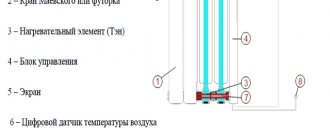
When installing or restoring a heating system, radiators most often need to be replaced. Some have already worn out so much that they simply cannot continue working, others are simply tired. In any case, the question arises: “Which heating radiators are better?” After all, you want them to be beautiful and effective. The appearance of heating devices is, of course, important, but the choice of heating radiators must begin with selection according to the technical characteristics of your heating system. After all, first of all, this is a part of engineering systems, and the operating pressure, maximum temperature of the coolant or its composition are much more important than shape and color. And then, having decided on the type of suitable batteries, you can start selecting a model from the point of view of aesthetics, but again you will have to keep in mind one more technical parameter - the thermal power of a radiator section or an entire battery. So, choosing heating radiators is not an easy task.
Choosing a heating radiator is not an easy task
The choice of heating radiators today is huge. There are six large groups, differing in structure and/or material:
- cast iron;
- steel (tubular and panel)
- aluminum (cast and extruded);
- bimetallic (full and partial bimetal);
- convectors (floor, wall, in-floor);
- baseboard heating.
Radiators are different both in appearance and in characteristics, but an ideal and universal heating device has not yet been invented. Each has advantages and disadvantages, and it is possible to say exactly which heating radiators are better only in relation to each specific case. So that you can make an informed choice, you need to know about the pros and cons of each group.
Cast iron batteries
The oldest heating devices. They are distinguished by high reliability, long service life, can easily withstand overheating of the coolant (up to +135°C), and react normally to water hammer. All due to the fact that they have thick walls. But the greater thickness of the metal is not only advantages, there are also disadvantages. The first is a large mass. Not all modern building materials can support the weight of cast iron. Even though today they are far from being as heavy as in Soviet times, they are still significantly more massive than all the others. Large mass also means difficulties in transportation and installation. Firstly, powerful hooks are required, and secondly, it is advisable to install them together - the mass of the radiator for 6-7 sections is 60-80 kg. But that's not all. The large mass of the metal means high heat capacity and significant inertia. On the one hand, this is a minus - until the batteries warm up, the room will be cold, but on the other hand, it is a plus, because they will take a long time to cool down. There is another disadvantage to high inertia - cast iron batteries are ineffective in systems with thermostats. All this together leads to the fact that cast iron heating radiators are not installed very often today.
This is only a small part of modern cast iron radiators
But they have their own area of application - high-rise buildings. If the number of floors is higher than 16, such systems create high pressure, which can only withstand cast iron and some types of bimetallic radiators (full bimetal). Their properties are also optimal in heating systems of private houses and cottages with conventional solid fuel boilers without automation. These boilers have a cyclic operating principle, either heating the coolant to boiling temperature or even higher, then cooling down. Cast iron reacts normally to high temperatures and, due to its inertia, smoothes out temperature changes.
Until recently, cast iron heating radiators had an unattractive appearance - the well-known and long-tired “accordion”. Today there are models that look like aluminum or bimetallic - with smooth front edges, painted with powder enamel (most often white). There are many designer models, mostly on legs, decorated with cast ornaments. This option is generally only available in cast iron; all others generally have a more strict, ascetic design.
Top 10 best heating radiators according to KP
STI Nova 500×10
STI Nova 500. Photo: STI
The cast iron radiator is 100% protected from corrosion. The heat transfer of a well-thought-out design is 34% greater than that of steel radiators. The white heat-resistant enamel used to coat the radiator makes it attractive and protects it from damage from household chemicals. Does not corrode from hot water in the heating system, regardless of its chemical composition. Looks stylish in a modern interior.
Technical specifications
| Installation | wall |
| Connection | lateral |
| Center distance | 500 mm |
| Working temperature | up to 150 °C |
| Operating pressure | up to 12 bar |
Advantages and disadvantages
Enhanced heat dissipation thanks to thoughtful design
Heavy weight, installation on a plasterboard wall is impossible
show more
Royal Thermo Vittoria 500
Royal Thermo Vittoria 500. Photo: Royal Thermo
A bimetallic radiator with an all-steel manifold allows the use of not only water, but also various antifreezes as a coolant. The main feature of this radiator is the specially designed shape of intersectional air pockets and fins; it creates convection currents that promote rapid and uniform distribution of heat throughout the room. Seven-layer painting with ultraviolet drying. There are several dozen colors in the nomenclature.
