Any private house, cottage, bathhouse and sometimes even a garage require heating in the winter season. But any prudent owner is faced with the question of how to reduce fuel costs and use the heating device more efficiently. One of the modern promising directions for increasing efficiency is the use of heat from hot exhaust gases.
I welcome my dear reader and bring to your attention an article about what a heat exchanger for a chimney pipe is and how to make it yourself.
What is it and what is it for?
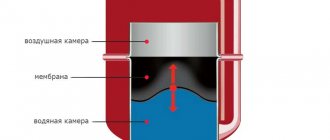
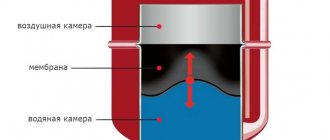
Heat exchanger is a device for transferring heat from a heated medium to a colder one. One principle, many designs. A heat exchanger for a chimney allows you to select part of the energy of the exhaust gases and use it to heat an adjacent room or heat hot water.
The gases coming from modern gas and pellet boilers are not hot – about 200 °C, so you won’t be able to get a lot of heat from the chimney. Solid fuel boilers emit hotter gases - up to 600 °C, and the recuperator allows you to obtain a fairly significant amount of heat for heating or heating water.
The maximum amount of heat from exhaust gases can be obtained by using not very modern traditional stoves, fireplaces, and homemade potbelly stoves. The efficiency of these heating devices is low, the temperature of the flue gases is high, so a considerable part of the wasted heat can be captured using a heat sink. The use of heat collectors on the chimney of a homemade potbelly stove allows you to capture up to 30-40% additional energy.
The main reason for installing a heat exchanger is that it allows you to maximize the use of fuel combustion energy and save on heating costs. In addition, sometimes when heating small houses it is not economically feasible to purchase a heating device with a heat exchanger and install a heating system.
A modern fireplace or stove heats well houses with an area of up to 70 m² and even more; only some rooms need heating - bathrooms or back bedrooms, second floor rooms or attics, so for their heating you can use the heat from the recuperator for the chimney. Sometimes a chimney heat exchanger is used to heat water.
Rules for installing a heat exchanger on a sauna stove
The following rules must be followed:
The heat exchanger must consume no more than 10% of the total energy produced by the furnace, then the latter will operate with good efficiency. The pipes must be laid so that the water flows by gravity, that is, at a 250-degree slope on the direct supply and 30-degree on the return one. It is important to reserve power for cooling after fuel burns. It is necessary to provide a sufficient volume of water for each individual model, because if there is too little of it, it will boil quickly, which can lead to the formation of deposits on the walls and a fire hazard, and if there is too much, you will have to wait a long time before taking a shower.
How to connect a heat exchanger if the tank is in a steam room:
- The entrance to the hot water tank should be at least 5 cm higher than the upper register fitting. This is necessary for better circulation.
- The upper register is from 1.4-1.5 m from the floor, despite the fact that the podium under the stove is 15 cm. The bottom of the tank in the steam room should be at least 1.5 m, and preferably higher.
- If the tank is 0.5 m high, then we have a total installation of 2.0 m. That means there is still half a meter to the ceiling. And here the question arises: how to fill the liquid. If there is a running water supply, then water will flow without problems.
Second connection option: we place the tank lower, and place the fitting for the supply circuit on the side. But there is a nuance: if the water level is below the upper fitting, there will be no circulation. It will stand in the heat exchanger and periodically reach a boil, but in the tank it will remain cool.
If you need to place the tank in the wash room, you should follow the same principles as when placing it in the steam room.
Types and designs
Heat exchangers are primarily divided according to the coolant into air and liquid (water). In principle, it is allowed to fill in oil and antifreeze, but not in homemade designs, since antifreeze is poisonous and expensive, and the oil can catch fire if leaks occur.
By design, water devices are usually made in the form of a coil or register (pipe) with water (water jacket); air ones are a cap with warm air removal or a wide insert into the chimney with welded transverse elements.
When deciding how to remove the residual heat of flue gases, it should be borne in mind that heat extraction in the chimney reduces draft, and condensation may fall on the heated walls of the chimney. This drawback is especially noticeable in gas boilers, in which the temperature of the exhaust gases is low. But on inexpensive homemade stoves you can ignore condensation.
Water
The advantage of water for recovery is that it has a high heat capacity and more efficiently removes the heat from the flue gases. But water recuperators require higher quality manufacturing - the system cannot leak; When operating it, it is necessary to ensure that there is no overheating, since boiling water can rupture the pipeline.
If water structures are used in a garage, workshop, “weekend cottage,” or a free-standing bathhouse, the water will have to be drained in the winter, since frozen liquid can also rupture the pipeline.
A circuit with water is heated through the metal walls of the chimney; when heated, the water rises up, then into the batteries, cools, falls down in the battery, goes into the return line and is sucked back into the heat exchanger.
To optimize the operation of the system, an expansion tank is included in it - this reduces the possibility of boiling. Some craftsmen install a pump, which creates a complete small heating system.
