Elimination
If you notice that the bottom is significantly colder than the top, then urgent action is required. It is necessary to follow the following algorithm to find the cause:
- Checking the correct connection.
- Inspect the radiator, bleed and clean it.
- Assess the condition of the control valves.
- Check the pipes.
- Determine the type of heating system, install or replace the circulation pump.
The first step is to check the correct connection. To do this, it is necessary to estimate the temperature of the lower pipe. If the return and supply were connected incorrectly, it will be hot. You will need to reconnect and build the circuit correctly. When connected correctly, this element remains slightly warm.
Often the cause is an air lock in the battery, which does not allow the coolant to spread throughout the radiator. The design must include a Mayevsky valve or bleeder for air removal. It is necessary to shut off the supply, open the drain and remove all air and batteries. After the tap is turned off, the heating valves are turned. In some cases, this procedure turns out to be effective.
If an adjustment valve is installed in the system, then there is a high probability that the problem is there. It is necessary to dismantle this element and carry out an inspection. If the section is narrowed, you will need to expand it using specialized tools. But it is better to purchase a higher quality part and reinstall the tap into the system.
I will describe my problem in detail, since the mechanics of the local management company shrug their shoulders, and I myself cannot understand what the reason is ((And it all started like this: We have 2 risers in our apartment - one in the hall, the other in the kitchen, which is connected through crosspieces in the kitchen and children's room. Last year everything was changed to propylene from the basement, we have a second floor, there is a bank below us, there are 2 more floors above us, the neighbor in the 5th compartment has his own apartment and is heated independently. Riser systems are based on the "supply-return" system , last year they worked well, and this year, as soon as the heating was turned on, everything was fine. It worked for a month without interruptions, the return and supply were hot. 2 weeks ago the return cooled down, and then the pipes completely cooled down. They gave a request, a mechanic came, He said that we need to wait for the cold weather, that maybe the boiler room is not adding pressure or whatever. I go upstairs to my neighbor - there is circulation above me, both risers are hot, return and supply. I go up to my neighbor on the 4th floor - everything is there, both risers heat perfectly. I am perplexed - why am I having a problem on the second floor? I think maybe something is clogged? But the pipes are new, sawn everywhere - what could be there? I don't understand. A mechanic comes, lowers something in the basement, and the risers begin to heat up. They heat up normally, cool down after 15 minutes. There is no airing, I constantly bleed through Mayevsky - only water comes out, no air. Yesterday I shut off the American 3/4ths in front of the battery, removed it, washed it (Sandital radiators, aluminum with anti-corrosion coating), put it in place (first I drained the water from the riser - both from the return and from the hot one in case there was something there got into trouble), filled it with water - the supply and the upper part of the battery began to heat up. I turn off the supply, release the return through the battery - it starts to heat up, I stop draining - it cools down. Thus, the upper half of the battery worked until 23:00, then it began to cool down. This morning the mechanic came again, threw up his hands and went up to the neighbor: everything was fine with him. As a matter of form, he went down to the basement and pumped something there - it began to circulate, then died out again. In general, help me solve the puzzle! I can't figure out what's wrong:
- Everything worked for 1.5 months, there was circulation. Return and feed worked.
- Two weeks ago everything disappeared, but only here, on the second floor. The neighbors above have everything.
- There is no blockage or clogging in the radiators, and no in the risers either.
- There is no circulation. What the heck? We didn’t change anything structurally, the circuit worked the same way last year, everything was warm!
- The housing department said that some residents also have this problem, which means I’m not alone. But they may just be airy.
- There is no airiness, everything is lowered 100 times through Mayevsky and removing the batteries.
Quite often in residential apartment buildings during the heating season you can encounter the following problem: the riser is hot, but the radiators are cold. This applies to both new buildings and old houses. Residents in most cases do not know how to cope with such a situation. That is why their attempts to repair the heating system on their own do not lead to the desired result. In this matter, you definitely need help or advice from a specialist. After all, only a person who has the necessary knowledge and experience can solve the problem of why the pipes are hot and the radiators are cold.
