It is well known that the heat output of heating devices must correspond to the amount of heat consumption required to heat the room. But another concept is closely related to heat transfer - the size of heating radiators. The larger the surface area of the heater, the higher its thermal output. You also need to install it correctly, so that the interior of the room is not damaged. You should decide in advance where and what size you can install the batteries, and only then select them according to power. We will discuss this issue in this article.
What is center distance?
The technical passport for the heating device indicates all the main characteristics, including the inter-nipple distance. Usually this parameter is also in the model name (indicated by numbers). Sometimes experts call it not only the inter-nipple distance, but also the center-to-center or connection distance.
But all these are just different “names” of a quantity that determines the distance between the centers (axes) of the input and output collectors of a device or a separate section.
What is the difference between a 500/100 radiator and a 500/80 radiator?
In Russia today there are many types of heating equipment. When choosing a heating radiator (battery) for your apartment or private house, the first argument should be the type of heating of the house:
Autonomous heating of a private house up to 500 m2 Autonomous heating of premises over 500 m2 (roof boiler rooms) Centralized heating in apartment buildings or non-residential premises of any size.
Why do these three types affect the choice of a 500/100 or 500/80 radiator?
Each version of this type of heating operates according to different parameters and the composition of the coolant in the pipeline and radiators. Autonomous systems up to 500 m2 - the pressure in the system cannot be more than 3 Bar (kilogram) and the coolant, if desired, can be filled without unnecessary chemicals that accelerate the aging process of equipment.
Autonomous systems over 500 m2 - roof boiler room for residential apartments in a multi-storey building, the pressure depends on the height of the building, but not more than 6 bar (kilogram) with a conventional coolant (tap water).
Centralized heating of apartment buildings and non-residential premises is the most problematic heating system throughout our homeland, the pressure in such systems reaches 9 Bar (kilogram) with a coolant that contains chemical reagents and a lot of dirt.
All of the above affect the durability of your batteries and the connections (pipes and taps) to them. Knowing the system and the factors of their problems, consider the heating devices themselves, and in the next article we will decide which pipes and taps to install.
These devices are available to choose from:
Cast iron - irrelevant, ugly and ineffective in terms of heat transfer 160 W per 1 m2. Aluminum - modern, beautiful, efficient 199 W per 1 m2 for a burst of up to 25 Bar. Bimetallic - modern, beautiful, 187 W per 1 m2, but with a burst power reserve of up to 40 Bar.
A steel panel radiator is modern, efficient, reliable, but not always affordable.
Cast iron batteries do not need discussion!
Aluminum radiators:
The most common type of heating equipment today, so much has already been said and written about them, but aluminum radiators are still worthy of attention. Their technical data for all manufacturers is almost the same if we consider the 500/100 model, since the properties of aluminum are unchanged. A good manufacturer improves the design and convection of the device for greater heat transfer to each section. The working pressure of the radiators is 16 Bar (kilogram), the burst pressure is 25 Bar.
The difference between height and center distance
The center-to-center distance of bimetallic radiators of different models may be the same, but the installation height may differ, depending on the design and design features.
The height of a bimetallic radiator and the center-to-center distance are different characteristics that should not be confused. The difference between the concepts is especially “manifested” in the case when a heating device is to be installed in a niche or opening under a window:
- The standard center-to-center distance of a bimetallic radiator is 300, 350 or 500 mm; such devices are considered universal.
- Less common are models in which this parameter is 200, 400, 600, 700, 800 or 900 mm, but they are also produced.
When choosing a suitable model, you need to take into account both the center distance and the height of the bimetallic radiator . When installing, you need to not only “fit” the device, but also maintain the recommended distances to the wall, floor and window sill. Otherwise, there will be insufficient space for airflow to move, causing the heater's efficiency to be significantly reduced.
For example, a bimetallic battery with a center distance of 500 mm has a standard installation height of 570 to 590 mm.
Types and types
There are two types of steel radiators, the most common being the panel radiator. less popular tubular radiator. Panel-type radiators are panels mounted on a floor surface or on a wall. This type of steel radiator has a high level of aesthetics, and the heat supply factors are also higher.
