Warm floors create coziness and comfort in a living space. But it is not always possible to install such structures in multi-storey buildings. In addition, it is unclear whether pipes inside the floor can completely replace conventional radiators. The presented instructions will help you correctly install underfloor heating (HF) in an apartment using central heating.
What is a water heated floor
In panel houses, the outer walls and floors in winter most often do not provide sufficiently comfortable living conditions. This problem is especially acute if the family has small children who like to play on the floor.
If you warm up the entire surface of the flooring, drafts will be eliminated. Dusty carpets, warm slippers, and woolen socks at home will no longer be needed even during the most severe frosts. To do this, it is necessary to lay pipes under the floor throughout the entire area of the heated room, in which warm water will circulate.
What does it consist of?
The design of TP is technologically more complex than traditional heating using radiators. Typically, heating pipes are poured on top of a concrete monolith. There are more modern methods of dry installation with standard blocks.
To reduce heat loss, polystyrene foam is laid on concrete floor slabs. Waterproofing made of polyethylene film is placed under it, wrapping the edges and securing with tape.
Before pouring the concrete screed, a damper tape is installed around the perimeter of the room. It compensates for the thermal expansion of concrete.
List of main components of a monolithic warm circuit:
- Waterproofing film of concrete base.
- Insulation - polystyrene foam 3-5 centimeters thick.
- Damper tape around the perimeter of the room.
- The heating pipe is metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene with a diameter of 16–20 mm and a wall thickness of 2 mm.
- Concrete, layer thickness 80–100 mm.
- Flooring: laminated boards, linoleum, ceramic tiles.
- Three-way valve of mixing unit with thermostat.
- Circulation pump.
- Manifold with shut-off valves for supply and return pipes.
- Automatic air vents.
- Heat exchanger.
- Filter.
- Expansion tank.
- Pressure gauge.
Operating principle
Since the entire floor in the room is heated, the temperature of the heating system coolant (CO) is usually maintained within 25–35 degrees. This is quite enough to compensate for heat loss through external walls, windows, and balcony doors.
The heating intensity is controlled manually or by thermal heads on the shut-off valves. In this case, the dependence on the temperature of the coolant of the centralized CO remains.
Advantages
The main advantage of TP is reflected in the name of this system. Increased comfort is also explained by the absence of drafts, since the air inside the room is heated evenly over the entire area.
Heating costs are reduced by 10–15% compared to using conventional radiators, which first heat the ceiling. Hot air from the batteries rises, then, as it cools, it falls down and moves in a cooled stream to the heating devices. The floor remains cold.
TP has other advantages:
- Creates and maintains an ideal microclimate in the apartment. Children can play on the floor without the risk of catching a cold.
- Uniform heating eliminates the appearance of dampness and mold on the walls.
- Service life - up to 50 years.
- There is no harmful electromagnetic field, which is inevitable for electric floor heating in a living space.
Flaws
Thin pipes must be reliably protected on top by a concrete monolith to support the weight of heavy furniture. Additional load on floor slabs can negatively affect the stability of an apartment building.
Setting up all TP branches takes a lot of time due to the inertia of the entire system. The length of one pipe reaches 60–80 meters. In addition, a change in the temperature of the floor surface will become noticeable only after the concrete monolith has warmed up.
There are other disadvantages:
- High installation cost. Specific skills, knowledge, and experience are required.
- If the pipes were of poor quality, then repairing the concreted system is almost impossible.
- Difficulty in obtaining permission to change the design of the heating system.
- The payback period for the costs incurred is tens of years.
The advantage of heated floors over radiators
Unlike radiators, heating with warm water floors leads to uniform heating of the room. In addition, this device provides more comfortable conditions for a person, since, with floor heating, the temperature below is higher than at the top.
Therefore, your feet will be warm and your head will be in a cooler space, which is good for your health.
Another positive aspect of such heating is savings, heat loss is reduced by up to 20%. Without a doubt, a big plus is the aesthetics of the design. The “filling” of the heated floor is hidden under the floor covering, thereby not spoiling the interior of the apartment, in comparison with radiators that are placed on the wall.
Of no small importance is the fact that the air does not dry out and hot currents do not drive dust particles around the room, as with radiator heating.
The disadvantages of such a structure include a rather labor-intensive and lengthy process that requires significant financial costs. In addition, when connecting a heated floor to a radiator, it will only function if there is heating in the radiators.
