The need to install a ventilation system applies not only to the rooms in which residents spend most of their time - bedrooms, living rooms, kitchens - but also to non-residential premises. Ventilation is especially necessary if heating equipment is installed in utility rooms and boiler rooms.
Both for the safe life of people and for the trouble-free operation of a heat-producing unit, a well-organized air exchange system is required. You will learn everything about how ventilation for a gas boiler in a private house should be arranged from the article we presented.
We will tell you what you need to consider at the preliminary stage. We will explain what should be done before installing ventilation ducts, what rules to follow during the installation of the system. This information may be useful if you want to do some of the work yourself, without involving specialists.
Types of ventilation systems
Ventilation for rooms with gas heating equipment, as for other objects, is of two types: natural and forced. The installation of natural and forced ventilation is permitted and regulated by current regulations.
Natural ventilation of boiler rooms
Natural ventilation ensures the ventilation of the room using multi-format pipes and pre-made holes in the walls, ceiling or floor. In fact, natural ventilation works thanks to pressure differences.
It allows the design of vertical and horizontal bends. In accordance with the requirements of SNiPs, the system can have horizontal sections up to 8 m long, but it is better to make them no more than 2 m long. In this case, designing no more than three is allowed.
The design of large horizontal sections of the exhaust system is not a gross violation, but the speed of air flow through them is quite low, which makes normal ventilation difficult
Most often, exhaust vents are located above the boiler. Natural ventilation does not require the use of special supply and exhaust equipment.
Calculation of air exchange for natural ventilation in a boiler room with a gas boiler is quite simple: you need to add 5 degrees for external air temperatures and 18 degrees for internal air temperatures. The ventilation operation is checked subject to the specified temperature difference.
When accepting a natural exhaust system, calculations are made to determine whether it will work in the summer. If not, then you will have to design forced ventilation, because... According to standards, the hood must operate year-round.
Forced ventilation system
Forced (artificial) ventilation is a whole automated system with an exhaust duct and the installation of fans and air conditioners.
The power of this engineering structure can be adjusted using programs or mechanisms (depending on the characteristics of the equipment). Moreover, it is better to design an automatic control system that will start when the boiler is turned on and turn off when the fuel is completely burned out.
However, it is completely dependent on electricity supply. When installing an artificial hood, it is recommended to install an additional generator. If possible, it is better to use a combined exhaust system, in which automated devices are activated only when natural ventilation cannot cope with air exchange.
Diameter of flow hole in ventilation systems
According to the standards, natural and artificial ventilation differ in the diameter of the vent (in another way it is called the inlet opening) to ensure normal draft and standard speed of air movement in the ventilation ducts. Although the diameter can also be calculated based on the cubic capacity of the room.
When choosing pipes of a certain diameter for ventilation systems, you need to take into account the effect of the grilles and information on gas consumption, which is indicated in the gas equipment passport
For natural ventilation, the value should be: 30 cm2 cross-sectional area of the inlet opening per 1 kW of gas boiler power. For forced ventilation of a gas boiler room, according to standards, the cross-sectional area can be smaller - 8 cm2.
Calculation of ventilation cross-section
To correctly calculate the cross-section of the boiler room ventilation system pipeline, you will need the following data:
- The cubic capacity of the boiler room, depending on the height of the room. According to SNiP requirements, its height should not be less than 6 meters. Obviously, in the conditions of a village house such a requirement is impossible to fulfill. When calculating, it must be taken into account that when this indicator decreases by 1 meter, the amount of air required for fuel combustion must be increased by 25%;
- Air mass flow velocity (at least 1 m/s).
- Air exchange rate. The value depends on the height of the boiler room.
The result of the calculation will be the air requirement, on the basis of which, using special tables, the cross-section of the ventilation system pipeline can be determined.
The calculation is made using the relationship V = L x SX (6 - H) x 1.25 xn, where:
- V is the volume of air for fuel combustion;
- L is the length of the room;
- S is the width of the room;
- H is the height of the room;
- n is the frequency of air change in the boiler room, equal to 3.
Thus, when determining the air requirement, the actual size of the room and the increase in air turnover are taken into account. Having received the desired value, the diameter of the air duct can be selected from the table.
