How to connect a boiler to a boiler? Connection options and diagrams
How does the DHW function work in heating system boilers?
For example, you have one boiler in your heating system and you need to make sure that you also heat water with this boiler for hot water supply.
What methods are there for heating water through a boiler?
We will look at 5 schemes and tell you how each scheme works. Let's consider the advantages and disadvantages of each scheme.
Scheme of work No. 1.
Dull coolant intake from the boiler
Do not use a blunt water intake from the boiler!
This is a very uneconomical hot water system if the boiler temperature does not exceed 60 degrees.
Well, firstly, the boiler temperature can be set to 50 degrees. At this temperature, you will not be able to heat the water in the boiler above 48 degrees. Secondly, heating will take a very long time, since heat transfer drops significantly if the temperature of the water and coolant do not differ greatly. That is, to quickly warm up, you need to use a high temperature difference. 90-60=30 degrees. Because of this, indirect heating coil boilers use an increased coolant temperature.
There are indirect heating boilers, tank in tank.
This method uses a large heat exchanger area upon contact (coolant-DHW).
Such boilers have a much higher heating rate than a snake. This is achieved by increasing the contact area (coolant-DHW). And also due to the fact that the heat transfer limit is increased. Such a boiler increases the intake of more power due to the preservation of the coolant in the boiler, which has an inertial nature of maintaining temperature. Due to this, the very cooled coolant is immediately taken from the external tank. This process accelerates the extraction of thermal power to heat water. In this case, you can use the boiler, provided that the boiler temperature is 60 degrees or more. If the boiler temperature remains at 40-50 degrees, then you will have a low temperature in the boiler.
I would like to draw your attention to the accumulation of hot water. If you have heated water in the tank at 45 degrees, then you, for example, will have 10 minutes to wash with normal water in the shower. If your boiler temperature is 90 degrees, then you will be able to use the shower for more than 60 minutes. That is, by increasing the temperature, you increase the accumulation of hot water in the boiler with the same capacity. That is, the volume of hot water use will increase.
If you are not satisfied with the temperature change in the boiler, which changes over time and you have to reconfigure the mixer. Then there are special thermostatic valves for domestic hot water. They are called thermostatic mixing three-way valve.
This scheme allows you to always obtain a stable temperature at the outlet for DHW consumption
Work scheme No. 2.
Crutch method. We increase the boiler temperature.
According to this scheme, we simply set the boiler temperature, for example, 80 degrees, and the heating system will receive, for example, 60 degrees. By mixing through a three-way valve with cooled coolant backflow, the set temperature will be achieved.
I can't say how good this method is. On the one hand, they say that the boiler efficiency becomes higher if the coolant temperature is 60-80 degrees. This is due to the fact that at such temperatures chemical combustion is better and the gas burns better. That is, at low temperatures the gas does not burn out. That is, particles of combustible material do not completely release thermal energy. But for condensing boilers this efficiency rule does not work. There they specially lower the temperature of the coolant to 55-45 degrees.
On the other hand, high temperatures increase scale in heat exchangers and pipes, which in the future can lead to a decrease in power and failure of the boiler due to overheating. Also, build-up appears more often on steel pipes with high-temperature coolant. That is, steel pipes become overgrown.
What's wrong with this scheme?
It becomes bad compared to other DHW connection schemes. Well, for example, in some boilers there is weather-dependent regulation - equithermal mode. Also, when there is a need to turn off the boiler for heating and keep it running on DHW (automatically), it is problematic to do so. Because there are boilers with a function to turn off the heating using the room thermostat, but the DHW function remains working.
Work scheme No. 3.
Buy a ready-made double-circuit boiler and do not use a DHW boiler
Such a double-circuit boiler has an additional heat exchanger for domestic hot water inside the boiler. That is, the first-main heat exchanger is for transferring heat from the burning gas to the coolant.
