Heat recovery in ventilation systems: principle of operation and design options During the ventilation process, not only exhaust air is recovered from the room, but also part of the thermal energy. In winter, this leads to higher energy bills.
Heat recovery in centralized and local ventilation systems will allow you to reduce unjustified costs without compromising air exchange. To recover thermal energy, different types of heat exchangers are used - recuperators.
Peculiarities
The rotary recuperator has a heat exchanger rotating at a given speed.
It contains two channels - exhaust and supply. They allow for high-quality ventilation.
The advantages of rotary recuperator models include the following points:
- very high efficiency (efficiency 70-90%), especially in winter;
- reducing the operating time of the air conditioner in the summer due to effective cooling of the room;
- the recovery process is fully automated;
- There is no need to worry about condensation as there are no defrost cycles.
However, like any technical devices, rotary-type recuperators also have their disadvantages, among them:
- high cost compared to other models;
- there is some noise during operation;
- mixing of cold and hot air may occur;
- some models have very large dimensions, which makes them impossible to use in small rooms;
- the device requires frequent maintenance, as it consists of many moving elements that can sometimes fail.
There are several types of rotary recuperators.
- Sorptive. These models use silica gel as a sorbent. Thanks to this material, the drum of the rotary heat exchanger perfectly absorbs moisture, preventing condensation from forming and disrupting the operation of the device.
- Epoxy. This type of coating of the inside of the recuperator allows you to protect the aluminum drum from the aggressive effects of certain chemical compounds in the air. The epoxy-coated recuperator perfectly resists the influence of sea salt, chlorine and chemical reagents in large-scale production.
- Enthalpy. In this type of device, the inner drum is covered with a material that absorbs not only moisture, thereby preventing condensation from forming, but also thermal energy.
- Condensation. On such models there is no special coating on the drum. They are not able to drain condensate, hence their name.
- Antibacterial. In this case, a special impregnation with an antimicrobial effect is applied to the inner surface of the recuperator. Such a device can purify and protect indoor air from 600 types of known pathogens.
In normal (non-production) conditions, the most budget-friendly condensing recuperators are most often used.
If there are high humidity levels in the room, then it is justified to install hygroscopic rotor models. Other types are intended to a greater extent to ensure effective ventilation of premises in hazardous industries.
Main components of the recovery system
The recovery system includes, in addition to the main unit with plates, a fan. In addition, recuperators are equipped with:
A system for removing condensate that inevitably forms on the plates in order to avoid water getting into the air channel or the formation of ice in it. Such a condensate collector must be equipped with a water seal that blocks the operation of the fan in the event of excess moisture. A special bypass valve is used as a device for regulating the intensity of air flows
An important design feature of such a valve and plate recuperator is the complete absence of moving parts.
As mentioned above, plate recuperator heat exchangers can be made of various materials. Each of them has its own properties, advantages and disadvantages.
Let's try to compare them with each other:
- Aluminum plates or galvanized steel heat exchangers. Such systems are quite popular due to their relatively low cost. However, such a plate recuperator has a relatively low efficiency, since it regularly requires the use of a defrosting mode.
- Plastic heat exchangers have higher efficiency and efficiency, but are also much more expensive.
- Plates made of special paper are also highly efficient, but such heat exchangers cannot be used in rooms with high levels of humidity (swimming pools, car washes, some industrial premises), since condensate quite easily overcomes the walls of the cassette.
- Recuperators with double paper cassettes are also used. Their efficiency is significantly higher due to additional heating of the air, but, nevertheless, they are also afraid of high levels of air humidity.
Principle of operation
The rotary recuperator operates on a heat transfer scheme from exhaust flows to supply flows. Fresh air entering the rotor is heated by the action of the plates and penetrates into the room. The device operates from the mains, and the settings allow you to select the optimal rotor speed. The two air flows do not mix with each other, but interact and it is due to the temperature difference that heat exchange occurs. Hot air in the recuperator is cooled, and cold air is heated.
Air recovery principle
To understand the advantages and benefits of using recuperative heat exchangers, you first need to understand the very essence of their work. Literally translated from Latin, recovery is called “return of used, spent.”
