 16 atmospheres. Such radiators are pressurized under pressure up to 24 atm.
ATTENTION! When installing a heating system, an important condition is to use pipes of equal strength to the radiators, otherwise emergency situations may be created.
Low
Radiators with small center distances have two nice features:
- They can be placed under a low window sill.
- They have the maximum heat transfer per unit surface area. The higher the radiator, the warmer the air is in contact with its upper part and the less heat flow from the surface of this part of the fin.
What options can we find here?
Cast iron
Let's turn again to MS radiators made in Belarus.
- The MS-140M-300-0.9 radiator has a section length of the same 93 millimeters with a height of 388 mm and a depth of 140.
- The heat flow, of course, decreased with the change in dimensions and is now equal to 106 watts per section.
- The working pressure has not changed: the same 9 kgf/cm2.
Aluminum
The spread of center distances between domestic and imported low radiators is more than large. Sizes available are 150, 200, 250, 300, 350 and 400 millimeters.
What does this mean in terms of the characteristics we are interested in?
- The section length starts from 40 millimeters, which makes the battery unusually compact. Height - from 200, while depth in many models compensates for the lack of the other two sizes and reaches 180 mm.
- Thermal power varies from a ridiculous 50 to a quite respectable 160 watts per section. The defining moment is the area of the section fins.
- The change in dimensions had little effect on the working pressure: most of the radiators are designed for the same 16 atmospheres with tests at 24.
Bimetallic
How will the size of heating radiators change if a steel core is placed inside the aluminum fins? But nothing. We can see absolutely all standard sizes characteristic of aluminum structures among bimetallic heating devices.
Thermal power also remains within the same limits: you can find low radiators with heat output of both 80 and 140 watts per section.
The working pressure, of course, remains high: after all, the material is different. The same 25-35 atmospheres are typical.
There are two interesting nuances:
- Among bimetallic radiators, you can find radiators not with solid steel cores, but with steel tubes inserted between aluminum collectors. In this case, the manufacturer, as a rule, is careful with the declared parameters, and for a bimetallic radiator you can see the declared 16 and even 12 atmospheres.
- Low radiators made of aluminum and bimetal often do not have vertical channels and, when connected to the side, are heated by the collectors only due to the thermal conductivity of aluminum. Circulation is ensured by the last section: it is made flow-through.
We advise you to study - What is better to use metal tiles or ondulin as a roof for a private house
Heating devices of single-pipe systems
An important feature of the horizontal “Leningrad” is the gradual decrease in temperature in the main line due to the admixture of coolant cooled by the batteries. If 1 ring line serves more than 5 devices, the difference at the beginning and end of the distribution pipe can reach 15 °C. The result is that the latest radiators emit less heat.
Single-pipe closed circuit - all heaters are connected to 1 pipe
To ensure that long-distance batteries transfer the required amount of energy to the room, make the following adjustments when calculating heating power:
- Select the first 4 radiators according to the instructions above.
- Increase the power of the 5th device by 10%.
- Add another 10 percent to the calculated heat transfer of each subsequent battery.
Classification of heating devices
Depending on the material used for manufacturing, heating radiators can be:
- steel;
- aluminum;
- bimetallic;
- cast iron
Each of these types of radiators has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is necessary to study their technical characteristics in more detail.
Cast iron batteries - time-tested heating devices
The main advantages of these devices are high inertness and fairly good heat transfer. Cast iron batteries take a long time to heat up and are also able to release the accumulated heat for a long time. The heat output of cast iron radiators is 80-160 W per section.
These devices have many disadvantages, among which the most serious are:
- a large difference between the flow area of the risers and batteries, as a result of which the coolant moves slowly through the radiators, which leads to their rapid contamination;
- low resistance to water hammer, operating pressure 9 kg/cm2;
- heavy weight;
- requirement for regular care.
Aluminum radiators
Batteries made of aluminum alloys have a lot of advantages. They are attractive, do not require regular maintenance, and are not brittle, which makes them better resistant to water hammer than their cast iron counterparts. Working pressure varies depending on the model and can be from 12 to 16 kg/cm2. Another undeniable advantage of aluminum batteries is the flow area, which is less than or equal to the internal diameter of the risers. Thanks to this, the coolant moves inside the sections at high speed, which makes it almost impossible for dirt to accumulate inside the device.
Many people believe that a small cross-section of radiators leads to low heat transfer. This statement is incorrect, since the heat transfer of aluminum is higher than, for example, that of cast iron, and the small cross-section in the batteries is more than compensated by the area of the radiator fins. According to the table below, the heat output of aluminum radiators depends on the model and can range from 138 to 210 W.