Technical specifications
| Installation | wall |
| Connection | lateral |
| Center distance | 500 mm |
| Working temperature | up to 110 °C |
| Operating pressure | up to 30 bar |
| Heat dissipation | 1365 W |
Advantages and disadvantages
High heat transfer, formation of convective flows
Some users report poor quality paint
show more
BOHEMIA R 800
BOHEMIA R 800. Photo: BOHEMIA
Not everyone knows that heating radiators are the invention of the Russian entrepreneur Franz Karlovich San Galli. In the middle of the 19th century, he founded a workshop on Ligovsky Prospekt where they made cast iron pipes for water supply and sewerage.
The style of the first radiators is recreated in cast iron models of the RETROstyle series from the manufacturer BOHEMIA. Such devices are suitable for the interiors of a private home, restaurant or hotel.
Technical specifications
| Execution | floor |
| Connection | lateral |
| Center distance | 0.8 m |
| Operating pressure | up to 5 bar |
Advantages and disadvantages
Aesthetic appeal of the Art Nouveau style
Heavy weight requires special preparation of the installation site
show more
Bathroom heating
How to effectively heat a bathroom in apartments and private houses
Axis Classic 22,500
Axis Classic 22 500. Photo: Axis
The radiator consists of two steel panels with additional fins. Serves for heating residential and work premises for various purposes in closed systems. It is possible to connect both on the right and on the left. The low thermal inertia is explained by the high thermal conductivity of steel and the small volume of coolant. The radiator is equipped with a lightweight removable grille and side covers. Painting is done by powder coating in an electrostatic field. It is possible to use cast iron units together in one heating system.
Technical specifications
| Number of panels | 2 |
| Steel sheet thickness | 1.2 mm |
| Connection | lateral |
| Center distance | 449 mm |
| Working temperature | up to 120 °C |
| Operating pressure | up to 9 bar |
Advantages and disadvantages
Mounting kit available, easy to attach to any wall and looks stylish
The center distance differs by 6 mm from the same DeLonghi model, to replace it you have to change the pipes
show more
Royal Thermo Indigo Super+ 500
Royal Thermo Indigo Super+ 500. Photo: Royal Thermo
The bimetallic radiator has a complex molded body shape. Thanks to this, natural reverse convection is created, effectively cutting off the cold coming from a wall or window. A plug with a nano-membrane and a vertical manifold reliably protects the radiator from leaks. As a result, the unit is suitable for operation in systems with sudden pressure changes, so-called water hammer. The radiator is protected from corrosion by paints and varnishes applied using a special multi-stage technology.
Technical specifications
| Installation | wall |
| Connection | lateral |
| Center distance | 500 mm |
| Working temperature | up to 110 °C |
| Operating pressure | up to 30 bar |
Advantages and disadvantages
Excellent appearance, talented design, increased heat dissipation due to the shape of the radiator
Inaccuracies in the data sheet, you must check all parameters when purchasing
show more
Shapes of heated towel rails
Which shape is best for installation in the bathroom?
Global ISEO 500
Global ISEO 500. Photo: Global
Aluminum radiator with high heat transfer, thanks to which it warms up the room several times faster than cast iron counterparts. Quick response to changes in ambient temperature ensures comfort and coziness.
The ergonomic design of the unit helps maintain temperature even when installed in a window sill. The cross-section of the intercollector pipes has been increased, so that they do not become clogged. The internal surface of the radiator is protected from corrosion by a fluorine-zirconium coating.
Technical specifications
| Installation | wall |
| Connection | lateral |
| Center distance | 500 mm |
| Working temperature | up to 110 °C |
| Operating pressure | up to 16 bar |
Advantages and disadvantages
High heat transfer, providing quick heating of the room
The need to use a chemically neutral coolant
show more
Rifar SUPREMO 500
Rifar SUPREMO 500. Photo: Rifar
The full bimetallic radiator is made of high-alloy steel pipes coated with aluminum alloy. The coolant can be water, antifreeze or oil.
The design has no sharp edges or edges, which eliminates the possibility of injuries and cuts. This feature is relevant for families with small children. A body without closed and hard-to-reach cavities prevents snouts from collecting and makes cleaning easier. The paint has high resistance to mechanical damage and ultraviolet radiation.
