By installing a control valve on a heating radiator, we are able to control the movement of the coolant, thereby influencing the temperature in the room. Naturally, today there are many types of locking devices, so a beginner should take the time to analyze the theory before purchasing equipment for connecting batteries.
Locking equipment may have different operating principles
Locking devices
Ball Valves
By and large, any tap installed in a heating system can control the movement of the coolant, regulating the temperature. However, experts still divide the valves into shut-off valves and shut-off and thermoregulatory valves.
Photo of ball valve
The main function of the shut-off valve is to cut off the flow of hot water from the radiator or reduce its intensity. For this purpose, ball, cone and needle valves are used, which differ both in design and functionality.
Below we will describe their features and start with the simplest - ball:
- A ball valve is the simplest device that regulates the flow of coolant. The limited functions of the crane are determined by its design: the device can be either in a fully open or fully closed position.
Note! The instructions strongly do not recommend installing the valve in an intermediate position, even if this is possible: in this case, the shut-off element is damaged by solid particles suspended in the water, and the tightness of the fittings is significantly reduced.
- A sphere with a hole in the central part acts as a locking element . A rod connected to a handle-flywheel is attached to the top of the sphere. When the flywheel is brought to the open position, the hole is aligned with the lumen of the pipe, and the coolant enters the radiator.
Ball valve design diagram
The adjustment process itself is carried out exclusively manually: as soon as the room becomes too hot, we close the valve with our own hands, and the battery, deprived of hot water, simply stops functioning.
Cone valves
Cone-type valves, unlike ball valves, provide finer tuning:
- A conical rod with a surface pipe thread acts as a locking device.
- When the flywheel rotates, the rod moves up and down, respectively, opening or closing the lumen of the pipe in the seat - the inner chamber of the tap.
- To ensure tightness, the rod is equipped with gaskets made of elastic material, which periodically require replacement.
Sectional view of a cone-type device
As in the case of a ball valve, only manual adjustment takes place: we can only approximately reduce or increase the intensity of the coolant flow in order to adjust the microclimate in the room.
Needle valves
Needle valves are a type of cone valve, and therefore operate on a similar principle:
Needle valve diagram
- The water flow is blocked by moving a long threaded rod.
- At the bottom of the rod there is a gasket, which in the lowest position completely covers the valve seat, blocking the movement of the coolant.
- Needle-type valves can operate either manually or in conjunction with a servo drive connected to a temperature sensor. Such a system is, in fact, an analogue of a full-fledged thermoregulatory valve.
In addition to the examples of shut-off valves mentioned above, there are other devices that are installed in heating systems. For example, a balancing radiator valve, a device with variable hydraulic resistance, deserves attention. Balancing valves ensure the maintenance of uniform coolant flow, which is one of the conditions for stable operation of the heating system.
Balancing valve components for heating systems
Note! Balancing valves can be either manual or automatic. The use of models with manual adjustment is undesirable if the system already contains a device that automatically changes the pressure or flow of hot water.
Thermovents
Operating principle
A thermal valve for a heating radiator is a device that, unlike direct-acting shut-off valves, regulates the movement of heat flow automatically.
The system consists of two functional parts - a thermostatic element and a shut-off valve.
- The thermostat is based on a bellows - a cylinder filled with a working substance that senses the air temperature in the room and reacts to its changes.
- Liquids or gases can be used as a working substance. Gas-filled bellows respond more quickly to temperature changes, while the liquid provides more precise control of the movement of the rod.
Note! In the discussion about the comparative effectiveness of gas-filled and liquid bellows, there is no consensus even among professional heating engineers.
- As the temperature increases, the volume of the substance in the bellows increases, causing the valve stem to move. This element partially blocks the lumen of the valve seat, reducing the volume of incoming coolant.
- When the temperature drops, the opposite situation occurs: the corrugated bellows compresses, the rod rises, opening the lumen of the heating pipe.
- The operation of this unit can be adjusted manually. At the same time, the required temperature is set, and it is this value that the system will maintain.
