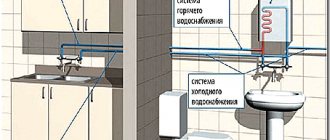
Process description
To describe the pyrolysis process, you first need to understand combustion. Combustion is the process of rapid oxidation of a substance. In this case, every 2 hydrogen atoms are combined with 1 oxygen molecule, and 1 carbon atom is combined with 2 oxygen particles.
As a result, carbon dioxide and water are formed. The latter evaporates because a lot of thermal energy is released during combustion.
Pyrolysis is a combustion that occurs under the influence of high temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
The technological process can be described as follows:
- The fuel is placed in a closed reactor.
- It is heated to a temperature of 500 degrees.
- The fuel breaks down into carbon dioxide, hydrogen and a solid residue.
- Carbon dioxide and hydrogen escape through a special pipeline, and the remainder is cooled.
Pyrolysis is used to safely dispose of chemicals that can release toxic compounds when burned.
The formula underlying the pyrolysis process.
Advantages:
- virtually waste-free process;
- Efficiency is about 90%;
- possibility of processing solid residue;
- creation of irreplaceable resources, including synthetic oil;
- production of hydrocarbons and organic acids;
- generation of large amounts of thermal energy.
Most types of hazardous waste should not be burned because they pollute the atmosphere. Pyrolysis is virtually smokeless combustion, so it is suitable for the disposal of any waste.
Material balance
The products obtained in the reaction depend on the composition of the feedstock, the ratio of hydrocarbons to steam, as well as the cracking temperature and residence time in the furnace. The yield of pyrolysis products, depending on the type of raw material, is quite variable. Light hydrocarbons such as ethane, propane, butane, LNG or light naphtha produce a range of products rich in light olefins, including ethylene, propylene and butadiene. The heavy hydrocarbons produced by the pyrolysis process are rich in aromatic hydrocarbons and hydrocarbons suitable for inclusion in gasoline or fuel oil.
| Products, % wt. | Raw materials | |||||
| Ethane | Propane | Butane | Naphtha | Gas oil | Liquefied natural gas | |
| H2+CH4 | 13 | 28 | 24 | 26 | 18 | 23 |
| Ethylene | 80 | 45 | 37 | 30 | 25 | 50 |
| Propylene | 2,4 | 15 | 18 | 13 | 14 | 12 |
| Butadiene | 1,4 | 2 | 2 | 4,5 | 5 | 2,5 |
| Butylene mixture | 1,6 | 1 | 6,4 | 8 | 6 | 3,5 |
| S5+ | 1,6 | 9 | 12,6 | 18,5 | 32 | 9 |
Pyrolysis methods
There are several pyrolysis methods. They differ in the heating method, as well as in the raw materials suitable for disposal in this way.
Dry
Dry pyrolysis is a combustion that occurs in the complete absence of oxygen. This completely prevents oxidation.
The operating principle of dry pyrolysis.
The process uses dehydrating agents. Pyrolysis plants operate on electricity.
Dry pyrolysis can occur at different temperature conditions:
| Name | Temperature |
| Semi-coking | Up to 550 degrees |
| Medium temperature | 550 to 800 degrees |
| High temperature | From 800 degrees |
The dry pyrolysis method is suitable for processing hydrocarbon waste. The solid residue obtained from the process can be used as a recyclable material for the chemical industry.
Oxidative
Oxidative pyrolysis is the most environmentally friendly method. Raw materials in installations are heated to 900 degrees. Combustion occurs under the influence of hot flue gases, which catalyze the reaction.
The substance begins to burn and release thermal energy. As a result, the solid residue is heated to a temperature of 16 thousand degrees.
Oxidative pyrolysis is used for recycling waste from industrial enterprises, wastewater, rubber and garbage, which may contain residues of petroleum products.
Modern approach
In addition to those described above, several modern recycling methods are used in the industry.
Namely:
- Catalytic low temperature. Pyrolysis occurs when exposed to low temperatures - up to 200 degrees. The reaction takes place under the influence of catalysts. As a result, the raw material breaks down into a solid residue, which is superior in performance to recycled materials.
- Initiated. Used for processing hydrocarbons. The reaction uses so-called “initiators”. Due to this, the amount of solid and liquid residue increases.
- Thermal contact. The catalyst for the reaction is molten metal, particles of heated refractory material. As a result, a large amount of thermal energy is generated and less coke appears.
- Hydropyrolysis. It is carried out under the influence of high temperatures of 900 degrees, as well as water supplied under pressure of 100 bar. Instead of coke, more hydrocarbons and tar are released.
