Having realized the dream of purchasing a country house, many buyers are faced with difficulties in choosing a suitable boiler for heating the building. How much power is enough to maintain a comfortable temperature level? What type of boiler will satisfy the buyer's needs? The purchase is important, so when choosing a gas boiler, you should carefully study all its characteristics.
What characteristics exist
First of all, gas boilers differ from each other in their circuit design. It is possible to install a boiler with one or two circuits. In this case, the main circuit provides temperature control in the building, and the second circuit maintains hot water supply (DHW). Accordingly, if the house has a boiler for heating water using other energy sources, then the need for a second circuit remains at the discretion of the buyer, because this will allow saving on water heating during the heating season.
It is also worth considering such characteristics as the type of chimney for exhaust gas removal and the installation method (wall-mounted or floor-mounted), since these parameters depend on the need to place the boiler in a separate room, observing fire safety rules. Another problem is that most of the heat is removed through the chimney into the atmosphere along with the spent fuel. This is inevitable, but efficiency can be increased by installing a coaxial chimney and a boiler with a closed combustion chamber.
The main defining characteristic of a boiler is its heating power, measured in Watts. The larger the area of the building that needs to be heated, the more power will be required. It is worth considering that over time, the efficiency of the boiler decreases if its maintenance is neglected - cleaning the combustion chamber and heat exchangers will get rid of carbon deposits and condensate, thereby increasing the quality of heating.
In addition, it is worth considering the many additional features provided by the manufacturers of such heating systems. Temperature control using a remote control or even a smartphone program, protection against temperature changes or automated indoor climate control - this is not a complete list of functions of modern boilers that may be of interest to the buyer.
Electrode heating boilers
Electrode heating boilers are known to everyone from the sensational advertising of Galan boilers with their miniature sizes.
This is true, electrode heating boilers can be compared with instantaneous water heaters, only in them the water is heated due to the passage of current through the coolant. In these devices, the coolant itself heats itself. This is achieved by placing special electrodes in the coolant medium that excite the oscillations of free electrons of water, as a result the water heats up.
Electrode boilers are distinguished by:
- Cylindrical shapes;
- Small sizes;
- Cost-effectiveness when installing NOT cast iron radiators;
- Safety. They do not work in the absence of water;
- Automatic switching on/off based on temperature sensors.
Disadvantages of such boilers:
- You cannot adjust the power, only on/off;
- Scale formation, as a result, reduction in power;
- Water requires preparation;
- You cannot use traditional coolants antifreeze and antifreeze;
- Distilled water is not suitable for coolant;
- There is a possibility of direct current leakage to the housing and heating pipes;
- Electrolysis, which occurs during processes in an electrode boiler, leads to the formation of toxic gases and requires periodic replacement of the coolant.
Floor and wall boilers. Differences
To choose a boiler installation method, you should familiarize yourself with the general requirements for the placement of the heating system. So, the boiler room must be a separate room with an area required by fire safety standards, the walls of which must be made of fire-resistant materials. An exhaust gas removal system is required, and the possibility of their accumulation in the room must be completely excluded. Based on these requirements, the buyer must provide appropriate premises or build an extension outside the residential building. For heating a small building, it would be optimal to purchase a wall-mounted boiler, which is easier to install and the requirements for it are not so significant. The height of the placement is at least 80 centimeters from the floor, and the space around it must be completely free. If wall installation is excluded for some reason or the required heating power is simply impossible given the dimensions of wall-mounted boilers, then a floor-mounted method of installing the heat source is assumed. In this case, the boiler must be placed on a concrete or metal slab that creates sides of at least 50 centimeters around the boiler.
Characteristics of wall-mounted boilers
Wall-mounted boilers are a ready-made heating system that is easy to install, takes up minimal space and is much easier to maintain than floor-mounted ones. Modern models assume control using a remote control to set temperatures and control additional capabilities (for example, protection against freezing of heat exchangers when the boiler is turned off). This is the best choice for heating an apartment or small house, and manufacturers take into account their location in the living space and try to give them an attractive design. But it is worth considering that such heating systems are very susceptible to changes in the power supply. This leads to their complete shutdown or switching to minimum heating mode, which entails damage to the heat exchangers (for example, the occurrence of condensation due to a sudden change in temperature). So, if the power lines in the building are unstable, it is worth taking care of an uninterruptible power supply.
The main characteristics that you should pay attention to when buying a wall-mounted gas boiler:
- Power. Here you can select without stock. If the heat loss of the house is 20 kW, then the boiler can be selected with the same power. If you purchase a boiler of higher power, then this is also not a big deal.
- Functions. Wall-mounted boilers are essentially all the same, plus or minus. They differ only slightly in the internals. So perhaps you might be intrigued by certain features of certain brands.
- Economical. Here, too, all boilers have the same efficiency, plus or minus.
- Noisy. If you install the boiler in a residential area, pay attention to the noise level of the boiler.
- Type of heat exchanger. Basically, all heat exchangers are copper. But some people use aluminum ones. They are slightly worse in performance.