Is the installation legal?
Any unauthorized changes to the central heating scheme are prohibited. Such actions are punishable by significant fines. To obtain permission to install a transformer substations, you need to agree on the design of changes with the heat supply organization.
To maintain the thermal balance of the entire house, there are only three options for legally connecting the TP of a separate apartment to central heating:
- Initially, the project provided for a two-pipe connection scheme for heating radiators in each apartment. Then a resident of any floor can obtain permission.
- If the main pipeline is located in the basement, then for the first floor you can obtain permission to separately enter the supply and return pipes.
- If the house has upper wiring in the attic or technical floor, then residents of the last upper floor can obtain permission for an individual connection.
Only in these cases there is no likelihood of deterioration in the heating conditions of other apartments. Tapping into a single-pipe CO will definitely disrupt the hydraulic balance. Other residents of the house will be cold. Complaints will follow, the violator will be identified and fined.
If it is not possible to connect the indoor heating system directly to the main pipeline, then it is impossible to obtain legal permission to install heated floors.
The procedure for obtaining a permit consists of the following steps:
- Contact the heating supply organization with the appropriate application and obtain permission. Along with the document, technical specifications for the installation and connection project of floor heating circuits are issued.
- Develop and approve the project.
- Install, launch the system and commission it to a special commission from the heat supply organization.
Difficulties that may arise during installation
When installing a hydrofloor in an apartment, you may encounter a number of problems:
- The water in the batteries has a high heating degree (90), which is not suitable for the sex pipeline. For heated floors, the permissible maximum temperature is 50 degrees. Exceeding will result in damage to the system and the finish.
- It is prohibited to install water floors without a special permit in apartment buildings. Otherwise, you will be subject to a fine.
- The heating system is connected through an elevator, and the heated floor is connected only using copper pipes, the price of which is high. In addition, working with them requires special equipment and the help of professional craftsmen; this is also quite expensive.
- In old houses, installing warm floors is problematic, since previously a single-pipe heating system was installed in apartments. When connecting a TP to such a structure, the neighbors' batteries will be cold, so you will not be able to obtain permission to install hydrofloors.
Therefore, having decided to install water-heated floors in an apartment, you need to carefully calculate everything, prepare design documentation and obtain permission.
Types of connection diagrams
There are many options for TP schemes for connecting to a centralized CO. At the same time, you need to know that without forced circulation of liquid, stable operation of the TP is impossible.
The contour under the floor is at the same level, so natural movement of water is excluded. It is also impossible to connect directly to the main pipeline. A coolant can circulate there with a temperature 2 times higher than the permissible temperature for the TP.
There are only two options for connecting to a common CO:
- with mixing unit;
- with heat exchanger.
With mixing unit
In such a TP system, coolant circulates from a centralized CO. As it cools, the water is gradually discharged into the return pipeline, and hot water comes from the supply pipeline. The speed of this process is controlled by a three-way valve with a thermostatic head.
Central heating coolant always contains suspended particles and hardness salts. Installing a filter at the entrance to the TP system cannot completely protect the heating circuit from gradual clogging. Hardness salts are initially in dissolved form, so they freely enter the pipes and then settle on their walls in a thick layer.
In order to extend the service life of the TP to several decades, it is better not to use a connection diagram with a mixing unit. Over time, the circuit will gradually become clogged, the resistance to movement will increase, and the flow rate will decrease. The pump power will no longer be enough to ensure the design temperature regime.
With heat exchanger
The long service life of the transformer substations is ensured by the completely autonomous circulation of pre-prepared coolant. The ideal option is distilled water. You can simply boil tap water and then let it sit.
Heat transfer occurs in a heat exchanger, where coolants from a centralized CO and TP circulate separately from each other. Usually this is a non-demountable structure, so filters must be installed at the inlet.
Equipping the TP system with a heat exchanger has the following advantages:
- Regulation of floor heating in relation to changes in outside air temperature occurs automatically. The temperature of the centralized CO coolant changes in the boiler room in accordance with current weather conditions.
- Rust, suspended particles, and hardness salts do not enter the TP and do not clog the circuit, so the system will serve properly for decades.
- Plate heat exchangers are made of corrosion-resistant steel and therefore have a long service life.
- There is no risk of water hammer.
