The sun is a virtually inexhaustible source of energy for the Earth. However, people use only a small part of it. Today the issue of energy saving is especially relevant.
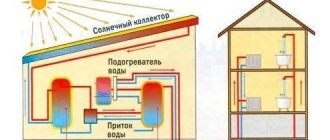
The operating algorithm of the solar collector is based on the transformation of solar radiation energy into thermal energy. This is done with the help of a coolant that heats up in the collector, which transfers the accumulated energy to the heating or hot water supply system. Typically, this coolant is water; in some cases, antifreeze is also used.
Therefore, special devices are increasingly being put into operation that make it possible to direct solar energy to solve practical problems. One such device is a solar collector. It can be effectively used for heating or hot water purposes.
In order to choose the right solar system and make the most of its capabilities, you need to understand the principle of operation of a solar collector for heating a house and hot water supply.
Advantages of solar collectors and solar systems from Oventrop
Economical.
Solar collectors significantly reduce the cost of hot water supply and heating the cottage during the cold season. The use of solar power plants reduces the annual cost of heating water by up to 60%, and the cost of heating a building by up to 30%;
Ecological cleanliness.
The solar collector is absolutely safe, because... does not pollute the environment and does not have a negative impact on human health. In addition, in water exposed to high temperatures and vacuum, the appearance and spread of bacteria becomes impossible;
Long service life.
The reliability and durability of Oventrop solar collectors is due to the use of modern high-quality materials. The glass and metal elements of the solar installation are impact-resistant and resistant to sudden changes in weather, in particular gusts of wind;
Autonomy.
A solar system can heat buildings even in the event of long-term interruptions in the heating system. A similar situation occurs when hot water is turned off.
Application specifics
Unlike heat generators and heat pumps, which convert energy from groundwater and air masses warmed by the sun, solar collectors operate from direct sunlight acting on their surface. The only nuance of solar collectors is that at night they are in passive mode.
The daily performance of a solar installation is influenced by factors such as:
- Length of daylight , which in turn depends on the geographic latitude of the region and the time of year. So, for example, in the central part of Russia, the solar collector will function at its maximum in summer, and at its minimum in winter. This is due not only to the length of the day, but also to the change in the angle of incidence of sunlight on the solar panels;
- Climatic features of the region. As a rule, on the territory of our country there are many areas over which for more than 200 days a year the sun is hidden behind layers of clouds or behind a veil of fog. Despite the fact that the solar collector can capture even scattered sunlight, in cloudy weather its productivity is significantly reduced.
Stagnation of the system
Let's talk a little more about the problems associated with an excess of generated heat. So, let’s assume that you have installed a sufficiently powerful solar collector that can completely provide heat to the heating system of your home. But summer came, and the need for heating disappeared. If you can turn off the power supply to an electric boiler, or turn off the fuel supply to a gas boiler, then we have no control over the sun - we cannot “turn off” it when it gets too hot.
System stagnation is one of the main potential problems of solar collectors. If not enough heat is taken from the collector circuit, the coolant overheats. At a certain moment, the latter may boil, which will lead to the cessation of its circulation along the circuit. When the coolant cools down and condenses, the system will resume operation. However, not all types of coolants easily tolerate the transition from liquid to gaseous state and back. Some, as a result of overheating, acquire a jelly-like consistency, which makes further operation of the circuit impossible.
Only stable removal of the heat produced by the collector will help to avoid stagnation. If the calculation of equipment power is done correctly, the likelihood of problems occurring is almost zero.
However, even in this case, the occurrence of force majeure cannot be ruled out, so methods of protection against overheating should be provided in advance:
1. Installation of a reserve tank for storing hot water. If the water in the main tank of the hot water supply system has reached the set maximum, and the solar collector continues to supply heat, a switch will occur automatically and the water will begin to heat up in the reserve tank. The created supply of warm water can be used for domestic needs later, in cloudy weather.
