Types of heating boilers used in a private home
There are different types of boilers for the homeowner to choose from:
- — Electric heating that does not require the installation of a chimney. They are as easy as possible to manage.
- Gas heating. The main advantage of such a boiler is its efficiency.
— Solid fuel devices, which are considered the simplest. The solid fuel boiler runs on coal, coke, and wood.
Regardless of which boiler is chosen - gas, electric or solid fuel, it must be grounded in any case.
How to choose the right ground electrode?
Steel pipes, corners, and strips that are driven into the ground are chosen as an artificial grounding conductor. The requirements for the grounding conductor and circuit element are:
- carrying out special anti-corrosion treatment (copper plating or galvanizing);
- the presence of at least two contacts with individual parts of the boiler surface when using natural grounding.
Depending on the level of circuit resistance (optimally 30 Ohms for a voltage of 220/380 volts), circuit materials, tires, and the number of electrodes are selected. The circuit electrodes are made of pipes with a diameter of 2 inches or angle steel material with a cross-section of up to 50 square millimeters and a length of two meters. The tire is knocked out in the form of a steel or copper strip.
Grounding quality requirements
When installing grounding, it is necessary to pay attention to the type of material and cross-sectional area of the wires that connect the circuit to the zero phase of the electrical panel. When using copper wire, the recommended cross-section is more than 10, aluminum - at least 16, steel - more than 75 square millimeters
Steel pipes and angles (electrodes) are connected to the busbar using spot welding.
Ground loop resistance
The type of soil also matters. A circuit can be installed in silty soil if its resistance does not exceed 10 Ohms (with a standard voltage of 220 volts or a three-phase voltage of 380 volts). A ground loop can be installed in sandy soil with a resistance value of up to 50 ohms (for devices operating at 220 or 380 volts). If such requirements are met, there will be no claims from the gas service.
Why is it necessary to ground the boiler in the house?
In the old days, no one did grounding when constructing buildings, because there was no particular need for it.
The grounding that a solid fuel or any other boiler receives is a certain wiring that connects the heating system in a private house with a grounding device.
Grounding the boiler will allow:
- - eliminate the possibility of electric shock to a person who touches the body of a working device;
— ensure stable operation of the gas boiler (as mentioned above, it can also be a solid fuel or electric device);
— reduce electromagnetic radiation and the amount of interference in the network.
According to safety rules, you can connect a gas, electric or solid fuel boiler only if there is grounding.
Grounding of a gas boiler must be done regardless of its service life. It must be taken into account that static voltage is generated on its body, which under certain conditions can lead to:
- - Possibility of fire. This is the most important reason why it is necessary to ground a gas boiler in the house. One random spark will be enough to cause an explosion or fire of natural gas.
— Failure of automation, the replacement of which will be expensive.
To carry out work on zeroing or grounding boilers with your own hands, you must have certain electrical knowledge.
They will get the job done as quickly as possible. In addition, experienced craftsmen know the requirements for grounding conductors:
- — no more than 50 Ohm for sandy soils;
- no more than 10 Ohms for clay soils.
Efficient methods of heating with electricity
It depends on the area of the heated premises and the total length of the heating pipelines.
Usually it is 1.5 atm. It is necessary to carefully calculate the length of such a structure, taking into account the layout of the TP contour. In addition, electric boilers differ in power.
In most cases, a heated floor is an auxiliary element of the heating system in the house.
This is not the most important thing here. Although a system with forced circulation does not necessarily require compliance with the slopes of the pipes, as with a natural one, since circulation here is provided by a circulation pump, they still must be observed so that, if necessary, all the water can be drained and so that it does not become airborne. during operation
Related article: List of materials in the electrical installation estimate
Pros and cons of heating your home with electricity
There is one important subtlety in this work: low-power boilers can operate from a conventional network, the voltage of which is V, but for more powerful equipment the network must be three-phase. Natural circulation turns out to be very slow, and because of this, energy consumption for heating increases.
There it cools, transferring thermal energy to the air in the room, after which the cooled liquid is again sent to the boiler. All installations operate absolutely silently, since the system does not have a fan or circulation pump.
Types of heating schemes
Types of boilers The main task when organizing heating with your own hands is to create an effective system, mostly automatic, with minimal human participation in its operation. By analyzing the types of foundations, we can immediately say unequivocally that a monolith will be more expensive than a strip foundation. This device ensures the circulation of coolant in the system and uniform heating of the house. This is a closed system where water circulates under the influence of a pump or by gravity.