In a heating radiator, the top is hot and the bottom is cold. What to do?
If the top of the heating radiator is hot and the bottom is cold, this indicates that it is not functioning correctly. In this case, it is necessary to look at the entire heating system and, of course, the radiator itself. Let's figure out what the problem might be here.
Typically, this problem occurs if any work has been done on the heating system, including when changing the radiator. There may be two problems here. Either there is an air lock in the heating radiator, or the taps on the heating radiator are clogged. The reasons may be different, including incorrect starting of the heating system or heating radiator.
Now let's figure out how to fix this defect. There are two options. Let's start with something simple. As mentioned earlier, the reason for such operation of the heating radiator in 99% of cases is an air lock. To remove it using the first method, there must be a Mayevsky tap or drain on the battery. It is installed instead of the top plug.
What should be done? It is necessary to close the connection to the heating radiator - this is the top pipe. Leave the return line open. Next, open the bleeder and wait until all the air comes out of the battery. Then close the drain and open the feed. Often such a simple manipulation helps.
What to do if there is no drain in the heating radiator or the previous method does not work? For apartment buildings with a central heating system, the answer is clear: call a locksmith. For those who have an individual heating system, the work procedure is as follows.
First, you need to turn off the supply. Open the drain at the top point of the heating system and use return pressure to squeeze out all the air from the system. If we are talking about dumping air from one riser, then you can turn off the supply only on it. But at the same time, there must be a drain on this riser.
Bottom of radiator is cold
No circulation, heating failure - why
Failure in the heating system, deficiencies, imperfections, all lead to cold radiators.
If there is no coolant circulation, then the reason needs to be determined. Most often, the answer to why the heating does not work is on the surface, obvious. Let's look in order at the main causes of heating malfunctions, why water does not circulate through the pipes, and what needs to be done first.
Let's start with the simplest and most obvious reasons.
It's clogged and clogged.
Every heating system must have a coarse filter. A very small device with a fine mesh and a sump (installed downwards! or at least to the side) saves equipment, pumps, and the boiler from coolant contamination that will be present in any system. Wood shavings, broken threads, rust, water sediment…. everything is retained by the mesh in the filter.
The sedimentation tank must be periodically untwisted and the mesh cleaned.
If the circulation in the heating system of a private house is disrupted, then the first thing you need to do is check the filter, which should be installed on the return line in front of the boiler.
Air in the system, airing
Airing can occur in any closed piping system where air removal measures have not been taken. Air is always present in the coolant, including in a dissolved state, is released during pressure changes, and accumulates at the highest points. Including in the boiler.
Automatic air vents are installed at characteristic, highest points of the system, as well as on collectors and special separators - the normal circuit is equipped with a special air catching device in which air bubbles are released from the coolant.
In addition, Mayevsky valves (manual air vents) should be on each radiator, and also possibly in other elevated places.
Checking the air supply, bleeding the air, installing air vents are common actions if circulation stops and the batteries are cold.
The circulation pump does not work
In private homes, the reason why the heating system stops working is a breakdown of the electrical equipment that controlled the movement of the coolant through the pipes.
If the heating suddenly stops working, then you need to check the functionality of the circulation pump near the solid fuel boiler or the pump in the automated boiler. In addition, the same unit can be installed in each circuit, which must work properly.
Bad polypropylene pipes
Often the consumer (customer) believes that polypropylene pipes are absolutely reliable and cannot cause heating problems or cold radiators.
But polypropylene is much more insidious than old steel or metal-plastic pipelines. Each place of soldering (welding) is a potential increased resistance in the system or a cause of cessation of circulation (weakened movement of water through the batteries), due to deposits of material inside.
It is impossible to control the quality of connections from the outside; all that remains is to cut out pieces, resolder, and remake polypropylene pipes.
Poor performance of a polypropylene system is a real problem for the home installer. Good professionals don’t take on this material at all.