But, despite all the advantages, most experts do not recommend them for installation in apartments, since aluminum batteries may not withstand sudden pressure surges when testing central heating. Another disadvantage of aluminum batteries is the rapid destruction of the material when other metals are used in conjunction with it. For example, connecting to radiator risers through brass or copper pipes can lead to oxidation of their inner surface.
Bimetallic heating devices
These batteries do not have the disadvantages of their cast iron and aluminum “competitors”. A design feature of such radiators is the presence of a steel core in the aluminum fins of the radiator. As a result of this “fusion”, the device can withstand colossal pressure of 16-100 kg/cm2.
The flow area of the device is, as a rule, smaller than that of risers, so bimetallic radiators are practically not contaminated.
Despite its many advantages, this product has a significant drawback - its high cost.
Steel radiators
Steel radiators are perfect for heating rooms powered by an autonomous heating system. However, such radiators are not the best choice for central heating as they may not withstand the pressure. They are quite light and resistant to corrosion, with high inertia and good heat transfer rates. Their flow area is most often smaller than that of standard risers, so they rarely become clogged.
Among the disadvantages are the rather low operating pressure of 6-8 kg/cm2 and resistance to water hammer, up to 13 kg/cm2. The heat transfer rate for steel batteries is 150 W per section.
The table shows the average heat transfer and operating pressure for heating radiators.
Euro-cast iron: modern cast iron batteries
Cast iron is a material with many excellent performance characteristics, so radiator manufacturers did not completely abandon its use. Let's just say that the internal components of the batteries remained the same, but the design has changed to suit the times.
A modern cast iron radiator also consists of sections; they are connected to each other by sealing gaskets. But what the design will be depends on the manufacturer. Today's models can be very original; beautiful cast iron heating radiators in a retro style are especially popular.
Advantages of Euro-cast iron:
- The material is durable, it will last at least 50 years;
- The fins of the batteries are vertical, which increases their heat transfer;
- Modern models also have high temperature resistance;
- The structures are very durable, withstand pressure up to 18 atmospheres;
- The batteries are coated with a special compound that prevents corrosion;
- Radiators can work with any type of coolant - both water and antifreeze;
- The hydraulic resistance of such a battery is small, which means that the circulation pump does not need to be used at all.
Modern cast iron batteries look great in an interior made in modern or high-tech style
Finally, the price of the battery is very attractive. They are inexpensive, and if you consider the life of the battery and the fact that it rarely needs repairs, the purchase is quite economical. And an attractive appearance can be another compliment to the interior.
Influence of aluminum radiator size
Aluminum batteries are made in a wide range of sizes. Length has a primary influence on power.
Accordingly, to achieve the required heating it is necessary to increase the number of sections. The total length of the battery depends on the calculations.
Depth and height also change the indicators because they affect volume. Unlike length, these two values are variable, which is why there are many different models.
The next indicator is the center distance. It is responsible for the heating rate of the radiators, since it means the gap between the supply and return pipes.
The performance is also affected by the manufacturing method:
Metal casting increases the strength and durability of the device. In this case, each section is a single unit from which the device is assembled. This is done in a certain sequence: first the upper parts are welded, then the lower ones. The extrusion method involves pressing heated aluminum through a lattice plate of metal. Thanks to this, a profile of a given shape is obtained, which is divided into parts and assembled into a radiator
Attention! Such heating devices are rarely found and are usually made to order. This is due to the impossibility of making changes to the design after production has ended.
Center distance
The indicator represents the gap between the axes of the radiator. They are located symmetrically, one on top, the other on the bottom. They are adjacent to pipes through which they are connected to the heating circuit.
Photo 1. Aluminum radiator model 350/80, center distance 350 mm, China.
Depending on the manufacturer, the value ranges from 150-2000 mm. For most devices, this figure is set to 500. This is due to heating systems in apartment buildings: in old buildings, calculations were made for cast iron radiators. When replacing batteries, the cost of digesting the pipeline is undesirable.
Reference! Most models have a number in their name indicating the center distance.
Depth
Depends on the material from which the battery is made. The minimum value is 52 mm. It is enough to create high power in small sections. The maximum value is 180 mm. It is quite rare and requires strength. There are models with greater depth, but their use is impractical due to insufficient heating.
Determining the volume of a section
To calculate, you need to know the value described above, as well as the length and height. The first value, visually, is width.
It is 80 or 88 mm, which is indicated in the passport.
The second is variable. Typically, the vertical component of the section dimensions is 570 mm.
To find the volume, just multiply the three indicators.
Terminology
The main selection parameters are the width and height of the radiator.
