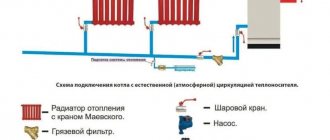
Why is a check valve needed?
During operation, hydraulic pressure appears inside the heating system, which may be different in different areas.
The reasons for this phenomenon are very different. Most often, this is uneven cooling of the coolant, errors in the design and assembly of the system, or its breakthrough. The result is always the same: the direction of the main fluid flow changes and it turns in the opposite direction.
This is fraught with very serious consequences, including the failure of the boiler, or even the entire system, which will require significant repair costs in the future.
For this reason, experts strongly recommend installing a check valve. The device is capable of passing liquid in only one direction. When reverse flow occurs, the locking mechanism is activated and the hole becomes impassable for the coolant.
Thus, the device is able to control the flow of liquid, passing it in only one direction.
The principle of operation of the check valve is very simple. It passes the coolant fluid in a given direction and blocks the path when it tries to move in the opposite direction
For normal operation of the system, it is necessary that the device does not create additional pressure and freely passes the coolant moving to the radiators
Therefore, it is extremely important to choose the right product
Natural and forced circulation - what's the difference?
Natural is built on the physical process of heated water rising upward. The density of hot water is less than that of cold water, so warm layers are displaced by less heated layers. This phenomenon occurs without human participation, you just need to create the conditions to start the process.
However, natural circulation is unstable, without the necessary pressure. The speed of movement of layers of water is low; it cannot push the flow through the pipeline. In addition, it is almost impossible to regulate the natural process, just start or stop it.
Forced is the movement of water using special pumping equipment. The process occurs evenly, it can be adjusted, flow parameters changed or stopped as needed. The pump creates pressure that allows water to move through a branched, extended system.
The natural process is used where slow, ineffective mixing of layers of water at different temperatures is sufficient. As a rule, it is used in small water supply systems of a private home, when only a small exchange of layers is needed.
Installation
Installation of make-up is possible after performing the following steps:
- Find a place in the harness with the least pressure. Typically this point is located near the pump unit.
- To prevent mixing of liquids, additional fittings are purchased.
- To protect against overfilling, purchase a second pump.
When choosing a device, you should focus on the size of the building. For small apartments or houses, a simple make-up with supply or return with a small adhesion coefficient is sufficient. Such devices are protected from scale, which increases their service life.
The installation looks like this:
- A valve is placed at the point of minimum pressure of the piping.
- For mechanical systems, a faucet is used that is placed between the cold water supply and heating.
- After testing, a booster pump is installed if the discharge is found to be higher than normal.
- To protect the make-up from water, shut-off valves are installed.
- Connect the pressure gauge.
If the movement has stopped, what should you do?
Despite the high efficiency of operation, circulation in the DHW lines sometimes stops. Let's look at the main causes and ways to solve the problem.
In private
The main reason is the failure of the circulation pump. The solution to the problem will be to repair or replace this unit. Sometimes the cause of the malfunction is a simple lack of power supply - a broken wire or a false alarm of the RCD.
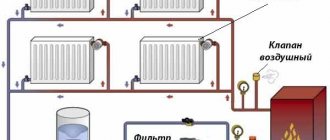
The second common reason is airing of the pipeline. This is due to improper line assembly where there are vertical bends in the pipe.
Air bubbles gradually accumulate in them, which sooner or later block the entire cross-section and stop the flow. The solution to the problem is to install a Mayevsky crane.
In MKD
The cessation of circulation in the hot water supply systems of an apartment building is almost always caused by the failure of the circulation pump. If a problem is discovered, you must immediately contact the management company so as not to delay repairs.
Another reason for the circulation to stop is the incorrect connection of the heated towel rail to the hot water riser in one of the apartments.
If a shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, it becomes possible to stop the circulation and completely stop the supply of hot water to all subscribers located further down the line.
Operating principle of the automatic refill valve
The principle of operation, as well as the installation process, of such a device is extremely simple. All operating parameters must be configured in advance. Pre-program future water losses - as a rule, you should additionally indicate the minimum pressure in the network. And if the volume of working fluid decreases, for example, by 10 percent, this will activate the valve, which, in turn, will start the pump.
Using this pump, cold water from the supply pipeline is pumped into the heating main in the required volumes. And as soon as the fluid losses are replenished, the valve will operate again and stop the automatic supply of coolant.
It is quite possible to handle the installation of the described device alone. First, you need to install a pressure gauge or any other electronic contact-type sensor on the pipeline supplying cold water (with the help of such a sensor, the user will be able to regulate the pressure simultaneously in two directions). One of the groups must be set to the minimum pressure in the network.
It is in this place that a contactor or intermediate relay should be installed. And as soon as the volume of hot coolant in the closed line decreases, this contactor initiates the activation of a mechanism that will start the extraction pumping equipment. There is a second group - it is necessary in order to deactivate all these processes when fluid losses are replenished. The actuating element in this case can be an electric valve - a kind of valve equipped with an electric motor.
Important note! If the heating system is recharged using automation, then it (the automation) will independently both control the operating pressure and calculate the compensation volume of liquid. Bypass make-up - when might it be required?
Bypass make-up - when might it be required?
It just so happens that almost all closed-type heating systems are capable of functioning normally only at high pressure of the working fluid. Although this is not the only important factor, since the temperature of the coolant also takes place.