Table: dependence of the duct diameter on the required air flow
| Air duct diameter, mm | Air flow in m3/hour at speed in m/s | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 100 | 28,3 | 56,5 | 84,8 | 113 | 141 | 170 | 198 | 226 |
| 125 | 44,2 | 88,3 | 132 | 177 | 221 | 265 | 309 | 353 |
| 140 | 55,4 | 111 | 166 | 222 | 277 | 332 | 388 | 443 |
| 160 | 72,3 | 45 | 217 | 289 | 362 | 434 | 506 | 579 |
| 180 | 91,6 | 183 | 275 | 366 | 458 | 549 | 641 | 732 |
| 200 | 113 | 226 | 339 | 452 | 565 | 678 | 791 | 904 |
| 225 | 143 | 286 | 429 | 572 | 715 | 858 | 1001 | 1145 |
| 250 | 177 | 353 | 530 | 707 | 883 | 1060 | 1236 | 1413 |
To ventilate rooms with gas appliances, it is advisable to install a duplicate ventilation system so that one of them works under any circumstances.
When there is a power outage, ventilation of the premises will be carried out through natural circulation channels.
Video: calculation of air exchange in a boiler room
How to do it yourself?
Schemes and calculations
Natural ventilation scheme:
- The air supply is located opposite the hood.
- The air is exhausted through an exhaust pipe, the beginning of which is on the ceiling, and the end is above the roof ridge. If the ventilation system is located on the wall, then this should be done as close to the ceiling as possible.
Mechanical ventilation scheme:
- The pipe with the fan must be discharged either through the roof to the street or through the wall outside the house.
- The air duct exits into the existing ventilation shaft with a fan.
During the heating season, it is recommended not to turn off the exhaust fan, leaving it to run on a regular basis.
Calculation of ventilation for a boiler room with a gas boiler is carried out taking into account the area of the room, the frequency of air exchange, and the number of family members regularly living in the house. Using these parameters, you can calculate the required hood cross-section for a gas boiler.
Attention Formula for calculating the amount of air exchange:
L (boiler power, kW/h) = N (air renewal rate) × S (room parameters) × H (boiler room ceiling height, m).
Attention Formula for calculating the number of family members:
L (boiler power, kW/h) = N (number of family members) × Lн (minimum air consumption per person, m³/h).
Generally accepted minimum air consumption standards per person:
- sleep – 20 m³/h;
- rest – 40 m³/h;
- vigorous activity – 60 m³/h.
Boiler room ventilation diagram:
Materials and tools
Basic materials and tools:
- Hammer or drill with a crown attachment.
- Saw for processing pipes.
- Tools for marking - ruler, pencil.
- Air ducts and adapters for them.
- Protective grilles.
- Adapter with check valve.
- Protective sleeves for slabs.
- Self-tapping screws, dowels, mounting clamps.
- Sealant or polyurethane foam.
- Hacksaw.
- Protective equipment: gloves, glasses.
Installation
Installation of natural ventilation:
- The installation location is outlined. The necessary calculations are made, a diagram or drawing is created.
- A pipe is applied to the wall, its dimensions are noted.
- A perforator is used to make a through hole with a slope of 60 degrees outward to drain the condensate (with exhaust ventilation, the slope is not made, the pipe is installed evenly).
- A pipe with insulation and a grille on the outside is inserted into the finished through hole.
- A housing with a check valve is attached to a part of the pipe inside the house and the wall with dowels (how to make a check valve for ventilation with your own hands?).
Installation of forced ventilation:
- A through hole is made in the wall with a slope towards the street. It is recommended to use a hammer drill or a drill with a diamond bit.
- A pipe is installed in the hole.
- The gaps between the wall and the pipe are filled with sealant or foamed.
- A duct fan is installed.
- Electrical wiring is laid and connected.
- The rest of the equipment is installed - filters, sensors, sound absorber.
- Grates are attached to both sides of the pipe.
separate article
Gas supply to an apartment building
When moving it into the house, a number of safety requirements must be met. These include the following:
- the presence of independent, isolated premises;
- good ventilation with exhaust hood in corridors with high ceilings that are fire resistant;
- non-explosive device intended for the introduction of natural gas.
For your information
Liquefied gas with odorants supplied to residential buildings has many advantages. It is cheap, burns to the end, is characterized by a high combustion temperature, as well as a high heat generation capacity. However, when mixed with air, it creates a mixture that can explode.
Because the gas is twice as heavy as air, if there is a leak, it fills basements and can travel considerable distances. Even a small leak in apartments can cause death by suffocation or cause a fire.
Air duct materials in gas boiler houses
Properly selected material for the air duct ensures longer operation of ventilation.