Bad project
It is not uncommon for poor circulation to occur where there is poor design. Typically, the batteries are not connected correctly, according to some sequential circuit, where the last battery in the circuit receives much less coolant.
Another bad design is single-pipe circuits, where it is also difficult to establish the necessary coolant circulation through each battery.
If the radiators do not heat up evenly, or there is poor coolant circulation on individual heating devices, first of all you need to consider how the connection corresponds to the classic circuits - shoulder, associated, radial. It is necessary to bring home heating to normal design standards, and then expect good circulation and uniform heating of the radiators.
Small diameter, overgrown pipes
Old steel pipes become overgrown with rust and deposits from the inside, their throughput capacity decreases significantly over time, and there is only one solution - they need to be replaced with modern ones.
But even during installation, for the sake of economy, mistakes can be made with the choice of pipeline diameter - on mains, on groups of heating devices, diameters of 16 or 20 mm can be installed. The result is noise in the pipes, excessive consumption of electricity, and insufficient coolant flow. What pipe diameters should you choose?
A complex system
A type of bad design is an incorrectly designed complex heating system consisting of many heating circuits and several boilers. Here entire circuits will not work correctly if the work of one affects the neighboring one.
As a rule, one boiler (the backup one does not count) and three circuits - boiler, radiators, heated floors with their pumps are coordinated normally, and no questions arise. But if you connect another working boiler plus a circuit (for example, heating a garage and greenhouse), then the system will become complex. It is difficult to say how the coolant will circulate in it without equalizing the pressures at the connection points.
In complex systems, a competent design is important, installing a hydraulic arrow or an equal pressure ring; more information about the hydraulic separator can be found here
No balancing
Many home heating schemes involve balancing; balancing and control valves are installed in them. For example, between floors, between shoulders, and for each radiator. The taps cover the direction with less hydraulic resistance; accordingly, more coolant will flow to other points.
Children can play with the taps. Or the system is initially unbalanced. Setting up, as a rule, is no problem, you just need to find this tap... How to set up home heating
Neighbors don't provide heat
But complex heating project schemes are of little concern to residents of high-rise buildings, who have a separate riser for each radiator in the apartment. And if any radiator stops heating up normally, it means there is no circulation through the riser, therefore...
You need to contact the heating network, housing office (service organization) to adjust the power in the risers, and if this does not help, then with the requirement to check the neighbors.
Methods for installing return flow in a heating system
Radiators used in heating are made using excellent technologies from different materials, known varieties are steel panel, bimetallic (sectional) made of steel and aluminum, tubular, slightly reminiscent in appearance of old cast-iron radiators. For connection, three methods are used to connect their outlet pipes to pipes.
Lower
In modern cottage-type houses or dachas, it is fashionable to use heating of rooms with heated floors without the use of radiators that degrade the aesthetic appearance of rooms and take up a certain area. Most often, a combination of two methods of heating rooms using floors and radiators is used, while in order to level the floor levels on the entire floor, the pipeline leading to the radiators is placed in a screed. Pipe outlets are mounted from the floor or wall at a low height, to which the radiator is then connected using an N-shaped unit (binoculars). In addition to ease of connection, this liner has an aesthetic appearance, and when placed in the walls it creates additional advantages when cleaning rooms and washing floors.
A special bottom connection unit is used in one-pipe and two-pipe distributions; one of the single-pipe varieties, “Leningradka”, used for horizontal placement, has also become widespread.
Schemes with lower piping, despite their aesthetic appearance, have a significant drawback, which is weak heating of the upper part of the radiator and, accordingly, 20% less heat transfer. To eliminate this phenomenon, some lower connection units have an external bass-pass connected to the upper pipe - this is how more efficient carrier liner.
Rice. 11 Where is the supply and return in a heating system with bottom supply
Lateral
The most common, but not very effective method in terms of heat transfer, is used in all heating systems of apartment buildings, gravity circuits of individual houses and cottages, the hot coolant enters the upper radiator pipe, and the return flow exits through the lower pipe in the same plane.