It is the energy return effect that is used in climate control devices of this design. Air flows passing through the unit exchange thermal energy with each other, allowing the air conditioner to subsequently maintain a comfortable temperature, using less energy. On particularly cold days, this allows you to significantly save on heating the room.
Example: the air temperature outside has reached minus 20°C. For residents to feel comfortable, the air conditioner must create a room temperature of at least + 25 C. The temperature difference is easy to calculate - 45 degrees Celsius. Of course, some part of the air will heat up due to the heat capacity of the walls, furniture, and heat exchange between the incoming and outgoing flows. But the air conditioner will still require a significant amount of energy to maintain comfort.
Plate and any other recuperator of the chosen design allows you to move the point of contact of cold and warm air outside the room. The device conducts active heat exchange between them, allowing the incoming flow of fresh air to reach a more comfortable temperature value than the original one.
How is it different from lamellar?
Plate recuperators are clearly inferior to rotary models, mainly due to their lack of an electric drive. In plate devices, you can only change the direction of the plates and limit or increase the throughput. In rotary devices everything is arranged better. It is more flexible in settings, does not freeze in winter and shows better energy saving results compared to plate models. As a result, the latter are much cheaper than rotary models.
Comparison with plate models
Compared to rotary units, plate models do not have a drive and carry out heat exchange in autonomous mode. The user can manually change only the throughput of the mechanism by changing the direction of the accumulating plates. From this we can draw conclusions about the pros and cons of both systems. But first, it’s worth talking about the general advantages. Both rotary and plate heat exchangers are small in size and have sufficient performance. This eliminates the need to use additional devices, including power ones. If we talk about differences, then the rotary mechanism is more flexible in adjustments, free of the risk of freezing in winter, and energy efficient. But at the same time, it has a more complex design and provides for a certain amount of mixing of exhaust flows and fresh air.
How does a rotary recuperator work?
This device is cylindrical in shape and consists of a main element - an aluminum rotor, made up of smooth and corrugated plates. The aluminum rotor is covered by a housing made of galvanized steel.
Rotary air recuperator
In addition, the device includes a drive mechanism that has a belt for rotation, as well as axial bearings, a sensor for controlling the rotation of the rotor itself, and a sealing tape. The latter is designed to isolate air masses.
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of the device is quite simple. The device is put into operation by engaging a V-belt drive. If the product is operated at high temperatures, the electric motor is mounted outside the body of the heat exchanger. Also in this case, a chain is used instead of a belt.
Inside the rotary heat exchanger, heat is transferred from heated gas to cold gas. A rotating cylinder rotor, which is made of small metal plates, is responsible for this. Subsequently, the hot gas heats up these plates, and then the plates go into the flow of cooled gas, after which they transfer thermal energy to it.
Operating principle of a rotary recuperator (video)
Types of rotary drum coating
There is a classification of recuperators according to the type of coating of the rotary drum. There are currently five types of products:
- condensation type - in this case, the rotor is an aluminum drum, which has no coating and can only remove the thermal energy of air masses, but it is not capable of moving the heat of moisture from air masses;
- hygroscopic type - in this case, the drum is covered with a special hygroscopic coating, which has sorbing properties - the drum collects moisture during operation, and then transfers it from stream to stream, during which both moisture and latent heat of air masses are removed;
- sorption type - in this case we are talking about a modification of the hygroscopic type using a coating in the form of silica gel - this sorbent has a huge surface area, approximately 800 m2/g, which makes it an extremely powerful means for absorbing moisture;
- epoxy type - this coating is used in cases where it is necessary to additionally protect the aluminum drum from the possible destructive effects of chemical compounds present in the treated air (for example, if the air in the room contains chlorine or various vapors, such as ammonia);
- antibacterial type - in this case, the drum is protected with an antibacterial coating that can withstand about six hundred types of pathogenic and non-pathogenic microorganisms (usually such a coating is required for enthalpy rotors).
Types by area of application
Now there are three main types of air mass recuperators, differing in the scope of operation and additional “filling”.
Product types:
- Standard view. In this case, the regenerator is divided into several sector parts (from 4 to 12). This type of device is used to remove excess heat from exhaust air. Also, such a device transfers moisture when working out air flows below the “dew point” temperature.
- High temperature type. This type of device is used to remove heated air currents, the initial temperature of which reaches approximately +250 degrees.
