The dry lines of the scientific definition say that ventilation of a private house is a process of specially organized air exchange (from the Latin ventilatio - ventilation) in the residential and utility rooms of the building, in order to maintain the required sanitary and hygienic parameters of the air environment (air composition, its purity, temperature, humidity ). Ventilation is also called a set of technical means and measures that ensure controlled air circulation in a separate room and throughout the building.
The result of all these words is the same - in order to have fresh air in the house, it is necessary to install additional equipment, and what exactly - we asked the specialists of ATM Climate, a company that occupies one of the leading positions in the climate equipment market, to tell us.
General diagram of air exchange in the house Source socialmec.com
Proper arrangement of ventilation, both in apartment buildings and in private buildings, is the job of specialists, since here you will need to make a large number of calculations. At the same time, it would not hurt the owners of private houses to learn the basic principles of how ventilation works - this will help them at least in general terms understand what work will need to be done and how much it will cost.
Why is ventilation needed in a private house?
Air quality must fully ensure the comfortable state of the human body. This is unanimously stated by GOSTs and SNiPs, which regulate the microclimate parameters in premises. The most important factors of a comfortable microclimate include the following indicators of the air environment:
- cleanliness and degree of freshness of the air;
- air temperature and humidity.
To ensure that these indicators always remain within acceptable limits, a ventilation system is installed in a private house, the scheme of which is individually calculated for each individual case.
Ventilation has two main tasks:
- removal of air with a high content of dust and carbon dioxide into the external environment;
- an influx of clean, oxygen-rich air from the street.
8 reasons to install ventilation Source technosip.ru
Why ventilate the underground?
If an uninsulated foundation is not ventilated, the basement quickly becomes very damp and sooner or later turns into condensation. Moisture in the form of water vapor seeps through the floor slabs from the house, as well as from the ground. The foundation cannot be ventilated, so it accumulates in the soil under the house, in the basement walls, on the floor beams, on the floor boards and/or on the soffits.
In the same rooms where the temperature and humidity are positive and high (in a heated house the temperature is always above the freezing point, even in deep frosts), bacteria, fungi and decomposing materials are very active. As a result, very unpleasant odors enter the house and materials deteriorate.
The second reason to weatherize your basement is radon gas, which is released from the soil, sometimes in significant quantities. It is a naturally occurring radioactive gas. Without ventilation, radon will accumulate at the top of the basement, gradually seeping into the house. What the presence of radioactive gas in your living space can lead to is probably not worth talking about. So this is another good reason to ventilate your basement.
There are two ways to ventilate the space under the floor:
- Make ventilation holes in the foundation. In this case, moisture is removed by a draft - ventilation holes are located in opposite walls.
- Organize an air intake from the basement - run a ventilation pipe to the roof, and air flow through the blinds into the rooms. In this case, there are no holes in the foundation, but it is necessary to carefully insulate the outer foundation + basement + blind area. Next, waterproof the basement foundation.
The second solution offers the opportunity to improve aesthetics and avoid freezing through drafty basements, but requires a significant investment in materials. This option is suitable if you are going to build an energy efficient, well insulated house. In all other cases, foundation openings are more suitable.
Ventilation requirements - air flow rates
The basic indicators for designing a ventilation system are the incoming air flow rates and air exchange rates provided for by the relevant SNiPs:
On a note! The frequency of air exchange or ventilation is the ratio of the volume of air entering during one hour to the volume of the room. The multiplicity parameter characterizes the hourly number of air updates.
- The ventilation system must provide air supply in an amount no less than that required for comfortable stay of people in the room. For one person this is 30 m³/hour if the area of the room is more than 20 m² or 3 m³/hour for each square meter if the area allocated for one person is less than 20 m².
- For residential and associated premises with certain functionality, air flow is determined by the following standards:
- A minimum of 3 m³/hour must flow into the living room for each square meter of area.
- To the bathroom and toilet – 25 m³/hour.
- In a combined bathroom - over 50 m³/hour.
- For the kitchen - depending on the type of stove and the number of burners: electric and gas two-burner - 60 m³/hour; gas four-burner – 90 m³/hour.