- The hydraulic resistance of the centralized CO does not change.
- The temperature of the heating circuit does not exceed 40 ºС, so a relatively inexpensive pipeline made of cross-linked polyethylene can be used.
Pipe selection
For water heated floors, it is allowed to use materials that meet specific requirements. These include: durability, no welds. There are a number of standards regarding the outer diameter of the pipe and the permissible length:
- 16 mm – from 50 to 80 m;
- 20 mm – up to 100 m;
- 25 mm – up to 120 m.
The heated floor is configured to work with coolant at low temperatures. But the reserve must take into account unforeseen circumstances. Therefore, the characteristics should include temperatures up to 95 0C.
Stainless steel corrugation
These pipes can be spliced. The fittings that are used in this case are considered the most reliable among others. The material meets all requirements and is easily bent while maintaining position. The outside is covered with high-density polyethylene.
Copper
When metal oxidizes, it becomes covered with a layer of patina, so copper protects itself from corrosion. Thanks to this fact, pipes last from 50 to 200 years. Positive aspects are also high heat transfer and ductility with mechanical strength. For heated floors, products in a polymer shell are used.
Copper pipe for underfloor heating Source wieland-plumbing.com
Polypropylene
Such pipes are not used for water heated floors. The material is resistant to bending, so it is impossible to organize a step of 20 cm without soldering. And this is unacceptable. In addition, polypropylene has low heat transfer, which is not relevant for the operation of a low-temperature system.
Polyethylene
Such pipes are made of cross-linked polyethylene. The material has a classification, which is designated by letters from PEX-a to PEX-d. For water heated floors, only the first group is recommended for use. The second option shrinks over time, the third is cheaper, but inferior in quality characteristics. The latter product is being withdrawn from production, since production is accompanied by the participation of nitrogenous compounds.
An alternative material for making pipes is PE-RT. This polyethylene lasts for more than 50 years and can withstand several freezing cycles with water inside without loss of characteristics or shape. Connections can be made by fittings or welding.
Metal-plastic
Polyethylene pipes with aluminum reinforcement last no more than 30 years. The flexible material is sold in coils up to 50 m long. If you need more, you can place an order with the manufacturer and increase the size to 80 m. The best option would be material made from PEX-a, PEX-b or PE-RT.
Metal-plastic pipes for heated floors Source zkheizung.de
It is important to purchase quality materials. Different thermal expansion of polyethylene and metal leads to delamination. Thin layers of 0.8 mm and 0.2-0.4 mm, respectively, cannot always cope with interruptions without consequences. Therefore, before choosing, you need to require accompanying documentation: certificates of quality and compliance.
Nuances of installation and selection
Design work is needed not only to obtain a permit. The customer will receive a fairly accurate list of necessary materials, parts and components. After carrying out simple marketing, the exact cost of creating additional comfort will be calculated.
How much higher will the floor become?
For apartments with high ceilings, raising the floor level by 10–15 cm will be almost unnoticeable. But for most of the housing stock this can be a problem, with the exception of balconies and loggias.
A layer of insulation - expanded polystyrene with a thickness of at least 30 mm - will need to be laid on the floor slabs. A heating circuit will be located on it, which is poured from above with monolithic concrete 85 mm thick. Finishing with tiles or laminated boards will add at least another 10 mm of height. As a result, the total height of the mounting layer will be 125 mm.
You can reduce the rise in floor level in the following ways:
- Completely dismantle the old screed down to the floor slabs.
- For thermal insulation, instead of polystyrene foam, use multifoil up to 1 cm thick.
- Reduce the screed height to 60 mm. In this case, there must be at least 30 mm of concrete above the pipes, the strength of which will need to be increased by reinforcement with steel mesh.
- Use flooring systems - “dry” heated floors 6–10 cm thick. They are installed without concrete.
Thermal insulation mats
As the floor temperature rises, possible additional heat losses through the ceiling to the lower floor increase. Therefore, pipes must be laid only with thermal insulation. Usually this is foil polystyrene foam. The foil should be at the top, then this significantly increases the heat-reflecting ability of the insulation.
Thermal insulation materials come in various types:
- Rolled. Made from foamed polyethylene with a thickness of 2–10 mm. On one side there is a coating of aluminum foil. It will not be possible to fix the pipes on such a base, so a reinforcing mesh is laid on top.