In accordance with current standards, the following can be used as a material for organizing the ventilation of rooms with gas equipment:
- brick;
- ceramics;
- asbestos;
- galvanized and stainless steel.
It is not advisable to use plastic for air ducts, because... this reduces the fire resistance of structures. Some regulations (for example, paragraph 7.11 of SNiP 41-01-2003) indicate that air ducts can be partially made of flammable materials.
When using plastic elements, you must remember that the presence of flammable elements in the structure will complicate the commissioning of boiler equipment and its acceptance by gas service employees
Regardless of what material is used, all ventilation ducts passing through cold areas must be insulated. In these places, draft may decrease, condensation may form, and the ventilation duct of a boiler room with a gas boiler may freeze and stop performing its functions. That is why it is better to stretch pipes along a warm circuit, eliminating the possibility of them freezing.
Brick exhaust ducts
Brick is not durable because... due to temperature changes, condensation forms on its surface, leading to the destruction of the material. If brickwork is taken as the material for the shaft, then the chimney is assembled from single-circuit galvanized metal pipes, the thickness of which depends on the temperature of the gases emitted.
Ceramic ventilation pipes
Air ducts made of ceramics are universal, easy to use and durable. The principle of their assembly is similar to the technology for constructing ceramic chimneys. Due to their high gas density, they are resistant to severe pollution of various types and aggressive chemical environments.
But in such hoods it is necessary to install condensate drains, because... ceramics absorb moisture well. Structurally, such a hood consists of 3 layers:
- ceramic inner layer;
- middle insulating layer of stone and mineral wool;
- outer expanded clay concrete shell.
This ventilation system cannot have more than three elbows. A drip and inspection are installed at the bottom of the ceramic chimney.
Steel air ducts
Steel exhaust ducts are convenient and practical.
A metal chimney in a gas boiler room can have a rectangular or round shape in cross-section, but in this case the width of one side should not exceed the width of the other by 2 times
When installing a steel ventilation system, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- The collection of segments is carried out using the “pipe to pipe” method.
- Wall brackets are attached in increments of no more than 150 cm.
- The length of horizontal segments should be no more than 2 m, if the system does not provide forced draft.
According to standards, the thickness of steel walls should be at least 0.5-0.6 mm. The temperature of the gas produced by boilers is 400-450 C, which is why thin-walled metal pipes can quickly burn out.
Fire hazard of industrial premises
The premises of single-apartment and multi-apartment buildings have been dealt with. Now let's talk about heat generators for industrial and warehouse purposes. According to Federal Law No. 123 TR on fire safety requirements.
The designation helps determine what and in what cases is necessary to ensure the safety of people and their property in buildings in the event of an emergency. For example, equipping a building with a fire alarm, a fire extinguishing system, the degree of fire resistance of finishing materials, the type of emergency evacuation, and so on.
To determine the degree of explosion/fire hazard of an object, division into classes and categories is used.
According to PP No. 390, a gas boiler house is classified as a hazardous production facility and belongs to category F5. According to the standards, premises of this type are standardized to a fire hazard category from the most dangerous under the letter A to the least dangerous, designated by the letter D:
- Increased fire/explosion hazard is A.
- Explosion and fire hazard - B.
- Fire hazard falls into category B - from B1 to B4.
- Moderate fire hazard - under the letter G.
- For a reduced fire hazard, to which it is difficult to classify such a gas installation, the symbol is D.
As a rule, it is difficult to coordinate the design of a gas facility with the D-subclass, so we will consider boiler houses from A to D.
You can't just go ahead and define a specific subclass. To do this, the necessary research and calculations should be carried out with the help of specialists with experience in designing gas-fired heat generators.
The subclass should be calculated based on:
- Type of fuel used.
- According to the degree of fire resistance (I, II, III, IV and V).
- The equipment that is installed indoors.
- Design features of the boiler room itself (hazard class according to the design of the gas boiler room C0, C1, C2 and C3). Determined by Article 87 of Federal Law No. 123.
- Characteristics of the processes being carried out.
The subclass is also conditionally determined on the basis of SP 12.13130.2009, NPB 105-03, SP 89.13330.2011, Federal Law No. 123. In principle, it is not necessary to determine which hazard class a particular gas boiler house belongs to, if the task is simply to determine whether it is a hazardous production facility.
The boiler room, in any case, is a gas consumption network. OPO is determined by the following criteria:
- The presence of boilers that are under excess pressure or temperature indicators of the working environment above 115 degrees.