A hood over a gas stove as one of the ventilation options in the kitchen in a private home Source deskgram.net
- The air exchange rate of a private house should be within the following limits:
- at least one volume per hour if there are always people in the room;
- at least one volume every 5 hours (0.2 volume/hour) for technical rooms.
Note! The given standards are calculated for indoor air temperature +18 °C and outdoor air temperature +5 °C.
Types of exhaust devices
Depending on the design features and purpose, the product may have the following designs:
- with a flat surface;
- domed or inclined;
- desktop;
- built into a kitchen cabinet, for example.
Models with a horizontal flat surface are the most common type of devices and stand out among other models due to their compact dimensions. They usually work autonomously because they have built-in replaceable filters. When such hoods operate, the heated air is cleaned of fatty fumes in the filter element of the device, after which it is again supplied to the kitchen.
Dome products are also in high demand among consumers. In them, polluted air is discharged through an air duct in the kitchen directly to the street. However, in this series there are models equipped with built-in filters. Samples of products with an inclined plane are classified as a type of standard dome devices. The height of the hoods above the hob for this option will be somewhat less, which is explained by the features of the design itself. For their manufacture, heat-resistant glass is used, which, in addition to its main purpose, performs a decorative function.
Devices built into the closet are good because they allow you to hide outlet boxes that are not very aesthetically pleasing in appearance. Desktop samples are mounted directly into the equipment itself (into a hob, for example).
Methods for calculating ventilation parameters
Accurate calculation of ventilation in a private home is performed using specialized software, to work with which you must at least know in what order and what data to use. Therefore, in order to do it once and wisely, you need to start with the development of an individual ventilation project for a private house.
But along with such calculations, there are methods of simple calculations that will make it possible to approximately estimate the necessary parameters.
- According to consumption standards.
According to SNiP, air consumption by one person (Vnorm) is approximately 60 m³/hour. This means that to calculate ventilation performance, the formula V=Vnorm*N is used, where N is the number of permanent residents of the house. But the problem with this approach is that residents may be in different rooms or congregate in one. For this reason, this approach is used only for air heating (air climate systems) with air circulation inside the house and with the addition of fresh air in the specified quantities. - According to the frequency of air renewal (calculation by area).
SNiP standards require at least one hourly air renewal. If, in this case, for the comfortable well-being of people in the room, one-time air circulation is not enough, use the formula V=K*S*H, where K is the air exchange rate, S is the total area of a private house, H is the height of the ceilings. The multiplicity index varies from 1 to 3. This approach is the most common, but is associated with a significantly larger volume of air supplied to and removed from the house than in the previous case.
SNiP requirements for air exchange rates in the table:
Source vodakanazer.ru
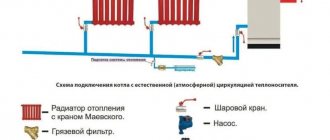
Hood duct and grille with non-return valve
The first is that instead of corrugation, a plastic pipe is taken (for example, d-125mm), and through one or several bends it is led into the hole in the ventilation duct. In this case, a certain division is made in the hole itself under the ceiling.
An entrance to the pipe is mounted on top, and a small rectangle is left below through a grate with a valve for natural inflow.
Moreover, the grille should be at the bottom, and not at the top. Otherwise, the air flow from the hood will blow upward and lift the so-called non-return valve.
Although, of course, if you have a more advanced valve design - a circle or rectangle with an offset axis, and not simple strips of polyethylene, or there is a solid partition, then you can safely install it as you want - on top, side, bottom.
However, in fact, this whole structure often does not work as intended. When you turn on the exhaust unit and create pressure, a small part of the dust still seeps through the cracks and micro-holes, after which it safely ends up in your kitchen on the dining table.
No check valves are 100% effective. The bulk of the air, of course, goes outside, but the gradual formation of dust inside the apartment is a fact.
And even when the hood is turned off due to the reduction in the diameter of the original hole, natural ventilation through narrow grilles will be much worse.
Everything can be done much better.