2. Heating the water in the pool. Owners of houses with a swimming pool (whether indoor or outdoor) have an excellent opportunity to remove excess heat energy. The volume of the pool is incomparably larger than the volume of any household storage tank, which means that the water in it will not heat up so much that it will no longer be able to absorb heat.
3. Drain hot water. If it is not possible to use excess heat profitably, you can simply drain heated water from the hot water storage tank into the sewer in small portions. The cold water entering the container will lower the temperature of the entire volume, which will continue to remove heat from the circuit.
4. External heat exchanger with fan. If the solar collector has a high productivity, the excess heat can also be very large. In this case, the system is equipped with an additional circuit filled with refrigerant. This additional circuit is connected to the system via a heat exchanger equipped with a fan and mounted outside the building. If there is a risk of overheating, excess heat enters the additional circuit and is “thrown out” into the air through the heat exchanger.
5. Discharge of heat into the ground. If, in addition to the solar collector, the house has a ground source heat pump, excess heat can be directed to the well. In this case, you solve two problems at once: on the one hand, you protect the collector circuit from overheating, on the other, you restore the heat reserve in the ground that has been depleted over the winter.
6. Isolation of the solar collector from direct sunlight. This method is one of the simplest from a technical point of view. Of course, you shouldn’t climb onto the roof and curtain the collector manually - it’s difficult and unsafe. It is much more rational to install a remotely controlled barrier, like a roller shutter. You can even connect the damper control unit to the controller - if the temperature in the circuit rises dangerously, the manifold will close automatically.
7. Drain the coolant. This method can be considered radical, but at the same time it is quite simple. If there is a risk of overheating, the coolant is drained through a pump into a special container integrated into the system circuit. When conditions become favorable again, the pump will return the coolant to the circuit and the operation of the collector will be restored.
Operating principle and device features
The main element of the solar collector is the adsorber. It consists of a copper plate with a pipe attached to it. When absorbing the energy of direct sunlight acting on the solar system, the adsorbing element instantly heats up, transferring heat to the coolant circulating through the pipeline.
The type of surface of the collector determines its ability to reflect or absorb solar rays. For example, a device with a mirror surface perfectly reflects light and heat, while a black plate completely absorbs it. Consequently, for maximum efficiency, the copper plate of the adsorber is most often coated with black paint.
To also increase the amount of thermal energy emitted from the sun, it is necessary to wisely choose the glass covering the adsorber. For solar collectors, special glass with anti-reflective coating and a minimum percentage of iron contained in it is used. Such glass differs from ordinary glass not only in the reduced proportion of reflected light, but also increases transparency.
In addition, to prevent contamination of the glass, which also reduces the efficiency of the solar installation, the collector body is completely sealed or filled with inert gas.
At the same time, the adsorber plate releases part of the received thermal energy into the environment, heating the air interacting with the solar system. To reduce heat loss, the adsorbent element should be insulated. The search for the most effective methods of thermal insulation has led to the emergence of many types of solar collectors. Some of the common types are flat and tubular, or vacuum.
DIY absorber
You can make a flat absorber for a solar system with your own hands at home. First, you need to make a collector from a copper pipe through which the liquid will circulate. You can bend the pipe with a snake or solder the collector in the form of a ladder.
In terms of price, steel tubular heating radiators are cheaper than bimetallic and cast iron ones.
Read about the distance between the radiator brackets here.
Then you need to cut out a sheet of tin of the required size. The collector is placed on this sheet and soldered. You need to make several such elements (3-4 pieces) and connect them together. It turns out that the absorber will have 4 pipes for coolant supply and 4 for return. All layers of the absorber can be assembled into a single structure by connecting the pipes in series or in parallel. With a series connection, the water will spend more time in the collector and, accordingly, will heat up better.
The absorber must be painted with matte black paint and placed in the housing. To reduce heat loss, foam is placed on the bottom of the housing. All joints must be sealed, and the materials must be resistant to moisture. Do not forget that the solar system will always be located outside.