So, if the temperature rises, this leads to thermal expansion of individual technical network nodes. And in order to compensate for this expansion, a special hydraulic accumulator (also known as an expamzomat) is installed, which is capable of absorbing excess hydraulic energy or, conversely, releasing it in case of deficiency. The hydraulic accumulator is connected in the same way as a plumbing bypass.
Feeding open type systems: diagrams, instructions
A distinctive feature of an open heating line is that there is no high pressure in it. In this regard, an expansion tank, albeit a somewhat modernized one, can serve as a kind of sensor for reducing the volume of liquid. This tank should be installed at the highest point of the system.
Note! In this case, replenishment will be carried out exclusively when the volume of coolant in the tank decreases. To find out whether the level has really dropped, you need to open the control pipe: if there is a shortage of coolant, there will be no pressure there
Often the outlet of this pipe is installed in the kitchen or bathroom. And if there is no pressure during the inspection, it means that working fluid needs to be added to the system. For this purpose, another element of the feeding system is used - a node that connects the heating network to the water supply. From a constructive point of view, this unit will include such elements.
- A ball valve that closes/opens the flow of water into the network.
- Non-return valve - it is needed to prevent the backflow of liquid from the network into the water supply. This can happen, for example, if there is no water in the centralized water supply pipeline.
- Filter. As you know, the quality of tap water does not always meet the requirements, so it must be additionally purified from various types of debris. If this is not done, a layer of scale will form on the internal surfaces of the metal elements.
It is according to this scheme that an open-type heating system is recharged. But it is worth remembering that you need to install an air vent in advance, with the help of which excess air will be removed. Let us also add that in order to properly replenish the volume of water, its minimum temperature is needed.
Note! A simpler recharge scheme may consist of an ordinary storage tank, although the water level in this case must be monitored visually
Finally, about the safe addition of coolant
When filling water or partial replenishment, follow our recommendations:
- Replenish the heated system slowly by opening the valve a quarter of the lever stroke. In this way, it will be possible to avoid the formation of air locks and protect the boiler heat exchanger from temperature shock.
- Refill from scratch with the heat generator not working and the circulation pump turned off.
- Check the pressure in the expansion tank and go through all the radiators, opening the Mayevsky valves to release air.
- If your boiler is equipped with modern electronics, be sure to study the instructions regarding make-up. Often it is necessary to activate a special service mode in the unit.
- Excess pressure is easily released through the nearest air vent.
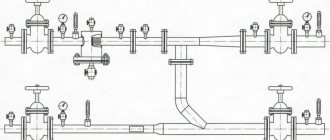
The complex system make-up module can be connected to a hydraulic separator and a comb
Reference. Cast iron heat exchangers easily crack from sudden temperature changes, and steel fireboxes become covered from the inside with condensation. The latter mixes with soot and forms a dense coating.
Injecting antifreeze with a hand pump does not have any pitfalls. Pressure testing units are equipped with their own pressure gauge, which allows you to monitor the current pressure at the insertion point.
Make-up device for heating system
Actuating mechanism
If replenishment is carried out mechanically, then all manipulations are carried out using one valve. Automatic units use various types of remotely controlled valves. But in most cases, a pressure reducing valve for automatically recharging the heating system is used. Typically this is a combination device that includes a shut-off valve, a check valve and a pressure reducer. It can be mechanical or have electrical contacts to control the pump.
The device is adjusted to the required operating pressure range. When the lower coolant pressure threshold is reached (say, 5 or 10 percent), the membrane releases a spring, which moves the working rod with a cone that closes the flow hole of the valve. After pumping the system to the required pressure level, the membrane compresses the spring and closes the flow with a rod.
Pressure reducing valve device for automatic replenishment
The valve response pressure is adjusted using a screw located on top of the device. Once installed in the desired position, it is secured with a lock nut. To visually monitor the pressure during adjustment, the valve is equipped with a pressure gauge.
Check valve
Under no circumstances should hot water from the heating system enter cold water supply pipes. Firstly, it can lead to the development of bacteria in drinking water. Secondly, waste coolant can be quite harmful to humans, since corrosion products accumulate in it. Thirdly, this way we lose coolant, which again negatively affects the operation of the heating installation. Reverse movement of the coolant can occur during replenishment if the pressure in the supply line is insufficient (in the water supply it is lower than in the heating system), or during operation if the shut-off valve “does not hold.”
The check valve is always installed at the rear of the actuator and is often built into the pressure reducing valve body. Recently, the make-up unit is also equipped with a check valve at the front or a so-called “flow breaker” is used.
Pump and accumulator
The main task of the pump is to increase the pressure in the supply pipeline, for example, when the pressure in the cold water supply pipes is lower than in the heating system. Therefore, it will not be possible to add water to the heating either manually or automatically. And if the check valve is absent or malfunctioning, there will also be an additional loss of coolant.
Floor-mounted make-up unit with vertical pump
A storage tank connected to the make-up unit allows you to always have a supply of water with which you can replenish the system, regardless of the pressure level in the drinking pipeline. To manually replenish the coolant in gravity circuits, a container is used that is located above the expansion tank, that is, somewhere in the attic. Automatic recharge systems often use a hydraulic accumulator with a membrane, which is always under pressure.
Filter elements
Impurities found in water can negatively affect the operation of heating and even damage heating appliances and devices. It is best to filter and prepare water immediately at the “inlet”. For mechanical cleaning of the coolant, mesh filters are used, which are mounted upstream of the pressure reducing valve. Sometimes mud collectors are an integral part of the actuator. To soften water (mainly to combat calcium salts), filters are used that bind and precipitate “unnecessary” substances using chemical reagents.