Such devices can be very different:
- The simplest are mechanical valves with a rotating head, on which a scale of maintained temperatures is applied. Setting the desired value is carried out by rotating the valve.
Note! Most often, mechanical products operate in the range from 18 to 28-30 0 C.
- Electronic models are equipped with a small display and several control keys. Their price is slightly higher, but they are also much more convenient to use.
- If you want to fully automate the climate control system, then the control valve must be connected to several remote sensors and a control unit. In this case, we will be able to schedule the operation of the radiators, increasing and decreasing the temperature at specified periods of time.
As for the shape, the more common model is the straight radiator valve. At the same time, you can easily find corner models on sale, in which the locking part is located at an angle of 90 0.
Radiator corner valve: 1 2inch
Installation and configuration
When installing such devices, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- For one-pipe systems we use models marked RTD-G, for two-pipe systems - RTD-N.
Note! RTD - G valves can also be used in two-pipe systems of old multi-storey buildings, as well as in cottages without circulation pumps.
- We mount the device body in the radiator inlet, observing the direction of water flow (indicated by an arrow on the side).
- Sometimes a temperature sensor is installed after the repair is completed, so for some time the system can be controlled manually using a temporary cap.
Control valve
Reinforcement AIII 6mm A500s in coils
Total: 194
| № | Name | |
| 2 | Stop valve 15b1p 20 | |
| 3 | Stop valve 15b1p 25 | |
| 4 | Shut-off valve 15b1p 32 | |
| 5 | Stop valve 15b1p 40 | |
| 6 | Stop valve 15b1p 50 | |
| 7 | Stop valve 15b3r 15 | |
| 8 | Stop valve 15b3r 20 | |
| 9 | Stop valve 15b3r 25 | |
| 10 | Stop valve 15b3r 32 | |
| 11 | Stop valve 15b3r 40 | |
| 12 | Stop valve 15b3r 50 | |
| 13 | Shut-off valve 15kch16p 32 | |
| 14 | Stop valve 15kch16p 40 | |
| 15 | Stop valve 15kch16p 50 | |
| 16 | Stop valve 15kch16p 65 | |
| 17 | Stop valve 15kch16p 80 | |
| 18 | Stop valve 15kch16p1 32 | |
| 19 | Shut-off valve 15kch16p1 40 | |
| 20 | Stop valve 15kch16p1 50 | |
| 21 | Shut-off valve 15kch16p1 65 | |
| 22 | Shut-off valve 15kch16p1 80 | |
| 23 | Stop valve 15kch18p 15 | |
| 24 | Stop valve 15kch18p 20 | |
| 25 | Stop valve 15kch18p 25 | |
| 26 | Stop valve 15kch18p 32 | |
| 27 | Stop valve 15kch18p 50 | |
| 28 | Stop valve 15kch18p 65 | |
| 29 | Stop valve 15kch18p 80 | |
| 30 | Stop valve 15kch19p 25 |
Pages 1 - 30 of 194 Home | Prev. | 1
|
Track. | End | All At its core, a control valve
is a locking device that is usually mounted on a spindle. Valves are widely used to shut off industrial liquids and gaseous substances (cold and hot water, steam and other chemically neutral liquids). Most often they are installed in pipes in which the nominal diameter is approximately 250-350 mm, with a typical operating pressure not exceeding 2500 kg/cm2. The control valve blocks the cross-section of the passage only in the horizontal plane. The design of the throttle mechanisms used in the manufacture of such valves can be divided into two parts: with profiled spools and needle valves. Housing designs are divided into the following types: through-flow, direct-flow, mixing and corner.
In straight pipelines, straight-through types of valve bodies are used. They have high hydraulic resistance, they have a stagnation zone, they have rather large construction dimensions and heavy weight, plus, the design of the body is very complex.
The control valve also has a direct-flow type of body, which, unlike a straight-line one, has low hydraulic resistance, a compact design and an eliminated stagnation zone. However, this type also has disadvantages, which are expressed in its long length and relatively heavy weight.