In apartment buildings, when the coolant is supplied from above, its temperature decreases as it passes through the entire circuit, and the radiators below emit less heat. Therefore, to equalize the temperatures on the lower floors, the number of radiator sections is increased compared to the upper ones, but they are often faced with the main disadvantage of the side connection system - poor heating of the most distant sections.
There are not too many methods to combat this phenomenon; in addition to increasing the diameter of the supply pipes, they use homemade flow extenders in the form of a regular tube, inserted into the inlet radiator pipe and directing the main coolant flow to remote sections.
Rice. 12 Supply and return in a heating system with side, diagonal and bottom connections
Diagonal
As mentioned above, the side connection does not always cope with sufficient heating of extended radiators along the entire length; in this case, diagonal connections come to the rescue. When organizing the supply diagonally, the coolant from the boiler enters the upper radiator pipe and exits into the return line through the outlet located below at the opposite end.
Diagonal connection is very often used for single-pipe and two-pipe connections in individual houses; compared to other types, it ensures maximum heat transfer from radiators.
Rice. 13 Options for side cross (diagonal) and bottom eyeliner
You might be interested: Do-it-yourself heating in a private house from polypropylene pipes
Causes of heating problems
Most residents of city apartments believe that they have no need to know the structure of engineering systems. Any central heating problems that arise in their high-rise building must be resolved by the employees of the management company. And it is right. It is better if only one responsible owner is involved in all matters. Indeed, in an apartment building, problems with heating often arise precisely because of unauthorized interventions in the smooth functioning of the heating system.
But individual homeowners are forced to understand problems with heating in a private home and keep the situation under control. The owner of the house must know at least in general terms about the causes of problems and be able to correct them.
The following reasons can lead to problems with the heating system:
- the system is not properly designed;
- equipment does not meet design requirements;
- the system was unbalanced due to unauthorized connections;
- installation was performed poorly;
- air pockets interfere with coolant circulation;
- radiators are installed incorrectly;
- pipelines have become unusable;
- the tightness of the connections is broken.
Let's take a closer look at each of these reasons and ways to eliminate heating problems in an apartment and in a private house.
Signs of poor heating
When rooms are not heated enough in winter, you can feel it right away. Problems with heating in an apartment make themselves felt by discomfort for the inhabitants, the appearance of dampness on the walls and strange noises spreading through metal pipelines throughout the entire house.
Problems that arise with the heating system can be characterized by a number of symptoms:
- the system as a whole is functioning poorly;
- the heat supply on different floors is not the same;
- radiators in one room are hot, in another barely warm;
- the “warm floor” system warms up unevenly;
- noise and seething in the pipes is heard;
- Coolant is leaking from pipes or radiators.
Operating pressure in the heating system
Working pressure is considered to be the pressure whose value ensures optimal operation of all heating equipment (including the heating source, pump, expansion tank). In this case, it is taken equal to the sum of pressures:
- static - created by a column of water in the system (in calculations the ratio is taken: 1 atmosphere (0.1 MPa) per 10 meters);
- dynamic - due to the operation of the circulation pump and the convective movement of the coolant when it is heated.
It is clear that in different heating schemes the operating pressure will differ. So, if natural circulation of the coolant is provided for heating the house (applicable for individual low-rise construction), its value will exceed the static value by only a small amount. In forced schemes, it is taken as maximum permissible to ensure higher efficiency.
Numerically, the working pressure is:
- for one-story buildings with an open layout and natural circulation of water – 0.1 MPa (1 atmosphere) for every 10 m of liquid column;
- for low-rise buildings with a closed layout - 0.2-0.4 MPa;
- for multi-storey buildings - up to 1 MPa.
Pressure, water speed and return temperature in the heating system
Basically, the requirements for heating systems imply dividing the specifics of heating into two types:
- independent, here the source of heat energy is located directly in the room - used in an individual house or in multi-storey buildings of an elite type;
- dependent, where a network of pipelines is connected to the heating complex - used in most houses in the urban area and urban-type settlements.