- Enthalpy view. This device is used to remove total thermal energy, but in addition to this, the device also transfers moisture.
Operating principle of the air recuperator
Recuperators are also divided according to their design. In this regard, there are two types of products: horizontal and, accordingly, vertical rotor.
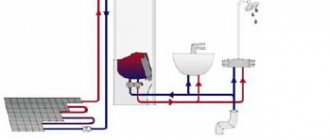
Water recirculating air recuperator.
Water recirculation air recuperators are a type of air recuperator used in supply and exhaust ventilation systems, which has its own interesting features. The principle of operation of a water air recuperator is to transfer thermal energy from a separate exhaust heat exchanger to a supply heat exchanger using water, antifreeze, or other coolants. The supply and exhaust heat exchangers of such an air recuperator can be located at a distance from each other and connected by a heat-insulated pipeline. They are not used so often due to their low efficiency and the need for frequent maintenance. They are used mainly for the purpose of modernizing separate supply and exhaust ventilation, or when it is not possible to locate the exhaust and supply lines close to each other.
Advantages of water recuperators
Plate heat exchangers have an efficiency of 50-65%.
The exhaust and supply flows never mix, which prevents partial transfer of contaminated air from the exhaust to the supply.
It is possible to place the supply and exhaust heat exchangers at a distance from each other, which gives this system flexibility in design and installation.
Possibility of combining several exhaust and several supply systems into one recovery system.
Disadvantages of water recuperators
The presence of an additional water line requires the installation of a water pump and additional devices responsible for the correct operation of this system.
The energy consumption for operating the water circulation system and the heat loss of the coolant, if the supply and exhaust heat exchangers are remote from each other, makes this system impractical.
These recuperators are only capable of heat exchange. Moisture exchange in this type of recuperator is impossible.
For Russia, issues of heat conservation are very relevant: we are one of the northernmost countries on Earth. For comparison, New York is actually located much further south than our beloved warm resort of Sochi. And Moscow is located much further north than the seemingly cool London.
However, we constantly have problems with the use of energy efficient technologies. This applies both to heat-insulating materials and to various heat pump installations. Advertising plays a significant role in wasting the overall energy and heat of your own home. Manufacturers try by any means to convince us that their materials are the very best, and often the decisive argument is the fashionable and incomprehensible word “thermal insulation”. Moreover, according to advertisers, any material has high characteristics in this field - shell rock, expanded clay concrete, cinder block, polystyrene foam, wood.
Some of these designs, when installed correctly, can actually reduce energy costs somewhat. But even if, for example, the heat loss of foam concrete is 27% lower than that of polyurethane foam, this does not mean that the total energy costs for heating a building built from it will be at least 10% less! This is because only 20% of the heat from the house escapes through the walls, windows and ceiling. Another 25-30% falls on the foundation and floor, and the main part is occupied by losses through ventilation: from the vents to the central air conditioning units. Moreover, it would seem that we cannot do anything about this - we need to breathe something!
So our compatriots spend tens and hundreds of thousands of rubles on heating. At a time when developed Western countries literally pray for energy-saving technologies, Russians prefer to overpay and rely on the super-thermal insulating properties of cinder blocks with a unique coating.
And we will be smarter and first read an article about heat recuperators (“recuperators”).
General information about recuperators
In winter, ventilation systems for large premises (offices, multi-storey buildings, factories, etc.) must ensure heating of the supply air. For this, gas, water or electric heaters are usually used. Their energy consumption cannot be called modest: on average from 400 kWh for electric ones or 4.2 cubic meters. m per hour for gas devices. You can calculate for yourself how much it costs.
At the same time, the warm air that is already in the room is mercilessly thrown out into the street. But the energy spent on processing it cannot be returned. Or is it still possible?
In order to transfer energy from exhaust air to supply air, so-called heat recuperators were invented (from the Latin word recuperatio - “return receipt”).
We’ll talk about their structure and operating algorithms later, but for now – a minute of statistics.
According to expert estimates (read here), using recuperators saves up to 75% of energy. The specific value, of course, is calculated individually for each object, and the more the building relies on ventilation, the higher it is.
