It is unlikely that anyone will dispute that during the cold season the temperature in the house is the main factor of comfort. Therefore, the heating system in any home must be equipped with high quality. The main heating devices, which are essential components of any heating system, are radiators. There are a huge variety of them today. But even today in Russia and in many foreign countries, cast iron radiators are most often used in heating infrastructure.
Like other heating devices, cast iron batteries have certain advantages and disadvantages. But their most important advantage is that they can be used for a long time. Cast iron radiators are time-tested, as they have been used for decades. At the same time, during operation no additional financial investments are required for repair work.
Construction of cast iron batteries
Cast iron heating devices consist of the following parts:
- heating section filled with coolant;
- connecting nipples – bushings with external threads used for joining adjacent sections;
- end caps;
- transition plugs for connecting pipes or taps;
- gaskets made of paronite or rubber - artificial rubber EPDM.
Note. The minimum number of sections (fins) in one radiator is 3 pieces. It is not customary to do less - the heat transfer is too low, and it looks ugly.
The heating elements are pulled together by nipples, and the joints are sealed with gaskets to avoid leaks. Paronite is used on old Soviet-made radiators; the modern analogue is EPDM sealant. The nipple shown in the drawing is tightened with a long socket wrench with a special nozzle.
The side openings of the outer sections are closed with blind or through plugs, where pipelines are connected. The manufacturing plant or the store selling the products can additionally equip the batteries with hanging brackets and a manual air release valve - a Mayevsky valve.
Technical characteristics of cast iron radiators
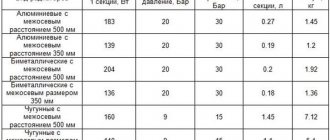
Among the many criteria for choosing cast iron radiators, heat transfer parameters are undoubtedly the main ones. They must be selected depending on the volume of the room that is planned to be heated. The size and weight of cast iron radiators are of no small importance, since these characteristics can lead to difficulties during transportation and installation. As for the pressure indicator, for country houses you can use this type of heating device at 6 atm.
To determine the required power of a cast iron radiator, it is necessary to take into account the fact that in order to maintain a comfortable temperature in a heated room of 10 square meters. m of area must be provided:
- in a room with one window and an outer wall - 1 kW;
- in a room with one window and two external walls - 1.2 kW;
- in a room with two windows and two external walls - 1.3 kW.
Of course, when professionally calculating the amount of heat energy required to heat a room using cast iron radiators, more complex methods are used, but at the household level the above values are quite sufficient. The power of one section, which is the basis for calculating the total number of sections of a cast iron battery, is indicated by manufacturers of cast iron radiators in the technical documentation.
How much does one section weigh?
For many builders, the term “cast iron heating radiator” is associated with a heavy structure. Indeed, on the construction market you can find a huge number of heating devices in question, and their weight varies over a fairly wide range. According to experts, the heating radiator section, which was used during the Soviet Union, has a mass of just over 7 kilograms. If water is poured into this container, the weight of the section will increase to 8.6 kilograms.
At that time, a standard heating radiator consisted of 6 sections, which means that the weight of each battery without water was within 43 kilograms . If we take into account that the thermal power of each of the individual sections is within 170 watts, then two such radiators will be needed for a room with a total area of 20 m2.
Connecting sections in a cast iron radiator
Modern analogues of cast iron heating devices have much less weight than the batteries that were used during the Soviet era. For example, the weight of a single section of a Czech heating device is 3.8 kilograms. This container contains 800 milliliters of water, which increases the weight to 4.6 kilograms.
If we take into account the thermal efficiency of each section within 140 watts, then for a room with a usable area of 20 square meters you will need 14 such sections. With detailed calculations, one can easily determine that the weight of such a device is 40% less than the mass of its Soviet counterpart.