But often, for objective reasons, such an opportunity is not available everywhere. Today, a lot has changed - the abundance and range of modern heating equipment allows you to do heating in the house yourself, even without the involvement of specialists. Heating the garage with an electric boiler
How to properly ground a gas boiler?
Before grounding the boiler, you need to select a ground electrode. It is in direct contact with the earth and is part of the entire system. Grounding electrodes can be artificial and natural. Which one to use depends on your own preferences.
Natural grounding conductors are various metal structures in contact with the ground. Such grounding conductors must be connected to the boiler by several conductors (at least there should be two of them).
Artificial grounding conductors are steel pipes and angle steel, which are located in the ground in a vertical position.
Connecting the boiler to grounding is more difficult than with conventional devices (washing machine, refrigerator, electric stove). It is necessary to check in advance both the total resistance of the structure and the conductivity of the soil.
Grounding a heating boiler involves a number of works:
1. Making a ditch model on the ground. To do this, draw an isosceles triangle, the distance between the corners of which is two linear meters.
2. After this, a ditch is dug 35-40 cm wide and 50 cm deep.
3. At the corners of the triangle, holes are drilled, for which a motor drill can be used.
4. Three-meter corners (sixty millimeters wide) are hammered into the holes.
5. Next, the triangle is scalded with a four-centimeter strip. A similar strip is stretched from the ditch to a private house.
6. Next, a 10 mm pin is welded at the end of the strip. It is hooked to the plinth in the building. If you want to hide the hairpin, you can use a polyvinyl chloride box. From the stud, the wires are led to the grounded heating device.
To quickly install grounding, you can buy ready-made kits. They can be easily found on sale.
By taking care of grounding the boiler with your own hands, you can count on reliable and, importantly, safe operation of this heating device.
Subtleties of the circuit device
The grounding system can be natural or artificial. The first option includes structures made of metal or reinforced concrete that are in direct contact with the ground. This could be the foundation of a building, a pipeline or other underground utilities.
But for a gas boiler, natural grounding requires the presence of at least two contacts with individual parts of the housing, and sewerage, heating and gas pipes are excluded in this case. Therefore, during installation, an artificial system is often used, the organization of which we will consider.
What material to choose for grounding conductors?
For artificial grounding, rods or pipes become conductor-electrodes, which are connected to each other by metal strips. They are installed vertically in the soil to ensure operation of the system even in winter, when the top layer of the earth freezes.
An important condition is that metal elements should not be protected from corrosion by insulating material.
The service life of the grounding circuit largely depends on the presence of anti-corrosion protection on its electrodes - copper-plated and stainless steel elements will last the longest
You can also find ready-made kits for a grounding system on sale, which consist of steel rods (usually copper-plated) and special pointed tips for soil of varying densities.
The kit also includes an anti-corrosion agent for treating the system before installation and connecting elements - brass couplings, clamps. The main advantage of this solution is that the circuit can be assembled without welding and lengthy preparation.
Although regulatory services advocate for ready-made grounding kits, it is feasible to make the structure yourself - this will not be a violation, but will cost several times less
To assemble a system from scrap materials, you should consider several important nuances:
- Metal structures intended for installation in the ground can be made from a profile pipe, an I-beam, a channel, or an angle.
- The metal of the grounding conductor must be protected from destruction by galvanizing, copper plating or, as a last resort, anti-corrosion paste.
- The cross-sectional area of the wire connecting the zero phase of the shield to the ground loop depends on the type of metal from which it is made. For copper, the optimal value is 1 cm2, for steel - 7.5 cm2, and for aluminum - 16 cm2.
- The grounding resistance for sandy soil should not exceed 50 Ohms, for clay soil - a maximum of 10 Ohms.
- Electrode materials must also be selected taking into account the circuit resistance. The best option is two-inch pipes or corners with a length of 2 m and a cross-sectional area of 5 cm2.
- The grounding bus is made of copper or steel strip (aluminum is prohibited for this case).
Compliance with these requirements and correctly installed grounding loop will help eliminate claims from gas service inspectors, regardless of whether you used a ready-made modular system or assembled it yourself.
Image gallery
Photo from
Stainless steel ground loop
Using electrically conductive graphite grease
Series ground circuit arrangement
Tinned copper grounding bar
Calculation of circuit parameters
The list of requirements for grounding arrangement contains several indicators, the algorithm for obtaining which may be incomprehensible to a beginner in the electrical business - for example, exactly how many electrodes are required for the correct operation of the system or how to measure the resistance of the circuit. Let's try to clarify the basic principles for determining these parameters.