In addition, the efficiency of the devices is highly dependent on operating conditions: temperature, humidity and air pressure inside and outside the building. On average, at a given outside air temperature of -22 °C and an internal air temperature of 26 °C, according to manufacturers (they are quite similar), the efficiency of the recuperator will be 55%. Then, with the efforts of air heaters or batteries, it remains to heat less than half of the air entering the building. The cost of 400 kW of electricity per hour instantly becomes 200 kilowatts. Although, in general, heaters can no longer be installed with recuperators.
Types of recuperators
When making a device with your own hands, you should decide on its type. There are several types of recuperators:
- rotary;
- lamellar;
- recirculating water;
- chamber;
- freon
Rotary
The rotary recuperator consists of corrugated steel plates. Externally, the design is a cylindrical container. A rotating drum alternately passes warm and cold flows. During operation, the rotor heats up, which transfers heat to the cold air. The rotary apparatus is highly economical. You can set the required number of rotor revolutions and adjust the power. The advantage is that this type can be used throughout the year, since an ice crust does not form on it.
The disadvantages include the size of the structure. It requires a large ventilation chamber.
Lamellar
The plate recuperator consists of aluminum, plastic and special paper plates. In some models, air flows move perpendicular to each other, in others they move in opposite directions.
If aluminum plates are used in the design, the system is characterized by a low efficiency. This is due to the fact that the device often freezes and needs regular thawing. The advantage is its low cost. In addition to aluminum plates, galvanized steel can be used. Heat exchangers made of plastic have greater efficiency, but are also more expensive.
If the material is special paper, then the output of such equipment is high. However, there is a significant drawback: the device cannot be used in a damp room. The resulting condensate impregnates the paper layers.
Recirculating water
A distinctive feature of this type is the separation of supply and exhaust heat exchangers. With the help of antifreeze or water, thermal energy is transferred from the exhaust part to the supply part.
The system has its advantages:
- no possibility of mixing flows;
- separated heat exchangers facilitate work at the design stage;
- the ability to combine several supply or exhaust flows into a single one.
Flaws:
- the need for a water pump;
- Recuperators are only capable of heat exchange, and moisture exchange is impossible.
Chamber
Both flows are directed into a single chamber. It is divided by a partition. After heating one part, the partition is rotated. The heated part, which heats the room, begins to accept supply air. The disadvantage is the high probability of mixing air flows, which leads to contamination.
Freon
Based on the physical characteristics of freon, which is located in hermetically sealed tubes. At the beginning of the pipe, air is heated along with freon, which boils and evaporates. The heat moves on. Freon vapors come into contact with cold streams and condense. Then the cycle repeats.
Energy efficient system that conserves heat
In addition to the material from which the heat exchanger elements are made, recuperators also differ in the direction of air flow. In the most common cross-flow type of recuperator, the flow of supply and exhaust air flows perpendicular to each other, and in the counter-flow type - in opposite directions. This is due to the fact that for effective heat exchange, the flows, ideally, should not come into contact with each other and mix.
Using this principle of operation, a plate heat exchanger ensures uninterrupted heating of incoming air during the cold season and reduces to a practical minimum that common effect of ventilation and heating systems, which is commonly called “street heating”. Which is the main feature of the so-called energy efficient systems.
Recuperators, unlike conventional air ventilation systems, are capable of not only successfully performing heat exchange functions, but also combating unpleasant odors, and certain types can cope with high room humidity. If you are not ready to purchase a plate recuperator, you can try to make it yourself using these instructions.
Rivals of the rotary recuperator
There are other types of recuperative heat exchangers, which often become elements of supply and exhaust systems.
Lamellar
These devices are the most popular because they are relatively simple, they do not require electricity and serious maintenance. Low cost is another big advantage. Such devices are heat exchangers consisting of a large number of plates, between which minimal distances are left. The materials for their manufacture vary greatly: it can be metal, plastic or cellulose. Recuperation in devices occurs in different planes, so the flows of warm and cold air do not mix.
There is a downside - the accumulation of condensation, freezing in extreme cold, so the devices require regular thawing in winter. For this reason, in cold weather, the ventilation unit is turned off, or an additional element is installed - a supply air flow heater.
Mermen
If they are called correctly, they are glycol or alcohol, since ordinary liquid will quickly freeze in winter. This equipment consists of two heat exchangers that are connected by a liquid circuit. Such elements are installed at a distance from each other, so the air flows also do not mix.