Due to the specific nature of the circulation of the coolant, water is predominantly used, where the speed of water in the heating system directly affects the temperature in the radiators. Circulation is divided into natural (based on the principle of gravity) and forced (heating system using a pump). According to distribution, it is customary to distinguish between a heating system with lower and upper pipe distribution.
Temperature
Despite the wide selection of heating systems provided, the options for heat supply and return are quite limited. The maximum temperature in the heating system must also be set according to the rules in order to avoid further malfunctions.
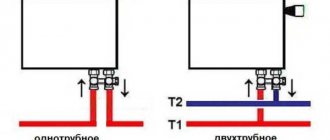
Radiators are connected to the heating system in one of three ways: bottom, side or diagonal.
Also, the lower connection is also called differently: “Leningradka”, saddle. According to this scheme, the return and supply are installed at the bottom of the battery. In most cases, it is used when pipes are laid under the baseboard or under the floor surface. The return temperature in the heating system should not differ from the supply temperature.
Water speed
If there are few sections, heat transfer will be extremely ineffective compared to other schemes - the speed of water in the heating system decreases, which leads to heat loss.
Side heating is the most popular type of connecting radiator batteries to heating. The supply of water as a heat carrier is carried out in the upper part, and the return is connected from below, so that the return temperature in the heating system is considered equal.
To avoid a decrease in the efficiency of this type of connection when increasing the radiator sections, it is recommended to install an injection tube.
Pressure
The diagonal type of connection is also called a side cross circuit, because the water supply is connected at the top of the radiator, and the return is organized at the bottom of the opposite side. It is advisable to use it when connecting a significant number of sections - with a small number, the pressure in the heating system increases sharply, which can lead to undesirable results, that is, heat transfer can be halved.
To finally settle on one of the options for connecting radiator batteries, you must be guided by the methodology for organizing the return flow. It can be of the following types: single-pipe, double-pipe and hybrid.
The option you should choose will directly depend on a combination of factors. It is necessary to take into account the number of floors of the building, where the heating is connected, the requirements for the price equivalent of the heating system, what type of circulation is used in the coolant, the parameters of the radiator batteries, their dimensions and much more.
Most often, their choice is made on a single-pipe heating pipe layout.
As practice shows, such a scheme is used precisely in modern high-rise buildings.
Such a system has a number of characteristics: they are low in cost, fairly easy to install, and the coolant (hot water) is supplied from above when choosing a vertical heating system.
Also, radiators are connected to the heating system in series type, and this, in turn, does not require a separate riser for organizing the return. In other words, water, having passed the first radiator, flows into the next, then into the third, and so on.
However, there is no way to regulate the uniform heating of radiator batteries and its intensity; high coolant pressure is constantly recorded in them. The further the radiator is installed from the boiler, the more heat transfer decreases.
There is also another wiring method - a 2-pipe scheme, that is, a heating system with return. It is most often used in luxury housing or in individual homes.
Here is a pair of closed circuits, one of them is intended for supplying water to parallel-connected batteries, and the second is for draining it.
Hybrid wiring combines the two schemes described above. This could be a collector circuit, where an individual wiring branch is organized at each level.
What Causes Return Problems?
Of course, first of all, you should consider what reasons may cause problems with the return line.
These include:
- Poor water pressure;
- Inappropriate pipe diameter (less than the established norm) through which water is supplied;
- Improper installation and installation of pipes;
- System clogged.
When a cold return is detected, it is recommended to first pay attention to the water pressure inside the system. In order for the return to work as it should, the system must be designed in such a way that water continuously circulates within the circuit.
When the speed of water pushing decreases, the coolants will not be able to push cold water through in a timely manner. This in turn will cause the batteries to cool down. Rooms on the upper floors of houses are most susceptible to the problem of insufficient water pressure.
The second most common problem is a clogged system. Unfortunately, cleaning of heating pipes in multi-storey buildings is carried out much less frequently than required by the rules. Consequently, sediment settles inside the pipes, which over time clogs the circuit and causes poor water permeability, significantly reducing its speed.