At the junction of two separate parts of the pipeline, which are located relative to each other, as well as at turns during installation, angle valves are used.
And the last, mixing type, is used when it is necessary to mix several streams of liquids or gaseous media to stabilize such indicators as the concentration of reagents, temperature, quality, degree of dilution of the main working medium and many others. The best mixing occurs according to the scheme when the process itself takes place directly inside the housing, and not outside it. This also brings good savings, which is manifested in the absence of the need to use two valves and a special mixer, but only one is enough to operate.
The control valve, compared to its other types, has the following capabilities and key characteristics:
- has a high degree of fit;
- its internal structure does not require special care;
- has compact dimensions;
- has an opening indicator.
The profile of the valve and seat distinguishes the control valve from other types of valves. It can use both single-seat valves and double-seat valves. As a result, this helps the design avoid special axle forces that can occur due to differences in outlet pressure compared to inlet pressure. One of the features of this type of valve is its excessive leakage, which arises due to the difficulty of achieving a complete seal between two different surface areas at the same time. For this reason, the regulation of the flow of the working medium at a small rod level will be weak.
Also widely used are needle valves, which are essentially universal, similar in properties to both a shut-off valve and a control valve. The main area of their application is the regulation of small gas flows, and their throttling even during intense pressure surges on the throttle mechanism.
Types of device
It would seem that there is nothing difficult about going out and choosing a high-quality battery tap. But not everything is as simple as it seems at first glance. After all, in a plumbing store the buyer will be offered several types of locking mechanisms. Which one is better? It is difficult to answer this question unambiguously. And all because each device has its own purpose and its own area of use.
For example, flanged ball valves have one distinctive feature. It lies in the fact that the valve can only be used in one position. It can be completely open or closed. Therefore, such a valve will not be able to provide average coolant flow. After all, half adjustment is impossible.
Because of this, flanged shut-off mechanisms are installed only on pipelines. They are not suitable for radiators. But their design copes well with the load associated with high pressure inside the pipeline. Therefore, flanged valves are durable, reliable in use and very durable.
For radiators, it is necessary to purchase coupling ball valves. These locking mechanisms are so called because they have threads on the edges. It ensures reliable fixation of the valve on the battery. But the coupling valve can be used both when assembling water mains and when installing gas pipelines.
Coupling taps are presented in a large assortment. They differ from each other in that they are able to pass liquid of a certain density through their mechanism. And when purchasing a model, you must take this circumstance into account. As a rule, all technical characteristics are clearly stated in the product passport.
Removing blockages and painting
Often, a water valve needs painting, which is a great time to check and clean it. It is necessary to completely remove the old paint, inspect the surface of the mechanism, and prime the metal with drying oil.
We must not forget that complete removal of the valve will inevitably entail shutting off the water intake on the riser, so if it is possible to make repairs without turning it off, this should not be neglected.
It is often necessary to remove blockages that are preventing water from flowing with sufficient pressure. Serious blockages require complete removal of the valve, but small ones can be removed very simply, even without the use of special tools.
This can be done like this: you need to turn on all the taps in the house, including the tap on the cistern. Then open and close the water valve a couple of times. The pressure will rise significantly, and a small blockage will simply be washed away by the pressure of water on its own.
The gasket itself is very similar to the material for the tap, but it is stronger and denser, because it is under high loads.
We recommend installing fiber, paronite or heat-resistant rubber under the gasket, because elevated temperatures (for a pipeline with hot water) significantly deteriorate the properties of the rubber gasket.
Replacement may be necessary for both the stem and the spindle, also remember to lubricate the handle to turn off the water pressure, make sure that the valve fasteners are tight.
What other taps are suitable for radiators?
When installing radiators, the question naturally arises as to which control valve is best to choose. Experts recommend giving preference to conventional ball locking mechanisms. But we must not forget that each radiator must be equipped with one more element - a needle tap, also known as the Mayevsky tap. What is this device?