Natural and forced ventilation
All ventilation systems are divided into two main types:
- Natural (convective or natural) ventilation. The circulation of air masses here occurs in the same way as in nature - under the influence of draft, which arises due to the difference in temperature, and therefore air pressure in the room and outside the house;
- An artificial (forced) air exchange system, which is carried out by air blowers such as fans or compressors.
Natural ventilation - operating principles and features
The operating principle of natural ventilation is convection - the movement of warm air currents to the upper part of the room and the replacement of departed air masses with cold street air that flows from below. In addition to the temperature difference, the speed of air circulation here is also affected by the wind speed.
Previously, leaks in windows and doors were used to allow air to enter the home. However, modern plastic windows do not have such micro-slits and ventilation valves have to be purposefully installed in the frame or walls. In turn, the “exhaust” air leaves the house through exhaust ducts located in the kitchen, toilet and other rooms.
The principle of operation of convection (natural) ventilation Source bolts-master.com
See also: Contacts of companies that specialize in ventilation and air conditioning.
Natural air exchange has the following advantages:
- economical, since no additional equipment is required to move air flows;
- energy independence;
- trouble-free operation;
- noiselessness.
The disadvantages include:
- low intensity of air exchange, not always able to fully combat the accumulation of unpleasant odors or the formation of condensation;
- poor circulation efficiency due to the dependence of draft on the height of the building and time of year;
- almost complete impossibility of regulating the intensity of air exchange (dampers can be used, but they can only reduce draft, which means they do not always help);
- in summer there is almost no air movement, since the temperatures inside and outside the house are almost equal;
- a large outflow of heat to the street, which significantly increases heating costs;
It is important! In winter, the traction force in the air channels increases, as the temperature difference between inside and outside becomes significant. This leads to an increase in heat loss up to 40% of the total heat loss of the entire house!
- When installing sealed double-glazed windows, the natural flow of air practically stops.
- the need to additionally install special supply valves in windows or external walls.
Ventilation valves - outside and inside the room Source ventazbuka.ru
Features of artificial ventilation
The circulation of air masses in the artificial ventilation system is carried out forcibly due to the operation of electromechanical equipment. Fresh air from the street enters the ventilation unit through the air intake, which distributes the air throughout the rooms of the residential building. Exhaust air is forcibly sucked out of the premises and discharged into the street through exhaust air ducts.
The forced circulation ventilation equipment includes the following elements:
- fan;
- air purification filter;
- silencer;
- air heater/heater;
- air valve.
Even in modern systems, a recuperator can be added to the listed equipment - a device that, by removing heat from the air exhausted to the outside, heats the incoming air.
When installing a ventilation network you will need:
- air vents;
- air intake grilles, diffusers, anemostats.
Ventilation system in a “smart home” Source restate.ru
Advantages of artificial ventilation:
- autonomous operation, independent of environmental conditions (temperature and pressure, building height);
- the ability to bring the parameters of the air supplied to the house to the required values to create a comfortable microclimate (dust removal, heating/cooling, humidification/dehumidification).
Disadvantages of forced ventilation:
- energy dependence of technical means and significant energy costs for heating a large volume of supply air, which provides the necessary air exchange rate, especially in winter;
- significant costs for purchasing equipment;
- the need for regular maintenance.
Mixed ventilation type
If there is no need to install forced ventilation in all rooms of the house, then you can consider the option of mixed ventilation. This is what is commonly called the combined use of natural circulation with the installation of mechanical hoods and fans. Typically, forced ventilation is used in the kitchen or bathrooms, and air exchange in other rooms occurs naturally.
Mixed ventilation system Source linternaute.fr
Types of air ducts
There are three types of exhaust pipes:
Corrugated aluminum. The easiest to install. Usually it is enough to buy one such pipe, stretch it to the required length, put it on the flanges and secure it with clamps. The ribbed surface creates turbulence and air noise can be clearly heard.
Plastic round. Installation will require the use of elbows and possibly couplings. It will be necessary to cut the pipe sections to the required size. Air passes through such pipes with the least turbulence and noise.