- What are the internal parts made of? Budget models are made of plastic, more expensive ones are made of brass. Plastic is made naturally from the point of view of reducing the cost, but at the same time scale does not form on it.
Characteristics of floor-standing boilers
In the case of heating a large building (more than 300 square meters), it will no longer be possible to get by with a wall-mounted boiler and purchasing a floor-standing boiler becomes a necessity. Its installation is complex and quite costly, and incorrect installation can lead to problems in the form of dampness and insufficient heating due to loss of efficiency. But such boilers have significant advantages, not to mention greater heating power. This is significant design flexibility - the buyer can independently design a heating system based on the building layout and various needs. A tangible advantage will be independence from the stability of power lines. It would not be amiss to mention the durability of such heating systems and the possibility of freely replacing failed components, which significantly extends the overall service life (for example, heat exchangers of proper quality can last for several decades).
The main characteristics of floor-standing boilers that you should pay attention to when purchasing:
- Dimensions. Floor standing units have quite a wide range of sizes. Choose what suits you.
- Chimney requirements. Some boiler models may have greater requirements for the chimney.
- Efficiency If the efficiency of wall-mounted ones is similar, then the spread is a little larger. But it’s rare that a manufacturer writes an honest efficiency rating about their boiler. Pay attention to the recommendations of those who already use the same boiler.
- Heat exchanger type. Cast iron or steel.
- Energy dependence. Advanced floor-standing boilers have advanced automation powered by electricity.
- Power . A reserve is usually put in here, since the power of boilers decreases in cold weather.
Gas heating boilers: the secret of popularity
A gas boiler is a timeless classic of heating systems. In terms of its characteristics, it is ahead of almost every one of its “competitors”. So, even despite the built-in automation, the operation of a gas appliance does not leave an imprint on electricity bills and is not so dependent on the state of the electrical network. Compared to diesel devices, such a boiler is beneficial both at the purchase stage and during use. And, unlike traditional heating with solid fuel, heating a house with gas does not require special maintenance during operation.
Device and design features
As the name implies, a gas boiler is a device that runs on gaseous fuel. The latter is most often natural gas.
, however, alternative options can also be used -
liquefied gas
(propane-butane mixture) or
main gas
(mainly methane). The not so high popularity of these energy carriers is explained by their “whims”: liquefied gas cylinders require special storage conditions, and to heat a house with main gas, additional permits from government agencies are required.
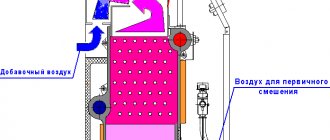
A standard gas boiler for heating a house includes the following elements:
- gas burner
(responsible for the flow of fuel into the chamber and its most uniform distribution over the entire combustion area. There are two types: atmospheric or ventilation); - heat exchanger
(heats the coolant during gas combustion. It may be present in a single copy or supplemented by a second one that works for the hot water system); - circulation pump (allows you to regulate the pressure in the system, included in boilers with forced circulation);
- expansion tank
(serves to remove excess coolant, which invariably occurs during heating and, accordingly, expansion of the liquid. Gas boilers serving large areas are often equipped with an additional tank); - combustion product removal device
(represents a double coaxial pipe, which is included with the boiler, or a special element attached to a separate chimney); - automation unit
(regulates the operating mode of the boiler, based on temperature changes - both inside the building and outside. Prevents the occurrence of emergency situations, such as increased gas pressure, water leakage, and so on).
Advantages and disadvantages
The abundance of advantages of a gas boiler has made it a real leader among heating devices for a private home. The especially valuable properties of such devices are:
- availability
. Gas is the cheapest and at the same time energy efficient fuel. The heat generated by a gas boiler will definitely not be wasted, which also contributes to savings; - power
. Even a very compact wall-mounted boiler can supply heat to many radiators of a one-story private house. Its larger brother, the floor-standing gas boiler, does an excellent job of treating air in two- and three-story buildings. Of course, a lot depends on the specific area and performance of the device, but the overall result is the same: a gas heating boiler copes with its main function “excellently”; - multifunctionality
. A gas boiler can not only warm up the batteries, but also be a full-fledged participant in the hot water system, providing the house with hot water. However, this ability largely depends on the design features of the unit.
If you are the happy owner of a private home, the decision to buy a gas boiler for heating it becomes truly correct. But we should not forget about the shortcomings of devices of this type. For some they are insignificant, but for others they can become a serious obstacle to the purchase. So, the disadvantages of gas boilers include:
1.
The need to adhere to strict rules during the installation process
. The presence of a separate room with good ventilation, the construction of a chimney, a certain strength of pipes - this is just a small list of requirements for installing a gas device. After all, gas is an explosive substance. The condition of the walls (when choosing a suspended unit) and the area of the room (when installing a floor-standing unit) are also taken into account. The number of floors of the house and the purpose of the room also play a role - in the living room, for example, it is prohibited to install a gas boiler. It is also impossible to install such a device yourself - only professional craftsmen do this.