- If the gas boiler house contains gas pipelines with a pressure of 0.005 MPa or more.
- A boiler house is a centralized system or installation that serves socially significant segments of the population.
The fire hazard class according to all criteria is determined by design specialists.
Types of ventilation systems for gas boilers
For rooms with gas units in private houses, the following types of ventilation systems are installed:
- Natural and mechanical;
- Exhaust, supply and combined, based on their purpose;
- Ducted or ductless according to design features.
If ventilation is installed in a boiler room where a gas boiler with an open combustion chamber is installed, the following points are taken into account:
- the presence of a ventilation shaft to remove carbon monoxide to the street;
- installation of a general exhaust ventilation system;
- the presence of supply ventilation, which draws air masses from the street into the boiler room (take into account cracks and gaps in windows and doorways).
When choosing a boiler for heating a house, you should correctly calculate its power in order to justify the cost of installing ventilation. The amount of oxygen supplied must correspond to the needs of the unit so that the flame in the burner does not produce soot. If this is not taken into account, a layer of soot will quickly form on the heat exchanger and the boiler efficiency will drop. When calculating the required air flow, the volume of the boiler room should be taken into account.
The requirements for the exhaust of a gas boiler in a private house are mandatory; compliance with them will guarantee the safe operation of the equipment.
If there is not enough air flow in the boiler room, the volume of oxygen decreases and reverse draft may occur. As a result, carbon monoxide will be released into the room. This is especially dangerous when the heating unit is installed in the kitchen area. When oxygen is absorbed, a harmful atmosphere in the room will lead to residents showing signs of oxygen starvation: pain and stinging in the eyes, lacrimation, dizziness. This means that the air duct for a gas boiler in a private house does not fulfill its purpose.
Ventilation is the key to safe and efficient operation of equipment
Without oxygen, life is impossible
Not only does ventilation in the kitchen with a gas stove or boiler protect people’s health.
For high-quality combustion of gas, oxygen is required. If it is deficient, a lot of carbon monoxide and under-oxidized substances are released into the air during the combustion process. You can notice this by the yellow color of the flame, high with abundant soot.
The efficiency of gas equipment decreases - the same amount of fuel burns, but less heat is released.
An even greater danger is posed by natural gas itself, which can get into the air in the room, for example, if a draft blows out the fire on a burner, the gas supply hose to the stove cracks, or the gas boiler breaks down.
The choice of a gas ventilation system in a private house or apartment depends on the type of boiler and the characteristics of the boiler room.
Natural circulation in a room with a gas boiler
It is necessary to install a polypropylene pipe into the vent. If the heating equipment has a power of 30 kW, then the pipe is suitable with a diameter of Ø15 cm. A metal mesh protects the entrance from the outside. To prevent foreign odors and debris from entering the room, a valve is installed inside the pipe.
Combustion products go directly into the exhaust pipe installed above the heating equipment. The supply air pipe is designed to bring fresh air into the combustion chamber, so this air duct is installed immediately behind the firebox. The efficiency of natural ventilation in a boiler room directly depends on weather conditions. And according to the standards, the air in such a room must be renewed 3 times every 1 hour.
It is impossible to calculate the air exchange rates for this ventilation system. In practice, it often happens when, for natural ventilation, a hole is made through a wall with a diameter of 150 mm, a ventilation pipe is inserted into the hole, it is protected from the outside with a mesh, and a check valve is mounted on the other side. From a financial point of view, this option is quite inexpensive, and the performance is very good.
In what cases is it necessary to organize ventilation chambers?
Central ventilation equipment is known to produce noise and vibration during operation, and therefore should not be installed in rooms intended for constant occupancy (more than 2 hours at a time). It is located behind the false ceiling of technical rooms or in separate rooms specially designed for this purpose (ventilation chambers).
Moreover, the standards determine the value of the maximum performance of ventilation equipment, which can be placed behind a false ceiling - 5000 cubic meters per hour (clause 7.9.3 of SP 60.13330.2012). For more powerful installations, ventilation chambers should be provided. The requirements and arrangement of these premises will be discussed below.
Requirements for the premises for installing a gas boiler
Comprehensive information on the correct preparation of the premises is contained in one of the above documents. Among other things, there are regulations on the dimensions of the boiler room, the arrangement of the entrance door, the height of the ceiling and other important parameters (see key requirements below).