Typically, such a plumbing fixture is used to bleed air from the battery. The coolant in the central network always circulates unevenly. Air enters the system along with hot water. It forms bubbles, and if the pressure of the coolant drops, an air plug forms in places where its speed is particularly low, sharply reducing heating efficiency. The Mayevsky valve helps eliminate it. It is mounted at the top of the radiator.
How does this control valve work?
Its central mechanism is the needle valve. This assembly can be moved using a key or a locking screw. It has a square head that fits easily into existing slots. If the key is not at hand, a screwdriver can be used instead.
A valve is installed on the opposite side of the coolant inlet. The air accumulated inside the system rises and collects at the highest point of the radiator, where the control valve is installed. If the system has a Mayevsky valve, the air lock can be easily removed by slightly opening the needle valve. It is simply turned several turns counterclockwise to produce a characteristic hissing sound. As soon as it stops, turn the valve back and close the tap tightly.
The air will come out through a special hole. It can be located either in a plastic gasket or in the brass body itself. Both types serve equally reliably and efficiently. However, if the quality of the coolant leaves much to be desired, the described hole becomes clogged very quickly. Therefore, experts recommend periodically piercing it with a regular sewing needle. This can only be done with the valve closed.
Note! If the heating system has a circulation pump, then before the described procedure it is advisable to turn it off, wait a few minutes and only then turn on the Mayevsky tap. If this is not done, the air lock cannot be removed. The air simply won’t have time to accumulate at the top of the radiators.
When the pumping equipment is turned on, it will not be possible to bleed the air lock. Under pressure, water may flow through the valve, and it will be difficult to avoid a flood.
Automation at the service of man
Manufacturers are constantly striving to improve their products and offer consumers new generation locking mechanisms. Mayevsky's usual control valve was no exception. It was modified and equipped with a simple automated system.
The new know-how looks like a regular faucet that is installed on a radiator. And the principle of operation of the locking mechanism remains the same. But if air accumulates in the upper part of the radiator, a special needle float is lowered, the valve opens, and the air is released independently without human intervention. Very convenient, isn't it? No need to pick up a screwdriver and no need to constantly monitor the condition of the radiators. I installed the faucet and forgot about it.
Why do you need a needle tap, what is the difference between a valve and a valve and how to install them?
Author of the article: Alexander Burlakov (vseotrube.ru)
Often in the cold winter we freeze in our own apartments. The reason is simple and banal - central heating radiators do not warm up well. You have to connect electric heaters, subsequently receiving huge sums in electricity bills.
Unfortunately, not everyone knows that this problem was solved back in 1931 by the unknown Belarusian plumber S.A. Roev. His invention, a needle valve, allows excess air to be released from the batteries. It is airiness that is the main reason for the low temperature of the heater. Subsequently, the invention was improved by the Soviet engineer Mayevsky. The Mayevsky tap is one of the most famous representatives of the family of needle taps, which will be discussed in today’s article.
Useful information for those who want to choose a universal locking device
When choosing a faucet for a radiator, it is important to pay attention to the material from which it is made. The locking device operates in the most aggressive environment. It is constantly in water, exposed to high temperatures and hydraulic shocks. Therefore, it is important that the material can withstand all these negative factors.
Most often, radiator taps are made of alloys. Most models are made of brass. This is a very durable metal that is not afraid of corrosion. But for even greater strength, the brass is coated on top with a protective metallic compound. This is the best option for use in a heating system.
Sometimes, instead of brass taps, sellers can slip in counterfeits - silumin control valves, which look exactly like the original models.
After a year of operation, breakdowns often occur that can lead to utility accidents. After all, silumin rusts very quickly from the inside, and corrosion instantly corrodes the body, making its walls very thin. Therefore, any water hammer easily breaks the locking device. Even if this does not happen, there are often cases when, when simply opening or closing a tap, it simply remains in the hands of a person, falling off from the base. If there is hot water inside the battery at this time, burns will definitely occur. So beware of fakes!