- Expanded polystyrene mats. They have a film on the surface with markings along which it is easier to lay pipes in accordance with the design drawings. You will also need to lay reinforcing mesh on the mats to secure the pipes. Expanded polystyrene has high thermal insulation properties, a service life of up to 60 years in conditions of temperature changes from -40 to +40 ºС, and does not accumulate moisture. To increase fire safety, fire retardants are added to the insulation during production, which makes it a self-extinguishing material.
- Profile mounting plates EPS (extruded polystyrene foam). The most technologically advanced and convenient for installation. Protrusions with a certain pitch are formed on their surface for fixing pipes with a diameter of up to 20 mm. The ends of the mats have locking projections for connection with adjacent blocks. This results in a continuous surface with minimal heat loss. Mats are available in thicknesses from 10 to 35 mm.
Which pipes to choose
All elements that are laid under the floor are subject to increased requirements for strength, reliability, durability, and corrosion resistance. The pipes must be seamless, capable of withstanding a pressure of 8 bar, as well as dynamic loads in case of water hammer.
Polypropylene and steel pipes cannot be used. The heating circuit of the TP must be laid under the floor without joints or couplings.
The following types of pipe products are most often used:
- Products made from cross-linked polyethylene. Produced by extrusion under high pressure. Crosslinking occurs at the molecular level. The result is three-dimensional structures that increase the strength characteristics of the polymer. Such products are characterized by minimal hydraulic resistance to the movement of the coolant. They tolerate pressure changes well. Corrosion resistant.
- Metal-plastic. The walls of the pipes consist of several layers, so they combine the strength of metal and the resistance of polymers to corrosion.
- Copper. They have a long history of use, are durable and reliable in operation. Copper transfers heat very well to the surrounding space, but is rarely used for the TP circuit due to its high cost.
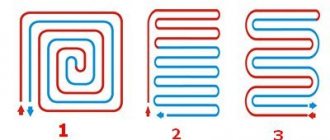
How best to lay pipes (diagrams)
The uniform heating of the entire floor area depends on the correct location of the circuit. When designing, it is necessary to take into account that areas near external walls and windows are cooled more intensively. In addition, we must remember that as it moves along the circuit, the coolant gradually cools down.
The following laying schemes are distinguished:
- simple snake;
- double snake;
- corner snake;
- snail.
The arrangement of the contour with a simple snake is the most common scheme. The best option for a room with one external wall. The supply pipe with the hotter coolant is located in the cold part of the room.
Double snake and volute are used for interior rooms when equal heating is required over the entire area. In such schemes, the hotter pipe is located next to the cooler one. The “snail” version has lower hydraulic resistance.
A corner snake is the best option for a room with two external walls. Here, the maximum heat transfer of the circuit occurs in the corner part of the room.
Pipe distribution rules
In places adjacent to external walls, to increase the heating intensity, installation is done with a smaller distance (step) between adjacent pipes.
To maximize the effectiveness of CO, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Installation of the circuit begins from the cold outer wall.
- A gradual reduction in the intensity of floor heating is achieved by laying pipes using the “simple snake” technology.
- Uniform heating is achieved by spiral laying from the edges of the room to the center with a double pitch of turns. Then the return contour will fall into the resulting gaps.
- The greater the heat loss in the room, the more often the pipes must be placed. The standard step is usually 10–30 cm. In this case, the foot should not feel the difference in floor temperature in different areas. For border areas, a minimum pitch of 100 mm is recommended.
- The number of bends and turns should be minimal to reduce the hydraulic resistance of the CO.
- It is prohibited to join pipes under the floor.
Selecting a collector-mixing unit
The layout of the collector depends on the number of heating circuits. Installation of shut-off valves, automatic air vents and control thermostats is provided for each lash.
The collector and mixing unit must be equipped with the following parts:
- thermal head with remote temperature sensor;
- pump;
- pressure gauge;
- safety valve;
- expansion tank.
This is useful for the project.
Friends, I tried my best for you. Therefore, do not consider it a labor. Like the video, share with friends on social networks, leave your comments under the video.
A special request to those who actually did such an installation on a warm floor. Write in the comments how you did it and what the result was.
I repeat the link to the collection of factory instructions for the equipment discussed in this lesson. Who needs it - download:
In city apartments, a radiator system is used for heating. All heating devices in an apartment building are interconnected. Violation of the integrity of the water main will change the heating of the rooms on the lower floors.