Flat solar collectors: device
A flat-type solar collector consists of an aluminum box, on top of which a protective glass with an absorption layer is installed. Inside the housing there are copper tubes, inlet and outlet pipes. The bottom and walls of the box are protected by the most reliable heat-insulating element - mineral wool.
Some models of flat-plate collectors may also have a layer of propylene glycol under the glass, which acts as a solar absorber. This increases its efficiency, providing the equipment with maximum performance regardless of the season.
Advantages and disadvantages of flat solar collectors
The main advantages of flat solar collectors include:
- The ability to self-clean in the event of precipitation in the form of snow or frost;
- High indicators in the price/quality ratio, which is typical for southern regions with a warm climate;
- High efficiency when operating in the summer season;
- Relatively low cost in contrast to other solar structures.
The main disadvantages of such systems are:
- High heat losses due to the design features of the installations;
- Low efficiency when operating in autumn and winter;
- Difficulties during transportation and installation of solar systems;
- Maximum costs in case of repair work;
- Increased windage of the solar installation.
Scope of application of flat solar collectors
Despite the disadvantages, this type of solar system is used for seasonal heating of hot water. Flat solar collectors are used:
- For hot water supply for summer showers;
- To heat the water in the pool to the desired temperature;
- For heating greenhouses.
FAQ
Do I need to obtain permission to install a solar collector in my house?
No. Permission from regulatory organizations is not required for the installation of solar systems. However, it is better to leave the installation to professionals.
Is it possible to use a collector with natural coolant circulation in the middle zone?
Devices with passive circulation are more suitable for the south. In regions with harsh climates, it is more advisable to use forced circulation systems.
Vacuum solar collectors
A vacuum solar collector is a high-tech complex device designed to collect thermal solar energy and its subsequent processing into thermal energy, which is used in everyday life and industrial applications to provide heating and water heating in water supply systems. The solar vacuum collector is highly efficient and ergonomic, has high efficiency even in low light conditions and low temperatures, which makes it possible to use the system at any time of the year. The device allows you to convert infrared radiation penetrating through clouds and scattered rays into heat. Oventrop solar collectors are capable of heating water up to one hundred degrees Celsius even at subzero ambient temperatures.
Scope of application of vacuum solar collectors
The use of the design significantly reduces heating costs in the winter and guarantees free water heating in the summer. The solar collector actively absorbs solar energy and captures 98% of the energy when the vacuum degree is 10-. The systems are installed on facades, flat or pitched roofs. When located in arbitrary places, the angle of inclination should be in the range of 15-750. Service life is at least twenty years.
The systems are widely used for:
- heating water in domestic and industrial water supply systems, swimming pools;
- operation of individual heating systems;
- heating greenhouses.
Collectors are easily connected to water and heat supply networks. To connect the system, a Regusol X Duo station with a built-in heat exchanger and controller is used, which, thanks to the layer-by-layer accumulation of coolant, increases the efficiency of the entire energy system.
Solar energy is an alternative heat source
The idea of using solar energy for heating is not new. Moreover, the feasibility of its use has been proven by the Americans, Chinese, Spaniards, Israelis and Japanese.
The market is replete with offers of various installations for converting solar energy and its further use for economic needs.
Solar systems are actively used as the main source of heat in many countries around the world. In our latitudes it is still used as an addition to the heating system
The cost of systems depends on their type, area, and material used in manufacturing. From year to year there is a steady downward trend in prices for all types of solar installations - solar systems.
This makes them more accessible to a wider population. But not everyone is ready to make such a purchase yet.
But, if you wish, you can build an effective solar heating system with your own hands, spending significantly less money.
Image gallery
Photo from
Pros of using solar energy
Functions and purpose of solar collectors
Solar panel based on photocells
Installation of solar heating elements
A conventional heating system that has performed its functions perfectly for many years is becoming more and more expensive. The reason for this is the global rise in prices of energy resources throughout the world. The owner’s natural desire is to save on heating, which eats up a significant share of the family budget.
So, a solar heating system can fully replace the usual solid fuel, gas or any other. It all depends on the type and size of the room in which it will be used.