Tips for choosing
Before purchasing, please pay attention to the following points:
- Scope of the element. Choose a product with appropriate technical characteristics;
- Material of manufacture (cast iron, steel, bronze, stainless steel). Usually the best option in terms of price-quality ratio is cast iron or inexpensive stainless steel. If you plan to operate in aggressive environments, choose bronze and stainless steel with a high nickel content (grade AISI304 or 12×18n9);
- If you choose a device for regulating high-pressure flows, carbon steel (grade U8, U10, etc.) is suitable;
- Pay attention to the quality of the part - when closing, the needle should not touch the support, and when opening, it should not come out of the socket;
- Choose your connection type wisely. It can be coupling or flanged;
- For centralized heating systems, it is better to use a Mayevsky manual tap, which allows you to bleed off the air accumulated in the radiators at any convenient time. For private homes, an automatic option is suitable. An automatic faucet is also suitable for use in places with difficult access.
You can find many reviews of needle taps on the Internet that can help you with your choice. But almost all of them are described in our article.
Generalization
So, the tap for the heating battery must be made of brass - only this alloy can easily withstand high temperatures and water shocks. It is better to choose ball locking mechanisms that have long warranty periods and demonstrate increased tightness. This crane can be installed in both horizontal and vertical positions.
The heating system often includes control mechanisms and mechanisms that ensure safe operation. They are otherwise called heating system valves. With the help of these adjustment elements, the heat supply parameters change; they also ensure stable operation and perform automatic adjustment. Let's look at the valves and regulators of the heating system, since their purposes and functions differ.
Three way heating valve
Typically, boiler automation cannot meet the need for water at different temperatures for several circuits of the heating system. A three-way thermostatic mixing valve of the heating system comes to the rescue, which maintains the necessary thermal parameters of the coolant in the circuits of the heating system, as well as in the small circuit of the system. The valve looks like a simple tee, the metal is bronze or brass. An adjusting washer is installed at the top of this tee, under which there is material sensitive to temperature changes. And if necessary, it presses on the working rod coming out of the housing. The main task of the valve is based on maintaining the temperature of the coolant at the outlet within specified limits by adding cold or hot water . During unsuitable temperature changes, the external valve actuator presses on the stem. Next, the cone leaves the saddle and a passage opens between all channels. During operation, the three-way valve is controlled according to temperature by an external actuator.
Features of operation
The faucet outlet is usually small and often becomes clogged. Therefore, it must be cleaned periodically with a needle. If the valve has not been used for a long time and the butterfly valve moves with difficulty, it can be lubricated with WD-40.
If you need to replace an element, use 2 keys. Some should unscrew the part itself, while others should hold the radiator cap. Despite the simplicity of the entire design, the system should be periodically checked and cleaned. In this case, its operation will be trouble-free and long-term.
Heating check valve
A complex heating system contains a fairly large number of auxiliary elements, the task of which is to ensure reliability and uninterrupted operation. One of these elements is the heating system check valve. A check valve is installed to prevent flow in the opposite direction . Its elements have very high hydraulic resistance. Due to this circumstance, there are restrictions on the use of check valves in a heating system with natural circulation. There is too little pressure in such a system. At minimum pressure, it is necessary to install gravity valves with a butterfly valve; some of them can operate at a pressure of 0.001 bar. The main part of the check valve is the spring, used in almost all models. It is the spring that closes the shutter when normal parameters change. This is the principle of operation of a check valve.
It is necessary to take into account the operating parameters in a particular heating system. Therefore, select a heating system valve that has the required spring elasticity. Shut-off valves used in heating systems are usually made of the following materials: steel; brass; stainless steel; gray cast iron. Check valves are divided into the following types: disc valves; petal; ball; bivalve. These types of valves are distinguished by a locking device.
Types and designs
Valves differ in the direction of flow: there are straight-through, angular and through (with a displacement of the water flow at the inlet relative to the outlet).