An alternative to radiator heating is underfloor heating. In city apartments, electric heating devices are installed: cable, carbon rods or thermal film. It is not allowed to run a water line from the battery.
If a boiler is installed in the room to provide the household with hot water, then a separate circuit for underfloor heating can be derived from it. In private homes, any heating options and connections to heating devices are allowed. What heating system is best to install in a cottage? How is the floor line connected to the batteries?
Which is better - warm floor or radiator?
Radiators are a common method of heating at a very affordable price. Warm floors are comfortable and cozy, but the cost of their installation is high. Most people who do not have a special heat engineering education find it difficult to make the right choice. Contrasting these heating systems is a common mistake. In fact, they organically complement each other.
One of the advantages of TP is the absence of drafts, since the entire floor in the room is heated. But there is also a drawback - inertia. If the outside air temperature drops sharply, then the TP circuit simply will not have time to sufficiently warm the apartment.
This happens often in winter. During the day the sun warmed up, the thermometer showed -5 ºС. At night, the temperature can quickly drop to -10 degrees, and if a strong wind blows, the frost will intensify. External walls will cool quickly.
In this case, radiators come in handy. Experts call them “draft cutters.” The coolant temperature in them can be twice as high as in the TP circuit. Therefore, radiators effectively cope with the cold air flow flowing down the external wall.
It remains only to decide whether the TP system will be the main or supplementary heat source. In the first case, it should compensate for approximately 70% of the total heat loss of the room, and in the second - about 30%. The rest of the heat will be provided by traditional radiators.
This is a warm floor from the hot water recycling system of an indirect heating boiler.
The point is this.
So that even from the taps farthest from the boiler, hot water flows immediately after opening, without draining the cooled water in the pipes, they came up with a recirculation system. Using a separate pump, the hot water of the boiler circulates along the hot water supply route to each, even the most distant tap, and returns back to the boiler. Therefore, as soon as we open any tap, hot water immediately flows out of it. But the idea went further. Why is this water spinning in vain?
Shouldn't we put it in the heated towel rails? And also in a small area of heated floor. In the same bathroom, for example. But of course not directly, but with an admixture in a three-way valve. Actually a great thing. In winter and summer, day and night, the floor in the bathroom is heated. If you have a boiler, then you need a pump, a three-way valve and that’s it. I wrote a short but detailed instruction on how to do this, and attached it for free to my courses on installing heated floors and installing boiler rooms. These textbooks are the result of my great and painstaking work, so they are not given away for free.
DIY system installation
Design, installation, startup, regulation of the TP system - all these technological processes require a fairly high level of knowledge, skills, and experience. Therefore, even at the stage of obtaining permission, it is advisable to acquire a qualified consultant. Any alterations will then be expensive, because the TP will be covered on top with a concrete monolith.
Material calculation
The design of the heating system must be carried out taking into account all factors affecting the thermal balance of the room: the size of the area, the material and design of the external walls, the type of finishing floor covering, the size of windows and entrance doors.
To calculate the length of pipes in TP circuits, use the formula:
L=S/N x k.
Here:
S is the area of the heated room;
N—step;
k is the safety factor for bending, which is usually taken equal to 1.1.
One linear meter of pipe is capable of transmitting approximately 11 W of heat. Multiplying the estimated pipeline length by this figure, we obtain the total thermal power of the designed heating system.
To overcome the hydraulic resistance of the CO, the pump must create an appropriate pressure, which can be calculated using the formula:
H=L x Q x 2/k.
Here:
L—pipe length;
Q - coolant flow, usually in the range of 0.3–0.4 l/s;
k is the hydraulic resistance of the system, which can be determined from reference literature.
When choosing a circulation pump, it is necessary to take into account that the speed of water movement should not exceed 0.8 m/sec. Otherwise, additional sound insulation will have to be provided. This will not only increase the cost of the project, but also the amount of floor level rise.
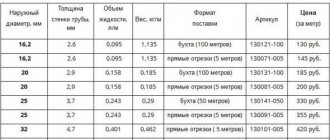
Specification for a room of 15 m2:
- Metal-plastic pipe 16 x 2 - 100 m.
- Damper tape 10/0.1-25 - 20 m.