The production of panel radiators occurs according to a certain method: two plates are welded together, and a heat flow is generated between them. The thickness reaches 2 cm, spot welding in this production is the main welding and production point. The advantage of the system is choosing the appropriate size. There are also advantages in connecting radiators. This connection can be different, the most famous are only three: installation from the side, from below, standard.
Panel steel radiator
Dependence of section capacity on center distance
The center-to-center distance of a bimetallic radiator determines an important parameter - the section capacity, on which the thermal power of the device ultimately depends :
- In models with an inter-nipple distance of 500 mm, the section capacity is 0.2-0.3 liters.
- With a distance between the inlet and outlet openings of 350 mm, the section capacity is 0.17 - 0.2 liters.
- In bimetallic radiators with an interaxial distance of 200 mm, the volume of coolant varies from 0.1 to 0.16 liters.
Installation features
Installation diagram
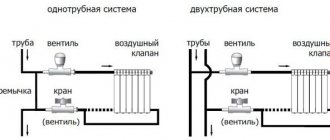
The process of installing a radiator of any type consists of a number of standard steps. First of all, old batteries are dismantled, if any, and places for placing the fasteners are determined, on which the brackets are then fixed. At the second stage of installation, you need to prepare and hang the battery itself and install shut-off valves, then connect the pipes, observing the center distance in the heating radiators. It is important to select the correct sizes of heating batteries and install them correctly, regardless of size.
Radiators are placed strictly horizontally or with a slight slope, taking into account the direction of flow of the coolant. In the second case, if clogged, it will be easier to remove air pockets.
You can connect the batteries to the main line from below, from the side or diagonally; a separate valve and Mayevsky tap are installed on each device, which makes it possible to repair the radiator without having to completely disconnect the entire system. The dimensions of the devices should be calculated in advance to determine their available power.
Center distance and height of a bimetallic radiator: expert advice
Expert recommendations:
- The height of a bimetallic heating radiator can be calculated according to the following scheme: 80 mm must be added to the center distance . For example, if the distance between the centers of the inlet and outlet manifolds is 350 mm, then the final (mounting) height is approximately 430 mm.
- If the center distance of a bimetallic radiator does not correspond to the height of the pipes, it is enough to bring them together or separate them . But a condition must be observed: the transition must be smooth and not at a right angle.
- The optimal height of a bimetallic heating radiator is determined so that after installation in a niche or area under a window, the distance from the wall to the device is from 3 to 5 centimeters . If the device is closer, the thermal energy is distributed irrationally. Also, the upper part of the device should be at a distance of 8-12 centimeters from the window sill. A small gap will reduce the heat flow from the radiator. The ideal distance from the floor to the heating device is 10 centimeters. If it is set lower, the heat transfer efficiency will significantly decrease. Another problem will arise - the difficulty of removing dirt from the floor in the area under the battery. The opposite option - placing the radiator too high in relation to the floor - will lead to uneven temperature readings in the room.
- The most popular are bimetallic radiators with a center distance of 500 mm ; this size is “standard” for most new buildings. Models with an inter-nipple distance of 200 are ideal for small kitchens and bathrooms. 800 mm devices are usually used for installation in commercial facilities, offices, and private residential buildings.
Are you having difficulty choosing the optimal parameters for your heating device? Do you want to know what the optimal height of a bimetallic radiator for your room will be? Then contact a SANTEKHPROM representative by phone. Our specialist will provide competent recommendations and tell you in more detail about the features of choosing equipment.
Device popularity
Before installation, most people wonder how to choose the right heating radiators. what is the main task when choosing them? In the modern world there is a wide range of such systems. This is great because there is variety in the choice, but such variety causes a feeling of uncertainty in the buyer. After all, most of these products are made by many manufacturers, differing in design, color scheme and other special categories.
Steel types of radiators are now recognized as the most popular type among heating structures,
Steel heating radiators are a device for insulating and warming apartments and houses; the equipment has a pair of stainless steel sheets welded together, having a water space, or place for water. Steel batteries should not be installed in places with a damp temperature; this equipment cannot be installed in baths and bathrooms, as it will deteriorate.