Depending on the method of sealing the spindle (stem), valves are of the following types:
stuffing box The most common type. On the outside of the housing, at the point where the spindle passes, a stuffing box is created, filled with stuffing box made of sealing material;
bellows. The bellows is made from a corrugated pipe welded to the upper and lower rings. The bellows assembly is fixedly connected by the upper ring to the valve body, and by the lower ring to the rod (or valve spool). The rod moves inside the bellows, while the corrugated pipe compresses and decompresses. Such a unit has better sealing than a stuffing box unit and is used when working with toxic and aggressive media. Disadvantages: design complexity and high cost;
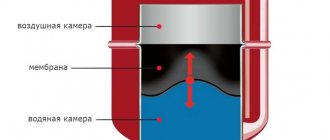
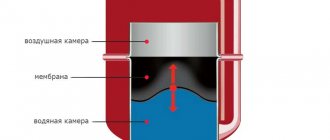
membrane fittings - the seal is made in the form of a membrane, the central part can bend with an amplitude sufficient to close/open the shut-off element. Disadvantages: short service life, low operating pressure and temperature.
Heating control (shut-off and control) valves
Regulating and shut-off and control heating valves systematically change the flow of coolant, from maximum to minimum , with the valve open and closed. Shut-off or shut-off valves control the coolant discretely when the valve is in the fully open or fully closed position. A control valve consists of three main blocks: the body, the throttle assembly, and the valve actuator. The closing and regulating element of the valve is the throttle assembly. When choosing a sleeve, seat, or plunger, you should pay attention to the operating conditions of the valve. The medium and its temperature, the presence of impurities, and throughput are taken into account. The main and important importance in the operation of the valve is the correct direction of supply of the working medium. It is usually marked with an arrow on the working surface of the case.
What it is
A needle valve is an element of control pipeline fittings.
The main purpose of the part is to reduce water pressure, gas pressure and its cooling (this process is called throttling). The main difference between a needle valve and a conventional ball valve is the special conical shape of the shut-off rod, which allows you to regulate the pressure of the working medium very smoothly.
Thermostatic valve
In modern realities, a thermostatic valve is a prerequisite for modern and reliable equipment in a heating system. The valve temperature is automatically adjusted. The operation of a heating system mixing valve for radiators is to limit the supply level to an individual heating radiator. The valve stem makes movements to open and close the hole. Through this hole, coolant enters the radiator. When the valve with a thermostatic head heats up, the inlet opening is closed, as a result of which the coolant flow rate decreases. The thermostatic valve constantly changes its position. And an important factor is the quality of the materials on which this product is made. The product may fail due to sticking of the rod, as well as significant corrosion and breakthrough of sealing materials. But even if the thermostatic valve fails, you can extend its service life by replacing the thermostatic element.
Heating system valves with thermal heads differ depending on the shape and type of supply to the heating system. They can be angular when connected to radiators from the floor, or they can be straight, which connect the pipes to the battery relative to the wall surface. Axial, mainly when connecting pipes from the wall to the battery. When connecting batteries sideways, a special kit is required. It uses thermostatic heads and valves. Batteries that come with a bottom connection are obviously equipped with valve-type inserts.
Pressure regulator
The operation of the batteries and the pump is disrupted due to high or low pressure levels. Correct control of the heating system will help to avoid this negative factor. The pressure in the system plays a significant role, it ensures that water gets into the pipes and radiators. Heat loss will be reduced if the pressure is standard and maintained. This is where water pressure regulators come to the rescue. Their mission is primarily to protect the system from too much pressure . The operating principle of this device is based on the fact that the heating system valve located in the regulator works as a force equalizer. Depending on the type of pressure, regulators are classified into: statistical, dynamic. It is necessary to select a pressure regulator based on throughput. This is the ability to pass the required volume of coolant, in the presence of the required constant pressure drop.
Application area
Needle valves are not as popular as ball and balance valves and should not be confused with them.