- Thermal insulation TP-25/1.0-5 - 18 m2.
- Three-way mixing valve 3/4″.
- Circulation pump 25-40.
- Nipple adapter 1″ x 3/4″ – 2 pcs.
- Nipple 3/4″.
- Tee 3/4″.
- Collector 4 outlets 3/4″ x 1/2″.
- Shut-off valve 3/8″.
- Adapter B-H 1/2″ x 3/8″.
- Adapter 1″ x 1/2″.
- Ball valve 1/2″ - 2 pcs.
- Straight connector with transition to internal thread 16 x 1/2″ - 2 pcs.
- Tee 1/2″.
- Barrel 1/2″ x 60.
- H-B adapter 3/4″ x 1/2″.
- Automatic air vent 1/2″ – 2 pcs.
- Drainage tap 1/2″ – 2 pcs.
- Bracket for manifold.
Preparatory work
Before starting installation, it is advisable to clean the floor down to the floor slabs. Then the rise in its level will not be so noticeable. The old screed will have to be dismantled. A regular hammer drill with a chisel attachment will not work here. You must use a jackhammer.
The mounting brackets must be cut with a grinder. Joints of floor slabs, irregularities, and cracks should be puttied. The surface must be level in a horizontal plane.
Collector installation
The TP system control unit is mounted in a standard metal box located above the level of the heating circuit. The size of the case depends on the dimensions of the equipment. The installation location is selected next to the input from the centralized CO.
System installation
The circuit must be laid in one piece, without connections under the floor. The length of one lash should be up to 60 m. If such a segment is not enough to cover the entire area of the room, then install two segments of equal length.
Perform installation work in the following order:
- Treat the cleaned surface with a polymer primer.
- Glue the damper tape around the perimeter of the room to the height of the future concrete screed with a small margin.
- Spread waterproofing - polyethylene film with an overlap of the edges of the sheets of 100-150 mm. Along the perimeter, make an overlap on the walls at the height of the damper tape. Secure the joints and edges of the film with tape.
- Lay the insulation boards tightly.
- Lay out and secure the reinforcing mesh.
- Roll out the coil, straightening the pipe. Lay the contour according to the design drawing. Secure the hinges with harpoon brackets and mounting rails.
- Connect the ends of the circuit to the manifold.
- Fill the circuit with water and perform a pressure test (check the system for leaks) with a pressure of 4–6 bar. Do not drain the water so that the pipe does not float in the liquid concrete.
- Prepare the concrete mixture and pour the screed.
- Finish the floor surface after 28 days.
Launch
After installation is complete, rinse the pipes thoroughly with water under maximum pressure. Then drain this water completely. Blow out the circuit with a compressor.
Now you can fill the pipeline with the working coolant - distilled or boiled water. If there are several contours, fill them one by one. The air must be completely forced out through the air vents.
Now you need to briefly turn on the pump to create pressure in the system. As a result of coolant circulation, air pockets will be displaced. Add water again and turn on the pump. Repeat the process until the system is completely filled.
The launch of the TP into operation begins with a minimum thermal regime. The coolant temperature is set at 20–25 ºС. Then add 5 degrees every day until the maximum mark of +40 ºС is reached. Then the thermostat is set to design mode.
Steps to construct an electric floor
Before purchasing a heating cable or mat, we focus on the free space in the bathroom. We do not take into account the area under the bowl with the screen, shower stall, plumbing furniture, washing machine, washbasin and toilet. There is no point in placing heating elements under these items. Moreover, the cable will overheat in such places and fail.
Electric floor power in the bathroom
The standard floor power for bathrooms is 170-180 W/sq.m. meter. We multiply this standard by the installation area. For example, the total area of the bathroom is 5.5 square meters. meters. Minus the area occupied by various objects, we get, say, free 3 square meters. meters.
We multiply the average standard value of 175 by 3, add a reserve of up to 10% to the result and get 525-575 W/sq. meter. This is the required power of the floor heating elements.
Instructions for installing cables and mats
Preliminary calculations make it possible to purchase components and consumables in the required volume, after which you can safely begin constructing the system.
Step 1. Clean the base from debris, remove dust with a vacuum cleaner, smooth out unevenness (1-2 leveling layers are enough).
Step 2. Lay thermal insulation. Thermal insulation sheets should be placed on the floor with the reflective surface facing up and the joints between them should be sealed with mounting tape (adhesive tape).