Plastic rectangular. You can lay it flat on the top of the cabinets so that they will not be visible. If the walls are sheathed with panels or plasterboard along the sheathing, then it is possible to lay such pipes behind the panels.
For each type and size of pipes, it is necessary to buy suitable ventilation grilles, which are attached to the vent opening, and to which the pipe, in turn, is attached.
If the air duct is longer than half a meter, you will also need to install intermediate supports. Special supports are available for various types of pipes, but it is also possible to use metal mounting tape with perforations and universal clamps.
Air exhaust can be carried out into an existing ventilation system, or into one installed specifically for exhaust hood. To control the air flow, valves can be installed to prevent its movement when the hood is turned off.
Ventilation operating diagrams
In the practice of arranging ventilation devices, depending on the functions performed, four types of ventilation are defined:
- Supply ventilation in a private house - supplies air from the street to the room.
When double-glazed windows are installed in the house, the “micro-ventilation” mode or special valves are used. But the intensity of air supply depends on weather conditions and is not always able to provide a comfortable microclimate. For artificial ventilation, additional ventilation ducts and devices are installed that purify the street air and heat it to room temperature using an electric or water heater.
What does supply ventilation look like schematically in a private house Source bir.bilagyteco.ru.net
- Exhaust ventilation in a private house removes “exhaust” air from the house to the street.
If a high intensity of air exchange is not needed, then use natural ventilation through ready-made ventilation ducts. But due to the obvious shortcomings of natural ventilation, forced hoods with exhaust fans are more often installed. They are installed both in ventilation ducts and in the ceiling space.
The principle of operation of supply and exhaust ventilation Source mojdominfo.ru
- Supply and exhaust ventilation in the house - in this case, two parallel multidirectional air flows are organized. The first is the supply of oxygen-saturated air into the room, and the second is the removal of “exhaust” air outside.
- Air climate system (air heating) in the house - in this case, internal air circulation is arranged inside the house with supply air mixed into it and exhaust air removed from bathrooms and technical rooms.
The advantage of such a system is that significantly less fresh air is needed for the supply (60 m³/h per resident) and, accordingly, less air is removed through the hood together, which means less heat leaves the house in winter.In addition, it is easy to organize heating or cooling of the air circulating in the house, cleaning and humidifying it, i.e. You can do without a traditional hydronic split heating and air conditioning system. For this reason, such a comprehensive solution is often used in smart homes.
Ventilation system in a “smart home” Source restate.ru
How to install a supply valve - instructions
Before installation, two problems need to be solved: where to place the air valve and how to drill a clean hole in the wall. Below are location recommendations:
- Fans with a pipe diameter of 50-60 mm are best placed between the radiator and the window sill, provided that the gap height is sufficient. Then the cold air from the street will immediately mix with the rising convection flow from the radiator.
- On the side of the window opening there must be a block with a channel larger than Ø100 mm, with a recess of 30 cm (to prevent freezing). The second option is between the window and the ceiling, the minimum distance from the ceiling is 15 cm. In both cases, the fan is located in the zone of convective flow from the radiator.
- The height of the passive damper above the floor is 180 – 200 cm.
- When installing an air recuperator, maintain a distance of 0.5 m from all structures - ceiling, window, nearest corner.
- Place the transfer unit in a convenient location without restrictions.
Attention. If the room is heated by floor heating, then a passive type fan can be placed at any distance from the window, the minimum distance remains the same - 30 cm.
Drilling a reinforced concrete wall is best left to professionals armed with a machine with a diamond drill of the appropriate diameter. You can drill a hole in the brick yourself, although this will require some work. Using a long, thin drill bit, make many holes around the perimeter and then carefully drill through the center.
Two important points. Before starting work, make sure that there are no electrical wires or hidden heating pipes in the selected area of the structure. Secondly, the hole is drilled with a slope of 2-3° towards the street to ensure condensate drainage.
How to properly install a power valve in a wall:
- Cut the duct with a structure or a slight overhang as specified in the manufacturer's installation instructions. The telescopic ventilation duct is not cut.
- Insert the pipe into the hole, filling the cracks with construction foam. Do not use cement-sand mortar.