It is believed that the most problematic reason is poor heating installation. That is, when an inexperienced beginner takes on the installation and laying of pipes, without the necessary knowledge, there is always a risk that he may make a mistake somewhere or select elements that do not fit together in size. That is why it is advisable to seek the services of specialists.
Control of operating pressure in heating circuits
For normal, trouble-free operation of the heating system, it is necessary to regularly monitor the temperature and pressure of the coolant.
To check the latter, deformation pressure gauges with a Bourdon tube are usually used. To measure small pressures, their varieties can be used - diaphragm devices.
Figure 1 – Strain gauge with Bourdon tube
In systems where automatic control and regulation of pressure are provided, various types of sensors are additionally used (for example, electric contact).
- at the inlet and outlet of the heating source;
- before and after the pump, filters, mud traps, pressure regulators (if any);
- at the exit of the main line from the thermal power plant or boiler house and at its entry into the building (with a centralized scheme).
Figure 2 – Section of the heating circuit with installed pressure gauges
Poor quality installation of the heating system
It happens that a new, recently installed radiator does not want to heat up.
Others in the system before and after it heat up normally, but this one does not. The reason is poor coolant circulation. The reason for the problem with the heating radiator could have been an oversight by the installer. Probably, when welding a polypropylene pipe, he overheated it too much, and as a result of melting, the internal diameter decreased. In such cases, the installer is obliged to redo his poor-quality work free of charge.
To avoid problems with the heating system, all pipes and fittings included in its composition must be a securely installed structure.
The boiler is working, but the radiators are not heating, why is there cold return in the heating system?
The heating system is a complex structure consisting of several elements combined into one circuit and put into operation through a chain reaction.
What is return in a heating system?
The return is a coolant located inside the heating system. During operation, it passes through all heating devices and gives off heat to them. Then, already cooled, the coolant returns to the boiler, where it is heated and begins a new cycle.
Photo 1. Heating diagram with a circulation pump and expansion tank. The arrows show the movement of the coolant.
Both ordinary water and antifreeze act as a coolant. It is put into operation either naturally (under the influence of gravity) or forcibly (using a pump).
Causes of problems with return flow in the batteries of a private or apartment building
- insufficient water pressure in the system;
- small section of the pipe through which the coolant passes;
- incorrect installation;
- airiness or contamination of the system.
If a problem with cold return occurs in an apartment, then the first thing you should pay attention to is the pressure. This is especially true for rooms on the upper floors. The fact is that the principle of operation of the return flow is to quickly and continuously circulate liquid through the system
And if its speed drops, then the coolant will not have time to push out cold water and the batteries will not heat up
The fact is that the principle of operation of the return flow is to quickly and continuously circulate liquid through the system. And if its speed drops, then the coolant will not have time to push out cold water and the batteries will not heat up.
The main reason for interruptions in the operation of the heating system in a private home is incorrect installation. Most often this happens when installation is carried out without the participation of specialists. Being incompetent in this matter, it is quite easy to confuse the supply and return pipes or choose pipes of the wrong size.
Troubleshooting methods. Why is cleaning necessary?
To understand exactly how to solve a problem, you first need to establish its source. If the batteries become cold due to insufficient water circulation, installing a special pump will help. It will regularly push water into the circuit under a certain pressure, thereby preventing the system from stopping or slowing down.
If the reason is that the pipes are clogged, then they simply need to be cleaned. You can do this in several ways:
- using a water-pulsating mixture;
- using biological products;
- by means of pneumatic hydraulic shock.
In the event of a malfunction resulting from improper installation of the equipment, contact a specialist. A qualified specialist will certainly understand the problem and eliminate all problems. In addition, he will give practical advice and recommendations on the care and operation of the system.
Useful video
Check out the video, which talks about one of the possible problems with the return flow - battery contamination.
What problems arise in the apartment due to cold return
Firstly, the batteries in this case do not heat up properly, or even do not work at all. Accordingly, the room itself becomes cold, which is certainly not encouraging.
