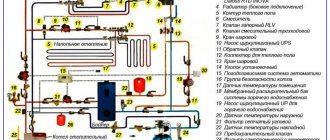
The heating system is an engineering structure built strictly according to a specific design principle. The main task of this system is to provide heating for buildings during the cold season. Ideally, the level of heat supplied should compensate for its losses in building structures. Also, the function of heating is to maintain a comfortable air level in all rooms located in the building. There are many options for wiring heating systems, which we suggest you read about in our material.
Operating principle of the heating system
There are many heating device schemes. Often, many customers make mistakes due to inexperience. And companies providing these services are trying to squeeze more money from such customers.
The basic rule of any heating system is that the network is closed. In a simple representation, the heating network diagram looks like a kind of ring of pipe connections in which water flows, constantly heated from the boiler. This boiler is in constant operation so that in any subsequent cycle of water flow through the pipes it does not cool down.
The heating system consists of:
- connecting pipes;
- fittings;
- boiler for heating;
- radiators or other heating devices;
- a pump to ensure the required speed of water flowing through the pipes;
- expansion tank.
Budgeting
When you are at the stage of calculating the heating circuit, proceed from the fact that 1 section is selected based on 1.2 square meters of room. Do not forget to take into account the margin; if two walls in your room are adjacent to the street, you need to add a margin of up to 30%. That is, for a room of 15 square meters adjacent to the street, which will have a warm floor, it is recommended to install a radiator with at least 12 sections.
To create excess intersection pressure in the circuit, it is necessary to operate with the diameter of the supply pipe. That is, from the boiler to the main collector there must be a pipe of at least 32 millimeters in diameter. Next, a pipe of the same diameter will go to each circuit, approximately 4-5 meters for each wing. This will create excess pressure in the circuit. Next, you need to narrow it, choosing a diameter of at least 25 mm for each radiator. When water rises to the radiator, it is necessary to narrow it up to 20 mm, inclusive.
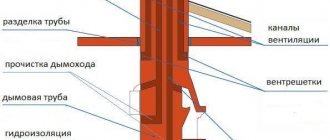
Using fittings when welding polypropylene pipes
More is not always good. It is not advisable to use pipes of larger diameter everywhere, since the permeability of water will be better, but its quantity will increase, which will lead to heating of a larger volume of liquid. This results in extra heating costs. The coolant is lifted to the floor above through a pipe of at least 32 mm.
An installation kit is included for one radiator. These are two taps, a plug, a Mayevsky tap, 2-3 hooks. Tees, transitions, couplings are considered individually, depending on the number of radiators in the house, their location, and the method of laying the pipe.
Types of installation of heating systems
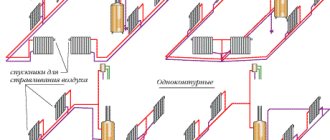
According to the method of conducting the coolant, the wiring of the heating system is divided into only two types:
- Single-pipe
- Two-pipe
Each system has fundamental differences and certain characteristics.
Single-pipe wiring
As a rule, it is used as a distribution of the heating system in a two-story private sector house, where an outdated central heating system or a gravity autonomous network is usually used. The main difference of this scheme is its simplified installation, due to which the labor costs and cost of such work are significantly less.
Radiators with such a system must be connected in a certain sequence. It is not possible to remove the coolant that has failed. This heating scheme represents a system of vertical risers installed along the floors of the house. Often this method cannot provide absolutely comfortable temperature conditions.
The main disadvantages of single-pipe wiring:
- The tendency for thermal energy to decrease during each individual cycle of water flow. That is, reducing the heating level of each subsequent heating device.
- Lack of ability to adjust the temperature level in any particular room. An increase or decrease in heating intensity will be reflected throughout the building.
- Maintaining the optimal pressure level is possible only by connecting additional pumping equipment.
Of course, there are also technical methods that partially solve the problems described above. For example, equipment such as radiator regulators, air vents, balancing valves and thermostatic valves can be added to the system to improve performance. But it is important to understand that these systems are already outdated.