It is immediately worth noting that if the maximum thermal power of a gas boiler is more than 30 kW, then it is necessary to allocate a separate room for its installation. Models with lower capacity and with a corresponding location of the outlet under the chimney can be installed, for example, in a kitchen area. Installing a gas boiler in a bathroom is strictly prohibited.
It cannot be installed in the bathroom, as well as in rooms that are considered residential. As an alternative, it is possible to install a boiler room in a separate building. At the same time, their own standards are taken into account, about which there is information below.
A boiler room in a private house can be equipped at the ground floor level, in the attic (not recommended) or simply in a room specially equipped for these tasks.
In accordance with the rules for installing a gas boiler in a private house, it must be equipped taking into account the following criteria:
- Area of at least 4 m2.
- One room is designed for no more than two units of heating equipment.
- The free volume is taken from 15 m3. For models with low productivity (up to 30 kW), this figure can be reduced by 2 m2.
- From the floor to the ceiling there should be 2.2 m (not less).
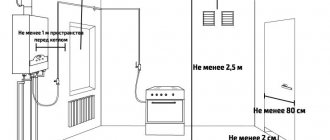
- The boiler is installed so that the distance from it to the front door is at least 1 m; It is recommended to install the unit near the wall, which is located opposite the doorway.
- At least 1.3 m of free space must be left on the front side of the boiler for setting up, diagnosing and repairing the unit.
- The width of the entrance door is taken around 0.8 m; It is desirable that it opens outwards.
- The room is provided with a window with an outward opening window for emergency ventilation of the room; its area must be no less than 0.5 m2;
- Surface finishing should not be made from materials prone to overheating or fire.
- A separate power supply line is introduced into the boiler room to connect lighting, a pump and a boiler (if it is volatile) with its own circuit breaker and, if possible, an RCD.
Particular attention should be paid to the arrangement of the floor. It must have a solid base in the form of a rough screed with reinforcement, as well as a finishing coating made of absolutely non-combustible materials (ceramics, stone, concrete)
To make it easier to position the boiler, the floors are made strictly level.
On a curved surface, installation of the boiler may be difficult or impossible due to insufficient reach of the adjustable legs. It is prohibited to place third-party objects under them to level the unit. If the boiler is installed unevenly, it may not operate correctly, with increased noise and vibration.
To fill the water heating system and replenish it during operation, it is necessary to introduce a cold water supply into the boiler room. To drain the system during equipment maintenance or repair, a sewer point is installed in the room.
There are special requirements for the chimney and air exchange in the boiler room of a private house, therefore this issue is considered in a separate subsection below.
If the premises for installing a gas boiler are equipped in a building separate from a private house, then the following requirements are imposed on it:
- your foundation;
- concrete base;
- presence of forced ventilation;
- doors must open outward;
- the dimensions of the boiler room are calculated according to the above standards;
- no more than two gas boilers are allowed to be installed in the same boiler room;
- the presence of a properly equipped chimney;
- it must be provided with free access for cleaning and other operations;
- for powering individual lighting and heating equipment, a separate input with a circuit breaker of appropriate power is provided;
- The water supply must be organized so that the main does not freeze during the cold season.
Mini-boiler room mounted near the house.
The floors, walls and ceilings of a separately equipped boiler room must also be made and finished with materials that meet the class of non-flammable and heat-resistant.
Why equip a separate boiler room at home?
When installing a heating system, the home owner is faced with a choice of where the gas-using equipment will be located.
The decision may be determined by aesthetic and design considerations, security issues (in the presence of incapacitated persons at home, as well as children). But in addition, this may be dictated by current equipment power standards
Let's consider the types of location of boiler rooms.
Boiler rooms can be located:
- inside the house - usually provided for at the stage of construction of the house, since there may not be a free room in the built one that meets the parameters;
- on a separate foundation as an extension, along a blank wall and maintaining a distance to the nearest door and window of 1 meter without permanent abutment to a residential building;
- detached - located some distance from the main house.
The regulations determine that if the power of gas-using equipment does not exceed 60 kW, it can be placed in the kitchen (except for the kitchen niche), in the kitchen-dining room, and other non-residential premises, except for bathrooms and bathrooms.
The minimum combustion volume for 30 kW power is at least 7.5 cubic meters. m. From 60 to 150 kW require the arrangement of a separate room. The minimum room volume is 13.5 cubic meters. m. From 150 to 350 kW. The minimum volume of the room is from 15 cubic meters. m.