Technical specifications
| Installation | wall |
| Connection | lateral |
| Center distance | 500 mm |
| Working temperature | up to 135 °C |
| Operating pressure | up to 30 bar |
Advantages and disadvantages
High heat transfer from any coolant, resistance to water hammer, preventing accidents
Excellent sound transmission from other rooms. Requires installation with soundproofing inserts on heating pipes
show more
Global STYLE EXTRA 500
Global STYLE EXTRA 500. Photo: Global
A bimetallic radiator with a rounded top can work in any heating system of a private house or city apartment. Able to withstand sudden pressure changes in the line thanks to a maximum pressure of 35 bar. External surfaces are protected from corrosion by a durable enamel coating. The steel frame completely isolates the coolant from the aluminum body. The special fin design increases heat transfer.
Technical specifications
| Installation | wall |
| Connection | lateral right |
| Center distance | 500 mm |
| Working temperature | up to 110 °C |
| Operating pressure | up to 35 bar |
Advantages and disadvantages
Resistant to water hammer, reducing the likelihood of leaks
Insufficient heat transfer at water temperatures below 100 degrees
show more
Rifar Base 500
Rifar Base 500. Photo: Rifar
One of the most popular heating radiators in the Russian Federation. Structurally, it is a steel pipe coated with aluminum on top using casting; thin fins increase heat transfer. The special design of the sections requires only one gasket at the joints. Models with the number of sections from 4 to 14 are commercially produced. The rear part of the housing is completely closed, so the unit does not disturb the interior when installed near French windows. Models with center distances of 300 and 200 mm allow you to decorate rooms with different radiator height restrictions in the same style.
Technical specifications
| Installation | wall |
| Connection | lateral |
| Center distance | 200 mm |
| Working temperature | up to 135 °C |
| Operating pressure | up to 20 bar |
| Weight | 9.6 kg |
Advantages and disadvantages
Elegant design that looks great in modern interiors
Specially prepared water is required as a coolant
show more
Aluminum
Aluminum heating radiators are made not from pure aluminum, but from an alloy based on it. This metal was not chosen by chance, as it has one of the highest heat transfer coefficients - 4-4.5 times better than cast iron and 5 times better than steel.
Table with thermal conductivity coefficients of different metals
That is why aluminum radiators are distinguished by their high power (180-190 W per section), no less high heating rate and low inertia. They work very effectively in tandem with thermostats, allowing you to maintain a stable temperature with an accuracy of one degree. The advantages of aluminum radiators include their low weight (one section weighs 1.5-2 kilograms), which makes delivery and installation easier. Another positive point is that the shape is designed so that it has a large cross-section of channels for the coolant (slightly smaller than that of cast iron “accordions”). This is good, since there is a low probability that these channels will become clogged and the radiator will stop heating.
Now about the disadvantages of aluminum radiators. They are related to the properties of aluminum. As you know, it is a chemically active metal. It actively interacts with most of the chemical table, and reacts especially violently with copper. And in modern heating systems, copper parts are often found. Such a proximity threatens the rapid release of copper parts of the system and system, as well as increased gas formation. They have learned to deal with gases - they install automatic gas vents (valves) in systems, and they save copper by not placing it close to aluminum appliances. The process, of course, is still going on, but not with such intensity.
Aluminum radiators look modern
The chemical activity of aluminum also manifests itself in demands on the quality of the coolant. Not in the sense of its contamination, but in the sense of its acidity. Aluminum radiators work normally in systems with coolant acidity no higher than 7 (Ph 7).
The softness of aluminum is also not very good for the operation of the heating system. The alloy from which heating radiators are made contains additives that increase its hardness, but still, they do not work in high-pressure networks. Typical operating pressure is 8-16 atm depending on the type and manufacturer.
Based on all of the above, there appears to be an area in which aluminum radiators will be the best. These are individual heating systems with boilers controlled by automation. They also do well in apartments, but only in small buildings (up to 10 floors), in which coolant with Ph 7-8 circulates.
Features of choosing heating devices
Now people no longer need to hide or decorate radiators, because modern appliances can become a worthy decoration of any interior. Radiators that are sold today may differ in color, size, material of manufacture and general design style, so it will not be difficult to choose the most suitable option.