Automatic make-up is located on the bypass
Manual recharge scheme
The easiest way to replenish the heating circuit with water is to refill it manually. In order to fulfill it, it is necessary to stretch a pipeline from the city water supply and connect it to the return line of the heating network. A shut-off valve and a water purification filter are installed in this area.
The scheme functions perfectly in simple heat supply systems for one-story small-area households. The line is connected to the return line before the circulation electric pump, since this section has the lowest pressure and temperature of the network water.
For open heating networks, the make-up system organizes the supply of water not to the return, but directly to the expansion tank. To do this, you do not need to go into the attic to check the recharge level. According to the diagram, the expansion tank is connected with 3 independent terminals: make-up, supply and return pipelines.
The level in the tank is controlled by opening the valve on the control pipe directed to the sewer. When water flows after opening the valve, this means that the system is full; if not, the make-up valve opens, which is kept open until there is overflow from the control pipe.
How to connect to the heating system
With a closed circuit, there is not much difference where to connect the make-up pipeline - to the supply or return. We recommend using the classic proven method - the insertion point should be located on the return line next to the boiler, after the circulation pump and expansion tank. Causes:
- the unit is located in the combustion room, next to the equipment and instruments;
- pumping water into the return line is immediately reflected on the pressure gauge installed in the supply behind the boiler;
- the insert is located at the lowest point, the flow is distributed in 2 directions - into the boiler and radiators, the air is squeezed out evenly.
Classic scheme for inserting a recharge module
In a similar way, the make-up flows into the return line of the open system. The second option is to add coolant directly to the tank; the disadvantage of this method is to lay the supply pipe into the attic.
The correct connection is shown on the left - inside the primary boiler circuit
Connecting the make-up line is also allowed at other points:
- to a separate fitting of a solid fuel boiler, provided by the manufacturer;
- to the bottom of the hydraulic arrow;
- to the return manifold of the distribution comb;
- to the outlet of the indirect heating boiler.
These options are usually implemented in complex and extensive systems of country cottages. Connecting the make-up to the boiler is demonstrated in the next video:
Video description
Video on how to top up a heating system:
Location of the make-up unit
It is best and easiest to recharge an open system from above - through the expansion tank. At the same time, it is still recommended to do the initial download from the lowest point. Since this will allow the bulk of the air to be displaced from the circuit.
In closed systems, pumping can be done from any point, since the coolant circulates through a sealed circuit. However, even in this case, there are special recommendations regarding the location of the point and the implementation of the recharge procedure itself:
- Modern models of wall-mounted and compact boilers are already equipped with special refueling and top-up points.
- For refilling, you must choose a place next to the drain valve at the lowest point of the system.
- The optimal location for the make-up unit is in the return pipeline next to the expansion tank. This will enable the system to immediately respond to an increase in pressure, and also eliminate water hammer.
How to choose equipment
One of the important points is the selection of a heat source based on power and type of energy carrier used:
- on natural or liquefied gas;
- on solid fuel - wood, coal, pellets;
- on electricity;
- on liquid fuel - diesel fuel, waste oil.
The power of the boiler installation is calculated in the standard way: the heated area of the home is multiplied by 0.1 to convert to kilowatts and by a safety factor of 1.3. That is, for a house of 100 m² you need a heat source with a power of 100 x 0.1 x 1.3 = 13 kW.
For a closed heating system, it does not matter which heat generator you buy, so we will not consider this issue in detail. But you will make your task much easier if you purchase a wall-mounted gas boiler equipped with its own circulation pump and expansion tank, as shown in the photo. For a small house, all that remains is to select pipes and heating devices, which will be discussed further.
Types of pipes
The heating network of a private house can be installed from the following pipes:
- PPR (polypropylene);
- cross-linked polyethylene – PEX, PE-RT;
- metal-plastic;
- metal options: copper, steel and corrugated stainless steel.
For self-installation at low financial costs, it is better to take polymer pipes. To assemble crimp connections from metal-plastic and polyethylene, you do not need special tools, but polypropylene will have to be soldered (a welding machine is rented). Of course, PPR material has no equal in cost, but for reasons of reliability and durability, we recommend using PEX pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene.
Copper and corrugated stainless steel can also be mounted on compression fittings, but the first has a high price, and the second has significant hydraulic resistance. As for ferrous metal, it is inconvenient in all respects - welding installation and susceptibility to corrosion relegate it to last place. More details about the choice of pipes are described in the next video:
Which radiators are better
The following types of heating devices are currently offered in the retail chain:
- steel panels;
- made from an alloy of aluminum and silicon (silumin);
- the same, but with a frame made of steel pipes, name - bimetallic;
- cast iron batteries are analogues of the Soviet “accordion” MC 140 and retro-style models.
Steel panel radiator
From the point of view of economy, it is more profitable to buy steel batteries, which have an affordable price. Aluminum appliances are more expensive, but give off heat more intensely. These 2 varieties are most in demand for closed heating systems in private houses.
Aluminum heating device
Bimetallic radiators are designed for heating networks with low-quality coolant supplied with pressure drops, which is typical for centralized heating supply of apartment buildings. It makes no sense to buy these expensive products for a country house with autonomous heating.