2. System autonomy carries additional costs and some risks.
Firstly, the block itself can have an impressive cost (sometimes it reaches up to one hundred thousand rubles). Secondly, the automation operates using electricity, which is one way or another reflected in the amount on the receipt. In addition, dependence on electricity can become a serious problem if power outages are regular - this is especially true for closed-type models.
3. Sensitivity to temperature changes.
Today it’s +2, dry and windy, tomorrow it’s -8 and sleet – residents of Russian regions are accustomed to such sudden weather changes. But for an imported gas boiler, this can become a real stress – just like persistent 40-degree frosts. Therefore, before you go to the store to buy a device, you should think better: it often makes sense to give preference to a domestic manufacturer who creates its products taking into account the climatic “swing” of the region.
Boiler power. How to choose it?
The heating power of the boiler is calculated based on the area of the heated building. The generally accepted figure is 1 kW per 10 square meters. This takes into account the power required directly for heating, with compensation for lost efficiency (efficiency factor) due to room ventilation, as well as taking into account a small power reserve. Thus, we can calculate that if the ceiling height is about three meters, then 10 square meters will require 0.6 kW of heat, which with an increase of 30% to compensate for efficiency losses from building ventilation and with a reserve of up to 30% of power will give us the same figure of 1 kW per 10 square meters. Too large a reserve of boiler power is also not desirable in order to save both on resource costs and on the cost of the boiler itself. Accordingly, an area of 200 square meters will require a heating system with a capacity of 20 kW. At the same time, it is worth taking into account the energy efficiency of the room - window area, insulation of walls and floors, as this significantly increases energy costs to create a comfortable temperature in the room.
conclusions
All types of modern electric boilers have both advantages and disadvantages. For example, heating element boilers can be used with heated floors, but induction boilers cannot. Or a heating element boiler can be used without an expansion tank, but electrode and induction boilers cannot. It is impossible to fit all these nuances into one article. Therefore, I will continue the series of electric boilers in the following articles, where I will analyze in detail each type of electric boiler separately.
©Obotoplenii.ru
Articles on the topic
- Installation of gas ventilation
- Safety valve diagram for a solid fuel boiler
- Main types of heating boilers
- Condensing heating boiler
- Kiturami liquid fuel boilers: descriptions of popular models
- Advantages of a condensing heating boiler
- How to choose the right solid fuel boiler
Types of heat exchangers: copper, steel, cast iron
The heat exchanger is also a very important characteristic when purchasing. After all, it directly determines the reliability, convenience and energy efficiency of the heating system. Thus, copper heat exchangers, due to their lighter weight and better heat conductivity, have smaller dimensions and are installed on the wall, while cast iron, as the heaviest, offer only floor installation. But copper tolerates any mechanical stress much worse than cast iron, since this metal is very easy to damage. Cast iron boilers are generally recognized as more durable (the service life can exceed half a century), but when the heating temperature drops below 60 degrees, cast iron can produce condensation, which will cause erosion and cracks may even appear on the heat exchanger. Copper heat exchangers do not suffer from temperature changes and are easier to install, so they are often suitable for heating small rooms.
In addition, gas boilers with steel heat exchangers stand out on the market, which in some way occupy a position between heat exchangers made of copper and cast iron. They are even stronger than cast iron, which facilitates the maintenance process before the heating season and at its end, including removing condensate, carbon deposits, as well as checking the integrity of pipes and the tightness of joints, during which the heat exchanger, given its dimensions and weight, can be easily damaged. But at the same time, they are more at risk of failure due to temperature changes, since steel is subject to extremely rapid corrosion with increased moisture condensation. In turn, steel heat exchangers offer a wider range of models, offering different energy efficiency and mounting methods. They come in three types: bithermic (in which heat exchange occurs in a dual way), monometric (directly from gas to liquid), secondary/plate (heat is transferred from the coolant liquid to the hot water liquid). Copper heat exchangers are more popular, as they are more suitable for the needs of small mansions. But they are used mainly in wall-mounted boilers.
Heating electric boilers
In boilers of this type, tubular heating elements (heating elements) are used to heat the coolant. Essentially, these are electrical conductors with very high resistance. Electric current flowing through the element causes its heating, which is transferred to the coolant.
The heating element itself is surrounded by dielectric material and placed in a metal tube of various shapes. The connection contacts are located at the ends of the tube. The tube itself (heating element body) is electrically safe.
At the household level, heating elements are well known from old electric kettles and portable water heaters.
The disadvantage of this type of boiler is the same disadvantage as in a kettle - the formation of lime on the surface of the heating element and the walls of the boiler. This lime formation occurs when using so-called hard water. Therefore, when servicing the boiler, an element of cleaning lime deposits is introduced by adding various additives to the coolant. Or before use, water is artificially brought to a normal hardness level of 7–10 mEq. per liter
The main ways to soften water are pre-boiling, distillation or the use of special filters. This also needs to be taken into account before purchasing an electric heating element type boiler.
Another problem with the boiler heating element may be a coolant leak. A heating element that is not immersed in water overheats and, as a result, burns out, which in turn leads to a fire. Therefore, there is no need to skimp on boiler automation and pay special attention to its automation.