Steel radiator design
Quantitative characteristics
Quantitative characteristics must be confirmed during tests, the results of which serve as the basis for obtaining a certificate of conformity. The list of confirmed characteristics, as well as test methods and conditions are specified in regulatory documentation - Russian (GOST) and European (EN 442-2) standards, or specially issued and approved technical specifications (TU).
Number of sections
The vast majority of aluminum radiator models consist of separate sections. Division into sections allows you to select a device of the required power depending on the area of the heated room.
Five-section aluminum radiator.
The buyer can purchase both individual radiator sections and a ready-made factory-assembled heating device. As a rule, factory-assembled radiators include from 4 to 12 sections. When assembling sections together, a nipple connection is used.
The number of sections required to heat the room is determined by the approximate formula:
where S is the area of the room, m2;
P – thermal power of one section, W.
The Italian company Global produces twin models of the GL/D series, which have 2 rows located symmetrically relative to the plane of the rear wall of the sections. Double radiators are used if they need to be installed at a distance from the wall.
Thermal power (nominal heat flux)
This parameter (measured in W) allows you to determine how many sections a radiator should have to heat a certain area.
Separate sections of aluminum heating radiators.
According to GOST 31311-2005 “Heating devices. General technical conditions", thermal power is determined under the following conditions:
- temperature difference (difference between the temperatures of the coolant and the air in the room) ΔT= 70°C;
- atmospheric pressure B = 760 mmHg;
- The coolant moves through the heating device from top to bottom.
Some manufacturers additionally indicate thermal power measured at a temperature difference of 30°C and 50°C.
External heating surface area
This value includes the area of all surfaces of the radiator section that are in contact with the air in the room, including the area of the fins. The outer surface area is usually:
- for sections with an interaxial distance of 350 mm – 0.3…0.4 m2;
- for sections with an interaxial distance of 500 mm - 0.4...0.5 m2.
Geometric characteristics
Overall and installation (connection) dimensions determine the possibility of installing a heating radiator under specific placement conditions. Also, the dimensions of the heating device affect its thermal output.
Center distance
Center-to-center is the distance between the axes of the upper and lower collector. Among mass-produced radiators, models with center distances of 200, 300, 350, 500, 600, 800 mm predominate. A center distance of 500 mm is the most common, and radiators of this size are present in the model range of all manufacturers. Global produces Oscar series models with center distances from 900 to 2000 mm.
Counting the number of sections, knowing the height of the radiator
Knowing the thermal power and height of the radiator, you can choose its model or calculate the number of sections if it is not solid. If a heating device with the required characteristics is not on sale, you need to buy a battery of higher power, otherwise the heating efficiency will decrease.
Sometimes heating radiators have dimensions that make them impossible to install under the windowsill. In order not to violate recommendations regarding the distance to the floor and window, you need to choose low heating devices. Longer radiators distribute heat evenly and create a dense thermal curtain.
In sports and industrial premises with high ceilings, it is often necessary to use tall appliances, since a large volume of air needs to be heated. In this case, they are hung on the walls. The types of tall radiators are as follows:
- R – with side connection;
- RD – with bottom connection.
Such batteries have good heat transfer and high convection characteristics. The height of the radiators can be 760, 940 and 1120 millimeters, the width varies from 400 to 1400 millimeters. The standard depth of a heating radiator is 90 millimeters.
The most important characteristics of steel radiators
Heat dissipation
With heat transfer, things are not bad at all - the heat transfer rate varies from 1200 to 1800 watts and even more. This parameter depends on the dimensions of the radiator, its brand and the type of specific model. Note that the big advantage of these devices is their low inertia. They heat up very quickly and begin to give off heat to the room.
The process of heat transfer occurs in two ways: direct heat radiation and heat transfer by convection.
Operating pressure
The maximum operating pressure for this type of radiator ranges from 6 to 10 atmospheres for plate radiators. This parameter is limited due to the properties of steel such as ductility. However, tubular radiators can withstand higher pressure - from 8 to 15 atmospheres. All this means that steel radiators cannot be used in central heating systems. They will not be able to withstand the pressure of the central heating network.