To select a heating device based on power, make a simple calculation: divide the heat transfer indicated in the passport by 1.5. This way you will find out the real power of the radiator, because the documentation reflects characteristics for certain operating conditions that do not coincide with reality.
Pump and expansion tank
In closed heating systems of private homes, 3 types of household circulation pumps are usually used, developing a pressure of 4, 6 and 8 m of water column (this is a pressure of 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8 bar, respectively). We suggest that you do not delve into complex hydraulic calculations, but select a pumping unit based on the following characteristics:
- For one- and two-story buildings with an area of up to 200 m², a pressure of 4 m is sufficient.
- A cottage with an area of 200-300 m² will need a pump with a pressure of 0.6 Bar (6 m).
- Circulation in the network of a three-story mansion of 400-500 m² will be provided by a unit with a pressure of 8 m of water column.
To select the size of the expansion tank, you should calculate the volume of water in the entire closed heating system along with the boiler tank. Considering the fact that when heated from 10 to 90 °C, water expands by approximately 5%, the capacity of the tank should be 1/10 of the total amount of coolant.
Types of coolants and requirements for them
In autonomous heating systems for a private home, the following types of liquid coolants are used:
- Water.
This is the most common type of coolant, which has the following advantages:
- Minimum price.
- Availability.
- Maximum heat capacity (ability to transfer heat).
- Low viscosity, which means the least load on the circulation pump.
- Low corrosiveness - only in the presence of dissolved oxygen.
- Ecological cleanliness.
- Small expansion coefficient - no more than 0.03%.
Water is the most common and accessible coolant for most heating systems Source eurosantehnik.ru
The disadvantages of using water as a coolant are manifested in corrosion activity on unprotected steel parts of the system, as well as high crystallization temperatures. Therefore, if the house is left in cold weather long enough to cool the premises to 00C, then the water will need to be drained. Otherwise, under the force of expansion, freezing water will rupture pipes, batteries and heat exchanger.
- Antifreeze.
It is an antifreeze for radiators of cars operated in cold weather. Recently, they have preferred to fill autonomous heating systems of only closed types - due to the high toxicity of the vapors, they are not used for open circuits. It is marked with numbers - 65, 40 or 30 - which means the freezing mark of the liquid at a temperature below zero.
It is characterized by the following number of features:
- Average market price.
- The heat capacity is average, but lower than that of water.
- High viscosity - which characterizes a high load on the pump.
- Almost complete absence of corrosive activity.
- Toxicity - due to the ethylene glycol included in the composition.
- The expansion coefficient is up to 0.05% - almost 2 times higher than that of water.
Antifreeze contains harmful ethylene glycol, so it can only be used in closed systems Source otoplenie-gid.ru
Unlike water, antifreeze does not cause corrosion, but this is not always a good thing. So, for example, if a heating circuit becomes depressurized, fluid will begin to leak, while water and other corrosive liquids will quickly “heal” the leakage points by forming rust.
- Propylene glycol.
Antifreeze liquids based on propylene glycol are produced on an industrial scale specifically for autonomous heating systems.
Main operational features:
- Low heat capacity. In its pure form, it is almost 2 times lower than that of water. However, when diluted with water, the indicator increases to an acceptable level.
- High viscosity, which creates additional load on pumping equipment.
- Expansion coefficient – no more than 0.05%.
- Harmlessness.
- Lack of corrosive activity due to additives.
Although propylene glycol is the most expensive on the list of antifreezes under consideration, its popularity is high due to its absolute harmlessness. In purified form, it is added to both cosmetics and confectionery products.
Propylene glycol is the best antifreeze option for the heating system of a private home Source santehexpress.ru
- Brine.
The product is a solution of simple salts - common table salt, calcium chloride and some others. It is used as a budget alternative - to fill the heating system in a private home instead of water. The higher the salt concentration, the lower the freezing point of brine.
Features of operation:
- The lowest cost is based on the price of the amount of salts used.
- Sufficient heat capacity - 2/3 of that for water.
- Minimum viscosity.
- Expansion coefficient – 0.03%.
- No toxicity.
The main disadvantages manifest themselves in the form of low fluid mobility with a high concentration of salts and high corrosion activity on the walls of the metal elements of the system.
Metal elements rust quite quickly when in contact with salts Source vyborradiatora.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in engineering systems (heating, water supply, sewerage and others) and related work
Selection requirements
The liquid poured into the heating system as a coolant must meet the following series of requirements:
- High specific heat capacity.
The parameter characterizes the amount of thermal energy that must be supplied to 1 kg of a substance to raise its temperature by 10C. For heating fluids, this figure should be as large as possible. Ordinary water has the highest indicator among other liquids poured into the circuit.
- Operating temperature range.
Each individual coolant has its own characteristic operating temperature spectrum. Violation of these conditions leads either to equipment damage or to irreversible loss of coolant properties.
For example, when water freezes, it expands and ruptures the pipes or radiators in which it is located. On the other hand, organic coolants, when heated above 1000C, decompose into individual components, forever losing their original characteristics.
Any industrially produced coolant has a strictly specified operating temperature range Source sdvor.com
- Corrosivity.
The chemical activity of the coolant can lead to rusting of the metal parts of the circuit. The problem can be solved with inhibitory additives. For this reason, many coolants include special additives.
However, the problem most often manifests itself when the coolant is in constant contact with oxygen, and is practically absent when dissolved gases are removed from it.