An option suitable for a granary will not be suitable for a residential building, and a system that satisfies the needs of a summer house cannot cope with the heating of a 2-story mansion.
Completely replacing traditional heating with solar is sometimes problematic. The owner is afraid that the system may not cope or there is not physically enough space to install the required number of panels.
Therefore, they often use a combined heating system without completely abandoning the installed gas (electric or other) equipment. The level of replacement of conventional heating with solar can reach 90%.
Also, the annual number of sunny days of the area in which the home is located is important. Moreover, the average daily temperature is not so important. Many installations effectively absorb light on frosty winter days (solar collectors using antifreeze as a coolant).
In addition to heating, a solar installation can provide a home with warm water and electricity.
Solar collector installation
The efficiency of the design directly depends on the correct installation of the collector. To avoid the risk of pressure increase due to water overheating, solar collector calculations are performed exclusively in special programs. Calculations are made taking into account weather conditions at the point where the collector is located and the average annual heat consumption. The power of the solar corrector is calculated based on the area data, the insolation value of the system and the efficiency of the collector.
Before starting calculations, it is determined whether the system will be year-round or seasonal.
- Seasonal solar correctors are intended for use during the warm period of the year (mid-April - mid-October). This design consists of a storage tank and a collector. The coolant is water, which freezes at subzero temperatures, so its use in the cold part of the year is impossible.
- Year-round systems can be used effectively regardless of the ambient temperature. The design uses non-freezing ethereal liquid, which ensures high efficiency of the solar collector even on the coldest days of the year.
Vacuum solar collectors, with proper installation and installation, cover up to 60% of the average family in hot water and provide heating from the second half of spring to mid-autumn. For example, when installing a system in the middle latitudes of Russia, a collector with an area of two square meters provides daily heating of one hundred liters of water to 40-600.
The efficiency of the installation in the summer is much higher. In one clear day, 1 m2 of collector will warm up about eighty liters of water to a temperature of + 650. The average annual productivity of a solar collector with an absorbing area of 3 m2 will be in the range of 500-700 kW/h per 1 m2.
Review of the best models
The best collectors
Among flat designs, the FPC-2200 is considered the best. This device has an active area of 2.1 square meters. The efficiency, if the product is installed correctly, will reach 94%. With its help, you can reach a coolant temperature of 135 degrees, the highest pressure in the system will be 1 MPa. Installation without a frame is prohibited. Costs about 30 thousand rubles.
He considers SOLARVENTI SV3 to be the best air collector; it is capable of working completely autonomously. Designed not only for residential premises, but also for warehouses, various other technical premises. The maximum area that it can heat is only 25 square meters. The product is compact in size, weighs about 6 cm, and can be installed in both horizontal and vertical positions. It is quite expensive - 40 thousand rubles.
To date, vacuum models are not represented on the Russian market. Such a collector will be a good addition to the standard heating system of a house or apartment.
Construction of a vacuum solar collector
Oventrop offers vacuum solar collectors with heat pipes. Systems with a heat pipe are structurally reminiscent of a thermos: a glass/metal tube of larger diameter is inserted into another one of smaller diameter. The space between them is evacuated, which ensures the most effective thermal insulation from the effects of external temperatures and minimal losses due to radiation. The vacuum layer allows you to save up to 95% of the absorbed thermal energy.
All evacuated tubes are equipped inside with copper absorber plates with a heliotitanium coating that effectively collects solar energy. A heat pipe filled with a special ethereal liquid is installed under the absorber and connected to a condenser located in the heat exchanger. The solar energy received by the absorber turns the liquid into vapor, which rises into the condenser and gives off heat to the collector, condenses and returns to the lower part of the flask. Thanks to cyclicity, a continuous heat exchange process is created.
The system is capable of generating significant temperatures and provides high efficiency even in low light conditions and temperatures of -30 - -450C (depending on the type of collector with glass or metal tubes). Vacuum solar collectors are simple and inexpensive to operate. Special design connections allow tubes to be replaced or rotated in a filled, pressurized installation.