Scheme of a modern technical solution for solid waste processing.
Modern pyrolysis methods are more efficient, environmentally friendly and bring more benefits.
Advantages and disadvantages
Flaws
- high capital costs due to the presence of extremely high and low temperatures at the installation (from -160 to +900 °C)
- coke deposits in the furnace coils, pyrolysis vapor cooler due to high temperatures
Advantages
- high and constantly growing demand for pyrolysis products
- the ability to design a plant for any possible types of raw materials from gas to gas oil to obtain the required basket of petroleum products.
By the way, read this article too: Scheduled preventive maintenance (PPR)
Types of installations
Installations that produce pyrogas are divided into domestic and industrial. Household ones are relatively small in size.
Industrial ones can process fairly large volumes of waste, however, they are large and require a separate area for work.
Pyrolysis plants differ in the following parameters:
- performance;
- weight;
- dimensions;
- power;
- energy source;
- number of levels.
In everyday life, small and compact installations are used, but even they are capable of providing thermal energy to a small area.
Types by type of material burned
All installations also differ in the type of raw materials processed. Somewhere hydropyrolysis is used, somewhere the dry method is used.
Pyrolysis of solid waste
Safe recycling of waste, during which no harmful compounds are released, is one of the main environmental tasks. Pyrolysis helps to significantly reduce the aggressive impact of solid waste on the environment. In this case, during the recycling process, a solid residue appears, which can be used as recyclable materials.
The plants can process waste:
- wood processing industry;
- electrical engineering;
- automotive industry;
- pharmaceutical industry.
During the recycling process, no heavy metals are formed, only biodegradable and safe materials.
Methane pyrolysis
Methane utilization takes place at different temperature conditions. First, under the influence of high temperatures, the gas decomposes into acetylene. However, this is useless and has no economic justification.
After this, activated carbon is added to the installation, and disposal takes place at low temperatures. As a result, the trimerization reaction begins.
Wood pyrolysis
Another name is wood cracking. Processing takes place at a temperature of 2 thousand degrees. As a result, large amounts of carbon monoxide are produced, as well as thermal energy.
After this, the pyrolysis installation is heated to 5 thousand degrees. As a result, methanol, tar, acetone and acetic acid are produced. In addition, charcoal is formed.
Charcoal production
The advantage of a business based on the use of very cheap or free raw materials is high profitability and quick return on production.
Nature “produces” wood in sufficient quantities, so a coal production enterprise can operate year-round and at full capacity.
In addition, unlike the wood processing industry, the quality of the raw materials is of little importance, which allows the use of dead wood and trees that are dry and in an upright position.
This article will discuss a detailed plan for organizing a business for processing wood raw materials into high-quality coal for barbecue or for further use for medical purposes.
Our business assessment:
Starting investments – from 300,000 rubles.
Market saturation is average.
The difficulty of starting a business is 5/10.
Household use
Pyrolysis of hydrocarbons has found wide application in everyday life. The installations are used to generate cheap thermal energy.
Pyrolysis boilers
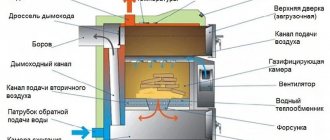
Pyrolysis boilers with natural oxygen supply are thermal installations with a high efficiency. Wood is used as a source, as well as wood gas released in the process.
Comparison of a conventional solid fuel boiler and a pyrolysis boiler.
A domestic installation consists of two combustion chambers. In the first, wood is converted into gas under the influence of high temperatures. The second chamber contains difficult-to-burn residues.
They are utilized at temperatures above 1 thousand degrees, generating thermal energy.
Cleaning the oven
Simple pyrolysis units are used in the self-cleaning process in modern cabinets.
Under the influence of high temperatures, dirt and adhering fat carbonizes. The process takes up to four hours.
After this, ash forms, which can be easily wiped off with a regular rag or sponge.
Preparation of charcoal
Domestic installations are also used to produce charcoal. Deciduous or coniferous wood is recycled in special installations. The process produces coal, tar and gas.
Processing occurs in 2 stages. To begin with, at a temperature of 300 degrees, a large amount of thermal energy begins to be generated. Then, at 500 degrees, a solid residue is formed - charcoal.
Industrial pyrolysis
Pyrolysis plants are actively used in industry.
They can be used for:
- industrial waste processing;
- solid waste processing;
- obtaining hydrocarbons;
- methane processing;
- obtaining charcoal.
Technological design
Processing of raw materials in industrial pyrolysis plants takes place at several stages.
The equipment consists of several units:
- Pyrolysis. It consists of several ovens, where direct processing takes place.