Another advantage of the device is minimal fat deposition, which means less fire hazard. For this reason, they are often installed in cafes and restaurants, even in hot shops. The device does have some disadvantages: it is large in size, not very impressive efficiency, barely exceeding 50%, and high price due to the need for additional equipment - a heat pump.
Other types - chamber, tubular recuperators - are not used for ventilation in private homes, so there is little point in describing them. If we consider this “trio” of candidates as models for self-assembly, then there is only one leader - a simple plate device.
Main functionality
The purpose of the recuperator is to automate the process of air recovery, that is, returning it to its original characteristics (in this case, temperature). The design of a standard recuperator is quite simple - it is a double-walled heat exchanger design for the simultaneous passage of two air flows: exhaust and supply.
These flows do not mix with each other, but only influence each other. Since there is a difference in the temperature of the supply and exhaust air flows, in the process of mutual influence an exchange of thermal energy occurs. Masses of cold air are heated, and warm air, accordingly, are cooled.
Another function of recuperators can be considered air dehumidification, since in the process of cooling warm air masses, the released moisture condenses on their walls.
How to increase efficiency
Careful assembly and attention to detail when creating a homemade heat exchanger will allow you to achieve good efficiency indicators. However, the assembled air recuperator with your own hands can be significantly improved and its efficiency increased. To do this, when calculating the design and its implementation, it is necessary to provide for the following nuances:
- Maximum sealing of the device;
- Use of high-quality heat-insulating materials;
- Increase the size of the recuperator and the area of the heat exchange surface. This will reduce the speed of air passing through the device, and accordingly allow it to warm up or cool down better;
- The use of corrugated plates or plates with stampings, which will significantly increase the heat transfer surface area while maintaining the total volume of the device;
- Increasing the exhaust volume compared to the inflow. Thus, a larger volume of outgoing air will better transfer heat to a smaller volume of incoming air.
A do-it-yourself air recuperator is a simple, affordable, cheap and effective way to save expensive thermal energy and effectively use irreplaceable natural resources.
Recuperator efficiency
The most important characteristic of a recuperator is its efficiency. It shows how much the recuperator was able to heat the supply air relative to the ideal option. The ideal option is taken to be the case when the supply air is heated to the temperature of the exhaust air. In practice, this option is unattainable, and heating occurs to a certain intermediate temperature Tp. The efficiency formula is as follows: K= (T_P-T_N)/(T_B-T_N), where:
- TP – supply air temperature after the recuperator, °C,
- ТН – outside air temperature (supply air to the recuperator), °С,
- TV – temperature of the exhaust air to the recuperator, °C.
This formula takes into account the change in sensible heat in air flows. However, the relative humidity of the flows may also change, and then it is better to resort to calculating the efficiency of the recuperator based on the total heat. The formula is similar in appearance to the previous one, but is based on the enthalpies of air flows: K = (I_П-I_Н)/(I_В-I_Н), where:
- IP – enthalpy of supply air after the recuperator, °C,
- IN – enthalpy of outside air (supply air to the recuperator), °C,
- IB – enthalpy of exhaust air to the recuperator, °C.
The first formula allows you to quickly assess the efficiency of recovery. For more accurate results, use the second formula.
Advantages and disadvantages of different types of recuperators
The advantage of recuperators is obvious - they allow you to significantly save on heating the supply air in winter and cooling the supply air in the summer. Among the disadvantages of recuperators are the following:
- They create additional aerodynamic resistance in the network. Indeed, like any other element in the ventilation network, recuperators have some resistance, which should be taken into account when choosing a fan. However, this resistance is not high (usually no more than 100 Pa), and does not lead to a significant increase in fan power.
- Recuperators increase both the cost of the ventilation unit and the cost of its maintenance. Like any other solution aimed at increasing the energy efficiency of the system, recuperators cost some money and require regular maintenance. However, experience has repeatedly proven that the costs of heat recovery are much lower than the benefits obtained.