A freestanding gas boiler room must be designed before construction or installation. Follow all the rules for its arrangement, otherwise the location of gas-using equipment in it will not be approved
We are talking specifically about individual boiler houses, that is, with equipment power from 60 to 350 kW.
Coaxial chimney as a ventilation element
Due to their design, coaxial chimneys are justifiably popular. They are assembled according to the “pipe in pipe” scheme, which allows you to perform two functions necessary for gas equipment at once: removing combustion products to the outside and supplying air to ensure the combustion process.
Coaxial chimneys are divided into two types: horizontally and vertically located. The first ones are installed in the wall, the second ones are brought out through the ceiling into the attic, then onto the roof. The vertical gas exhaust system is longer, more expensive, more difficult to install and requires the installation of a condensate collector.
The only disadvantage of the equipment is the risk of condensate freezing on the external part vented outside. The problem can be solved by insulating the pipe with mineral wool or other heat-insulating material, although this will not help in cold weather
To combat ice, the end of the pipe is equipped with a lattice cap.
Several rules for the correct installation of a coaxial chimney:
- It is recommended to install the pipe outlet at a height of 2 m above the ground.
- The distance from the pipe to the window located on top is at least 1 m.
- A condensate collector is not necessary if the pipe is installed at an angle of 3-12° towards the street.
- It is prohibited to route the main line into an adjacent room.
If there is a gas pipe near the chimney outlet, the distance between them should be 0.2 m or more.
The standard set of horizontal equipment consists of a pipe, an elbow for connecting to the boiler, adapters, decorative overlays, crimp rings, and mounting bolts.
An example of installing a horizontal coaxial chimney that goes out through a wall:
The installation of a horizontal coaxial chimney is considered the easiest to implement, and is therefore recommended for self-installation. At the end of the work, the boiler is put into operation and the tightness of the connected pipe is checked.
Safety regulations
During any construction, established standards must be followed. It is thanks to compliance with these standards that people gain confidence in the safety of their homes or their stay at industrial facilities. For example, gas supply regulations give instructions on where to lay the pipeline to houses, its distance from the ground or underground.
The rules must be followed when installing gas equipment, as well as operating the facility. Gas supply will be installed in residential buildings only when construction standards are met during their construction.
All components must meet certain requirements. For example, steel pipes installed indoors must be different from those installed outside the home. Rubber or rubber-fabric hoses may be used if they are sufficiently resistant to passing gas. The pipes are connected by welding. A threaded connection can also be used, but then a shut-off valve is installed.
To ensure the safety of gas supply, special rules have been developed for the design, construction and operation of supply systems, as well as the release and use of equipment. According to them, the requirements are established:
When should you invite specialists?
When arranging ventilation ducts in a private house, you can go in two ways:
- invite specialists who will complete everything turnkey;
- deal with all the issues yourself, completing the work on your own.
Each option is appropriate for specific conditions. All design options for the ventilation duct system can be divided into traditional and the latest ready-made systems. In the first case, you need to select equipment based on calculations. Here we must not forget about the smallest details that will be useful when assembling the system.
Secondly, we are talking about a comprehensive solution from a specific manufacturer. For example, the German Selfwind ventilation system, which is purchased as a ready-made kit for a certain area of the house. All components required for assembly have been selected. The system itself resembles a collector heating system, only many tubes surround the entire house from the inside.
These flexible plastic ducts with a diameter of 75 mm or 50 mm are pulled together into a manifold. They are poured with a concrete screed on the floor, and those areas that run like a circulatory system throughout the house are skillfully masked by the designers.
In the future, this technology provides an ideal microclimate in each room with the ability to regulate humidity, temperature and other parameters
If you choose such a complex ventilation system, which costs several thousand dollars for a country house with an area of 800 m2 or more, then there is no point in saving on installation. And it will take a lot of time to arrange such ventilation.
When building a house with your own hands “from scratch,” laying out ventilation shafts from bricks and providing holes for installing supply valves is not difficult. In the future, all areas of the natural ventilation system are equipped with special valves and, if necessary, hoods. This option is relevant for houses with an area of up to 250-300 m2.
Complex and expensive polymer ventilation duct systems are equipped with all the necessary parts for installation
Requirements for ventilation equipment
Service requirements for ventilation chambers are mainly determined by the requirements for servicing ventilation equipment, which in turn are declared by the manufacturer of this equipment.
Complete ventilation systems consist of various sections - filtration, heating, cooling and others - each of which must be accessible from the maintenance side. Usually this is one of the sides of the ventilation unit. By the way, when ordering a ventilation unit, you should indicate which side (left or right along the air flow) it will be serviced.