Documentation discussing the dimensions of heating radiators often talks about the center-to-center distance. This parameter indicates the length of the gap from the center point of one connecting hole to a similar place in the other. Sometimes this value is called the center-to-center or inter-nipple distance. If the pipelines supplying the radiator are in working condition and there are no plans to change them, the new heater purchased should have the same center-to-center indicator as the old one, so that changes to the connections do not have to be made. Sometimes the names of models - both Russian and foreign - contain three-digit numbers. They indicate this parameter in millimeters (for example, Modern 500).
Linear dimensions include:
- installation height of the radiator - it must be selected so as to ensure the required distances to the window sill and floor;
- depth;
- width - for models with a sectional design, it, like the previous parameter, also refers to the dimensions of the elements, but if the depth of the radiator and its individual sections is the same, to calculate the total width you need to multiply the indicator of an individual unit by their number and add approximately 1-2 cm, attributable to sealing gaskets.
Knowing the linear parameters of the radiator, you can purchase a protective screen for it. When installing floor-mounted flat options, dimensions are important for selecting suitable components of the heating system.
How to choose the correct size of radiator sections
Determining the dimensions of the sections and their number is the most important step in creating a classic heating system.
With standard arrangement
The power they can develop depends on the size of the batteries and the material.
The length is almost always the same and is 80 mm. First determine the height. To do this, choose the installation location, which determines the available space.
And design also plays a big role. Using these parameters, the vertical component is determined. Usually decide between 350 and 500 millimeters.
Depending on the characteristics of the room, you can purchase devices from 200 mm. If a radiator is purchased for a bathroom or toilet, we recommend a narrow model that can completely cover the space between the floor and ceiling. High-altitude devices have different variations from one and a half to three meters.
Having determined two linear characteristics and the material, we move on to calculating the depth and number of sections. The number of the latter is usually taken to be 10, but others also occur. The thickness is found from the volume. The cubic value is divided into length and height. The determination of power is also closely related to these indicators: knowing the required power, you can find the number of sections.
With original interior
To create a design, manufacturers often sacrifice technical characteristics.
First of all, this applies to cast iron products. Domestic radiators look serious, but are simply covered with paint.
European ones are more elegant, but weaker in heating. In any case, you need to find out from the documentation about the power that they are capable of developing, since you need to select devices based on heat transfer.
Reference! There are batteries in “retro” style. They have a pleasant appearance, but are expensive.
Aluminum ones have the same shape, with the exception of custom ones, but they differ in a variety of colors. In addition, a wide range of dimensions helps them fit into almost any area of the room.
Bimetallic radiators, unlike their analogues, are made not only straight, but also curved. This makes them look good in rooms with smooth angles.
Regardless of the material chosen, before purchasing you should read the technical documentation and find out the dimensions of the internal parts of the sections containing the coolant.
This will help you decide on the batteries not only by their external appearance, but also by their ability to heat.
You should remember the possibility of combinations. So, if a certain device suits the design, but its power is not enough, you can install additional heating by hiding it behind the side panel. Or combine radiator heating with warm floors.
A good option for guest rooms would be to install a fireplace. Although the latter more often serves a decorative role, it is also capable of reducing the number or size of sections installed in the room. Sometimes it's better to sacrifice beauty than to freeze every winter.
If you want to create a special design, you should contact the battery manufacturers. They will help you do the calculations. Thanks to this, the finished product will look beautiful and perform its direct function.
Heat transfer of one section
Today there is a wide range of radiators. While most are similar in appearance, thermal performance may differ significantly. They depend on the material from which they are made, on the dimensions, wall thickness, internal cross-section and on how well the design is thought out.
Therefore, it is possible to say exactly how many kW in 1 section of an aluminum (cast-iron bimetallic) radiator only in relation to each model. This data is provided by the manufacturer. After all, there is a significant difference in size: some of them are tall and narrow, others are low and deep. The power of a section of the same height from the same manufacturer, but of different models, may differ by 15-25 W (see the table below STYLE 500 and STYLE PLUS 500). There may be even more noticeable differences between different manufacturers.
Technical characteristics of some bimetallic radiators
Please note that the thermal power of sections of the same height may have a noticeable difference. However, for a preliminary assessment of how many battery sections are needed for space heating, we calculated the average thermal power values for each type of radiator
They can be used for approximate calculations (data are given for batteries with an interaxial distance of 50 cm):
However, for a preliminary assessment of how many battery sections are needed for space heating, average thermal power values were calculated for each type of radiator. They can be used for approximate calculations (data are given for batteries with an interaxial distance of 50 cm):
- Bimetallic - one section produces 185 W (0.185 kW).
- Aluminum - 190 W (0.19 kW).