Advantages
1. They do not need deeply purified water
The hot water supplied to the radiators of residential buildings is not of high quality. It has a high alkaline content. And as it passes through the pipeline, it also washes away sand particles from the walls of the pipes. As a result, a chemically aggressive liquid with a high content of mechanical impurities flows through the batteries. The solid particles in it, like sandpaper, begin to rub the walls of the battery, made, for example, of steel. But for cast iron this is not a problem. Its walls are protected by a thin layer of natural protection, so chemical elements do not have any effect on it. Even when the heating season comes to an end and the batteries are dehydrated, its walls will not become covered with rust from the inside. In addition, the walls of cast iron batteries are much thicker.
2. Ability to withstand maximum pressure
The operating pressure of cast iron radiators is higher than any other (more than 0.9 MPa). From different manufacturers you can find models with the required operating pressure. They are not susceptible to fluid shocks.
3. Long service life
It is known that in some houses in St. Petersburg you can still find cast iron batteries cast more than a hundred years ago! And this is not surprising. If you properly maintain cast iron radiators (namely, change gaskets on time, carry out flushing), then they can easily serve you for 50 years, or even more.
4. Affordable cost
Compared to new developments in the field of radiators, cast iron ones are many times cheaper. Moreover, when it comes to replacing the entire heating system in the room, the cost savings in this case will be quite significant.
Let's start disassembling
To do this, it is better to choose a period when the heating is turned off. Before disassembling the radiator, we recommend removing it from the wall. This will make it much easier and more convenient to work with. In addition, if you have never removed the battery before, then most likely there are no taps at the entrance. This is how radiators were installed during the construction of the house.
It is recommended to install shut-off valves on the pipes at the junction with the battery, in case you make a mistake during subsequent assembly of the radiator and a leak appears. For further dismantling, you will need to shut off the access of water to the radiator, or again wait until the end of the heating season.
Disassembled battery
When disassembling the radiator, it is not recommended to apply too much force to the plugs. To unscrew them, take a gas burner and start heating one of the plugs evenly on all sides. It will take about 5 minutes. During this time, you will get rid of the old paint on the edges of the plug, and will also cause the plug to expand where it connects to the battery section.
Take a 55 mm wrench and try to turn the plug clockwise. If the plug does not turn, there is no need to apply extra effort - turn on the burner and start heating the plug again. It is not advisable to use a pipe wrench. Although it has a wide range of sizes, it can ruin the edges of the cork.
Remember that the blind plug has a left-hand thread. It needs to be unscrewed clockwise.
The older your battery is, the longer it will take to heat the plug. During the period of operation, a lot of dirt, debris, and rust may accumulate at the joints. It often happens that the lower part of the battery is completely clogged and does not heat at all. Be prepared for the fact that the cork will have to be heated red hot. But after that it will easily unscrew. Do the same procedure with the second blind plug.
To remove the passage plugs, take a 36 mm wrench. In the same way, use a torch to heat the connection between the plug and the battery section for 5 minutes. This time unscrew the plugs counterclockwise - they have right-hand threads.
Heating the battery plug
Flaws
Despite many advantages, cast iron radiators have a number of disadvantages. This was facilitated by both the design features and the properties of the cast iron itself. For example, cast iron batteries have difficulty integrating into automatic temperature control systems.
Due to the inertia of heat transfer, it is quite difficult to control the set temperature in the room. After all, after turning off the boiler, cast iron radiators will give off their heat for another hour, warming the surrounding air.
There are also other disadvantages, including:
- large volume of coolant;
- significant weight of one radiator;
- design uniformity.
The large volume of water in the battery also has its disadvantages. Warming up the entire coolant requires more time and energy resources.
In addition, the load on the pump increases, which is forced to pump a significant amount of water in one heating cycle.
The heavy weight of the devices is also a disadvantage that worries installers and service departments more than residents. However, when assembling a heating system yourself, you cannot do without an assistant when attaching the cast iron battery. The weight of one section is about 7 kg.
Such a disadvantage as design uniformity is due to the technological features of cast iron - they do not allow creating elegant parts from this material. The batteries look the same.