Heating radiators
Attention! Despite the fact that we are accustomed to light-colored batteries, the heat transfer of black devices is approximately ¼ higher solely due to color. Although when choosing a color, it is better to focus on the design of the home and personal preferences.
Heating radiators
Regarding the shape, it must be streamlined. For safety reasons, it is advisable to avoid sharp corners altogether, especially if children live in the house. Before purchasing, familiarize yourself with the strengths and weaknesses of each of the existing types of radiators to determine which one is best suited for a particular room. The first thing you should pay attention to is the operating pressure of the devices.
Which heating radiators to choose?
Depending on the material, radiators are divided into:
- aluminum;
- bimetallic (from alloys of two metals);
- cast iron;
- steel.
Radiator in the interior
The above-mentioned pressure, heat transfer coefficient, heat capacity, resistance to mechanical and chemical damage, as well as service life depend on the material.
Radiators in the interior
Also pay attention to the method of connection to the heating main. The connection can be side, bottom and universal. It is typical that modern radiators provide all these connection methods.
Radiator connection options
Attention! The environmental friendliness of the material used in the manufacture of heating devices is also very important. There should be no formaldehyde in the internal elements, and high-quality polymer coating on the surface is also welcome.
Now in more detail about each material.
Bimetallic radiators
To correct the shortcomings of aluminum radiators, bimetallic radiators were invented. Stainless steel tubes are sealed inside the aluminum jacket. Stainless steel is known to be chemically neutral and very durable. This solves two problems at once. But the cost of bimetallic radiators becomes significantly higher - the manufacturing technology is more complex, and the thermal power becomes slightly lower. On average, the heat transfer of one section of standard size bimetallic radiators is 170-180 W. Another plus is the higher operating pressure with which these heating devices can operate. On average it is 20-30 Atm, which is more than enough even for high-rise buildings.
What is the difference between bimetallic radiators and aluminum ones?
At the same time, another problem is added - the cross-section of the coolant channels in bimetallic radiators is much smaller than in aluminum ones. Therefore, it is advisable to install filters in front of the radiator. As you can see, there are not many disadvantages, but there are some nuances. There are simply two types of bimetallic radiators: full and partial bimetal. In a full bimetal, all collectors (channels through which the coolant moves) are made of stainless steel. If you are deciding which bimetallic heating radiators are better, then this is a full bimetal. For partially bimetallic radiators, only the vertical collectors are made of stainless steel, and the horizontal ones are made of aluminum. That is, such products have a slightly lower chemical activity, but still at a fairly high level and the operating pressure is much lower.
Now for heating systems for which bimetallic radiators are the best. These are high-rise buildings with any type of coolant (including very acidic or alkaline). In individual heating systems, their properties will not be in demand, so you should not overpay.
Characteristics of aluminum radiators
Aluminum heating radiator cross-section
Heating devices made of aluminum are considered one of the most popular types of radiators. Aluminum is a light and ductile metal, therefore, batteries made from it weigh a little and have increased heat transfer.
The devices consist of sections, each of which is a set of interconnected plates. Thanks to this, heat saving here is also at a fairly high level.
Cast aluminum radiator section
Radiator made by extrusion method
The advantages of such units are as follows:
- fast heating;
- high heat capacity;
- light weight;
- affordable cost (especially when compared with bimetallic units);
- wide model range.
Technical characteristics of aluminum heating radiators
At the same time, after turning off the heating, such radiators cool down quite quickly. Other disadvantages :
- instability to chemical influences (the problem can be solved by polymer coating on the inner surface);
- low strength;
- poor quality of the threaded connection in the top valve for releasing air from the system.
In view of this, before purchasing it is necessary to inquire about the operating pressure of the heating system. The maximum pressure of a particular product must be looked at in the data sheet, since it is different for different models.
But still, according to its characteristics, aluminum is excellent for the manufacture of radiators, and its fusibility has made it possible to significantly expand the model range. Today you can choose exactly the battery that fits perfectly into the interior of your home.
