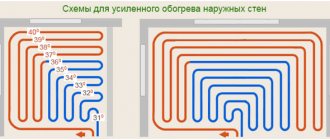
The problem of maintaining a comfortable temperature, solved in most apartment buildings by connecting to centralized heating, in a private house sometimes requires the use of complex and expensive technical devices.
The main task in this case is to find the optimal balance between the cost of heating equipment and pipelines, their operating efficiency, design life and operating costs. Three-way valves are designed to simplify temperature regulation, as well as create a comfortable microclimate in individual rooms with minimal losses.
Connection diagrams for a three-way valve to a heating network
After all the analysis regarding the design of the valve and its operating principle, an understanding emerged of how it can be used in various heating systems. Most often it is used in three cases.
- In a heated floor system, the coolant temperature should be within +45°C. It is this mode that is supported by the device. This has already been discussed above, and it has been shown how it should work.
- To protect solid fuel boilers from the formation of condensation inside the firebox. This happens when relatively very cold return water enters the generator heat exchanger. This causes water droplets from condensed steam to form on the outer surfaces. This should not be allowed, because condensation shortens the life of the equipment.
- If there is a need to maintain different temperatures in different parts of the heating system.
The first option will not be considered, because it has already been described. As for the second case, we need to take the photo below as a basis for analysis.
Piping diagram for a solid fuel boiler with a three-way valve
The diagram shows a double circuit: one large one passes through the radiators, the second is a short one through the bypass (this is a vertical red line, the beginning of which is at the top to the radiators, the end rests at the bottom of the valve). Until the boiler warms up, the coolant moves along a short circuit. The temperature has risen to the required level, the valve closes the bypass and opens the return (lower blue line).
And the third position, which is based on the distribution of coolant among consumers, in them the required temperature is not always the same. For example, an indirect heating boiler requires water at a higher temperature, for radiators at a lower temperature, and for heated floors even less.
The wiring diagram for installing a three-way valve should be approximately as shown in the photo below.
Coolant distribution among consumers
Some useful knowledge
Three way rotary valve ESBE
A three-way valve is a control device in pipeline systems with a liquid working medium. In simple terms, built into the design of the heating network, it will act like a well-known faucet that switches or mixes flows. Installing the valve allows you to solve a number of practical problems:
- Redirection of flows coming from different pipelines.
- Achieving the required temperature of the working fluid by mixing hot and cold flow.
- Achieving a jet with a constant temperature through dynamic redirection.
Difficult? Only at first glance. In order to understand the principle of operation of the device, let's consider its design features.
Need for use
This design, on the one hand, is quite simple, but on the other, it is designed to perform an extremely important task, being part of engineering networks. Everyone knows the rule that demand creates supply, which is why on the market today you can find many models that are represented by all kinds of manufacturers. However, valves produced by Esbe have excellent performance characteristics. A three-way valve of this type can be purchased at an affordable cost. This is confirmed by user reviews.
Selecting and installing a three-way valve in the heating system
It is forbidden to supply coolant above 95°C even to radiators, because in the event of any minor accident, due to a sharp drop in coolant pressure, intense steam formation will occur, people will be boiled alive, and now imagine that steam comes out of your mixer. But here, in order to ensure the standard temperature of hot water, management companies, service organizations and a local plumber are required to work. From a technical point of view, this problem is successfully dealt with by temperature regulators (TRZh - liquid thermostat), which should be installed on each DHW system from a thermal power plant, i.e. in our homes.
Let's give an example of the most commonly used (in our case, cheaper) TRZ in the Russian housing and communal services sector.
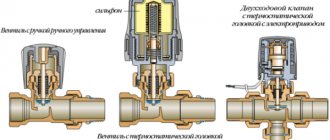
The temperature regulator most used in housing and communal services is the bellows-type TRZh (see sketch):
- Welded steel body
- The bellows (filled inside with an easily evaporated substance) has the appearance of a cylindrical metal “accordion”.
- Case cover.
- Rod for temperature control.
- Rod seal.
The principle of operation is very simple: network hot water enters the TRW from above through a sleeve with holes, water, cooled after heat transfer in the batteries, enters from the right, inside the TRW they mix and from the left pipe the water goes to the consumer in the apartment. If the water is very hot, the bellows lengthens, the holes in the sleeve are blocked and the supply of mains water decreases; if the water has cooled, the bellows contracts and more hot mains water flows. Everything happens automatically. The TRF can be manually adjusted to supply water from 30 to 90°C. By turning the rod clockwise, we raise the bellows up and thereby reduce the flow of hot network water; counterclockwise, we lower the bellows and the water at the outlet will be hotter.