This entails the accumulation of condensate on the walls of the boiler, which begins to react with carbon dioxide released from fuel combustion. The consequence of this process is the formation of acid, which corrodes the walls of the boiler, thereby destroying it.
To live without fires and explosions: how to ground a gas boiler in a private house with your own hands?
What is needed to connect a gas boiler to a gas source?
Are the pipes cracking angrily and not heating well? It's time to flush the gas boiler and its heat exchanger
Requires extreme caution! Principles for replacing a gas boiler in a private house
Fine-tuning the heating system, accessible to everyone: how to connect a room thermostat to a gas boiler
You can save money, just be careful: do-it-yourself instructions for repairing a gas boiler
This is interesting: How to bend drywall for an arch with your own hands at home: read in detail
Why is the riser hot and the batteries cold?
Sometimes, with a hot supply, the return of the heating battery still remains cold. There are several main reasons for this:
- installation was performed incorrectly;
- the system or one of the risers of a separate radiator is airborne;
- insufficient fluid flow;
- the cross-section of the pipe through which the coolant is supplied has decreased;
- The heating circuit is dirty.
Adjusting the check valve in the heating system
Cold return is a serious problem that must be eliminated. It entails many unpleasant consequences: the temperature in the room does not reach the desired level, the efficiency of radiators decreases, and there is no way to correct the situation with additional devices. As a result, the heating system does not work as it should.
The main trouble with cold return is the large temperature difference that occurs between the supply and return temperatures. In this case, condensation appears on the walls of the boiler, reacting with carbon dioxide, which is released during fuel combustion. As a result, acid is formed, which corrodes the walls of the boiler and shortens its service life.
Air locks in heating
If the radiators are not heated in any of the rooms, it means that the air accumulated in the system is preventing the free movement of the coolant. An air lock can form due to many reasons, including the following:
- air enters when water is drained from the system and then refilled;
- Oxygen is released from water when heated;
- a faulty expansion tank creates a local area of low pressure;
- air is sucked into the system through connections with broken seals;
- air diffusion occurs through the surfaces of plastic pipes.
Air bubbles can accumulate either at the highest point of the piping system, or only in one of the radiators. Then the bottom of the battery will be hot and the top will remain cold. The presence of air in the pipes also provokes the appearance of unpleasant gurgling sounds. Most often, heating devices on the top floor of a building stop heating.
Due to air bubbles, not only does the heat supply through the piping system stop, but also corrosion of metal elements begins. The smooth operation of the circulation pump is also disrupted.
The use of simple technical devices will help get rid of the problem of clogging the heating system with air locks.
The most effective way to remove air from a closed heating system is to use automatic air vents. If they are mounted in several problem areas at once, then the air from each group of system elements will be released as it accumulates.
In addition to automatic ones, there are also manual air vents (Maevsky valve). Such a device is installed at the end of the radiator, located on the topmost floor. You can learn how to use it from the video presented here.
How to bleed air through the Mayevsky tap
Depending on how the heating system is designed, it may sometimes be necessary to bleed air through an expansion tank in the attic. The circulation pump can also help expel air pockets from the system.
Inappropriate home heating equipment
With the current wide range of heating equipment, it is easy to make a mistake and purchase the wrong one. To avoid problems in the heating system, it is necessary to focus on the compliance of all its elements with the approved project. You need to buy radiators only of the type and with the number of sections as planned. All pipeline connecting parts, control and shut-off valves must be mutually compatible.
Heating problems in a private home often arise due to poor circulation. Circulation pumps help increase the speed of coolant movement in the pipes. But you need to select the right pump model correctly so that there is no noise in the pipes during its operation.
When arranging modern housing, old iron pipes are increasingly being replaced by more practical metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes. The absence of problems in each specific heating system will depend on their compliance with the specified project conditions. Although plastic pipes are lightweight and easy to assemble, it is better to entrust a specialist with the correct selection and subsequent installation of these products.
It is important to know that not all types of plastic pipes are suitable for heating systems. Some of them may become deformed or burst under the influence of hot water.