Coolant quality
An important detail is how “gentle” the radiator will be relative to the quality of the coolant. For steel, this is a real stumbling block - because it rusts so easily when air comes into contact with water. However, manufacturers are not giving up - they are trying to overcome this problem. Special internal coatings are applied for protection. But, unfortunately, this struggle often ends with the victory of corrosion. Therefore, it is better not to install steel radiators in an apartment in a multi-story building. In the summer, the water will be drained, and rust will begin to eat the radiators.
Coolant temperature
The maximum hot water temperature that steel batteries can withstand is from 110 to 120 degrees.
Center distance.
Steel radiators can have both side and bottom connections. The center distance is important for radiators with side connections. It determines at what distance the upper collector is from the lower one. This must be taken into account when installing the radiator. Steel panel radiators, depending on the model, type and manufacturer, can have an interaxial distance equal to the height of the radiator minus 50 - 70 cm. For tubular steel radiators, the interaxial distance ranges from 120 mm to 2930 mm.
dimensions
Now a few words can be said about the external parameters, in particular the dimensions. The length of panel-type radiators can reach 3 meters, their height is from 20 to 90 centimeters. A tubular radiator can be made to almost any length, and its depth is limited to 22.5 centimeters. Height varies from 19 to 300 centimeters.
Steel thickness.
Few people pay attention to this indicator, but manufacturers use steel of various thicknesses to make steel radiators. This indicator can vary from 1.15 to 1.25 mm. It is clear that the thicker the steel, the better.
Durability
Thanks to the material used – strong and reliable steel – these radiators are able to live a long life without letting their owners down. High-quality products with thick walls (0.12-0.15 centimeters) produced by reliable brands that are responsible for their products serve especially well.
Ease of installation
Installation of these heating devices is not very difficult. Moreover, it is very convenient that it is possible to choose a panel-type radiator with connections both from the side and from the bottom. In the latter case, the pipes can be hidden under the floor, and the temperature sensor is connected directly to the radiator. And the panels of the radiator itself can be connected in series or in parallel - both types of models can be found on sale.
Panel type radiator with bottom connection system.
Royal Thermo
Another Italian brand of radiators, distinguished by a wide range of products and original design. The PianoForte model looks especially interesting. It is possible to order radiators in various colors. The battery design is made using the patented Power Shift technology: additional fins are installed in the vertical collector to increase heat transfer.
Compared to other brands, radiators from this company are designed for lower operating pressure - 20 bar. The coolant temperature is also not too high - 90 ° C.
Popular models:
- Royal Thermo BiLiner 350/500 – 117/171 W;
- Royal Thermo Revolution Bimetall 500 – 116/168 W;
- Royal Thermo Vittoria 350/500 – 114/167 W;
- Royal Thermo PianoForte 500 – 185 W.
Solid or sectional
There is another difference between bimetallic radiators, which concerns their design features. Basically, products with a certain number of sections are produced. The more there are, the more heat there will be. They can be collapsible, that is, if necessary, the radiator can be reduced or enlarged. In production, each section is completely manufactured, after which they are connected with nipples. The number of sections is paired.
But, there is a second type of radiator batteries - solid ones. Their core is made to a specific size and cannot be changed in the future. After that, the steel pipes are sheathed with a figured shell of aluminum coated with enamel. Such a radiator will not burst even in the event of a pressure surge of up to 100 atmospheres.
What are the dimensions of heating devices?
There are generally accepted standard sizes: thickness - 9 cm, width - from 40 cm, height - 76, 94 and 112 cm. However, the linear parameters of heating radiators can vary significantly. Their dimensions depend on the material from which they are made and their design.
By thickness (depth)
The thickness of heating radiators depends on the materials from which they are made and their shape:
- If you want to install thinner devices, then cast iron and bimetallic devices are clearly inferior in terms of material: the former due to fairly thick walls, and the latter due to the double layer of metal.
- The shape also affects the thickness. Panel devices are the thinnest: the thickness of steel and aluminum panels does not exceed 1 cm.