This is especially true for ordinary water - after it is saturated with air bubbles at the point of contact - the expansion tank - it more actively corrodes steel pipes, radiators and other elements. Therefore, only closed-type heating systems are allowed to be filled with any type of coolant. In addition, they are most often equipped with plastic pipes that are inert to corrosion.
- Viscosity.
The viscosity index determines the degree of internal friction, and, consequently, fluidity. This in turn affects the pumping speed. Therefore, the greater its value, the more energy will be required to move the coolant through the system.
The promotion of viscous coolant is facilitated by the installation of powerful circulation pumps Source zaggo.ru
Water has the standard of minimum viscosity. All other coolants used in autonomous heating circuits have a higher value, and therefore worse fluidity characteristics.
- Lubricity.
Modern heating systems include a number of equipment in which the coolant additionally acts as a lubricant. This is not only a circulation pump, but also make-up and emergency shutdown valves, a thermostat, protocol sensors, pressure sensors, etc. Therefore, it is also necessary to select the liquid based on its lubricity in accordance with the specific type of system.
- Safety for others.
The substance used as a coolant in domestic heating systems must be completely safe for others. It should not be used in a vapor state, as if it ruptures due to the high temperature, it can cause burns.
Also, antifreeze should not be toxic, as, for example, compositions with ethylene glycol have. Therefore, for a number of reasons, domestic heating systems are most often filled with water.
The design of the heating system of a private house does not exclude contact of the coolant with household members, so it should not include toxic components Source klimatlab.com
- Chemical activity.
The coolant components must not interact with the heating circuit components. For example, if the heating system of a double-circuit boiler with steel radiators is filled with ethylene glycol, then the internal zinc coating of the batteries will quickly become thinner.
Moreover, heating the coolant to standard 80-900C will lead to the loss of its basic properties - the fluidity will become higher than that of water. Over time, this will inevitably lead to leaks of various connections with seals based on rubber, paronite and other polymers.
Recommendation! In most cases, water is used to charge the heating circuit. However, if the use of antifreeze cannot be avoided, for example, when the house is periodically left for a long time without heating during cold periods, then the choice is recommended to be made in favor of products based on propylene glycol. At the same time, it is better to purchase products from well-known lines with technical documentation confirming the quality.
The use of antifreeze will help avoid freezing and rupture of pipes and radiators if the house is left without heating in cold weather Source santehplus72.ru
Subtleties of recharging a closed heating circuit
For a closed heating system, the best solution is to install an automatic make-up unit. If the pressure drops below the minimum level, the installation itself solves the “problem”. Various types of fittings can be used in automatic units, but it is best to choose a gearbox with a built-in filter, a check valve and a valve equipped with a pressure gauge. The pressure gauge is used to visually monitor the pressure indicator.
For schemes that involve the addition of tap water, it would be a good idea to install a full-fledged device for comprehensive filtration of liquid from impurities
It is optimal to install the make-up device on the bypass. Having packed all the threaded connections and soldered the mounting taps (for dismantling, replacing or repairing fittings), the assembled unit can be connected to the selected point of the heating system. To start the installation, it must be set to the desired operating pressure. This manipulation is carried out using the adjustment screw located at the top of the device. By smoothly tightening and monitoring the indicators on the pressure gauge, you need to set the required parameter value. Then secure the screw with a locknut.
Automatic make-up unit
If you are firmly confident in the reliability and quality of the system, you can install an automated circuit that adds water from the cold water pipe. What you need to buy:
- pressure reducing valve (simpler - reducer);
- 3 ball valves;
- 2 tees;
- pipe for the bypass device.
Important point. The water entering the reducer must be pre-cleaned with a coarse strainer, otherwise the valve will quickly become clogged. If such a filter is not provided at the entrance to the building, install it in front of the make-up unit.
In this diagram, the pressure gauge shows the pressure on the side of the heating network; bypass and taps are needed to service the recharge module
The main executive element of the circuit - the gearbox - consists of the following parts:
- fine filter on the inlet pipe;
- spring seat valve with rubber seals;
- pressure regulator handle with a printed scale, range – 0.5…4 Bar (or higher);
- manual shut-off valve;
- check valve at the outlet.
Note. There are more expensive models of make-up reducers with a built-in pressure gauge that measures the pressure on the side of the heating system. Since this device is already in the safety group or boiler, there is no point in spending extra money and duplicating it. The exception is the situation when the make-up is installed far from the heat source (read the next section).
As you can see, the pressure reduction machine already contains all the necessary elements - a filter, a check valve and a regulator. All that remains is to assemble a simple circuit with a bypass and service taps designed for removing and servicing the gearbox.
Operating the valve is simple - use the regulator to set the minimum pressure threshold in the heating network, open the direct line taps, and close the bypass.
Advice. If you plan to install a coarse filter in front of the gearbox, provide an additional service tap in order to clean the mesh without turning off the water in the entire house.
To organize the automatic addition of antifreeze to the system, you can adapt a “hydrofor” - a water station with an electric pump designed for water supply from a well. The pressure switch of the unit must be reconfigured to a minimum pressure of 0.8 Bar, a maximum pressure of 1.2...1.5 Bar, and the suction pipe must be directed into a barrel with non-freezing coolant.
The appropriateness of this approach is highly questionable:
- If the “hydrofor” works and starts pumping up antifreeze, you will still have to look for and eliminate the cause of the problem.
- If the owners are absent for a long time, replenishment will also not save the situation in the event of an accident, since the size of the container is limited. The pumping station will extend the heating operation for some time, but then the boiler will turn off.