Cold water passes through a plate heat exchanger under the pressure of the water supply system. There is a flow sensor on the DHW water supply pipe line. The flow sensor triggers a cascade of actions: Switches the three-way valve to redirect the flow towards the plate heat exchanger, and also increases the temperature of the coolant due to an increase in gas in the heater. That is, during DHW preparation, the heating circuit is switched off. And the movement of coolant through radiators and heated floors is turned off. During DHW, the coolant inside the boiler begins to circulate water through the DHW heat exchanger.
What does a double-circuit boiler with isolated circuits mean?
This is when the water supply circuit and the heating circuit do not interact in liquid. That is, liquids do not mix and liquids do not transmit pressure. Only temperature is transferred from one liquid to another liquid.
Water passing through a plate heat exchanger quickly heats up, usually to a maximum of 60 degrees. This temperature in some boilers is regulated only up to a threshold of 60 degrees. That is, the temperature cannot be raised above 60 degrees. This temperature is usually programmed and cannot be changed. Check with the manufacturer. Also in the passports are instructions for use.
Such a scheme with such a boiler is not suitable for high productivity. That is, it is problematic to service two or three appliances (sink, bath, shower). There's just not enough power. If you want to service several sanitary appliances (sink, bath, shower) you will have to install a storage tank. Making a storage tank for such a boiler is problematic. Next, we will consider schemes with hot water storage tanks.
Disadvantage of receiving hot water?
The hot water temperature will not be stable when the flow rate through the heat exchanger changes. There will be fluctuations in hot water temperatures. Practice has shown that with high flow rates, water may not heat up to the required 60 degrees. It happens that it doesn’t reach 45 degrees. Well, it depends on the power of the boiler and its response speed. Of course, in my practice I have come across boilers that respond well to heating water. The problem is that you have to wait for the water to become hotter due to the fact that the boiler takes a long time to think when it will switch to heating the water.
Electric water heaters
One of the options for organizing hot water supply (DHW) in a country house is an electric water heater that heats water using electricity. They are divided into flow and storage.
Flow-through models heat water as soon as the user opens the tap. A storage type water heater allows you to use hot water only after some time has passed (the duration of heating depends on the power and capacity of the water heater, as well as on the set temperature).
Water heaters spend the same amount of energy to heat a certain volume of water to the desired temperature. But since the “flow tank” must heat the water quickly, it consumes a lot of energy at a time and in many country houses the power may not be enough for its operation. Powerful (from 10 kW) instantaneous water heaters require connection to a three-phase network with a voltage of 380 V. Storage water heaters are simpler - to put them into operation, you just need to connect them to a water supply system and connect them to a regular single-phase electrical network.
Methods of heating water - flow-through
Water can also be prepared using the flow method, i.e. upon request only during filling. The principle is simple - turning on hot water turns on the device (boiler or water heater), and closing the tap turns it off. The system can be centralized, i.e. one boiler or powerful heater supplies the entire house, or, conversely, small heaters at each point of use. The first option is typical for houses with dual-function gas boilers, and the second - with electric heaters.
And so we don't have a large tank (which is valuable for small houses) and the hot water never runs out. Unfortunately, there are also disadvantages. The amount of hot water flow directly depends on the power of the heater, and for comfortable use of one shower you need about 20 kW. In the case of electric heaters, this is a serious problem, since the connection power in a private house is usually around 15 kW, and the maximum does not exceed 40 kW, but in many places you will not get that much due to the high load on the existing network.
With gas boilers and stoves we can usually afford more. However, if instead of a chimney above the roof we install a ventilation chimney and an exhaust hood through the external wall, then the maximum boiler power will be 21 kW. It should also be remembered that according to modern standards, heating a new house with an area of about 150 m2 does not require a boiler with a capacity of several kW. The power of a gas boiler for hot water supply can be much higher (negotiated and installed separately), but there is no complete freedom here. A boiler with very high power for domestic hot water will operate less economically for heating the building, but this is its main gas consumption.
Gas combi boilers are most often used for instantaneous water heating. They take up very little space and do not require a separate boiler room.
Electric instantaneous heaters are definitely less popular than boilers and storage heaters. However, their advantage is ease of installation, small size and no heat loss when we do not use water.