To diversify the model range, manufacturing companies produce cast iron radiators with a beautiful pattern on the surface, but their cost is 10-20 times higher than the price of simple models.
Another drawback is the equipment’s vulnerability to water hammer. The fact is that cast iron is a strong, but rather fragile material. According to GOST 8690-94, radiators must withstand short-term pressure of 1.5 MPa.
But sometimes the pressure can exceed this value. This happens when the pump starts abruptly and there are no compensators. As a result, cast iron batteries may crack or burst.
In many cases, the advantages of cast iron radiators greatly outweigh their disadvantages. It is this fact that helps such batteries maintain a good position in the heating systems market.
What is the difference between domestic and imported cast iron radiators?
The MS-140 cast iron radiator from a domestic manufacturer is a classic example of heating devices of this type. With a working pressure of 9 atmospheres and a pressure test of 15 atmospheres, this heating device is fully adapted to domestic heating networks. The quality of radiators of this type has been tested by time, because they have been produced and installed for many years.
The Russian market also offers a huge variety of foreign cast iron radiators, which are manufactured in Italy, Turkey, Spain, the Czech Republic, and England. Their main difference from Russian thermal appliances is the higher quality of surface treatment. As a result, the same power is provided by smaller battery dimensions. In addition, in imported cast iron radiators, due to smooth internal surfaces, hydraulic resistance is significantly reduced.
The main advantage of cast iron is that it is resistant to any quality of coolant used. That is, cast iron radiators can be installed in heating systems with poor, highly contaminated or aggressive coolant.
High corrosion resistance allows the use of cast iron radiators in open heating systems, in which the coolant is in contact with oxygen, which means there is an increased risk of corrosion destruction. The walls of cast iron batteries are very thick, so cast iron batteries are the best option for heating systems in which the coolant contains various impurities and solid particles. Without exception, all imported cast iron radiators go on sale painted or coated with a special anti-corrosion primer. Russian radiators, as a rule, require additional painting. But if we take into account the fact that domestic devices are much cheaper, then this drawback will seem insignificant.
Perhaps the only significant drawback of all cast iron radiators is that they are susceptible to water hammer. It should also be noted that cast iron radiators are characterized by a certain inertia during heating and cooling. Especially when used in heating systems with solid fuel boilers.
It has been proven that the heat from cast iron radiators is more beneficial than from other types of batteries. And it is very important that today manufacturers have begun to pay great attention to the design of these heating devices. Therefore, it is possible to choose a stylish cast-iron radiator that will fit perfectly into the design of the heated room.
New generation sectional cast iron radiators
Today, new cast iron one-, two- and three-channel sectional radiators of the ChM series from a domestic manufacturer have appeared on the market, characterized by their compact size and original design. They can be installed in any room, since they occupy a minimum of free space, while guaranteeing high-quality heating.
The optimal ratio of key indicators and aesthetic appearance rightfully allow us to consider this type of cast iron radiators one of the most promising.
Sections of these radiators are made of gray cast iron. Casting is performed in modern furnaces in sand-clay molds, which ensures stable quality and excellent performance of heating devices. High heat transfer is guaranteed by vertical fins. In addition, these radiators are improved in terms of practicality and hygiene, since they eliminate any cavities in which dust can collect.
How to rinse at home
In country houses, the heating system often loses its efficiency. This happens through poor heat transfer, as well as as a result of debris settling on the walls of the batteries. The coolant heated to a high temperature affects the inside of the radiators, where scale and rust settle. The presence of blockages leads to poor heating of the building.
The main reasons for flushing batteries are:
- Uneven heating of the radiator over the entire plane, when the upper part of the sections is hot, but the bottom of the tank remains cold;
- Warming up the heating system to the required temperature takes longer than usual;
- Increased fuel consumption.
To independently flush heating devices, aluminum or cast iron radiators, you need to drain the water and unscrew the radiator from the system. Removing blockages or flushing occurs using clean water with the addition of acetic acid, special cleaning agents or caustic soda.