- Cast iron - 120 W (0.120 kW).
More precisely, how many kW can you have in one section of a bimetallic, aluminum or cast iron radiator when you choose a model and decide on the dimensions. The difference in cast iron batteries can be very big. They are available with thin or thick walls, which causes their thermal output to change significantly. Above are the average values for batteries of the usual shape (accordion) and those close to it. Retro-style radiators have significantly lower thermal output.
These are the technical characteristics of cast iron radiators from the Turkish company Demir Dokum. The difference is more than significant. She could be even bigger
Based on these values and average standards in SNiP, the average number of radiator sections per 1 m2 was calculated:
- the bimetallic section will heat 1.8 m2;
- aluminum - 1.9-2.0 m2;
- cast iron - 1.4-1.5 m2;
How to calculate the number of radiator sections using this data? It's still simpler. If you know the area of the room, divide it by the coefficient. For example, a room of 16 m2, to heat it you will need approximately:
- bimetallic 16 m2 / 1.8 m2 = 8.88 pcs, rounded - 9 pcs.
- aluminum 16 m2 / 2 m2 = 8 pcs.
- cast iron 16 m2 / 1.4 m2 = 11.4 pcs, rounded up - 12 pcs.
These calculations are only approximate. Using them, you can roughly estimate the costs of purchasing heating appliances. You can accurately calculate the number of radiators per room by choosing a model, and then recalculating the number depending on the temperature of the coolant in your system.
Features of new cast iron batteries
The technical features of modern cast iron batteries have certainly been improved. As well as the appearance - previously these were rather clumsily joined sections, cast from the same material. The heating capacity of the battery depended on the number of sections. Multi-sectional models were installed in corner apartments and in apartments on the top floors.
The new cast iron batteries are compact in size, making them well suited for small spaces
Today, battery configurations make it possible not to be shy about such a unit in your home. They can be chosen to suit the style of the interior, look great in it, and do not need to be hidden under curtains. Such original models are created that cannot be called anything other than a work of art, both flat and round, and with decoration, etc.
Modern batteries use steam, hot water, and antifreeze as coolants. To generate steam, you need a special boiler, thanks to which the steam flows through the radiators. Typically, rooms are equipped with water batteries, for which the coolant is heated due to the operation of the boiler. It turns out that warm water circulates through the system, and after cooling it returns to the container for reheating. In such cases, process water is used, but the technology of the closed circle principle is considered very profitable in economic terms.
Infrared heated floors.
Read in detail how to install it in this article. I recommend placing an additional layer of aluminum foil underneath it on a wooden base.
And be sure to always follow the rules for electrical installation on combustible substrates.
- Video 24. Installation and connection of heating.
- Connection and installation of heated floors.
- Installation of heated floors.
- How to calculate a heated floor
Working and testing pressure
When it comes to the technical characteristics of radiators, pressure indicators are always listed among the first. The usual operating pressure of the coolant is 6-9 atmospheres. Any radiators can cope with this pressure; for cast iron batteries, the standard load is considered to be just 9 atmospheres.
There is also the concept of “pressure testing” - this is the maximum pressure in the system that can occur during its initial startup. For the MS-140 model, this is 15 atmospheres.
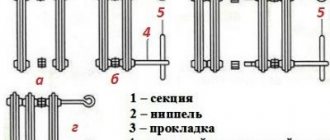
Various design solutions for cast iron radiators
According to the regulations, when starting the heating system, it is imperative to check the possibility of smooth starting of centrifugal pumps. In a good way, all pumps should be equipped with automatic equipment that ensures this smooth start. Well, in fact...
In fact, most homes either do not have one or are in poor condition. But even in such a case, the instructions provide a corresponding point: the initial start-up must be carried out with the valve closed, which can be opened (smoothly!) only after the pressure in the line has been equalized. Considering who starts the heating in our homes and how, it is not difficult to imagine the percentage of compliance with these instructions.
If the regulations are violated, the same water hammer occurs, in which an instantaneous pressure surge causes the permissible value to be exceeded, and one of the radiators along the flow of the coolant cannot withstand the load.
The further course of events is clear - its service life is not as long as we would like. Date: September 25, 2022
Possible problems during operation
Bimetal devices have a large number of advantages. Which of their features can be considered disadvantages?
- Despite the possibility of using bimetallic batteries in a system with any coolant, the low quality of the latter negatively affects the service life of the device.
- Different coefficients of expansion of the metals present in the battery design can, over time, lead to instability of heat transfer and a decrease in the strength of the device.
- The use of low-quality coolant in the system can lead to clogging of channels, corrosion, and deterioration of heat transfer.