- Placing a large barrel is dangerous - you could flood half the house with toxic ethylene glycol. Non-toxic propylene glycol is too expensive, as is spill cleanup.
Examples of organizing automatic refueling from containers of different capacities
. Conclusion. Instead of additional pumps and automatic gearboxes, it is better to purchase an electronic unit of the Xital type. After a relatively inexpensive installation, you will be able to control the heating operation via a cell phone or computer and quickly respond to emergency situations.
Autofill device configuration
Before turning on the installation, you need to configure it and indicate the pressure required for operation
If you pay attention to the top of the device, you will find a special screw there, which is designed to adjust the working pressure. Unscrew the screw until it stops and begin to tighten it back slowly, looking at the pressure gauge. When the pressure reaches the level you require, secure it with a lock nut
The lever, which is located at the bottom of the shut-off device, is rarely used, because it is only needed to release fluid into the circuit. This can be done by unscrewing the screw and, accordingly, blocking its output by tightening
When the pressure reaches the level you require, secure it with a lock nut. The lever, which is located at the bottom of the shut-off device, is rarely used, because it is only needed to release fluid into the circuit. This can be done by unscrewing the screw and, accordingly, blocking its output by tightening it.
Take a look around again and make sure that the device is configured correctly and all components are in working order.
Current advice on configuration and maintenance
Whatever power supply you choose, remember, first of all, it should be safe and easy to use, made of high-quality materials. If the heating system is small, give preference to a device with the simplest possible design. The central support with moving parts and the internal compensation piston must be made of materials with a low adhesion coefficient: the risk of lime formation in the unit must be minimized. It is no secret that they are the main reason for the poor performance of the device.
Please note whether the product has a replaceable cartridge: this will greatly facilitate and speed up the process of inspecting the unit for you.
Periodic maintenance of the make-up device will help avoid malfunctions in the entire heating system.
To clean or replace the entire cartridge, proceed as follows:
- Insulate the installation.
- Unscrew the control knob located at the bottom.
- Unscrew the adjustment screw until it stops and remove the cover.
- Remove the cartridge with pliers.
- After the necessary manipulations, reassemble the device.
All that remains is to set up the equipment again and continue to enjoy the uninterrupted operation of the heating system in your home!
Replacing water with antifreeze
If the system has already used water, and you want to switch to antifreeze, then two circumstances should be taken into account.
Secondly
.
It is never possible to completely remove water from the heating system. Some of the water remains. If you simply pour prepared diluted antifreeze, its concentration will be insufficient for reliable protection against freezing. Thus, a concentrate must be used. I usually mix concentrate with diluted antifreeze in a 1:1 ratio. After filling the system, you need to start the circulation pump (for a system with forced circulation) or turn on the boiler (for a system with natural circulation) so that the coolant is thoroughly mixed. Then you need to pour out some coolant and measure its density. There is a device for measuring density that is sold in most car dealerships. This device is used to prepare a car for winter (checking the properties of antifreeze in the engine cooling system), but it is also perfect for our purposes. If the device shows a freezing temperature lower than necessary, for example -50 degrees, it’s okay, but if the temperature is higher than we need, then we will have to drain part of the coolant and replace it with concentrate. The drained coolant must be disposed of carefully; it is poisonous and should not be poured into septic tanks or ditches. I would also like to draw your attention to the fact that different antifreezes may be incompatible with each other. There is an opinion that red composition should not be mixed with a composition of another color. This is true, but in fact there are other undesirable combinations
Supplements from different brands may react with each other or simply reduce each other's effectiveness. Unfortunately, manufacturers do not indicate what other antifreezes their product can be mixed with. My advice is to pick one brand and stick with it. If you still need to mix, then mix liquids of the same color and before pouring, pour a little coolant from the heating system, mix it in a jar with a new composition and see if a sediment forms, if the liquid becomes cloudy, or if it loses its homogeneity
This is true, but in fact there are other undesirable combinations. Supplements from different brands may react with each other or simply reduce each other's effectiveness. Unfortunately, manufacturers do not indicate what other antifreezes their product can be mixed with. My advice is to pick one brand and stick with it. If you still need to mix, then mix liquids of the same color and before pouring, pour out a little coolant from the heating system, mix it in a jar with a new composition and see if a sediment forms, if the liquid becomes cloudy, or loses its homogeneity.
Operating principle and types of node control
The main task of the make-up device is to add the missing coolant to the heating system so that the operating pressure returns to normal. When the required value of this parameter is reached, the feeding flow is interrupted. In the vast majority of cases, the equipment is connected to a cold water supply, but it is also possible to recharge from a storage tank.
In addition to the convenient automatic one, the recharge unit can also have mechanical control. Mechanically controlled make-up is convenient where the system is small, and pressure surges are regulated using expansion tanks. The loss of a small volume of water here can be compensated for independently by monitoring the pressure gauge and manually opening the corresponding tap. The liquid can be supplied either by gravity or using a make-up pump. In typical gravity installations, coolant is supplied until it comes out of an overflow pipe welded to the tank.
The key disadvantage of manual recharge control is the need to have experience in performing such manipulations and to have certain knowledge and skills.
Expansion tank diagram
Automatic make-up valves are more relevant for large branched systems. Very often they are already “included” in the boiler package, being part of its automation.