Penofol is suitable for thermal insulation, and on the first floors it is recommended to make the thermal insulation layer thicker using expanded polystyrene or polystyrene foam. But in any case, the front surface must be reflective so that thermal energy goes in the right direction
Step 3. Waterproofing. We roll out the film or rolled waterproofing membrane, carefully level it and press it to the base, lift the edges onto the walls (20 cm). If you have to use several panels, then lay them with an overlap of 10 cm, and fasten the joints with tape.
It is allowed to use both coating and cast waterproofing in several layers. Each previous layer must be thoroughly dried before applying the next one.
Step 4: Edge processing. We attach a damper (edge) tape along the perimeter along the walls. It is needed to create a “floating” screed to avoid the appearance of cracks and swelling on it. The tape should be up to 20 cm wide, so that it is enough to cover the height of the floor, including the tiled floor.
Step 5. Laying the cable (or mats). We check the working condition of the cables and begin installation. The heating cable is placed on a substrate to which it can be attached.
Metal mesh is suitable for this purpose. In addition to fixation, it will prevent the cable from sinking into the screed and provide strength. Make sure that the cable does not cross. We handle it carefully to avoid even the smallest damage.
We connect the end of the heating cable to the electrical coupling. It will need to be recessed into the screed, positioned as close as possible to the thermostat (thermostat), but maintaining a distance between the wall and the connection of at least 20 cm.
It is much easier to spread an electric mat on the floor. The process is somewhat reminiscent of cutting fabric.
If the electric mat rests against an obstacle (wall, etc.), it can be cut with scissors or a knife along the supporting mesh and turned at any angle or in the opposite direction. Sections from sections must be moved at a distance of at least 5-6 cm
Step 6. Install the thermostat with sensor. In the right place on the wall, a meter above the floor, we drill a hole, guided by the dimensions of the thermostat.
We drill a longitudinal groove from it vertically downwards and continue it along the floor towards the location of the sensor. It is advisable to place the sensor between the cables, and not close to one of them, so that it shows the temperature reliably. The distance from the wall is half a meter.
We place the sensor with the wire in a corrugated pipe. The corrugation will protect the equipment. We insert the wire from the heating mats into the same corrugated tube and direct both wires to the thermostat.
To do this, we stretch the corrugated pipe along the floor, put it into the groove on the wall, and try not to bend it too much at the junction of the floor and wall, so as not to damage the wires. When the screed is poured, the corrugated tube with the sensor should protrude slightly from it.
When laying a heated floor, the resistance of the mat is checked with a multimeter. A deviation of 5-10% from the factory figures is allowed. You also need to check the insulation resistance. If the megohmmeter shows at least 10 megohms, the mat is reliable
Step 7. Screed. The installation is nearing completion, so we once again inspect all the elements of the cable floor, make sure there are no defects and begin pouring. We prepare the cement mortar and distribute it over the surface carefully and evenly with a minimum thickness of 3 cm. There should be no voids in the screed. If mats have been laid, we skip this step.
Step 8. The final touch remains - glue the tiles to the screed or directly to the mats with tile adhesive.
This is followed by a long drying period. It will be possible to turn on the electric floor no earlier than 28-30 days after completion of the work. It is imperative to wait until the mortar and glue have completely dried so that the screed does not crack.
Tips for installing infrared film
Preparatory work - as in the previous version. The infrared film is laid in parallel sheets on the thermal insulation material. Overlapping sheets is strictly prohibited. Next, you should install a thermostat with a sensor and make sure the system is working.
The assembled structure is covered with polyethylene and reinforcing mesh. Secure the mounting grid with self-tapping screws, but be careful not to touch the contacts. The mesh needs to be filled with cement-sand screed on top and the system tested again. After the screed has dried, tiles are laid on it using glue.
The infrared sheet in the bathroom is laid out on the floor, at least 20 cm away from the walls and with an interval of 30 to 50 mm between the strips
The infrared floor can be tested no earlier than after 28 days, when it is guaranteed to dry.
Recommendations for use
It is important to remember that TPs are an inertial heating system. Therefore, noticeable changes in room air temperature occur several hours after adjustment.
Recommendations:
- Heating of the floor surface of residential premises should be maintained within 25–30 ºС. In the hallway, bathroom, along the outer walls, the temperature can be increased to 35 degrees.