Example of bellows-type temperature controllers: - TRTS-50-OS, - RTE-21M.
Fluid thermostat with thermostat.
For example, the most used and accessible model is TRZh-M-1. The principle of operation and adjustment is similar to the above device, but unlike it, in TRZh-M-1, instead of a bellows, a thermostat similar to a car is installed.
This model has advantages and disadvantages compared to the bellows TRZh.
Advantages: if the temperature sensitive valve fails, only the sensor can be replaced.
Flaws:
- The sensor regulates the water temperature in the range of 15°C (45-55; 55-65; 75-85...), each mode requires its own sensor.
- In the summer, when water is supplied through only one pipeline and the water temperature exceeds the upper gradation of the installed sensor by 20°C, it must be removed from the TRZ housing, otherwise it will fail and require replacement.
If a plumber is servicing 30-60 hot water systems, this is very troublesome.
Appearance of the thermostat and sensors installed inside the TRZh-M-1 housing (like in a car engine).
Collector connection diagram
The order of work is as follows:
- The collector box is mounted in a place that is convenient for access and at the same time so that it does not interfere. Pipes supplying heated water and return are connected to the cabinet. But before this, shut-off valves should be installed on the collector.
- In order to control the temperature and pressure in the system, a thermometer and a pressure gauge are placed in close proximity to the valves.
- To connect pipes connected to the manifold, compression fittings are used using a threaded connection.
- If it is necessary to combine pipes with different diameters, adapters or universal fittings are used, taking into account the connection diagram for the heated floor.
A complete heating scheme with heated floors has the following additional elements:
- circular pump;
- three-way mixer or pump-mixing unit;
- tap to drain water;
- air vent.
What is a three-way valve and why is it needed in a heating system?
The installation of this device is justified where the heating system takes into account the division of the circulation flow into 2 circuits, distinguished by the type of mode - constant and variable. Constant mode is very often used for use in those devices that need to be supplied with high-quality thermal fluid in a specific volume throughout the entire time. The variable flow is intended for those consumers for whom the quality indicator of the coolant is not important. For them, the main thing, first of all, is its strict quantity, according to which the feed is adjusted.
Among shut-off valves, there is another type that performs similar functions, but is considered a two-way valve. But the three-way valve does not stop working in a completely different way. Its design is such that it is not able to close a circuit for which a constant hydraulic regime is important. It will always be in the open state, and is adjusted to the required volume of coolant. This means that consumer devices will always be satisfied in both the qualitative and quantitative indicators of the supplied volume.
A three-way valve is not able to close the flow of coolant to the circuit where a constant flow is important. This is where it differs from the two-way one. But it copes with variable overlap very well. This makes it possible to regulate both the pressure and flow of the coolant. By the way, the same effect can also be achieved from two-way valves if two devices are combined in one design. At the same time, they must be configured for reverse operation: when one closes, the second opens.
What types of three-way valves are there?
These shut-off valves are divided according to the principle of operation into separation and mixing. The name itself explains the principle of their operation and how they differ. The mixing unit has one output and two inputs, thanks to which it qualitatively mixes two very different flows. This, for example, is necessary to reduce the temperature of the coolant for specific consumers. For example, for heated floors: water should be supplied to them at a temperature of no more than 65 degrees, while in radiators its temperature is much higher.
In order to properly adjust the supply of coolant to the consumer at the required temperature, it is important to know its indicator for two flows, calculate the mixing proportions and adjust the valve. This is how we acquire the desired temperature regime. The three-way separating valve behaves exactly the opposite
Its purpose is to divide the key stream into 2 secondary ones. In its own design, it has only one input, but two outputs. It is used very often for hot water supply, ensuring an equal supply of hot water to the consumer in terms of quantity and quality. Professionals also use it for air heaters.
A three-way separating valve behaves exactly the opposite. Its purpose is to divide the key stream into 2 secondary ones. In its own design, it has only one input, but two outputs. It is used very often for hot water supply, ensuring an equal supply of hot water to the consumer in terms of quantity and quality. Professionals also use it for air heaters.