Aluminum radiator assembly
Table 1. Comparison of aluminum batteries from well-known brands
| Manufacturer | Model | Weight, kg | power, kWt | Volume, l | Pressure, bar. | Dimensions, cm | Distance between axles, cm |
| 1. Rifar, Russian Federation | Alum 500 | 1,45 | 0,183 | 0,27 | 20 | 9x8x56.5 | 50 |
| 2. Fondital, Italy | Calidor Super-500 | 1,32 | 0,193 | 0,3 | 16 | 9.7x8x55.7 | 50 |
| 2. Rovall, (Italy) | Alux-500 | 1,31 | 0,179 | 0,23 | 20 | 10x8x54.5 | 50 |
| 3. Radiatori 20000 SpA | 500R | 1,6 | 0,199 | 0,58 | 16 | 9.5x8x57.7 | 50 |
| 4. Faral | Green HP-350 | 1,12 | 0,136 | 0,26 | 16 | 8x8x43 | 35 |
| 5. Faral | TrioHP-500 | 1,58 | 0,212 | 0,5 | 16 | 9.5x8x58 | 50 |
Aluminum radiators from STOUT Bravo are ideal for installation in apartments and houses with individual heating. These heating devices are manufactured at facilities in Italy. Each stage of production is controlled by European specialists. Each section is manufactured by injection molding and is a monolith of two collectors and fins connecting the sections. Available center distance is 350 or 500 mm. Manufacturer's warranty – 10 years.
Aluminum radiators from STOUT Bravo
Follow the link for details: www.stout.ru.
Aluminum radiators from STOUT are covered by a ten-year manufacturer's warranty
Prices for popular models of aluminum heating radiators
Aluminum heating radiators
Steel radiators - panel and tubular
There are two different types of steel radiators, with different characteristics and very different appearances. These are tubular and panel. Some are made from steel pipes, others from steel sheets. Both have a relatively low price, which is what attracts them. But steel in heating systems does not “live” very long, so these are also the most short-lived heating devices. Of course, there are exceptions - some manufacturers coat pipes or sheets with a protective layer, so the warranty period is a decade or even more. But the price of such steel radiators is also far from small.
These are tubular radiators. They can be either high and narrow or low and wide.
Other characteristics include low thermal inertia and demands on the coolant. Moreover, both in terms of acidity and the presence of foreign particles. Panel models are especially demanding - they have thin channels formed into them through which the coolant moves. They are even thinner than bimetallic ones, so filters at the input are strictly required. If we talk about the acidity of the coolant, the highest indicator at which steel radiators operate is Ph8. Working pressure is about 10-16 Atm.
With power, the spread is very large. The design of both panel and tubular radiators is such that they can be of different sizes. Panel radiators are produced commercially with heights from 30 cm to 90 cm, lengths from 40 cm to 3 m. There are special models that are elongated in height. Their maximum height is 2.7 meters (upon special order they can make it higher, but there will be problems with transportation).
Panel radiators can be of different configurations and power
The variation in the sizes of tubular radiators is even greater. They can be from 19 cm to 3 m in height, from 10 cm (two sections) to 3 meters in width, and from 6 cm to 21 cm in depth. The power of these radiators depends not only on the number of sections, but also on the number of columns (pipes in one row). There can be from two to six columns. Two or three columnar ones can be hung on the wall, wider ones are often placed on the floor. Unlike all others, the sections of tubular radiators are one-piece, that is, they cannot be expanded or reduced. They are welded together. On the one hand, there are fewer leaks, but on the other, less mobility. But this is compensated by their high ductility - tubular steel radiators can be curved - at least install them around columns or wrap large containers with plants (there is a minimum bending radius). By the way, there are models in the form of benches or tables.
Selection nuances
The operating pressure in radiators indicates the amount of permanent impact for which they are designed. In heating networks, it occurs due to the circulation of heated coolant and depends on the following features of the heating circuit:
- length of pipelines;
- number of batteries.
In addition, the magnitude of the resulting load is influenced by the method of organizing space heating, which can be autonomous or centralized. Each option has its own characteristics and allows you to install a certain type of radiator.
An autonomous heating network is used to create comfortable living conditions in low-rise private houses. It is in demand in the absence of a centralized system and operates at an operating pressure that varies between 3-5 atmospheres. If the heating network is laid in a one-story house and is closed, then this figure is 1.5-2.5 atm.
What is the operating pressure in the centralized system of an apartment building? This information can be obtained by contacting the management company or housing office. Usually the indicator varies from 8 to 16 or more atmospheres and depends on the following factors:
- height of the house;
- power and condition of the equipment with which the coolant is supplied;
- distance of the building from the heating point;
- diameter of the network pipeline in the apartment;
- location of the room and distance from the common riser;
- degree of wear of communication elements.