- Rotary, chamber and, to a much lesser extent, plate heat exchangers have one drawback, which can be critical at some facilities - leakage of air flows is possible in them. In this case, the danger is the flow of exhaust air into the supply air. Such leaks are undesirable in clean room ventilation systems and are not acceptable, for example, in infectious diseases departments of hospitals and operating rooms. The reason is the danger of viruses that have entered the hood from any room flowing into the supply air flow with subsequent spread throughout all rooms of the facility. As a result, recuperators with intermediate coolant or freon recuperators are used at such facilities.
- Recuperators increase the dimensions of the ventilation unit. This primarily applies to plate recuperators, since they are air-to-air heat exchangers and are quite large in size. In addition, this applies to recuperators with intermediate coolant due to the presence of two separate heat exchangers, two pipeline lines and piping units near each of the heat exchangers
Methods for organizing recuperative ventilation
Recovery is arranged in one of the following ways: centralized and decentralized. In the first case, ventilation flows from the entire room pass through the heat exchanger, in the second - from one room.
Centralized complex – air handling unit
A centralized system is installed at the stage of construction or major modernization of the ventilation system.
A forced supply and exhaust unit (PVU) with a built-in recuperator is selected. The main selection criterion is the overall performance of the complex based on the entire volume of air in the structure (+)
A PVU with a recuperator ensures sufficient air exchange even in houses with sealed windows. At the same time, air flows are distributed evenly without creating drafts.
Complex supply and exhaust units of monoblock type are equipped with:
- fans – round-the-clock supply of clean air and emission of jets saturated with carbon dioxide;
- heaters – preheating of inflow;
- filters – retain dust and microparticles;
- recuperator – different types of installations can be used.
The functionality of some PVUs is expanded with a delay timer, power regulator, humidity level sensors, etc.
The body of monoblock models is covered with noise-absorbing material, making the operation of the PVU very quiet. Vertical, horizontal and suspended versions of ventilation units are possible
Recuperative monoblock PVUs produced by: Vents (Ukraine), Dantherm (Denmark), Daikin (Japan), Dantex (England) have proven themselves well.
Local units - an addition to the existing ventilation system
To restore the circulation of air masses in the room being used, decentralized air inlets with heat recovery are suitable.
They cut into the façade of a building or are mounted through a window. Their main task is to improve the supply ventilation in the house.
Local recuperators are equipped with a fan and a plate heat exchanger. The inlet “sleeve” is insulated with sound-absorbing material. The control unit of compact ventilation units is located on the internal wall
Features of decentralized ventilation systems with recovery:
- Efficiency – 60-96%;
- low productivity - the devices are designed to provide air exchange in rooms up to 20-35 sq.m;
- affordable cost and a wide selection of units, ranging from conventional wall valves to automated models with a multi-stage filtration system and the ability to adjust humidity;
- ease of installation - no air ducts are required for commissioning; you can install the wall damper yourself.
Popular manufacturers of local recuperators: Prana (Ukraine), O.Erre (Italy), Blizzard (Germany), Vents (Ukraine), Aerovital (Germany).
Important criteria for choosing a wall inlet: permissible wall thickness, performance, efficiency of the recuperator, diameter of the air channel and temperature of the pumped medium
Handmade production
A do-it-yourself recuperator is not at all a difficult task for craftsmen. However, an ordinary person should understand some rules before making:
- The first is to accurately calculate the parameters of the required ventilation device.
- Secondly, get all the necessary materials and tools.
- Third, think through possible ways to mount the recuperator and purchase or manufacture the required number of fasteners.
It is best to use steel sheets for the manufacture of the housing, and aluminum sheets for the rotating rotor. It is important to remember that automating the recovery process requires installing a motor. To start the rotor, a V-belt drive is installed. It is also recommended to think about proper sound insulation of the device, for which mineral wool, fiberglass, or silicone sealant can be used.
The manufacture of a rotary recuperator in itself is not at all complicated, but it requires accurate calculations. Therefore, if you are not very well versed in this issue, it is better to consult with professionals.
Where are they sold and how much do they cost?
Rotary heat exchangers can be purchased at specialized ventilation and climate control equipment stores. The easiest way is not to select the product yourself, but to order it from special companies that design and install ventilation systems.
Diagram of air flow through the recuperator
They will select the most optimal option for you and then install the equipment. The average cost of a product at the beginning of 2022 is as follows (using the example of several models):
- RR 500x250 – 209,000 rubles;
- RR 1000x500 – 363,050 rubles;
- RR 800x500 – 361,000 rubles;
- RR 700x400 – 320,000 rubles;
- RR 600x300 – 253,000 rubles;
- RR 500x250 – 209,000 rubles;
- RR 400x200 – 208,000 rubles.