Battery before and after washing
It is advisable to carry out the work in the bathroom to prevent liquid from spilling onto the floor. At the same time, a mesh is installed in the bathroom drain hole to collect large contaminants. Pre-placed rags will help prevent damage to the container's coating.
At the initial stage of work in cast iron radiators, all plugs are unscrewed, and water heated to a boil is poured into the resulting holes. Next, shake out the heating device and drain the liquid and debris.
Next time, water with the selected cleaning agent is poured into the radiator. After this, close all the plugs, knock on the device with a wooden hammer, shake it and pour out the water. Similar operations are carried out until clean liquid flows from the holes.
Features of cast iron radiators
The selection of a cast iron radiator should be carried out in accordance with the technical characteristics specified in the manufacturer's instructions. In addition, it is imperative that you install it in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions, as this will help prevent possible ruptures.
All cast iron radiators are characterized by high heat transfer. Of the total amount of heat energy that is released into the air, 70% is distributed by radiation, and 30% by convection.
Cast iron radiators are the optimal heating devices for apartment buildings, especially in the northern regions. In cold climate zones, their inertia is not a disadvantage. Indeed, in the event of any emergency shutdowns, they are capable of retaining heat for a long time and transferring it to the room.
Today, many apartment owners prefer cast iron radiators because of their original design, which, for example, can perfectly emphasize the retro style of the interior, in which other types of radiators would look simply ridiculous.
The affordable price of cast iron radiators also plays an important role. Since a large number of batteries are usually required when installing a heating system in a house, the savings are significant.
Operating principle: convection vs. radiation
The operating principle of a heating radiator is extremely simple. Water, which has already been heated to the required temperature, flows from the boiler into the room through pipes. Then it enters the heating devices, which heat the air in the rooms of your home.
It is worth noting that if heat is transferred by convection - this is accelerated heating of air that flows through the heating surface, then such a heating device will be called a convector. If heat is transferred by radiation, that is, heating of the surrounding air is produced by a surface that has an increased temperature and heat capacity, then this will be a radiator.
The operating principle of a heating battery can also have a combined form - panel radiators-convectors.
Considering how a heating battery works, it is worth noting that in order to quickly warm up a room, a convector is more suitable. However, such a cross-sectional heating battery has one drawback - due to the passage of active convection, a lot of dust is released into the air, which will not have the best effect on the health of those present. That is why convector batteries are used only where there are problem areas of the heating system. For example, to create an air curtain in a room with a large glass area, where conventional devices cannot fit in size.
Regardless of the temperature in the heating radiators, they will give off approximately 60 percent of the heat by radiating thermal energy, while the rest will be given off by convection. Thus, a minimum of hot air convection is achieved and those objects located in the room are well heated. In this regard, it can be noted that the way a radiator works is similar to a heated floor system.
Calculation of the required number of sections of a cast iron battery
The simplest method for determining the required number of sections for heating a room is to take into account only the area of the room.
With great simplification, it is believed that heating 1 m² of area on average requires 100 W of thermal energy. Knowing the area of the room, it needs to be multiplied by 100 and then divided by the thermal power of the radiator model.
For example, a room has an area of 16 m², and a radiator model MS-140-M2-500 is purchased, each section of which has a thermal power of 160 W. In this case, the calculation is made as follows:
16 m² × 100 W = 1600 W – heat will be required to heat this room. 1600W: 160W = 10 pcs. - this is the number of sections required. If the calculation results in a non-integer number, it is rounded up to a whole number. However, this technique is overly simplified and does not take into account many criteria. To make a more in-depth calculation of the required number of sections, you need to take into account many parameters - the level of winter temperatures in the region, the quality and material of the windows, their number in the room and the total area, the degree of wall insulation, and more. Even the connection diagram of radiators and their location in the room matter. This calculation is usually carried out by specialists, and it is not easy to cope with it yourself. However, our reader is given this opportunity - at his service is a special calculator, which takes into account most of the factors affecting the size of the heating radiator. Just provide the requested information and get the desired result.