When purchasing a radiator, it is necessary to select a specific model so that its operating pressure exceeds the maximum value of the same indicator of the heating network by at least 2 atmospheres.
When selecting batteries, the test pressure must also be taken into account. It reflects the maximum impact that the product can withstand over a short period. This parameter is determined during testing in factory conditions at enterprises involved in the production of radiators.
It shows the resistance of heating devices to hydraulic shocks, which sometimes occur in centralized heating systems.
Convectors
Recently, floor-to-ceiling glazing has become increasingly popular. It’s really beautiful, but what about the heating….question. You can put low radiators on legs, but then all the chic will be lost. That's when in-floor convectors are used. A niche is made in the floor under them and the device itself is installed in the floor, covering it with a grate. In order to increase heat transfer (necessary during cold periods), fans are built inside. The solution is aesthetic, but such systems cost a lot. There is also a nuance - fans, even the quietest ones, are noisy. This noise does not bother some people, but it bothers others very much. In any case, there are more and less noisy models.
In-floor convector - an outlet for heating French windows and glass doors from floor to ceiling
So, if you need to heat a floor-to-ceiling French window, the best option is an in-floor convector.
How to decide on the type of radiator
Now it’s probably easier for you to decide which radiator to choose for your apartment - after all, out of the four options considered, there are only two left. As it turned out, neither steel nor aluminum radiators will withstand the test of either aggressive domestic coolant or pressure drops. So, what remains are bimetallic and cast iron appliances. What exactly to buy, look at your budget, as well as the characteristics of specific models. However, here you can give a couple of tips.
- In old houses (for example, “Khrushchev” buildings) it is quite possible to install cast iron products. If you live in a high-rise building, where the pressure of the heating system is higher, then it is still better to take bimetallic radiators.
- If the predecessors of your future new batteries are made of cast iron, then you can choose either of two options. Both bimetal and cast iron are suitable. If you are going to replace batteries made of another metal, then change them only to bimetallic ones.
Baseboard heating
The shape of baseboard heating resembles old-style plate radiators - these are two pipes with a large number of thin plates. The difference is that these thin pipes, usually copper, have such a small height and width that they are hidden behind a high plinth of a special shape (open at the top). Due to the high heat transfer coefficient of copper, the power of these small radiators is high, and it is gained thanks to the length - even along the entire perimeter of the room.
In addition to invisibility, baseboard heating has another advantage - most of the heat is transferred not by convection, but in the infrared range - from heated walls. A flow of warm air rises along the walls, warming them up. When walls heat up, they begin to emit heat, which our body perceives as more comfortable. Disadvantages of this system
Baseboard heating is almost invisible
The disadvantages of baseboard heating are its demands on the coolant and thermal conditions (it cannot be overheated), low operating pressure (up to 10 atm). All this suggests that such systems can only work in individual heating, and with boilers controlled by automation.
What parameters should you use to choose radiators for an apartment?
Now, knowing the weak points of central heating, you can already imagine what requirements good batteries must meet. Let's list them.
1. For radiators, the pressure declared by the manufacturer must exceed the pressure (both the working pressure and one and a half times the test pressure) in the heating system. Let's look at the numbers as an example. In five-story buildings with an old layout, this parameter is no more than 5 - 8 atmospheres. Modern multi-storey buildings are heated under pressure of up to 12 - 15 atmospheres.
2. Separately, we note the ability to resist water hammer. Because when living in an apartment, it is difficult to protect yourself from pressure surges in the heating; it is better to prevent trouble in advance. By the way, if you often hear humming and clicking noises from your batteries, contact your utility service. The pressure seems to be playing tricks in the system.
3. The quality of water in the domestic heating system is unimportant, so the batteries must withstand its “chemical attack” with honor without collapsing. It is necessary to use radiators with a special coating on the inside or chemically neutral material for the walls. And their thickness must be such that particles of sand and small pebbles do not rub it, acting like emery.
4. When deciding which radiators are best for an apartment, let’s not forget about their main function - to heat. That is, it is preferable to choose devices that have greater heat transfer.
5. Let’s not ignore the design of radiators - few people are satisfied with the ugly, poorly shaped cast-iron monsters that stood everywhere in Soviet times. I would like the radiators to harmoniously complement the decoration of the rooms - today this is quite possible.