You can find out the resistivity of the soil, grounding devices of any configuration, and even the presence of a connection between the electrodes using a special meter
Grounding is carried out after installing a gas boiler in a country house. The physical parameters of the grounding loop are selected mainly experimentally. This practical method is suitable for those who are afraid of getting bogged down in complex theoretical calculations.
The algorithm for performing the work is as follows:
- Let's take as a basis a contour in the form of an isosceles triangle of three metal rods 3 meters long.
- We connect the conductors.
- We take an ohmmeter (a device for measuring resistance) and measure the indicators for the circuit. The ideal value is 4 ohms.
- If the result obtained significantly exceeds the optimal value, we add another element to the circuit and check the resistance again. We continue until we get the ideal value or at least the maximum permissible value for the boiler circuit of 10 ohms.
But you can determine the required number of electrodes using formulas, choosing the appropriate options for your case.
Using this formula, you can find out the resistance for one electrode if, in the area where the house is located, the soil is homogeneous and does not lie in layers
In the formula you need to substitute the average value of resistivity, depending on the type of soil in which the ground electrode will be located:
- wet sand – 500 Ohm*m;
- hard sandy loam – 300 Ohm*m;
- clay-sand mixture – 150 Ohm*m;
- loam – 100 Ohm*m;
- semi-solid clay and chernozem – 60 Ohm*m;
- garden soil – 40 Ohm*m;
- refractory loam – 30 Ohm*m;
- peat – 25 Ohm*m;
- plastic clay and salt marsh – 20 Ohm*m.
Stone and rocky soil are least suitable for installing a ground loop. In this case, an artificial embankment will have to be erected.
For heterogeneous soil, it will be more difficult to calculate the resistance for one electrode, but this can also be done by substituting your data in the indicated formula
The value of the seasonal climatic coefficient of soil resistance depends on the area where your home is located. They are conventionally divided into 4 groups.
Correction for climatic features is especially important for areas with cold winters, since in frozen soil the efficiency of grounding is significantly reduced
There are also more complex algorithms for accurately determining the parameters of the electrodes and even special programs for their calculations. But for the gas boiler to operate correctly, it will be enough to follow the general recommendations for arranging a standard grounding loop.
The use of copper-plated steel grounding conductors allows the construction of systems in soils with any physical and mechanical properties:
Image gallery
Photo from
Copper-plated steel grounding kit
Packaging with vertical grounding conductors
Installation in the ground using a jackhammer
Innovation - the use of an electrically conductive composition
Installation and connection of an electric boiler to the heating system
Heating using electricity is not very profitable, but it provides a lot of advantages: comfortable operation, relatively low price of equipment, safety. This article is devoted to the installation and connection of an electric boiler in a private house. After studying our detailed guide, any skilled homeowner can easily install an electric boiler with their own hands.
Step-by-step instructions for installing an electric boiler
As a rule, electric boilers are used in combination with solid fuel or gas boilers. In the first case, a solid fuel boiler heats the house to a given temperature, and an electric boiler maintains it at a comfortable level. In the second case, the gas and electric boilers are integrated into the heating system in parallel, but operate in series. At night, subject to the corresponding reduced tariff, the house is heated by an electric boiler, and during the day by a gas boiler.
Correct connection of the electric boiler to the heating system is carried out as follows:
- According to the previously developed plan, the location of the boiler installation is marked in the room;
- Markings are being made on the wall. To do this, the electric boiler with the front panel removed is pre-installed at the installation site and leveled using a water level. The installation locations of fasteners are marked through technological holes
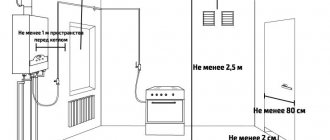
- The mounted boiler is installed at a height of at least 1.5 m from the floor level for more convenient maintenance;
- Fastening elements are selected depending on the wall material. Typically these are plastic dowels with steel screw hooks as anchors. However, some low-power models of electric boilers can be installed on plasterboard walls. In this case, the use of a butterfly dowel is allowed;
- Grounding installation. One of the key stages of installing an electric boiler. Some models will not turn on without grounding, while on others the warning light will light up. To arrange grounding, it is necessary to drive several reinforcing pins into the ground and connect them together with a metal plate. The neutral wire from the electric boiler must be connected to these pins.
- Power connection. The electric boiler must be connected through its own power supply line connected to a separate input circuit breaker;
- From the machine, the cable is laid to the residual current device, which is recommended to be located directly next to the boiler.
- The boiler is connected to the heating system through the inlet and outlet pipes. For some models, both outputs are located at the bottom of the device, for others, the supply pipe is on top and the return pipe is on the bottom.