Flow-through water treatment means that hot water consumption is limited. The more taps you turn on, the less water everyone gets. This is a problem especially if you are mixing hot and cold water because the ratio between them changes and as a result the temperature of the water coming out of the tap changes. Therefore, it is best to set the DHW temperature on the boiler so that it does not mix with cold water at all.
Flow heating means that circulation cannot be used. Therefore, after turning on the tap, you have to wait for hot water. The length of time depends on the length of the pipes through which the water will drain, and the time required to heat the heat exchanger itself in the boiler or water heater. Therefore, in some devices you can activate the so-called comfort mode. This means that the heat exchanger in the boiler is still heating up and can produce hot water immediately. However, this is an interim solution.
A combi boiler heats water in a stream.
A combi boiler heats water in a stream, so there is no way to circulate it. The problem can be solved by adding a DHW tank in series with an electric heater.
When is it recommended to use a flow-through system? First of all, in houses where all hot water supply points are located close to the boiler and there is not much space for a water heater. This is even an option with a gas boiler in the kitchen and bathroom behind the wall or higher on the next floor.
Gas water heaters
Water heaters operating on gas are divided into instantaneous and storage. Modern gas water heaters are quite efficient devices; gas is one of the cheapest energy sources.
A gas water heater is not the most popular way to solve the problem of organizing hot water in a private country house:
- Main gas is not available everywhere, and the option of gas cylinders is not very convenient;
- permits are required to install gas consuming equipment;
- a gas water heater requires a chimney in the house.
DHW system based on a double-circuit boiler
When the house is supplied with main gas, hot water supply can be realized using a gas double-circuit boiler. A double-circuit boiler is a boiler that can heat water (or a special liquid) for heating a house, as well as heat water used for domestic needs.
The preparation of hot water in a double-circuit boiler can be carried out using a secondary heat exchanger, a built-in boiler, or a bithermic heat exchanger. In the first and second cases, the water in the DHW circuit receives heat from the liquid heated by the burner flame in the primary heat exchanger; in the third case, the coolant and water for the DHW circuit are heated in one heat exchanger located above the burner.
A modern double-circuit boiler can operate in two modes: for heating and for hot water supply (in the cold season), and also only for heating domestic water in the summer.
Methods of heating water - flow-through from a small tank
More and more combined gas boilers are appearing on the market, i.e. instantaneous water heaters, but at the same time equipped with a storage tank for hot water with a capacity of several tens of liters. This combination makes sense because it allows:
- reduce the frequency of boiler starts, since with low water consumption from the tank there is enough water;
- provide a stable flow of water even when drawing from several points;
- use the hot water circuit for domestic needs;
- provide any amount of water for increased consumption (i.e. prepared tap water).
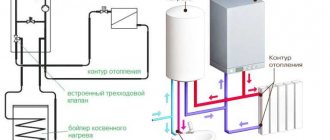
DHW from a boiler with an external boiler
For a large country house in which people live permanently and consume a lot of hot water, a system based on a single-circuit boiler and an external large-volume boiler is more suitable.
A single-circuit boiler itself only works for heating, but you can connect an external boiler to it - then the coolant heated in the boiler for the heating system will heat the water inside the boiler.
In summer, the boiler can be switched to an operating mode in which the heating circuit will be turned off, and the coolant will circulate between the boiler and the boiler, heating the water in the latter.
There are boilers equipped with heating elements. They are called thermoelectric or combined and can work both in conjunction with a boiler and without it, heating water using electrical energy.
Wood-fired hot water supply
For organizing hot water supply in a small country house with seasonal residence, a titanium wood-burning hot water heater may be suitable. It consists of a stove, a vertical water tank, a tap and a shower device.
Advantages of titanium:
- energy independence – the ability to use any type of solid fuel (with the exception of coal);
- maintaining a certain water temperature (for models with heating elements);
- heating the room in which it is located.
To remove combustion products, you will need to install a chimney and connect a column to it.
Solar water heaters
Currently, in the areas of heating and hot water supply, there is a tendency to increase the use of systems that operate using alternative energy sources. The hot water supply system for a private home can be built on the basis of a solar water heater.