6. The last parameter is the duration of service. No comments are needed here. The less often you have to bother with installing these bulky and rather expensive devices, the more profitable it is for the owners.
Which heating radiators are best for apartments and houses?
Now let’s systematize all the information a little from a different point of view - which batteries are better to choose for an apartment, and which ones for a private house or cottage. First, let's talk about what can be put in apartments. To choose everything correctly, you first need to visit a housing maintenance office or talk to plumbers. You need to find out what the pressure is in your heating system and what the acidity of the coolant is and its operating temperature (at least according to the documents). It would be nice to know what jumps in temperature and pressure there are. Armed with these numbers, you will need to choose a specific model from the types of radiators that are suitable for your situation.
Now about which heating radiators are best for an apartment. Here are your options:
- If you live in a high-rise (more than 12 floors), bimetallic radiators are most likely suitable; if the pressure is not very high, cast iron radiators can work. When choosing, look mainly at the operating pressure, acidity, and the temperature they will withstand (however, only full bimetal will do).
- If the operating pressure in your system is not higher than 14 Atm, and Ph (acidity) is not higher than 7-8 and not lower than 5, then steel and aluminum radiators can be added to cast iron and bimetal. Only for them, when selecting a manufacturer and model, you need to monitor all three parameters - temperature, acidity, pressure.
- If the system has a high Ph - from 8.5 and above, only bimetallic radiators (full bimetal) are suitable. They will also be an output at high operating pressure (from 20 Atm and above).
The best heating radiators for apartments are selected based on operating pressure and coolant acidity
Once again, we draw your attention to the fact that when choosing a specific model, you must definitely look at the technical parameters. Only in this case will the radiators work for a long time without repair or replacement.
Now about which radiators are best for a private house and cottage. These systems have a small volume and are distinguished by the fact that in them you control the condition of the coolant yourself, you can regulate the acidity and clean the filters. So selection by acidity in this situation is irrelevant. Something to consider is the type of boiler. If the system has a solid fuel boiler and does not have a heat accumulator to smooth out temperature fluctuations, cast iron batteries would be the best choice. They will withstand overheating and, with their thermal inertia, smooth out temperature fluctuations.
In all other cases, the optimal choice is aluminum radiators. They have low inertia and quickly respond to temperature changes. They heat up in literally minutes, and a noticeable flow of heat comes from them. True, they cool down just as quickly, so in the event of an emergency shutdown, the house will quickly cool down.
Heating radiators, by the way, can be very original
Steel radiators would also be good. This is an economical option, but even under normal operating conditions they do not last long - a short service life. For aesthetes, an option with baseboard or convector (built into the floor) heating is suitable. Both systems work perfectly with any automated boiler.
How to choose a heating radiator
We talked about the best heating radiators in 2022, and now we give the floor to an expert who will share tips on how to choose a device. Roman Sidlauskas, development director of the Russian representative office of the Italian radiator manufacturer Global Radiatori, tells the story .
This is interesting
Choosing the best electric convectors
Design and arrangement of flat radiators
Panel radiators are made of steel plates with a flat or perforated profile. These elements are made from sheet metal by pressing with a certain step, so that after welding the mirror elements, vertical and horizontal channels for the coolant are formed inside. Next comes the automatic painting and packaging process. Their biggest advantage is fast heating and high inertness.
To improve air circulation, “U” or trapezoidal sheets up to 0.5 mm thick can be welded to steel panels. The air between them will rise when heated, and its place will be replaced by a cold flow. However, this will transfer more dust masses, and the air in the room will be drier.
Steel radiator type 11, implies one panel with coolant and one row of convection fins at the rear.
Flat steel heaters can be connected to the heating system in four ways:
- Lateral - “supply” and “return” are located on one of the sides of the device.
- Diagonal - “supply” and “return” are located on different sides and at different levels of the heater.
- Bottom - “supply” and “return” are located next to each other on the bottom panel.
- Saddle (cross) - “feed” and “return” are located on different sides of the device at the bottom or on its side and bottom panels.
Methods of wiring and installation of radiators
battery installation
It does not matter what type of battery is purchased, but the general rules for installing them remain standard. It is better to entrust the correct installation of heating radiators to an experienced plumber. It is very difficult for a homeowner who is far from technical problems to determine the angle of the pipes or find the right place to mount the radiator.