Main Applications:
- Placement on auxiliary pipelines with pressure up to 10 MPa (with the exception of high-pressure taps) to control the flow of liquid, steam, and gases. The conical plunger head is more reliable than the straight seats of classic valves. This prevents scuffing of the sealing rings.
- Pipelines with increased medium pressure. Needle rods allow you to regulate the flow without interrupting the operation of the system.
- For connecting pressure gauges;
- In cooling water injection systems;
- In heating for air release;
- In carburetors of cars and motorcycles (in the form of a needle valve);
- When making moonshine. Here, needle valves are used to control the rate of release of the membrane (or any other) reflux condenser product from the distillation cube into the cooling system.
Heating bypass valve
To relieve the working medium, use the bypass valve of the heating system thermostat, which operates in the return direction when the pressure increases significantly . As a rule, the pressure increases due to the achievement of the maximum temperature set manually, the supply of coolant to the radiator decreases, as a result of which the pressure increases. Heating system bypass valves are basically designed to ensure a stable difference between the return and supply pipes. When the heat load decreases, the thermostatic valves close, resulting in a pressure difference between the pipelines. As a result of using a bypass valve, the load on the pump is reduced, the return temperature increases, and the boiler is protected from corrosion. The scope of application of the heating system bypass valve is quite wide; it is also used to prevent noise generation of thermostats. Bypass valves are installed not only on an unregulated pump, but also on riser jumpers.
Safety valves
Any boiler equipment is a source of danger. Boilers are considered explosive because they have a water jacket, i.e. pressure vessel. One of the most reliable and widespread safety devices that reduces the danger to a minimum is the safety valve of the heating system. The installation of this device is due to the protection of heating systems from excess pressure . Often this pressure occurs as a result of boiling water in the boiler. The safety valve is installed on the supply pipe, as close to the boiler as possible. The valve has a fairly simple design. The body is made of good quality brass. The main working element of the valve is the spring. The spring, in turn, acts on the membrane, which closes the passage to the outside. The membrane is made of polymer materials, the spring is made of steel. When choosing a safety valve, it should be taken into account that full opening occurs when the pressure in the heating system increases above the value by 10%, and full closure occurs when the pressure drops below the response value by 20%. Due to these characteristics, it is necessary to select a valve with a response pressure higher than 20-30% of the actual one.
Characteristics
Manufacturers produce needle valves with the following characteristics:
- working pressure - from 10 to 40 MPa;
- temperature range - from -600С to +2000С;
- service life - up to 15 years;
- type of transported substances - gaseous, liquid;
- types of connection - thread, flange, welded, coupling;
- case material - stainless or nickel-plated steel, copper, brass;
- bore diameter - 100–1800 mm;
- body length - 235–2800 mm.
Balancing valve
The balancing valve of the heating system is intended to regulate the coolant passing through . Liquid consumption depends on pressure. The higher the pressure, the more fluid is consumed. This device is installed on risers. A balanced system ensures continuous operation. The manual valve is used as a diaphragm, and the automatic valve maintains pressure and consumption in the risers. A manual balancing valve can shut off the system. The design is a valve type device. Manual valves can be installed in conjunction with shut-off valves.
Flow regulator
Having installed energy metering devices, the question naturally arises of how you can regulate and control the supply of coolant, limit or add its flow. For this purpose, there are all kinds of automatic regulators, the use of which allows you to save money; they operate from outside air temperature sensors and return pipeline sensors. Another advantage of temperature controllers is that they control the temperature directly at the radiator installation site, unlike other devices. This advantage gives priority in obtaining a uniform temperature background for a comfortable stay in the room. The regulator will prevent overheating of the air in the room, which sensors on centralized automation cannot always track. It is possible to adjust the temperature for each room separately. Sometimes, when solving the adjustment issue, ordinary taps are installed. Of course, this solution reduces financial costs, but deprives a number of useful advantages. The faucet has limited functionality to open and close. There is a danger of stopping or airing the riser. By adjusting the heating using taps it is impossible to achieve the required temperature. Using automatic regulators, you can adjust the system accurately and efficiently.