Width
The width of the battery can also be different: both small (less than 40 cm) and much larger - up to 1.5 m, which can be very convenient when planning a room with space restrictions for their placement.
An original solution for “wide” heating
Remember! To maintain the thermal balance in the room when the width of the heating apparatus is reduced, its height or the number of installed sections must be increased.
By height
Here, the sizes of radiators vary in the widest range - from 15 cm to 3 meters. They differ:
- Standard. The height of standard cast iron batteries is 588 mm, aluminum sections are 575 mm, bimetallic sections are 550-580 mm.
- Low. The height of “low” cast iron batteries can be about 35 cm, and aluminum ones – 15 cm. They have the enviable advantage of being placed under low window sills. An innovation is the so-called “plinth” radiators offered by some companies, the height of which can be only about 2 - 3 cm.
- Tall, or vertical with a small width, can reach 2 or 3 meters in height. They are installed in places where there is no suitable space for standard heating, but large volumes of air need to be heated. They are considered decorative and have wide design possibilities.
Interesting! Lower units have slightly greater heat transfer. This occurs due to the minimization of contact of warm air with the top of the device and the large heat flow from the fin surface.
Advantages compared to other batteries
- The undeniable advantage of a cast iron radiator over modern aluminum, steel, and bimetallic batteries is its durability. The half-century anniversary of the cast iron battery is a ubiquitous phenomenon. In some cities, the batteries that were cast in the century before last have survived to this day and continue to work properly.
- The cost of a cast iron product can only please the future owner - European prices for trendy aluminum or bimetallic batteries are not affordable for everyone. In addition, purchasing a large number of sections promises significant benefits.
- Another advantage of cast iron is the absence of any coolant requirements. Water of any quality is poured into the heating system.
- The thickness of the cast iron sections allows them to withstand the highest operating pressures. starting from 9 Atm and above. In addition, cast iron withstands water hammer very well, which is why it is preferred in centralized heating systems.
How to choose the size of a heating radiator
The selection of battery size is as follows. After making sure that the products from the manufacturer that suits you are suitable in height and depth, you need to find out the number of sections for each room. To do this, we calculate the required thermal power of heating devices using the algorithm:
- in a room with one external wall and 1 window, 100 W of heat is received per 1 m2 of its area;
- if there are two walls facing outside, then you need to take 120 W per 1 m2 of room;
- when there are 2 walls and 2 windows, then 130 W/m2.
Note. The algorithm will give the correct result for rooms up to 2.5-2.7 m high. If the ceilings are higher, it is recommended to take 40 W of heat per 1 m3 of room volume.
Multiplying these figures by the area of the rooms, we obtain the required thermal power, from which we determine the size of the battery, taking the heat transfer of 1 section as a basis. Below, as an example, are tables showing all sizes, center distances and heat transfer of aluminum and bimetallic GLOBAL radiators:
As a rule, the values of the thermal power of the sections are indicated taking into account that the difference between the average temperature of the coolant and the air in the room is 70 ˚С (in the passport it is written: at DT = 70). This means that at +22 ˚С in the room the supply water temperature should be about 100 ˚С, while in a private house it is rarely 70 ˚С.
And at this temperature, the battery section will give off 30% less heat, which should be taken into account.
Advice. In order not to make a mistake, you need to subtract 30%, or better yet, 50% from the power indicated in the product passport.
Having determined the real power of 1 section, it becomes clear how to find their number: divide the previously found heat consumption by this value. But after this, you may encounter a situation where the heater assembly does not fit into the window sill niche or, conversely, looks too unpresentable in it, as shown in the photo:
How to choose the battery size in such cases? If it does not fit under the window, then the solution is simple: you need to divide the number of sections into 2 parts, instead of one device you will get two. The length of the first will be 75% of the window opening, and the second will be all that remains. This part can be placed near the side wall, connecting pipelines to it. In the opposite situation (as in the photo), you need to take sections with a smaller center distance and height. Their heat transfer is less, which means that the total length of the heater after recalculation will increase, and as a result it will look great.