You can try to make a recuperator with your own hands, but this task is extremely difficult and achieving “store-bought characteristics” is almost impossible.
How to calculate?
Calculation of the overall efficiency of the device (or, more simply, its productivity) and its payback period can be done manually. The calculation should be carried out according to the following scheme:
- required amount of heat (parameter Q): Q = C (parameter of specific heat capacity of air) * M (parameter of the mass of heated air) * dT (parameter of temperature difference);
- consumption of electrical energy by the heater (parameter Ek): Ek = Q/heater efficiency;
- year-round costs for electrical energy (parameter E): E = Ek * 24 (days) * 30 (days of the month) * 7 (heating months);
- volume of potential savings in the amount of electrical energy (Rel parameter): Rel = E * efficiency at the cost of the recovery system, resulting in savings of Rel * cost of 1 kW/electric energy;
- payback period for the installation: T (cost parameter of the device) / E (saving parameter expressed in monetary terms).
As you can see, these calculations can be carried out independently, without resorting to consulting with specialized companies (which costs some money).
Recuperator control
The rotor mechanism is rarely controlled separately from the main supply and ventilation system. The latest designs use the ability to electronically control the device via a controller panel. In automatic mode, the owner can set parameters such as rotation speed, percentage ratio between air intake and exhaust volumes, degree of purification, time operating intervals, etc. The operating parameters of the mechanism are monitored using sensors, which, in particular, record the throughput of the equipment . Also, an air supply unit with a rotary heat exchanger can be configured for special operating modes. One of the modern modes of this type is operation in conditions of maintaining constant air pressure. This program eliminates the risk of overloading the electric drive with subsequent overheating.
What is it used for most often?
The main task of a rotary recuperator is to collect heat. Most often, thermal energy is distributed further among new air masses coming from outside. Less often, on the contrary, heat extinguishing is required. As a result, energy costs for using specialized heat exchange equipment are reduced significantly. At the same time, a recuperator is more of a ventilation unit that not only heats the air in the room, depending on the chosen modification, it can purify the air and even aromatize it if necessary. The most functional and expensive models allow you to regulate the temperature. In such a situation, the accumulated energy is transferred with certain parameters, which are configured manually or automatically.
The operation of recuperators of this type is based on the transportation of heat from the outgoing air flows to the cold masses of fresh supply air. By passing between the rotor plates, the air is warmed up, while new flows of fresh but cold air are already arriving from the opposite side, which is thus heated by the accumulated heat. The volume of outgoing and incoming air that will be processed by the recuperator is determined depending on its dimensions and power potential. Its operating principle provides for the possibility of interaction of rotating plates with a special drive connected to the electrical network. The presence of the latter allows you to fine-tune the operation, defining a specific speed limit.
Device maintenance
The surfaces of the rotor and the housing itself require regular cleaning. The plates are cleaned and, if necessary, additionally treated with anti-corrosion compounds. You should also regularly check the direction of rotation of the rotor, and in the drive system, the quality of the belt tension. Since the recuperator works in close conjunction with other functional ventilation components, it is important to check their condition too. In particular, the filter, air ducts, dust collectors, valves with sensors, etc. are subject to revision. If possible, it would be a good idea to remove the rotary heat exchanger from the installation site and completely check for leaks. The fact is that in the presence of even minor gaps, the quality of the incoming air sharply deteriorates.
In what cases is supply ventilation with air heating used?
Supply ventilation is different in that it takes air from outside, unlike most air conditioning systems. As a result, the air is not only cooled or heated, but also enriched with oxygen. Supply ventilation with air heating is used in those rooms where clean and warm air is constantly needed.
It can work perfectly in an apartment, in a private house, and in a production facility. The special design does not allow mixing of exhaust air from the room and fresh heated air. This is both an air purification and heating system. A heated supply valve to the wall is most often installed in apartments and private houses where there are plastic windows, since natural ventilation is impossible with them.