- Repair the mosquito net grill on the outside. Pay attention to the correct position of the element - the peephole on top, the blinds pointing down.
- Insert the insulating element into the duct, if necessary, cut it to the required length.
- Remove the valve head, attach the body to the pipe and to the inner surface of the wall with dowels. Install the filter, valves, and inlet cap face up.
The recuperator valve assembly technology is identical. First, a ventilation duct is built into the wall, an external grille is mounted, and then the components of the device are mounted from the inside - a ceramic heat exchanger, a fan and other components. Differences: thermal insulation is mounted outside the pipe, the power cable is connected to the fan.
Recuperator
When arranging supply and exhaust ventilation in private homes, significant savings come from the use of systems with heated supply air, called “supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery.”
Scheme of operation of ventilation with recuperation Source airclimat.ru
Recovery means the process of recycling heat from internal exhaust air with a temperature tb, which is emitted into the street during a cold period with a high temperature, to heat the supply external air. The process of heat recovery occurs in special heat recuperators: plate recuperators, rotating regenerators, as well as in heat exchangers installed separately in air flows with different temperatures (in exhaust and supply units) and connected by an intermediate coolant (glycol, ethylene glycol).
The last option is most relevant in the case when the supply and exhaust are spaced along the height of the building, for example, the supply unit is in the basement, and the exhaust unit is in the attic, however, the recovery efficiency of such systems will be significantly less (from 30 to 50% compared to the PPV in one building.
Preparing the ventilation shaft hole
Before all installation work, it is advisable to plaster the entry into the ventilation shaft itself and remove all sharp corners. This will give the entrance maximum aerodynamic qualities.
You should end up with approximately the same surface as a standard 90 degree round elbow.
It is recommended to add ceresit liquid (ceresit CT99) to the plaster solution.
This hole will be exposed to fat and moisture. And ceresite contains components that prevent the formation of mold.
However, do not use gypsum plaster under any circumstances. Its use in ventilation shafts is a direct path to the appearance of mold and fungi.
Attach sections of a standard air duct to the tee on both sides. From the side of the wall, 5-7 cm, wall it up in the ventilation duct. The exit itself is decorated with a square frame.
Video description
For more information about recuperators, see the following video:
It is important! Including a recuperator in the supply and exhaust system allows you to save up to 70-90% of the heat of the exhausted room air.
Phases of operation of the recuperator in the supply and exhaust ventilation mode in the house Source moydomik.net
Features of ventilation of premises of a private house
Any of the premises of a private house, residential and technical, need high-quality air exchange that corresponds to the functional purpose of the room. When arranging the ventilation system of a house, it is necessary to take these features into account.
Ventilation of the underground space
The underground floors of private buildings are characterized by the presence of damp, unventilated areas, which, in conditions of high levels of dampness, lack of sunlight and musty air, are a favorite place for the spread of various fungi. Rapidly growing colonies of microorganisms have a destructive effect on wood, concrete and metal structures.
To ventilate the subfloor of a private wooden house, ventilated openings are arranged in the basement along the entire perimeter of the foundation, creating natural circulation of air masses under the floor. The dimensions of basement ventilation openings for rectangular openings must be at least 100 mm, and for round ones - from 120 mm. The height of the holes is within 300 mm from the ground surface.
Example of underground (cellar) ventilation Source givewhereyoulivehamptons.org
If natural ventilation cannot cope with dampness and mustiness, mechanical means of forced circulation are brought to its aid - fan units located on opposite sides. The operating mode of the fans is determined in accordance with the task. They can work for half an hour several times a day or be turned on for a longer period.
Ventilation of upper floors
When using natural ventilation in two or three-story private houses, the biggest problem is the flights of stairs, which can be considered as large ventilation ducts. The already “exhausted” air from the first floor rises up the stairs, which means that in the building there will be a difference in temperature and humidity levels between the lower and upper floors.
Designers and builders solve this problem by blocking the access of air from the stairs to the floors, or by isolating each room separately. But the second option is practically not used due to its complexity, because in fact, here you will have to make separate ventilation in each room separately.