Sequence of actions when adjusting batteries
It should be noted that the adjustment of radiators in centralized heating systems comes down mainly to setting the control devices to a comfortable temperature regime. In autonomous schemes, this process is more labor-intensive, because It is not only the batteries that need to be regulated, but also the boiler. In addition, if several heating devices are connected to a closed heating circuit (one- and two-pipe systems with bottom wiring), it is necessary to achieve a balanced heating circuit.
To solve this problem, at the initial stage you should determine the coldest room in the house, because... Battery adjustment will begin with this. To do this, all taps are closed, and after the radiators have cooled, the temperature in each room is measured.
In the found room, the shut-off valve opens completely, and after reaching the required level of heating, they move to another radiator, adjusting the position of the valve, which ensures a comfortable mode. After all the batteries have been adjusted, begin setting up the boiler regulators.
There is another (simplified) option. To do this, it is necessary to determine the exact sequence of location of the radiators along the flow of the coolant. Then in the first battery the tap or thermal head is opened, for example, by one or two turns, in the next - by two or three, in the third - by three or four, etc. If the temperature in each room meets the needs, the adjustment process is considered complete. Otherwise, the procedure should be repeated, increasing or decreasing the number of turns of the tap.
When designing a heating system, measures must be taken to control temperature and pressure. To do this, it is necessary to install special fittings and devices. How to properly adjust the heating system: radiators, pressure and other elements? First you need to understand the principles of organization of these sections of the system.
Causes
As already mentioned, the bottom of any battery will be slightly cooler than its top. The level of heat transfer from any metal is quite high - the water manages to cool faster than it leaves the radiator sections. For this reason, a temperature difference occurs.
The problem can be diagnosed by the increase in temperature gap. The bottom of each section burns with cold, while the top part heats up (sometimes it is dangerous to touch the battery with your hands, the metal is so hot).
The most common causes of this condition are:
- Slow circulation speed of the working fluid.
- Incorrect connection (supply and return pipes were mixed up).
Violation of the correct installation scheme is not that uncommon. Many owners or unskilled craftsmen make mistakes when connecting pipes to batteries.
As for the circulation speed, it may drop already during operation. This happens for a variety of reasons, each of which requires immediate elimination.
Connection errors
Qualified craftsmen, of course, do not make such mistakes. But amateurs may well make mistakes when installing heating. Most often, the return line is connected to the upper branch pipe of the battery. In this case, the feed is attached to the bottom. As a result, the removal of fluid from the radiator is disrupted, its efficiency decreases, and the entire system does not function properly.
If you connect the supply pipe from below, water flows around the battery in a circle and leaves it, while individual sections do not fill or do not warm up. With the upper return line, the liquid cannot leave the inside of the structure, because the radiator is not able to create increased pressure and squeeze water out through the upper pipe.
When connected correctly, the working fluid enters from above and gradually flows through all sections of the radiator, going down. After which it enters the return line and is transported back to the heating boiler.
The error can be resolved quite simply:
- All pipes are dismantled (disconnected from the pipes).
- The correct connection diagram is ensured: supply from above, return from below.
- All elements are attached to their proper places. After which the heating is started and its operation is checked.
The only difficulty is the danger of stopping the system during the cold season. Therefore, for new heating it is recommended to carry out testing before the first frost.
Speed drop
There are three reasons for improper circulation:
- Violations were made during installation, namely, the cross-sections of the pipes were narrowed.
- The coolant moves too slowly within the system.
- The room temperature is too low.
Slow circulation is typical for circuits without additional equipment. As soon as a pump is installed that provides forced circulation, the problem is completely solved.
The narrowing of the section occurs for several reasons. An old heating system can accumulate rust or scale. Or an adjustment valve with an inappropriate cross-sectional diameter was installed. Alternatively, the polypropylene pipes are soldered incorrectly.
In order to accurately determine the reason that caused poor heating of the radiators, it is necessary to carefully inspect the circuit and analyze its condition.