- Product divisions. Pyrolysis products are divided into water, resins and pyrolysis gas.
- Compression. Pyrogas is compressed under high pressure.
- Drying. Water is removed from the pyrolysis products.
- Deep cooling. The pyrogas is cooled to a low temperature.
Raw material base
Pyrolysis raw materials in European countries and in Russia differ in composition.
The percentages in the world are as follows:
| Percentage | Raw materials |
| 27% | Ethane |
| 14% | Butane |
| 53% | Naphtha |
| 5% | Kerosene-gas oil fractions |
In Russia, the raw materials are also light hydrocarbons of a wide fraction, and kerosene-gas oil raw materials are not used. At the same time, their share is constantly increasing, due to growing oil production volumes.
Production of lower olefins
Not long ago, a ranking of countries for the production of lower olefins was published.
The situation is as follows:
- America – capacity 27 thousand per year.
- Japan – 7 thousand per year.
- Saudi Arabia - 5.6 thousand per year.
- Korea – 5.4 thousand per year.
- Germany – 5.4 thousand per year.
- Canada – 5.3 thousand per year.
- China – 4.9 thousand per year.
- Netherlands – 3.9 thousand per year.
- France – 3.4 thousand per year.
- Russia – 2.8 thousand per year.
From this we can conclude that pyrolysis plants have not yet received proper distribution in Russian industry.
Purpose
Pyrolysis or steam cracking is a petrochemical process in which saturated hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller, often unsaturated, hydrocarbons. This is the main industrial method for producing lighter olefins, including ethylene and propylene.
Ethylene is one of the world's major petrochemicals as it is the basis for the synthesis of many chemicals and products. World consumption of ethylene in 2022 amounted to 164 million tons, propylene - 106 million tons, butadiene - 16 million tons. According to studies, demand for ethylene will grow by 3.3-3.4% annually until 2025. Currently, steam cracking is the predominant technology for ethylene production. The total production capacity worldwide is more than 150 million tons per year.
Consumption structure of pyrolysis products
Technology system
Pyrolysis combustion takes place according to a complex technological scheme.
An example of a pyrolysis installation diagram.
Preheating
At this stage, the raw material is heated and then mixed with water vapor, achieving a concentration of 0.5.
The presence of water vapor avoids the reverse reaction. After this, the raw material is heated to 500 degrees.
Pyrolysis oven
The reaction occurs in the coils of the pyrolysis furnace for approximately 0.6 seconds.
Scheme of operation of a pyrolysis furnace.
Processing occurs under high temperatures of 800 degrees, which increases the production of olefins.
Cooling block
Cooling occurs with the help of water, as well as the liquid part of the C9+ product.
Method of cooling the source gas.
The so-called quenching involves feeding cooled raw materials into cold combustion products, due to which the pyrolysis reaction instantly stops.
Fractionation block
The gas enters the fractionation unit. Heavy components come out of the column cube.
The lungs cool and then separate into gas and liquid. After this, the gas is liquefied, cooled and fed to the demethanizer.
Demethanizer
At this stage, hydrocarbon components or gasoline are separated from the mixture. Non-condensed gas is used as fuel and also for cooling raw materials.
The rest of the gas is fed to the deethanizer.
Deethanizer
At this stage of the process, acetylene is converted to ethylene.
Deethanizer column block.
After this, the mixture of components C2 is separated in a distillation column.
Depropanizer
At this stage, metalacetylene is converted to propylene.
Schematic representation of the operation of the depropanizer unit.
After this, it is also fed into the distillation column.
Debutanizer
The distillate is mixed with gases and used as fuel for the furnace. Heavy hydrocarbons are sent for separation.
Fraction separation columns
At the last stage, heavy hydrocarbons are separated into aromatic ones. Ethylene and propylene are released.
Starting the boiler
When starting up a pyrolysis unit, it is worth taking into account the characteristic features in which it differs from classic boilers. The operation of the device in gas generator mode is carried out thanks to two chambers, which are equipped with gates (dampers)
But not everyone remembers that such a heating unit must first be warmed up.
Rice.
3 When the temperature reaches +500-+800 degrees, you can start immersing solid fuel, and only then set the damper to pyrolysis mode and start the smoke exhauster. A pure yellow-white flame (Fig. 3) indicates that the gas generator settings are correct and that there are no toxic combustion products in the smoke mixtures.
This sequence of actions during startup guarantees the combustion of fuel slowly and oxygen-free, effective release and combustion of pyrolysis gas (clean), and a constant comfortable room temperature for 24 hours.