A solar water heater is a whole system, the main elements of which are a solar collector, which is installed on the roof of the house and a boiler located on the roof or inside the house.
There are three types of solar water heaters:
- direct heating;
- indirect heating;
- split systems.
In the first case, water heated in the collector by the sun's rays enters the boiler, and from it to the water collection points. In an indirect heating scheme, a liquid is heated in the collector, which transfers its heat to the water in the boiler through condensers. Both of these systems are energy independent, but can only work during warm periods of the year (the boiler is located on the roof, since it is a single structure with the collector).
The split system is designed for year-round operation. Its collector, installed on the roof, contains a coolant that transfers heat to water through a heat exchanger in a boiler located inside the house. Such a system is energy-dependent because it includes a pump that circulates the coolant.
Hot water supply with heat pump
The hot water supply system for a private home can be implemented using a heat pump. Pumps, called heat pumps, are devices that can extract thermal energy from air, soil or water and transfer it to indoor air, water from heating and hot water systems. They consume a small amount of electricity - that is, they are economical devices.
There are several options for organizing hot water supply in a private country house using a heat pump. One of them is to use an air heat pump unit located inside the house. It is a monoblock consisting of an air-to-water heat pump, a water tank, control devices and safe operation. Such an installation can take heat to heat water from the outside (street) air or from the air of the room in which it is located.
Would you like to use hot water at your dacha or in your cottage? Contact . Our specialists know how to make hot water supply in a private home as efficient and comfortable as in a city apartment. Experienced engineers will develop an optimal and competent project for organizing hot water supply in your country house, and our highly qualified installers will perform all the necessary work quickly and with high quality.
Indirect heating boilers are considered to be one of the most rational and versatile devices capable of providing a private home with hot water. In this article we will talk about the economic feasibility, operating principle, installation diagram and operating features of these devices.
Condensing boiler
To heat water, you can also use a gas or oil central heating boiler, preferably a condensing boiler. Condensing boilers, due to the specifics of their operation, consume less fuel, producing the same amount of heat as traditional boilers. Their efficiency is even several percent higher. Condensing boilers running on natural gas are considered the most economical; next on the list are boilers running on liquefied gas, closed by boilers running on liquid fuel. Condensing boilers are designed to emit few pollutants, so they pose no risk.
Heating a home consumes on average a few percent of the energy needed to heat it. By choosing the right device - easy to use, environmentally friendly, energy saving - you can save a lot.
How does an indirect heating boiler work?
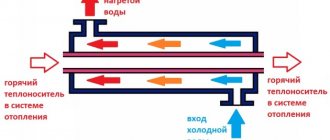
The design of the flask of indirect heating boilers is the same as that of electric or gas boilers: a stainless steel tank with an internal coating and thermal insulation. Instead of a heating element, a heat exchanger coil is installed in them, through which hot water from the heating system flows.
It may seem that a temperature of 50–70 °C will not be enough to heat water, because gas and electric water heaters have much higher values. But due to the large contact area, the heating rate is not inferior to other devices, and sometimes it is even higher.
Installation of an indirect heating boiler with a coil: 1 - cold water inlet; 2 - hot water outlet; 3 - protective anode; 4 — central heating input; 5 - thermal insulation; 6 - heat exchanger; 7 - central heating output
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The following videos will show you how to decide on the connection diagram and install the equipment correctly.
General information about connection diagrams:
Practical tips for connecting equipment:
You can learn how to properly piping an indirect heating boiler from the following video:
Professional review of an 80 l boiler:
In addition to installing and connecting the BKN, regular maintenance will be required. It consists of flushing the internal cavity of the tank, removing deposits and scale, and replacing the magnesium anode. Caring for the equipment does not require much effort. If the piping is done correctly, immediate repairs will not be required, but if problems arise with the equipment, we recommend contacting specialists.
Do you have any questions about piping an indirect heating boiler, have you found any inaccuracies, or do you have anything to recommend to visitors to our site? Please leave your comments below.
Types and selection of devices
In addition to tanks of a simple design, there are also boilers of a more complex design, which allow you to realize some wonderful functions when integrated into the heating system.