Rules for installing a hood in the kitchen
To prevent the structure from collapsing, the wall or furniture must support the weight of the hood
The selection and connection of the hood is carried out based on the layout and size of the room, the location of the stove and the characteristics of the device itself - type, shape, size, weight, set of options. Various models can be hung on a wall or ceiling, built into a set or countertop. Based on the principle of operation, the products are divided into exhaust, where contaminants are removed through pipes, and circulation, equipped with filters. In the first case, cleaning is more efficient, but the structures are more difficult to install and require additional investments. It is easier to install a circulation system, but it does not remove heat and does not retain all evaporation and moisture.
When installing the hood, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- correspondence of the strength of a load-bearing wall or element of a kitchen unit to the weight of the product;
- design and size that matches the interior of the room;
- lack of contact with the gas pipe;
- the distance between the hob and the appliance is within 65-80 cm;
- screen size is equal to or larger than the surface of the plate;
- power providing high-quality ventilation of the room;
- ease of maintenance and operation;
- possibility to connect yourself.
Video description
For a clear overview of ventilation in a private house, watch the video:
Usually, the doors from the staircase to the floor must be closed for the normal functioning of natural ventilation
In the attic it is always necessary to install forced ventilation, since the standard natural draft is not provided due to the low height of the ventilation ducts.
Kitchen ventilation
To ventilate the kitchen, builders of a private house must provide a separate ventilation duct into which the exhaust air flow will be sucked.
The channel is mounted from galvanized steel sheets or other stainless materials. The surface of the channel should be smooth so that greasy fumes from the kitchen and soot from the stove do not settle on it. The inlet and outlet openings of the channel are protected by grilles.
As in the whole house, air circulation in the kitchen is carried out by natural and forced methods. Those. vents and windows are opened, or a hood is purchased. The latter option is clearly preferable, since the inability of natural ventilation to cope with the odors that appear during cooking is beyond doubt.
What does distance affect?
Manufacturers pay attention to the permissible height of the hood from the stove for a reason. If the indicator is met, the device will effectively perform its tasks, and it will be easier for a person to use its capabilities
If you install the hood lower than recommended, this can lead to many unpleasant consequences. A tall person will experience discomfort while cooking and hit his head on the body. One of the main risks is the possibility of ignition of soot, which forms on the filter over a long period of time. Also, such a hood will be inconvenient to maintain (replace or clean the filter).
Also, the lower the hood is above the stove, the smaller its radius for absorbing steam and other emissions
Therefore, it is important to adhere to the manufacturers’ recommendations.
If the hood is installed high, the performance of the equipment will drop several times. To cope with the load, it will be necessary to turn on maximum power, which will entail high energy consumption and rapid wear of the exhaust system.
It should be noted that there are no state standards on this issue, however, manufacturers always indicate in the technical documentation of the hood the permissible height of the device above the stove.
There are factors that directly affect the calculation of the distance from the stove to the hood. These include:
- Man's height;
- Kitchen height;
- Dimensions and type of hob;
- Features of the kitchen layout;
- Type and power of the hood.
Also, it is necessary to take into account that there are standards for air ducts and electrical networks. Compliance with all recommendations and proper installation of the hood above the stove will reveal the full operating potential of the equipment and ensure its comfortable operation.
Video description
An example of combining natural ventilation with a hood in the kitchen in the video:
Since a kitchen stove is a constant source of fairly strong odors, the area above the stove needs ventilation most of all, and it is above it that the natural ventilation outlet channel or an electromechanical hood is placed.
When installing ventilation in the gas stove area, first of all, it is necessary to compare the number of burners with the volume of kitchen air space. The standards require:
- for a kitchen space with a volume of more than 8 m³, it is allowed to install a stove with two burners;
- for a kitchen with a volume of 12 cubic meters - no more than three burners;
- for a kitchen of 15 cubic meters - 4 burners.
If this standard is observed, for high-quality air exchange in the kitchen with a gas stove, an air exchange rate of 140 m³/hour is sufficient, and with an electric stove – 110 m³/hour.