- To reduce the shrinkage of the concrete screed, fiberglass and other fillers are added to the solution. The dosage is indicated on the packaging.
- It is necessary to add liquid in a timely manner, and also periodically monitor the heating temperature. The water transformer practically does not require additional maintenance.
The temperature control of heating circuits is usually done manually. But it is possible to install automation with a programmable controller that controls the thermostat servo drives and the pump. Such high-tech work should only be performed by experienced specialists. You can find out the warm floor in the apartment by following the link. Insulating the loggia floor you will find the answer in the link.
Prices for underfloor heating systems
warm floor
Alternative solution
If it is impossible to install a warm water floor from central heating, then the electric version of this system comes to the aid of the owner. It is easier to install and you can do all the work yourself. The advantage is that in an apartment building, such a system does not upset the balance and is allowed to be used.
It is only necessary to take into account the power of such a system so that there is no overload of the electrical network. Spatially, an electric heated floor takes up significantly less space, which makes photos of the room more aesthetically pleasing and anyone entering the apartment will not have the suspicion that there is something wrong with the floor.
At the legislative level, electric heating is permitted and can be used at any time of the year, while a water floor is dependent on the seasonal supply of hot water. Accordingly, it can function exclusively from autumn to spring - the heating season.
Scheme with pump-mixing unit
This scheme also applies to combined systems, when you have both radiators and heated floors at the same time.
However, here, instead of a 3-way valve, a more expensive pumping and mixing unit is used.
Specification of materials
In fact, the cooled return flow is also mixed into the main boiler feed here. But thanks to the balancing valve, cooled water can be mixed in in certain doses and given proportions.
This will ensure the precisely specified temperature of the coolant entering the TP tubes through the manifold.
This is the most effective and most comfortable scheme. The pumping and mixing unit itself can be assembled in various variations.
Depending on your needs and financial capabilities, the following components may be included:
How to connect
If you have not worked with plumbing before, then you should not take on such work - there are too many serious consequences if you make mistakes. Moreover, heated floors can be made from different materials, which require special tools to work with. If you are confident in your abilities, then you can act according to the instructions that we will now provide. We will connect the circuit already built into the screed to a two-pipe heating system. For this we need:
- A regular tap that we will install for supply. It will, if necessary, disconnect the heated floor from the system.
Radiator tap "male-male" - We will install an RTL valve on the return line, the operating principle of which we described earlier. It will be equipped with a thermal head that measures the temperature of the water in the circuit. Do not confuse it with a radiator head, which measures the heating of the air in the room.
RTL valve for return
Table 1. Connecting heated floors.
| Steps, photo | Description |
| We turn off the heating taps to stop the circulation of coolant in the system. After it has cooled, if it was hot, cut the pipes with special scissors. There are different ones for each type of pipe. In our example, the master works with reinforced polypropylene - all connections are made by hot soldering. The pipes are cut into tees, from which two outlets are made upward. As you can see, from the return pipe the master laid a multi-joint elbow to carefully bypass the upper pipe, and on the supply he limited himself to a tee with a thread for the tap. |
| Before soldering the bend from the elbow, he made a vertical level marking, along which he screwed a clip-retainer for the plastic pipe |
| Next, the bend is attached to the elbow using a soldering iron, as shown in the photo above. After that, it is fixed in the clip, and you get a precisely drawn thread into which we will screw the tap. |
| We install both taps, tightening all connections securely. We use only sanitary flax as a sealant. There can be no talk of any fum tape. Advice! On the RTL tap there is a mark indicating the direction of movement of the coolant in the form of an arrow - be sure to check this point during installation. |
| PEX leads with internal thread for return and external thread for supply are mounted on the terminals of the plastic pipes of the heated floor circuit so that they can be connected to the taps. These conclusions are made at the same level as the conclusions on the heating pipes. |
| Next, we screw the connecting corrugated stainless steel hose (inlet) onto the nuts - we connected the return line. We proceed in the same way with the coolant supply tap. |
| We screw the thermal head to the RTL tap. In our example, the master uses equipment from the Austrian company Herz, which can regulate the temperature within 25-60 degrees Celsius. |
Prices for heating cable and components
Heating cable and accessories
This concludes our article. Do it right, do it wisely, and the result will always please you.