One of the most popular functions is the use of a boiler as a heat accumulator. This is especially important for electric heating with an unstable power supply or when working at daily rates. Devices with heat accumulator mode have a significant capacity (more than 300 liters) and reliable thermal insulation.
Boilers with a recirculation system that provides instant supply of hot water to the mixer are considered more expensive. They have three pipes for connecting to the hot water system: one for supplying cold water and two for flowing hot water. Circulation is carried out by a small built-in pump. Boilers of this type are less economical, but with their help you can organize a small heating circuit, for example, to install a heated towel rail.
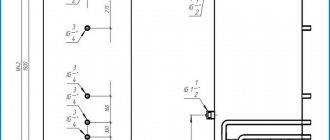
Some boilers have a “tank-in-tank” design; the name speaks for itself. The outer tank contains the coolant of the heating system, and the inner tank contains heated tap water. The advantage of this design is that water heats up very quickly, but due to the complexity of the device, such boilers are much more expensive than conventional ones.
Indirect heating boiler “tank in tank”: 1 - cold water inlet; 2 - hot water outlet; 3 - central heating input; 4 — internal tank made of stainless steel; 5 - central heating output
Advantages
Modern models of gas boilers with one circuit for heating the heating fluid could be called primitive water heating devices if they were not equipped with high-precision control and monitoring equipment to ensure the reliability and safety of all operating cycles. To solve the problems of regulation and safety of boilers, an automatic boiler protection system with gas flow and pressure regulators, fittings that regulate the flow, temperature and pressure of heated water, all kinds of sensors, instruments and safety devices is aimed. This is the main advantage of gas boilers.
Other important benefits:
- simplicity of design and installation of the boiler, which includes a combustion chamber with a gas burner, a loop heat exchanger in the firebox, a system of manifolds and pipelines, and pumping equipment;
- efficiency achieved by automation and adjustment work for optimal and efficient combustion of fuel, mixing processes and regulation of coolant parameters in accordance with standards;
- the ability to connect boilers to cascade heating systems within cities and large towns, which allows not only to centrally control the system, but also to ensure reliable and high-quality heat supply to consumers in residential areas, neighborhoods, microdistricts, as well as enterprises whose boiler houses are included in the cascade;
- more environmentally friendly emissions of gas combustion products into the atmosphere compared to similar boiler houses using liquid and solid fuels.
What heating systems use boilers?
Almost any heating unit can work in conjunction with indirect heating boilers, but the use of devices of different classes has its own characteristics. In general, the simpler the boiler design, the more clear the operation diagram, but the higher the complexity of the piping. For example, for a standard chimney boiler with a thermostat, you can independently choose the insertion location depending on the configuration of the heating circuit. This is not so easy to do with an integrated heat pump, and electronically controlled boilers may malfunction when operating in the summer.
Solid fuel and liquid fuel boilers cannot be used in summer, but in winter this is one of the most acceptable options. Electric heating boilers also work productively; for greater convenience, they can be equipped with an additional thermocouple or automation with remote sensors to regulate operation based on the temperature of the water in the tank.
It is most difficult to connect an indirect heating boiler to gravity-type systems. With slow circulation, the water does not heat up as efficiently, and to use the pump, you must select the correct insertion points into the heating system so as not to disrupt the heating operation mode. The correct solution would be a sequential connection to the return line with the organization of a long bypass, in which the pump and boiler are connected in series, and a check valve is installed on the flow branch.
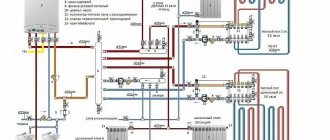
Installation and piping diagram of an indirect heating boiler
There are three options for connecting to the heating system and all of them involve installing the boiler at a minimum distance from the boiler. The boiler should be placed on a fairly solid foundation and strictly level. The coolant must be introduced from above and discharged from below. Hot water intake, on the contrary, is performed from above, and replenishment is performed from below.