Installation of such a device makes the operation of the heating system convenient and safe. The huge advantage of automatic recharge, like any other self-regulating installation, is that there is no need for human intervention. Apart from occasional preventive checks, it does not require any additional monitoring.
Installation of an automatic recharging unit can be carried out in both horizontal and vertical positions
It is worth noting that the make-up unit is used not only to add liquid to the heating system - it is multifunctional. It is used to carry out: initial filling of the heating system with water or antifreeze, complete draining of the coolant, water preparation, pressure testing and flushing of the system.
All elements of the automatic make-up valve for the heating system must be made of high-quality materials: stainless steel, brass, high-strength plastic
Filling closed heating with a pump
If the circuit is not connected to the water supply, the only option left to fill the heating system is a pressure test pump. This is a small rectangular metal reservoir into which liquid is collected. From the reservoir, the coolant is supplied to the pipes thanks to a pump-action hand pump on which a pressure gauge is installed.
Hand pump for pressure testing.
There is nothing complicated about how to fill a closed heating system. Work algorithm:
- connect the hose from the pump to the circuit;
- pour coolant into the pump reservoir;
- manually pump fluid into the system.
If there is no pipe for draining water from the circuit, then you can connect the pump hose to one of the ends of the battery. To do this, you need to unscrew the plug and put the adapter in its place. Before starting work, be sure to open all air vents so that air can leave the circuit.
When working with thermal insulation in sheets and rolls, you need to use an insulation dowel or nail to fix the material.
Watch the pressure gauge reading carefully. Using such a pump, pressure testing of the heating system is carried out. They can pump up pressure to 10 atmospheres (if you have enough strength). When filling the system, such pressure is not necessary, otherwise the boiler will break.
When is it necessary?
The need for circulation arises in long lines with a large number of subscribers, for example, in apartment buildings or public buildings. In a dead-end pipeline, the water will quickly cool down.
This phenomenon is pronounced at night, when water intake practically stops and the water loses thermal energy.
Starting circulation allows you to:
- constantly update the flow in the pipes,
- heat cooled water to ensure standard values.
In small water supply systems of one-story private houses, circulation is rarely used. The distance from the water heater to the water collection points is relatively small, so it is not advisable to spend money on purchasing or installing a pump, assembling a loop, and starting the process.
It’s easier to let a little water through, which has had time to cool down, to get a normal hot stream.
In what places should I install it?
The make-up valve, as well as the other technological components of the system, should be installed only in a strictly designated place. Let's look at the basic requirements for installing this device.
SNiP standards and recommendations for installation of heating systems
Previously, we talked about what SNiP standards and recommendations should be followed when installing heating systems; in addition to this article, we advise you to read this information; see all the details here
- All feed valves must be equipped with pressure gauges!
- The heating system recharge, or more precisely, the valve itself, must be installed in that part of the network where the pressure of the working fluid is minimal. If we talk about closed-type systems, then in them such a place is precisely the entrance next to the pumping equipment.
- To prevent water from the network from entering the make-up line, it is also recommended to additionally install a shut-off valve.
- If a valve with mechanical control is installed, then the installation of a valve or tap is also required. They need to be installed between the cold water supply line and the heating circuit itself.
- If the circulation pump reaches a pressure higher than the pressure created by the make-up valve, it is also necessary to install a booster pump.
For a more detailed introduction to the process, we recommend watching the thematic video material.
Video - Topping up the heating system
Types of recharge: mechanical and automatic
There are two ways to control the recharge device:
- mechanical;
- auto.
Control method No. 1 is appropriate where small heating systems are used. In this kind of lines, all pressure differences of the working fluid are regulated by means of special membrane tanks. In this case, it is much easier to resume coolant losses by manually opening the tap on the pipeline supplying cold water. This method is extremely simple, but is associated with certain inconveniences: to perform such seemingly simple manipulations, experience is required, in addition, appropriate technical skills and knowledge are needed.
Note! If a mechanical valve is used, you will have to control the intra-system pressure in a closed-loop network yourself. And if the volume of working fluid increases too much, this is fraught with emergency situations
But automatic replenishment of the heating system is used in large highways with significant branches. Sometimes they are equipped with heating boilers, which also become elements of their systems. Installing such valves does not cause any difficulties, since it can be done with your own hands. Although there is one “but”: after installing an automatic valve, the entire heating network will become volatile
And you should definitely pay attention to this when choosing this or that type of feeding unit
You can learn more about the technical parameters of the valves, as well as their average market value, from the table below.
Table. Comparative characteristics of popular feed valves
| Name | Material | Type | Diameter, cm | Limit temperature | Adjustment range | Price |
| Honeywell VF04 1/2 E | Brass | Mechanics | 1,5 | 70 degrees | Up to 6 bar | 2600 rubles |
| ISMA 1/2 | Brass | Mechanics | 1,5 | 90 degrees | Up to 4 bar | 1350 rubles |
| Meibes Fuelly 1/2 | Brass | Automation | 1,5 | – | 0.43 bar | 1710 rubles |
| Tiemme 1 | Brass + plastic | Automation | 3 | – | Up to 1.5 bar | 3680 rubles |
| Caleffi 1/2 | Brass + plastic | Automation | 1,5 | 65 degrees | Up to 4 bar | 3520 rubles |
| Watts Alimat Alomd 1/2 | Brass + plastic | Automation | 1,5 | – | Up to 4 bar | 3750 rubles |
This is interesting: Heat accumulator for heating boilers - design, types, installation rules
Calculation
How to calculate hot water supply with circulation?