Water systems are used for heating using radiators or hot water supply. A serious drawback is the inability to regulate the heating temperature of the water; if it overheats, it simply has to be drained. It is impossible to pour cold water into the system while the heating unit is running - the water can boil, rupture the pipes and damage the chimney, while condensation settles on the inner walls of the chimney pipe.
- Homemade coil
The easiest design to make. The coil is usually made from a tube that is wound in a spiral around a steel chimney. Tubes use copper, ordinary steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Aluminum should not be used for solid fuel boilers - its melting point is 660 °C, and the temperature of the exhaust gases of solid fuel heating devices reaches 600 °C.
When winding (bending), the pipe should be filled with sand and sealed on both sides - this will avoid defects (kinks, folds, kinks). To improve the heating of the coil, there should be a small distance between the turns - up to 1 diameter.
Corrugation is sometimes used, but this is not the most durable material for a coil (especially galvanized carbon steel).
- Register
Register - a casing with a larger diameter than the chimney. The register is placed on top of the chimney body and welded, the ends are welded with plates with cut holes corresponding to the diameter of the chimney. A pipe is welded or screwed in at the bottom for water supply, and at the top for discharging warm water. Otherwise it is used in the same way as a coil. The casings are made not only round, but also square.
Air
This option is more suitable for local heating of premises - one room, bathroom, dressing room. Air structures are easier to assemble. Sometimes a coil or register is used, sometimes a Kuznetsov or bell-type heat exchanger is used. The coil has too much resistance from the pipe walls; it should not be too long. Because of these difficulties, it is rarely used. Air recuperators cool the chimney less, so there is less chance of condensation forming on its walls.
Sometimes they do not build complex structures, but use available materials - they weld ribs from corners or bent strips to the chimney, pipes open on both sides, attach “skirts” or strips (aluminum or thin steel) bent into a corrugated structure.
- Kuznetsov heat exchanger
The Kuznetsov heat exchanger is an expanded cylinder, across which pipes are welded. The cylinder is mounted in the chimney, hot flue gases flow through the inside and heat the transverse elements. The air from the cavities exits into the room and heats it or is collected in an air duct and enters the adjacent room.
- Bell type
If a small house does not have a heating system and there is a need to heat a room in the attic or second floor, a bell-type heat exchanger is used. A cylinder is installed around the chimney, open at the bottom; at the top, air from the cylinder enters pipes going to the second floor. Warm air is released in the lower part of the room on the second floor - this way the hot air is better distributed in the room and heats it as much as possible.
Sometimes, instead of a cylinder above the stove, a hood is installed under the ceiling; air heated by the stove rises into it and flows through pipes into the room on the second floor. You can install a fan, in which case it is easier to heat the room on the same floor with the stove with warm air.
Which type is better
Which type is better is determined by what exactly needs to be heated and in what way. The efficiency is better for water recuperators - 50-60% (for a register parameter it is higher, for a coil it is lower). Air devices have lower efficiency.
For hot water supply or radiator heating systems, it is better to install water heat exchangers. Air heaters are more suitable for heating closely spaced individual rooms.
We use corrugation
This heat exchanger option is the simplest and requires the minimum amount of material costs. To do this, use a long corrugated pipe. It needs to be wrapped around the chimney.
Application of corrugated pipes for the manufacture of heat exchangers
The air inside the corrugation will heat up very quickly. It is enough to simply redirect it to the next room. To increase heat transfer, wrap food foil around the corrugation.
For safe operation of a heating system using heat exchangers of different configurations, it is necessary to constantly check the connections to the chimney. If you detect the slightest gaps, immediately restore the tightness of the seams.
[ads-pc-2][ads-mob-2]
Power calculations
Independently calculate the power of the recuperator in the absence of initial data (furnace power, temperature and amount of exhaust gases per unit of time, contact area of the heat exchanger and the metal of the chimney, speed of passage of air or water through the device). You can measure the power of an already installed heat exchanger.
Roughly, you should expect that the heat exchanger on the chimney of a solid fuel stove or fireplace will warm up a couple of small radiators, increase the temperature in the garage, or make a room in the attic or a dressing room in a bathhouse warmer.
Buy or make it yourself
If you want to increase the heat transfer from an expensive purchased boiler, it is better to buy ready-made high-quality devices - the industry produces them in a sufficient range. But if you want to modernize a potbelly stove in a bathhouse or garage, or increase the efficiency of a fireplace with a steel pipe in the country, you can save a lot of money by making and installing a heat exchanger on the chimney yourself. Installing a heat exchanger by a hired specialist will cost the same as the structure itself.
The simplest option - a coil - can easily be made by a home hobbyist even without much experience, but a home craftsman with at least some welding skills can handle more complex designs.
approximate price
The cost of industrially manufactured chimney heat exchangers varies depending on the design and manufacturer.
Running heat exchanger tanks for a chimney with a diameter of 115 mm and a capacity of 6 liters cost rubles; those with a capacity of 12 liters cost rubles.