The service area on the side of the ventilation unit is usually equal to the width of this unit plus 200-300 millimeters. The fact is that many sections must be able to be removed from the ventilation unit, and their width almost coincides with the width of the ventilation unit. Therefore, for comfortable removal of sections, the service area must have a width no less than the width of the ventilation unit. An additional 200-300 millimeters will provide convenience when moving or rotating these sections.
For narrow rooms, some manufacturers of ventilation units offer units with overhead service. In this case, the free space above the installation should allow one or another section to be pulled up and taken out of the ventilation chamber to the outside.
In general, all requirements for the geometry of ventilation chambers can be easily clarified by mentally moving in and out of all sections of ventilation units. This procedure allows you to quickly determine the width and height of the doorway, the width of the passage inside the ventilation chamber, the width and height of other doors and approach paths.
Yuri Khomutsky, technical editor of Climate World magazine
Types of ventilation for gas boilers
There are two ways to ventilate a gas boiler room - natural and artificial.
To ensure natural ventilation, it is necessary to make a hole in the wall opposite the boiler and lay an air duct with a diameter of 15 cm or higher through the hole, in accordance with the size and capacity of the installation. The flow of air masses is regulated by a valve in the pipe. Thanks to the natural supply of air from the street to the gas boiler, the combustion process is supported. However, the air in the room itself is not renewed.
Supply ventilation in a boiler room is the easiest to install and use, but it has significant disadvantages:
- The system can only be used for boilers with low power;
- The process of air intake cannot be controlled;
- Additional ventilation is required in a room with a gas boiler - gaps between doors and walls, windows, etc.
A more functional option for powerful gas boilers is forced ventilation, which is distinguished by the installation of artificial air exhaust. To do this, one or more fans are installed inside the chimney pipe, depending on the power of the gas boiler, the number of turns of the pipe and its diameter.
Hood for wall-mounted boilers with a closed chamber
Despite the seeming uselessness of the ventilation duct when operating wall-mounted boilers with a closed chamber, the current SNiP requirements regulate the installation of air exhaust systems:
- the cross-section of the outlet pipe must fully correspond to or exceed the cross-section of the outlet pipe of the gas boiler;
- the chimney of the exhaust pipe of the boiler equipment must be made of stainless or carbon sheet steel of sufficient thickness;
- It is unacceptable to use asbestos pipes and elements made from layered materials in close proximity to the boiler outlet pipe;
- connection of gas boilers equipped with an overhead outlet pipe must be made with the connection of a vertical section;
- the straight part of the vertical air exhaust pipe should not be less than a quarter of a meter, after which structural bends are permissible;
- regardless of the total length of the installed chimney system, the structure must consist of at least three elbows;
- between the outlet part of the chimney pipe structure through the wall and the surface of the ceiling, a minimum distance of 20-25 cm is maintained.
The ventilation duct is arranged in different ways: with a horizontal exit through the wall, with a bend and a rise, with an exit through the ceiling and with a bend, as well as through a direct vertical exit through the roofing.
Requirements for ventilation for a gas boiler in a private house
For the efficient and safe operation of a gas boiler, you must comply with the requirements for its installation.
First of all, for high-power devices, a separate room - a boiler room - is required.
It must be isolated precisely because of the inability of ventilation to remove exhaust air from residential premises, as well as because of the explosiveness of the fuel. This primarily applies to large private houses, which are heated by floor-standing boilers equipped with an open combustion chamber.
Attention! Using the basement as a boiler room if the boiler runs on liquefied gas is unacceptable. The boiler room is located in a separate building, since liquefied gas has a high specific gravity and in case of a leak it accumulates and creates a threat of explosion
According to SNiP 2.04.05. II-35, such premises must be equipped with a ventilation system. Ventilation is facilitated by opening windows and a separate, constantly open vent - also listed in the list of requirements. The ventilation duct should be located at the top of the room. It is equipped with an inspection hole for cleaning, since contamination of the air duct can interfere with air exchange. In this case, it is better if the duct ventilation duct is made of non-combustible material.
Photo 1. Diagram of the boiler room in a private house. The arrow indicates the location of the ventilation duct.
For small rooms where low-power wall-mounted gas boilers are installed, ventilation can be installed in utility rooms (bathroom, kitchen). In such devices, a closed combustion chamber operates, and air is supplied and removed through a coaxial (pipe-in-pipe) air duct, which is separately discharged to the street through the wall.