The two types of three-way valves do not stand out in any way from the outside. But, if you look at them in cross-section, the difference will be understandable. The mixing device has one ball valve on a rod, which is located strictly in the very center and closes the main passage. And the separating valve has two ball valves, which are located on the outlet pipes. When the first one closes one section of pipe, the second one tears off another.
How is a three way valve controlled?
Like every shut-off valve, the three-way valve required for a particular system is calculated based on the diameter of the pipe supplying the coolant and the pressure in the system. In order to certify a heating system, there are specific Standards for these devices. And deviation from them is a gross violation
Particular attention is paid to the discrepancy between the internal pressure of heating systems and the valve
Advantages of Esbe mixing valves:
- Easy to install drives.
- Compact size, lightweight and easy to install - installation requires a minimum of tools.
- Minimum dimensions of mixing valves, facilitating installation in cramped conditions.
- Reliable installation of valve with internal thread. The key edges are wider and have two edges instead of six. This provides a better grip and less risk of the pipe wrench or box wrench slipping.
- More flexible cable connection. The drives are supplied complete with a connecting cable and an additional cable contact. The advantage is that you can run a separate cable, for example, directly to the circulation pump without connecting through a central controller.
- High control accuracy.
- Minimum delay and high precision of the entire cycle, from full closing to full opening of the valve, the valves provide the ability to use the full angle of rotation. This adjustment is as close to ideal as possible and provides increased comfort and reduced energy consumption.
- Esbe valves are renowned for their minimal internal leakage and were awarded the 2003 Plumbing Product of the Year award.
- The leakage rate is reduced from 0.1 to 0.05%. And this is achieved at double pressure, i.e. at 100 kPa (1.0 bar). A valve that provides tighter closure is difficult to find and buy on the rotary valve market.
- Easy and convenient regulation, high performance
- Reliable and have a long service life
What is Kvs?
Each mixing valve has a Kvs characteristic (flow capacity m3/h at 1 bar pressure loss). The Kvs parameter helps determine which valve is needed for your heating system. You can determine the Kvs of the Esbe valve using the graph below.
Esbe mixing valve size selection
Selection of Esbe mixing valves of the VRG and VRB series for floor or radiator heating systems. We start from the thermal power of the boiler in kW (for example, 25 kW). We move vertically to the selected temperature mode t (for example, 15°C). Next, we move horizontally to the shaded area (pressure drop range 3-15 kPa) and select a lower value of the Kvs coefficient (for example, 4.0). In this case, we select the desired type of valve with a coefficient Kvs = 4.0
The Kvs value is taken for flow in one direction only. For 4-way valves, double the value of the differential pressure P shown on the graph is valid.
Purpose of a three-way valve for heating with a thermostat: areas of application
A three-way valve with a thermal head is the main element of shut-off valves for the heating main. Based on its operating principle, it is designed to mix or separate coolant flows:
- separation fittings - used to distribute liquid simultaneously in several directions. The tap is included in the water intake systems of an individual home or industrial enterprise;
- mixing fittings are designed to mix liquids in order to organize effective thermoregulation. The faucet has 2 holes for incoming flows and 1 for outgoing flows.
The main purpose of the product is to ensure continuous circulation of liquid throughout the heating line to maintain the same comfortable temperature of the coolant and ensure uniform heating of the room.
It is recommended to install a three-way mixing valve when installing heated floors. With the help of a needle, the temperature regime is controlled; overheating of the coating is impossible.
The principle of operation of the mixer in the heating system
Design
A three-way mixing valve has a control element, which is a rod or ball. The rod moves vertically, the ball moves around its axis. Since the movement of the control element does not completely block the flow of the working fluid, it is mixed and redistributed. The simplest models are a regular faucet. Their main advantage is low cost and design simplicity. The disadvantage is the impossibility of stabilizing the outlet temperature. Despite the disadvantages, the faucet can be installed in underfloor heating systems. Now let's imagine a faucet with an electric drive. This design is already more functional, since it is able to regulate the temperature automatically. A simple valve is a balancing valve. Its main function is to adjust the cross section for the passage of the work flow. Conventionally, the principle of its operation can be described as follows:
- The handle is turned 50% - uniform mixing of the two flows, since the inlet valves will be equal.
- The handle is turned 100% - the first valve is fully pressed and blocks the movement of liquid flow.
Modifications on the market may have different handle rotations, but the principle of their operation remains the same. The tap and its position are manually adjusted, thereby ensuring a balance between the two flows.