Scheme "Leningradka"
Usually, due to the simplicity of design, private residential buildings install a system invented back in the distant Soviet era. The so-called “Leningradka” heating distribution system is successfully used in current realities. The design technology and operating principle of this circuit are very simple. In the classic version, “Leningradka” is a network of heating devices (radiators, panels and converters) connected by a pipeline system. Radiators should be located around the perimeter of the walls of the room.
However, this heating system also has a number of disadvantages:
- Inability to maintain the same level of heat in all rooms of the building.
- Due to horizontal wiring, it is impossible to install a floor heating system.
- To maintain optimal pressure in the system, it is necessary to additionally install a circulation pump.
Two-pipe wiring
The main difference is that different pipes are used to supply hot coolant and remove cooled coolant. Thus, heat exchange is not carried out sequentially, as in a single-pipe circuit, but in parallel.
Advantages of a two-pipe system:
- The level of heat passing through each radiator does not change due to the principle of parallel operation.
- The ability to regulate the temperature of each individual room by installing a special thermostat on the radiators.
- Failure of a single battery will not affect the functionality of the others.
Disadvantages of two-pipe wiring:
- To design this heating device circuit, many pipes and connecting elements are required.
- High complexity of installation.
- Labor intensive and high cost.
Radial heat supply circuit
The principle of the radial (collector) wiring diagram of the heating system is that heating devices are connected to a separate pair of pipes to supply thermal energy using a special collector. Due to this technology, hot water for heating is distributed evenly throughout the room. The heat level is regulated by changing the temperature of the water and the speed of its flow through the pipes.
It is worth noting that the beam distribution is quite new and is an improved model of the two-pipe system. To distribute water in the coolant, a similar manifold is used as in a floor heating device.
The advantages of the beam scheme include:
- low probability of leaks due to the absence of joints in the structure;
- the ability to turn off each individual heating device without disabling the entire system.
The only significant disadvantage of beam wiring is its high (but justified) cost. Since this system uses a manifold and additional pipes, design costs also increase.
Bottom and top wiring
The upper wiring diagram of the heating system is a system where the supply pipeline is installed under the ceiling, and the discharge pipeline runs in the floor of the room. This design allows for natural circulation of water flow in the carrier. Due to large differences in the pipes, the water flow has time to gain high speed. However, the overhead wiring has not been widely used due to its unattractiveness compared to the interior of the room.
The scheme with lower heating wiring is used everywhere. The essence of the design is that the pipes are mounted from below. The supply pipeline is located just above the return pipeline. The big advantage of this scheme is the possibility of installation under the floor or even in the basement of a building. The disadvantage is the complexity of the design. To ensure natural circulation of water flow, the heating boiler must be at least 50 cm higher than the radiators.
Horizontal and vertical wiring
Horizontal distribution of heating systems is increasingly used in modern multi-storey structures. After all, it provides excellent performance and other technical characteristics. This scheme involves the use of two main risers (supply and return), located in a separate room of the building.
The main advantages of horizontal wiring include:
- if a single element malfunctions, you only need to turn off the required node, and not the entire system;
- the ability to control pressure fluctuations due to compensators;
- improved control over heat consumption;
- good aesthetic appearance that will not spoil the overall interior of the room;
- The average service life of the system can reach more than 50 years.
The only disadvantage is the need to manually configure all heating communications to ensure full operation of the system. This is done manually because the structure as a whole is quite fragile.
The vertical distribution system of the heating system is used to a lesser extent in modern multi-storey buildings. It was installed much more often in Soviet designs from the 1950s onwards. Its widespread use is due to several reasons:
- low cost;
- ease of design;
- saving of materials.
The disadvantages of vertical wiring are more significant:
- inability to shut off individual heating devices;
- inability to control the heating level of heating devices;
- inability to install heat metering devices.
Advantages
Using modern installation systems, it is possible to significantly simplify the process of installing and balancing the system. In addition, using taps when connecting radiators, you can disconnect and remove each individual radiator of the system, without resorting to completely shutting down the systems.