- A circulation pump is attached to the return pipe (the flow of cooled coolant into the boiler). The rotor location must be strictly horizontal. Location on the return side is preferable than on the supply side, since the high temperature of the coolant negatively affects the working elements of the pump and reduces its durability;
- A coarse filter “mud filter” is installed in front of the pump. It is also mounted horizontally with a sump (branch with a filter mesh) down;
- A branch for the expansion tank is cut into the return pipe. It compensates for the thermal expansion of the coolant, containing a certain volume of water;
- The installation of a safety group, consisting of a safety (break) valve, a pressure gauge and a valve for bleeding air, is carried out on the supply pipe. Through a small branch. The safety group should be located at the highest point of the heating system to remove air in a timely manner.
If you have not yet chosen an electric boiler
The choice of a heater operating in conjunction with a water heating system is made based on power and operating principle (the cost of the equipment depends on the latter). Electric boilers have no problems with functionality - any model is equipped with an automation unit. If desired, various peripheral devices can be connected to it - weather sensors, room or overhead thermostats and GSM modules for control from a mobile phone or via the Internet.
Important note. Some, Protherm or “Evan” require in the operating instructions that the installation and connection of the electric boiler to the network be carried out by specially trained personnel. Self-connection will result in a waiver of warranty obligations.
Before choosing and purchasing a heating device, check how much electrical power is allocated to your home by the management company. It may happen that it is not enough for individual electric heating. Point two: a single-phase 220-volt network is capable of powering boilers that consume up to 12 kW/h inclusive. More powerful water heaters are connected to a three-phase 380 V power supply.
Determination of thermal power
This indicator is calculated using the standard formula: calculate the heated area of a country house or cottage, then multiply the quadrature by 0.1 kW. Obtain the thermal energy demand that the electric boiler must cover.
Consider a number of nuances:
- the height of the ceilings of the rooms is up to 3 m, otherwise the calculation is carried out according to the volume of the premises: the cubic capacity is multiplied by 40 W;
- the heat generator must be selected with a minimum margin of 20%;
- if the heating unit is planned to be used to provide domestic hot water, the reserve must be at least 50%;
Dividing a quadrature by 10 is the same as multiplying by 0.1, the result is the same
- in the northern regions, the square footage of the building is multiplied by 0.2 kW, in the southern regions - 0.08 kW;
- The power of the boiler, which operates only at night and charges the heat accumulator, is assumed with a double margin.
- Traditional, equipped with tubular electric heaters (TEHs).
- Electrode, where the salted coolant is heated by passing current through the water.
- Induction devices heat the liquid using Foucault eddy currents that arise in the metal core of a multi-turn coil.
- loud switching sounds from the operation of a contactor or magnetic starter;
- gradual degeneration of salts in the coolant, which reduces heating efficiency, which is why the water in the heating system will have to be added with salt 1-2 times a month;
- The electric device works stably with radiators, but is poorly compatible with heated floors, where it is necessary to maintain a low coolant temperature of 35-50 ° C.
Example. A small house of 100 m² on average requires 100 x 0.1 = 10 kW of heat. The power of the electric heating installation is 10 x 1.2 (20%) = 12 kW. We need to heat water for household needs - multiply by a factor of 1.5 and get 15 kW.
To obtain more accurate results, we suggest studying the methodology for calculating the load on the heating system
Which type of heater is better
Next, you need to select a water heating device based on its operating principle. What types of household electric boilers can you buy:
Electric mini-boiler room with tubular heaters (TEN), fully equipped
Valuable advice. Do not listen to the tales of salesmen praising the efficiency of certain electric boilers. They like to use the expressions “energy-saving”, “eternal”, “economical” and so on. Remember: all types of heaters are equally effective at converting electrical energy into heat with an efficiency of 98-99%.
The first place in the user rating is occupied by heating element heaters. The only weak point - the heating element itself - has long been protected with ceramics, and in addition it is easy to replace. Modern models of heat generators are wall-mounted mini-boiler rooms with a built-in expansion tank and circulation pump. There are simpler versions that include only heaters and an automation unit.
The cheapest and most reliable option is an electrode boiler with a control cabinet, shown in the photo. Its disadvantages:
Induction electric boilers for heating a private home are quite expensive, and there are questions about the reliability of the devices. There are known cases of phase burnout inside the coil, the power of the heat generator dropped by a third. Fixing the breakdown is very problematic.