Only a professional will tell you which type of connection to prefer: one-sided, bottom or diagonal. It is advisable to resolve such issues in contact with the designer who creates the interior project. He will express his opinion on how organically the radiators can fit into the overall design style.
Features of the central heating system
Central heating is used to heat apartment buildings. The coolant comes from a thermal power plant or a city boiler house, which circulates through an internal pipeline using special equipment and is delivered to the apartments.
When choosing a radiator, it is important to take into account the operating features of central heating:
- changes in coolant temperature;
- the presence of rust, debris, lime and other aggressive components in the water;
- decrease in water temperature when circulating in the system (return);
- pressure surges;
- the occurrence of water hammer;
- draining water from the heating system due to repair work or the end of the heating season.
As a result of operation, the radiator is exposed to harmful factors, as a result of which the battery can burst, corrode and insufficiently heat the room.
For a long service life of the radiator, it is necessary to choose the right quality heating device.
Number of radiators
As a rule, heating radiators for a home are placed under each window, except for the attic. Even in the case of low window sills, it is possible and necessary to select heating devices with the appropriate parameters. Recently, some manufacturers have begun to produce home heating radiators with a height of 200 mm, so modern consumers have no problems choosing a device according to height. Moreover, this applies to both panel steel models and sectional aluminum ones.
The number of batteries rarely coincides with the number of windows in the house for the reason that heating is also necessary in those rooms where there are no windows: in the bathroom, in the vestibule, in the sauna, in the attic, in the basement, etc. If you can’t decide on this issue on your own, you can consult a specialist. But the rule “1 window - 1 radiator” remains unshakable in any case.
Correct placement of the radiator
If heating equipment is placed under standard conditions, the distance to the floor is selected at a minimum of 22 cm (for a steel panel model). If installation of a battery is required, and in extremely cramped conditions - at least 10 cm. The interval to the window sill should be at least 5 cm. It is also desirable that the window sill does not completely block the radiator, then the circulation of heated air will be ideal.
In rare cases, heating batteries for a home need to be placed behind a screen, which is extremely undesirable from a technological point of view. But if it is impossible to avoid this condition, the following points must be taken into account: the screen must either have technological holes or be located at some distance from the floor and from the window sill so as not to interfere with natural circulation.
But even if all these requirements are met, it is most likely impossible to do without increasing the power of the equipment. You will also need a special thermal head with a capillary tube. In this case, the working element will be located on the radiator instead of the thermal head, and it itself will be taken out into the room, usually onto the wall at a height of 1.5 m. The main requirement: warm air should not “wash” it, otherwise it will “lie.”
Otherwise, the room will be cold - the home heating radiator simply will not be able to perform its function.
The best cast iron radiators for an apartment
KONNER Modem
Cast iron radiators of the Modem series from the domestic company KONNER are manufactured in China, but are maximally adapted to Russian operating conditions. They are characterized by ease of installation, increased reliability, modern design, high heat transfer and long service life. The material is durable and does not corrode. The batteries have two versions with center distances of 300 and 500 mm.
Characteristics of a separate section:
- weight 3.11 or 4.14 kg;
- height 400 or 600 mm;
- width 62 or 60 mm;
- depth 92 or 96 mm;
- working pressure 12 atmospheres;
- heat output 80 or 128 W.
Design features:
- The main parts of radiators are made by casting from high-quality cast iron.
- Modem 500 sections have a center brace to increase overall structural strength.
Factory products consist of 4, 7, 10 or 12 sections. The side connection type is used. Radiators of this brand are produced in accordance with GOST 31311-2005 and the international quality standard ISO 9001. Manufacturer's warranty is 15 years.
It is important to know!
Sadly, the domestic heating system, created back in Soviet times, has long been in need of reconstruction and modernization. And, unfortunately, not every modern radiator is adapted to such specific conditions as pressure and temperature changes, poor water quality. The design temperature of our single-pipe open heating system in typical high-rise buildings is 105 degrees Celsius, and the pressure is 10 atmospheres. But during the launch of the system at the beginning of the heating season, these indicators often go off scale far beyond acceptable standards. This can lead to water hammer, which not every radiator can withstand. Therefore, when choosing a radiator, be sure to pay attention to such technical characteristics of the product as the permissible temperature and permissible pressure in the system.