Let us all turn to the same SP 30.13330.2016. According to Appendix “B” to the set of rules, the circulation flow rate of hot water supply is calculated using the formula Qc=Qht/(p*c*Dt).
In this formula:
- Qc - flow rate through the circulation pipeline in liters per second;
- Qht is the heat loss of the circuit in watts;
Specific heat transfer of a smooth steel pipe depending on the diameter and temperature difference with air
- p is the density of water in kg/m3;
Hint: with a simplified calculation, you can take it to be equal to its density at 0°C - 1000 kg/m3.
- c is the specific heat capacity of water in kJ/(kg*C);
Reference: the heat capacity of water changes as its temperature changes, however, if high accuracy of calculations is not required, it can be taken equal to 4.2 kJ/(kg*C).
- Dt is the target temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the circulation circuit.
Let's perform the calculation for the following simplified conditions as an example:
- The circulation circuit is a smooth pipe 3/4 inch in size and 50 meters long;
- It is heated to 75 degrees Celsius at an ambient temperature of +20°C;
- When passing through the circuit, hot water can cool by no more than 15 degrees.
A nuance: such a range of water temperatures in the hot water system (60-75 degrees) was allowed by SP 30.13330.2012. In the latest edition of the document, published in 2016, the requirements have become more stringent: now hot water cannot be heated above 65 ° C at the same minimum permissible temperature.
The previous version of the document had slightly larger tolerances for DHW temperature
So:
- At a water temperature of 65°C and air temperature of 20°C, the difference on the surface of the pipe will be 55 degrees;
- According to the table above, the heat loss of a meter of pipe under these conditions is 60 W/m, which, with a circuit length of 50 meters and the absence of thermal insulation, will give a total heat loss of 3 kW (3000 W);
- We substitute the data into the formula: Qc=3000/(1000*4.2*15)=0.047 l/s (0.17 m3/hour).
About connecting the make-up
The ideal place to create a recharge unit is an area with minimal pressure, preferably at the lowest point. Make-up is done on the return line, however, so that too cold water does not enter the heat generator (this is not very good for the heat exchanger of a working boiler), the pressure reducing valve is somewhat removed from the boiler or even placed on the DHW pipe if the heating device is double-circuit. In order to be able to service/repair the automatic make-up unit and not turn off the heating during this time, it is connected using a bypass and shut-off valves.
What it is?
It is impossible to organize continuous heating of water using conventional methods, so a simple and effective method is used - the hot water supply line is looped and the circulation process is started.
The flow leaves the boiler, passes in a circle and returns to the heating container.
All that remains is to adjust the speed of movement to ensure the supply of water at the standard temperature for all subscribers of the line.
Makeup valve manufacturers
The main manufacturers of the valves in question are Watts (Germany) and Emmeti (Italy).
Production by Watts Industries (part of the WATTS WATER TECHNOLOGIES concern) dates back to 1874. It is the largest manufacturer of engineered sanitary ware in the European Union. It produces heating, water supply and water treatment systems for residential, commercial and public buildings. The company's make-up valves have proven themselves to be high-quality, reliable, and efficient.
Watts> has over 20 awards from international industry exhibitions for innovations in the heating and water supply sector.
LV make-up valve EMMETI ALIMATIC
Emmeti is a company producing components for heating systems since 1976. Its main goal is quality. Scientific developments, innovative technologies and sustainable development are key success factors. Emmeti products have quality certificates in accordance with ISO 9001 standards. EMMETI make-up valves are distinguished by high quality materials and workmanship.
p, blockquote 23,0,0,0,0 —> p, blockquote 24,0,0,0,1 —>
An automatic make-up valve is a simple way to avoid interruptions in the operation of the heating system. There is no need to check the pressure from time to time, shut off the pump and manually replenish the amount of liquid. With a little investment and time for installation, the heating system will function without failure, and the house will always have a favorable microclimate.
Source
Approval for operation
To prepare an individual heating point in a house for permission to operate, you must submit the following list of documents to Energonadzor:
- Current technical conditions for connection and a certificate of their implementation from the energy supply organization.
- Project documentation with all necessary approvals.
- An act of responsibility of the parties for operation and division of balance sheet, drawn up by the consumer and representatives of the energy supply organization.
- Certificate of readiness for permanent or temporary operation of the subscriber branch of the heating point.
- ITP passport with a brief description of heat supply systems.
- Certificate of readiness for operation of the thermal energy meter.
- A certificate confirming the conclusion of an agreement with an energy supply organization for heat supply.
- Certificate of acceptance of completed work (indicating the license number and date of issue) between the consumer and the installation organization.
- Order on the appointment of a person responsible for the safe operation and good condition of heating installations and heating networks.
- List of operational and operational-repair persons responsible for servicing heating networks and heating installations.
- A copy of the welder's certificate.
- Certificates for the electrodes and pipelines used.
- Acts for hidden work, as-built diagram of the heating point indicating the numbering of the fittings, as well as diagrams of pipelines and shut-off valves.
- Certificate for flushing and pressure testing of systems (heating networks, heating system and hot water supply system).
- Job descriptions, fire safety and safety instructions.
- Operating Instructions.
- Certificate of admission to operation of networks and installations.
- Logbook for recording instrumentation, issuing work permits, operational records, recording defects identified during inspection of installations and networks, testing knowledge, as well as briefings.
- Order from heating networks for connection.