Instructions on how to make a recuperator with your own hands
Creating an air recuperator with your own hands is a completely feasible task for a person who knows how to use them correctly. Experts call the plate recuperator the most suitable for this purpose. This type of recycler is the most common, especially homemade models. The disadvantages of the design, which include freezing of the heat exchanger at low air temperatures outside and intersection of air duct pipes, are compensated by the low cost and simplicity of the design.
To make an air recuperator with your own hands, the following materials are important:
- metal sheet (galvanized sheet, roofing sheet, galvanized iron or any other sheet metal) with an area of 3–4 m2;
- cork, wooden strip or textolite;
- metal sheet or similar material to create the body;
- plastic flanges with tips corresponding to the diameter of the ventilation pipes;
- sealant;
- insulation;
- silicone
Creating an air recuperator with your own hands takes several steps:
- Sheets of metal are cut into plates measuring 20 x 30 cm. It is recommended to use at least 3–4 m2 of metal. Particular attention is paid to cutting. The plates must be cut almost perfectly evenly, which cannot be achieved with metal scissors. Engineers recommend using a hacksaw or grinder. Place the plates one on top of the other, ensuring a gap of at least 4 mm. To do this, glue frames made of thermal insulation material (cork, wooden strip, textolite) along the contour of the plates, providing holes for air flow in the appropriate direction, alternating cross flows. Upon completion of laying the plates, go through all the cracks with a neutral composition sealant.
- The body is made of tin or other sheet metal. It is a box of a suitable size to tightly fit the resulting block of plates. Cut holes in the walls of the box into which to insert pre-prepared plastic flanges corresponding to the diameter of the air duct pipes. The cracks must be carefully sealed to prevent loss of device efficiency.
- After the sealant has dried, place the resulting block of plates in the housing.
- It is recommended to lay thermal insulation (foam plastic, glass wool) on top of the resulting body with a laid block of plates. The entire resulting structure can be additionally packed in a wooden box.
The recommended air flow speed is 1 m/s.
According to expert calculations, with a total heat-transfer surface area of 3–4 m2 and a productivity of 150 m3/h, the efficiency of such a recuperator should be from 50 to 60%.
In winter, at sub-zero temperatures outside, there is a possibility of frostbite in the plate unit of the heat exchanger. To avoid blocking the operation of the recuperator for a long period, it is recommended to provide a bypass. Then, by switching the incoming air flow to it, the system will quickly thaw due to the temperature of the warm air blown out.
To make it easier to detect frostbite in the system, a pressure change sensor can be provided. However, periodic prevention by shutting off cold air and warming up the plate system will also help.
Due to the fact that condensation settles in the recuperator, it is recommended to equip the structure with a hose for draining water.
Process description
In order for the design to be correct and reliable, it is necessary to adhere to a certain algorithm of actions. You don’t need any special knowledge, but you will have to show ingenuity and intelligence:
- The material is laid on a flat surface, divided by a cutting tool into square plates with sides of 20-30 cm. Several dozen such blanks will be needed. Ideally even plates are obtained when using a jigsaw.
- Then wooden slats and cork material are prepared. Their parameters must exactly match the sides of the pre-cut squares. They are glued to opposite sides of the blanks, the latter remains empty. The process is suspended until the glue dries completely.
When assembling the recuperator yourself, it is important to perform the steps sequentially
At the next stage, the squares are assembled into a single cassette. Each sheet is carefully laid at an angle of 90° relative to the previous one. The final element of the recuperator is an uncoated plate. The prepared functional installation is fixed in the frame using a construction angle. Existing holes and cracks are treated with a sealant that prevents corrosion processes. Fasteners must be made to secure the flanges on the sides of the cassette with plates. The lower part is equipped with a drainage hole through which a tube with condensate is discharged. The cabinet walls are equipped with guides, which are made of durable corners. After this, the prepared work part is placed in a box that meets the parameters. Do not forget about the insulating material laid in the recuperator. It is firmly attached to the inside of the body walls of the structure. Ice accumulation in winter is prevented by installing a pressure sensor. It is usually mounted in an area through which warm air flows. The final stage is the installation of a ready-to-use recuperator into the general ventilation system.
There is a huge selection of cooling systems installed in residential and industrial facilities. But for your own needs, it is quite possible to manufacture a recuperator for a heat exchanger yourself, while saving money.