Option 1. The heating supply pipe is divided into two branches, each of which has a shut-off valve or a three-way valve. One branch passes through the boiler, the other short-circuits the line if heating the water is not needed. This method is optimal for constant use of the boiler or seasonal operation. In this case, the temperature can be controlled by two self-resetting solenoid valves connected through a three-contact thermostat relay.
1 - cold water supply; 2 - shut-off valves; 3 - mesh filter; 4 - check valve; 5 - security group; 6 — heating radiator; 7 - heating boiler; 8 - boiler safety group; 9 - circulation pump; 10 - three-way valve; 11 - solenoid valve; 12 — expansion tank of the hot water supply system; 13 - hot water to consumers
Option 2. The supply pipe has a branch to which the circulation pump and boiler are connected in series, on the other side the connection is made to the return flow pipe. The pump is switched on through the thermostat relay circuit, so when the temperature of the water inside the boiler drops, it activates forced circulation and accelerates heating. The heating circuit has its own pump installed on the supply pipe after the boiler insertion point. This option is optimal if the boiler is used infrequently or the water temperature is required lower than in the heating system.
1 - cold water supply; 2 - shut-off valves; 3 - mesh filter; 4 - check valve; 5 - security group; 6 - circulation pump of the domestic hot water system; 7 — boiler thermostat; 8 - radiator; 9 - heating boiler; 10 - boiler safety group; 11 — circulation pump of the heating system; 12 — expansion tank of the hot water supply system; 13 - hot water to consumers
Option 3. The boiler is connected in series to the boiler supply pipe through a circulation pump. With this connection, the boiler always operates in heat accumulator mode; the option is optimal for devices with recirculation. The presence of a bypass connecting the coolant outlet from the boiler to the boiler return makes it possible to use the hot water system in the summer.
1 - cold water supply; 2 - shut-off valves; 3 - mesh filter; 4 - check valve; 5 - security group; 6 - bypass; 7 — heating radiator; 8 - heating boiler; 9 - boiler safety group; 10 - circulation pump; 11 — expansion tank of the hot water supply system; 12 - hot water to consumers
For any connection scheme, it is necessary to install shut-off valves on all pipes of the boiler and circulation pump. Connecting a boiler to a DHW system necessarily requires installing an expansion tank with a membrane on the water supply side to compensate for the pressure of the heated liquid. A strainer and a check valve must be installed on the cold water supply pipe to the safety group.
Nuances of the strapping device
It is easier to do the wiring and piping if the KN boiler is installed together with a boiler, pumps and other equipment involved in the assembly of the hot water supply system. It is much more difficult to insert an additional device into an existing network.
In any case, for normal operation of the devices you will have to follow a number of rules:
- choose the right installation location - as close to the boiler as possible;
- provide a flat surface for mounting the boiler;
- to protect against thermal expansion, install a membrane hydraulic accumulator (at the heated water outlet), the volume of which is at least 1/10 of the volume of the BKN;
- equip each circuit with a ball valve - for convenient and safe maintenance of devices (for example, a three-way valve, pump or the boiler itself);
- to protect against backflow, install check valves on the water supply pipes;
- improve water quality by installing filters;
- correctly position the pump (or several pumps) - the motor axis must be in a horizontal position.
For safety reasons, do not attempt to secure heavy devices to plasterboard or thin wood partitions. Walls made of concrete and brick are suitable. Brackets or other types of holders are secured with brackets, anchors, and dowels.
When installing, the pipes are directed towards the boiler (even if they are masked in the back or behind a false wall). Do not use unreliable equipment, such as corrugated hoses that cannot withstand pressure and water pressure.
For normal operation of an indirect heating storage water heater, the following functional devices must be included in the piping:
Operation and Maintenance
Every 2–3 years, the boiler requires a set of maintenance similar to electric water heaters: flushing the tank, removing scale, replacing the sacrificial anode when it is thinned by more than 50%, replacing gaskets. It is reasonable to carry out an inspection involving the removal of the technical flange of the tank in the summer in conjunction with maintenance of the heating system. Flushing the heating circuit and the boiler heat exchanger with chemicals must be carried out separately using appropriate cleaning agents. Otherwise, these devices are very unpretentious.