Bath ventilation
The air in the bathhouse has its own specific specifics - during bathing procedures the humidity reaches 100%, and when the bathhouse is not in use, everything depends on the quality of air exchange in the room. To comprehensively solve these issues, mixed ventilation is used.
An example of air movement in a bath Source elektroservis-rostov.ru
But since the mechanical part is needed only during the operation of the bathhouse, then, in fact, the most effective natural ventilation is made and fans are added to it. Thus, during operation, the power of the ventilated installation allows you to comfortably steam in the bathhouse, and during its downtime, natural ventilation ventilates the room.
Technically, this is expressed in the arrangement of one or two supply channels and an outlet on which a fan is installed (preferably with an adjustable number of blade revolutions).
It is important! When arranging a bathhouse, one should not forget about floor ventilation. To do this, the floor covering is assembled from boards with a gap of 5 mm between them.
Number of sockets
How many minimum outlets are required in the kitchen?
Here, follow the rule - for each stationary kitchen appliance, plan your own socket + 2 blocks along the edges of the countertop + 1 piece near the dining table.
In addition, it doesn’t hurt to mount one socket immediately under or near the switch at the entrance to the room.
The area with switches usually remains uncluttered, and a free point where you can take voltage (for example, for a vacuum cleaner) is never superfluous.
Now mark the points on the apron for connecting non-stationary devices. Place at least two pieces on each part (right and left) of the kitchen.
This will include an electric kettle, blender, mixer, etc.
Tips, recommendations, nuances
Often, owners of private houses are lenient when it comes to ventilation requirements for their own home, especially if they may entail additional costs. Here are some misconceptions regarding the use of technical means in residential premises.
- Installing an air conditioner will solve all ventilation problems.
The air conditioner is able to change air parameters, cool or heat the air, and dry it. But it does not create an air cycle. In a house with a working air conditioner, a comfortable temperature will be established, but after a couple of hours the body will feel a lack of oxygen and an excess of carbon dioxide.
Ventilation is always installed along with air conditioners Source anantaircon.podbean.com
- If you install an exhaust fan, this will be enough for good ventilation of the house..
If plastic sealed double-glazed windows and doors are installed, there is no air flow, which means there will be no exhaust/removal of air masses. After a few minutes of operation of the hood, a pressure will be established in the room that simply will not push air to the fan blades.
- Periodic ventilation or an open window for micro-ventilation will solve all problems.
The issue of ventilation will not be fully resolved, since there remain fairly large periods of time during which it will not be possible to ventilate the house, for example, at night. If in the summer this is a solvable issue, then micro-ventilation in the winter is fraught with drafts that will quickly cool the room, preventing it from being ventilated.
- Using equipment with a heater will allow it to be operated at the lowest temperatures
As a rule, equipment with recovery has restrictions on the minimum outdoor air temperature. This is due to the capabilities of the recuperator and the limit is -25…-30 oC. If the temperature drops, the condensate from the exhaust air will freeze on the recuperator, so at ultra-low temperatures an electric preheater or a water preheater with antifreeze liquid is used. (The range of these installations is presented on our website)
Why does the valve freeze up?
This phenomenon occurs in areas with low winter temperatures. The source of frost is condensation falling on the very cool surfaces of the fan. To fix the problem, you need to determine the cause of the freezing:
- The natural exhaust gas removal system is ineffective or does not work at all. Result: water vapor remains inside the room and partially escapes outside through the supply valve.
- The power of the heating system is not designed for infiltration (influx of natural air) by the supply unit. The heater overcools and condenses.
- Incorrect installation, for example the fan is too close to the window, too far from the radiator or insufficient pipe insulation.
- The interior drapes too tightly, resulting in a cold zone along the wall. Frost accumulates on the cover.
Among the opinions of users there are complaints about a decrease in temperature after installing fans, literally strong shocks from the valves. We remind you of a simple rule: the passage of air through the element depends only on the operation of the hood. Try adjusting the flow at the wall damper or partially closing the outlet.
The photo on the left shows the correct installation of the fan, cold air is mixed with the warm flow from the radiator. On the right, the valve is too low.