An induction heater heats water with a metal core located in the vortex field of the coil
Grounding check
According to current regulatory state documents, the inspection must be carried out by the gas service represented by its representative. However, an objective conclusion requires an assessment from an electrical laboratory that measures the total resistance of the ground loop. It all depends on the location of the private house and its proximity to administrative centers. In some areas, gas service representatives themselves check all the characteristics of the ground loop. After the measurements are taken and if they comply with the standard, a “Protocol for checking the condition of grounding conductors and grounding devices” is drawn up. In addition, an employee of an electrical engineering laboratory is required to submit a document confirming the registration of the laboratory. Only in this case the conclusion has actual legal force.
The boiler grounding certificate is issued by the regional gas service department. It consists of several documents:
- technical report on the tests performed;
- list of technical documentation;
- Certificate of registration of the electrical laboratory:
- protocol for checking the presence of a circuit between the boiler and the circuit;
- ground loop inspection protocol;
- list of measuring instruments used;
- defective statement.
Operation of a gas boiler is possible only after receiving the certificate, since without it, even connecting the house to the main gas pipeline may be refused.
Installation of current protection
Selecting a location
First of all, you should determine the location where the grounding loop will be made, since the safe operation of the system depends on this. When the protection is triggered and electricity is discharged into the ground, neither people nor animals should be at the outlet site, as this can lead to death.
It is most convenient to place the outlet behind the house near the fence, at least 1 meter away from the edge of the foundation. To fence off the danger zone, it would also be useful to erect a small fence.
To hide the grounding in a private house with your own hands 220V and 380V, to improve the territory, on this site, for example, you can lay a sculptural composition of boulders. In this case, no one will be able to get too close to the danger zone, and the garden area will look beautiful.
Country house grounding diagram
Excavation
Do-it-yourself grounding in a private house 380V circuit consists of three metal conductors immersed in the ground at a distance of 2 m from one another.
Trench for current protection circuit
Using a shovel, a trench is dug in the shape of an equilateral triangle with side lengths equal to 2 m. Its depth should be 0.5-0.7 m. Exactly the same trench is dug to the porch of the house.
Triangular ground loop
Assembly of the structure
The assembly of the circuit structure can be called the main stage, at which do-it-yourself grounding in a private house 220V circuit involves driving electrodes into the ground to a depth of two meters. In this case, the tops should be left on the surface for tack welding.
When driving, the driven end should be slightly sharpened to facilitate driving into the ground.
Sharpening the end of the electrode angle
After all the pins are driven in, plates are welded to their tops to form a metal frame in the shape of a triangle.
Metal triangular frame
A separate plate must be placed in a trench dug towards the porch; it is also attached at one end to the near vertex of the triangle.
Output of the plate at the foundation of the house
So which circuit should you choose?
Let's first figure out under what conditions certain types of circuits are used.
Closed triangular outline:
- The 220/380V network is brought into the house through a power input panel.
- Continuous total power consumption is more than 3 kW.
- Availability of industrial-type electrical appliances with a provided grounding connection (lathe, circular saw, drilling machine, etc.).
Two groups of linear grounding conductors:
- The total power consumption is over 1 kW for 20 minutes.
- The electrical wire is routed underground through an external panel.
- The house has at least one of the communications (communications, gas, water, sewerage).
There are many other factors, so in this case it is best to consult a specialist and do the work yourself.
Installation work
The implementation of procedures for arranging grounding begins with preparing the territory. She suggests selecting an area free from outbuildings, and then building a model of a triangular, square or polygonal shape. Digging a trench is carried out according to a previously drawn up project. Rods are hammered into the corners of the recess. The distance from its bottom to the upper section of the electrodes should be in the range from 150 to 200 mm. From the corner closest to the building, a small ditch is created, which necessarily reaches the foundation.
A steel wire with a cross-sectional area of 48 square millimeters is laid along the bottom of the formed channel, with which the conductors are connected to each other. The master is also allowed to install a strip with a width of 40 mm and a thickness of 4 mm. The joints are connected using a welding machine or bolts. When introducing grounding into a home, a metal strip is welded to the cable. It is located on the site so as to rise above the blind area by 500 mm. A hole for the copper wire is drilled in the wall of the room where there is a gas boiler.
Its first end is fixed to the terminal of the grounding bus, and the second - to the metal base plate. The heating unit is then connected to the panel using automated protective devices and a voltage stabilizer. Before starting to dig a hole, the technician is advised to check the resistance to current propagation through the structure of the circuit. A similar operation is carried out using a light bulb with a carrier, which should be connected to the phase and circuit.
If the resistance values are reduced, you will have to install additional electrodes. The accuracy of installation work and the level of safety of self-made grounding of a gas boiler are checked by specialists. If the check for compliance with operating standards for electrical installations yields a positive result, the owner receives a certificate authorizing the use of the boiler.