How to make your own device
It’s easy to make a simple coil yourself from a copper tube. For a chimney with a diameter of 100 mm, a copper pipe with a diameter of ¼ inch and a length of 3-4 m is suitable. Threaded fittings should be soldered to the ends of the pipe. Then the tube is filled with fine sand, twisted and wrapped around the chimney.
It is convenient to do this work with an assistant. The sand is then washed out of the pipe with water under pressure. Connect the pipes leading to the radiators and expansion tank.
The Kuznetsov heat exchanger is made using welding. The simplest option is to make a housing from a gas cylinder or large diameter pipe.
For manufacturing you will need the following materials:
- Gas cylinder, large diameter pipe (300 mm) for the housing.
- Pipe with a diameter of 32 mm (it is better to take one piece with a larger diameter - up to 57 mm). The length of the blanks is 300-400 mm, the total quantity should be sufficient for cutting the blanks.
- Two small pipes of the same diameter as the chimney; It is advisable to use a chimney pipe - if the chimney is prefabricated, then on one side of the structure the pipe will have a socket, which is necessary for installing the heat exchanger.
- Two pieces of steel sheet, sufficient to cut out the end caps of the housing.
Air heat exchanger manufacturing technology:
- A large pipe or cylinder is cut to the required size.
- 9 blanks of the same length are cut from thin pipes.
- Circles are cut out for the plugs.
- 9 holes for small diameter pipes are cut in the circles; if one tube of larger diameter is taken, then a hole for it is cut in the center.
- Thin pipes are inserted into the holes of the plugs, attached by welding, and then welded.
Holes with a diameter equal to the diameter of the chimney are cut in the sides of the body.
A structure of thin tubes and plugs is inserted into the body and welded at the junction of the plugs and the body of a large pipe.
The pipes are inserted into the holes on the sides of the body and also boiled.
Alternative option:
What materials can be used
The ideal option is (for example, food grade austenitic stainless steel 08Х18Н10 or AISI 304) or copper. Industrially produced products are sometimes made from titanium. But the price of these materials is quite high. But they are durable, do not rust, are reliable and durable. If you have a potbelly stove in the garage or a homemade heater from scrap materials in the bathhouse, it is quite possible to use ferrous metal (carbon steel).
You can use a high-quality corrugated stainless steel pipe. Aluminum pipes can also be used for the coil (just not for chimneys of solid fuel stoves).
Sometimes galvanized steel is used, but it should be borne in mind that during welding work the zinc layer evaporates, and all the advantages of galvanizing (corrosion resistance) come to naught. At temperatures above 400 °C, zinc begins to evaporate (zinc vapor is toxic), so you should not use galvanization for heat exchangers on the chimneys of solid fuel boilers.
Conclusion
Installing a heat exchanger on a sauna stove does not require much work. To do this, just follow the instructions above. The main principle is compliance with slopes. Photo No. 1 shows one of the heat exchanger options for a bath and its installation. Otherwise, problems will arise with the pressure. When organizing water heating, you should adhere to the following rules:
- The length of the forward and return pipes should not exceed three meters.
- The remote tank is placed at such a height that the slopes are maintained. The excess must be at least 100 mm.
- Pipes for the heat exchanger of a sauna stove for heating water must be made of stainless steel or copper.
- The water in the system must not be allowed to freeze; it must be drained after each use of the steam room. A special valve is provided for this. It also serves as an emergency drain if an accident occurs.
- The power should be selected so that the device heats the required amount of water to +70C in 2 hours. The liquid in the system should not boil. Scale quickly damages the device.
- The diameter of the pipelines should not be less than 24 mm.
By following these simple rules, you will always have hot water and save money on installing an electric boiler.
Step-by-step instructions on how to install a heat exchanger with your own hands
The Kuznetsov heat exchanger is installed instead of one of the chimney sections - for this part of the chimney will have to be dismantled. If a chimney is installed from one long pipe, you will have to cut out part of the chimney and install the structure using welding.
Installation methods
The heat exchanger is installed at a certain distance from the heating unit - 200-500 mm, more is possible.
If the chimney is prefabricated, then it is necessary to disassemble part of the chimney. The heat exchanger pipes are cut so that the length of the heat exchanger structure is equal to the dismantled chimney section. The heat exchanger is mounted in the chimney and sealed using heat-resistant sealant. The top of the heat exchanger is painted with heat-resistant paint.
Installation of a furnace with a heat exchanger - features of the work
To install a stove with a heat exchanger for a bath without any problems, you need to follow a certain sequence of actions.
- The structure must be installed on a foundation poured to a depth of up to half a meter.
- The heating system is enclosed by a masonry of refractory bricks on a mortar of clay and sand.
- In the room where the stove is installed, the main heat exchanger is placed, and the firebox is led out into a hole pre-arranged in the wall of the bathhouse.
- Hot liquid flows through pipes wrapped in thermal insulation material into a water tank or heating radiators.
- The chimney is discharged through a hole in the roof.
- All joints are properly sealed.