Removal of combustion products from several boilers
The operating rules for heating systems indicate that when using several gas boilers, each of them must be connected to a separate chimney. However, if such boilers are installed in already built houses, a more flexible approach is allowed: several floor-mounted or wall-mounted units can use a collective exhaust system, provided that a distance of 75 cm in height between the combustion product input points is maintained. In this case, the cross-sectional area of the chimney must be no less than the area of the widest outlet pipe of all connected boilers.
Installing a chimney for a gas boiler is no less important a procedure than choosing the heating unit itself or calculating and designing the route of the heating system. If you follow all the rules given in the article, you will receive an effective and safe exhaust gas removal system that will ensure comfort and coziness in your home, no matter how frosty the weather rages outside.
Why do you need an air circulation system?
In such a small and sealed boiler room, very effective ventilation is needed; there are most likely dimensional violations here
Despite the development of high-tech gas boiler equipment, the number of poisonings and deaths from carbon monoxide is high. General weakness and headache are the least a person can feel. Ignoring generally accepted standards reduces the performance of heating equipment. Only with a continuous air supply is normal operation of the boiler ensured, and if there is a lack of oxygen, the fuel does not burn completely. This means that heat generation will be minimal.
It is necessary to understand that if, even at the initial stages of designing a building in the scheme, the boiler room is located separately from the house, the air that circulates in the room will be used by the boiler. When installing non-plastic doors and windows, there will be enough air in the boiler room. When installing modern plastic windows and doors, fresh air will not circulate from the street. When the boiler is running, it discharges the air, which means that the power of the equipment will decrease. There is a high probability that carbon monoxide will enter the boiler room
This example confirms the importance of a ventilation system in any room
Date: September 25, 2022
SNIP ventilation of industrial premises
It has the following varieties:
- The process of removing dust and gases from the working area, which are an integral factor in the operation of equipment, is called aspiration.
- For stable and complete filling of the room with air, as well as complete removal of contaminated air masses, a supply and exhaust ventilation system is used.
- The process of removing smoke emissions in the event of a fire or melting of equipment and/or its individual parts will help to avoid carbon monoxide poisoning of employees and specialists. This process is called smoke removal.
- Clean air masses must be ensured in all rooms used.
As for technological equipment and means of forced ventilation, they are different for each work area. But the main criterion for ensuring SNIP rules is to prevent repeated recirculation of air masses between rooms, i.e. Each room should be equipped with air inflow and outflow systems; it should not flow sequentially from one room to another, because the air mass may contain gaseous products.
They can cause fires or explosions, and also significantly increase the temperature or humidity in the room.
Building regulations
The gas supply must be safe. This is ensured by compliance with established building codes and gas supply rules (in short, SNiP). Thus, there is a separate document regarding single-family houses. The requirements are as follows:
- When consuming gas for cooking, it is allowed to use 0.5 cubic meters per day; for hot water produced by a gas heater - the same standard; for heating - from 7 to 12 cubic meters per day.
- The pressure must be supplied within 0.003 MPa.
- Gas pipelines located above ground are allowed to be laid in places where there is no passage of vehicles or people. At the same time, the height above ground level is at least 0.35 meters.
- Inside the house, the pipe is equipped with a device that turns off the gas.
- The distance between the pipes and the gas line must be sufficient to allow repairs to be made if necessary.
- Storage facilities should be located in the ground at a depth of 60 cm from the surface in areas of freezing in winter, and 20 cm in the absence of freezing.
- Inside the house, pipes must be open or located near special ventilation, and covered with shields.
- At the intersection of structures, the gas pipe is placed in a case, and the pipes should not come into contact with it (the gap is 5 cm, it is covered with a special material).
- Gas shut-off devices are located in front of the meters.
Organization of air outflow and inflow
The ventilation diameter is selected based on the boiler power.
The pipe diameter is determined based on the boiler power. For a 30 kW boiler, a size of no more than 20 cm is provided. Too high or low arrangement of the holes leads to slower air exchange. If the chimney outlet is located below the roof ridge, a cold flow will flow through the outlet, and combustion products will not be removed.
The chimney can be equipped with:
- horizontally;
- with lift and bend;
- vertically into the ceiling with a bend;
- vertically directly through the roof.
A yellow burner flame and a large volume of soot indicate insufficient oxygen levels, so you need to use a fan for the supply system.