Only one pipe is laid, it looks more aesthetically pleasing than if there were two, and it is also much easier to hide.
Wiring with polypropylene
In the age of new technologies, new materials are increasingly being used in construction, displacing traditional ones. Just a few decades ago, it was difficult to imagine that drainpipes could be made of anything other than metal. Today, water pipes are made exclusively from polymer.
The advantages of polypropylene pipes are:
- low price;
- simple installation diagram;
- high service life;
- light weight of materials.
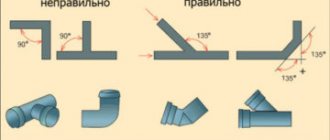
The disadvantage, but not significant, is the lack of bends on the pipes. To do this, you have to use special connecting elements: tees, angles, couplings, etc. About the disadvantages of polypropylene, watch the video below:
To fasten polypropylene pipes with another material (metal), so-called fittings are used. They themselves are made of polypropylene, but have metal threads inside.
Boiler power calculation
Regardless of the type of fuel used (solid or liquid, gas or electricity), the principle of connecting all heating systems is the same. The only difference is at the boiler installation stage. In this case, its power is calculated using a single formula:
where W is the specific power required for heating 10 square meters. m of room; S – total area of the house.
For Russian regions, the following power values are taken into account: • for houses located in central Russia up to 1.5 kW; • for Siberia and the North: for every 10 sq. m up to 2 kW; • for southern regions: up to 0.9 kW.
Since 10 sq.m. is sufficient for heating. m of a residential building located in central Russia requires up to 1.5 kW of power, then, for example, for heating 100 sq. m you will need a 15 kW boiler:
(100 x 1.5)/10 = 15 kW
This figure is increased by 15-20% (power reserve for possible heat loss, which is inevitably lost even with ideal insulation of the building). Thus, to heat a house of 100 sq. m will need (15 + 2.3) = 17.3 kW.
Recommended boiler power
Which heating system to choose?
A single-pipe scheme should not even be considered when living in a modern metropolis, where there are practically no buildings left with energy problems. Saving money should also not be a reason for choosing outdated technologies for designing heating systems. This option is suitable only in structures far from the city, for example, in a country house (not modern).
The best wiring in the house is a two-pipe radial one. The high cost of installing such a system is more than justified. Reliability and maintaining an optimal level of heat in the room are paramount.
It is also worth noting that before installing floor heating, it is necessary to carry out a calculation and balance the level of heat inflow and heat loss due to the specifics of the building. This way, you can find out whether standard heating is enough or whether additional radiators need to be installed.
Equipment classification
There are two types of system : open and closed. They differ in the design of expansion tanks. In the first case, an open container is installed at the highest point of the heating into which the coolant is poured.
In the second case, a membrane tank is used, which operates in high-pressure systems. Water or antifreeze is used as a coolant for heating. The use of automotive antifreeze fluids is not allowed, since they have a different chemical composition.
Closed heating is considered safer, so modern double-circuit boilers are designed to work in precisely such schemes. The disadvantages of an open scheme are:
- slow coolant circulation;
- corrosion of the pipeline, as oxygen freely enters the system;
- coolant evaporation;
- low efficiency.
Closed heating has a number of disadvantages.
The open system is mainly used for heating small and low-rise rooms.
Zoning
Thanks to the thoughtful distribution of thermal energy, you can not only create a comfortable atmosphere in your home, but also significantly save money.
List of recommended temperatures for different rooms:
- Average level of comfortable temperature: + 20-24 degrees.
- It is advisable to increase the temperature level in the bedroom slightly to + 22-25 degrees.
- The bathroom, toilet, living room and other rooms where apartment residents visit most often should be heated within the range of + 21 to + 24 degrees.
- In the dining room, kitchen and office, the temperature is reduced to +18-22 degrees.
- The hallway, garage and passage rooms should be heated within + 12 degrees.