When the question of which heating radiators is best to choose for a private home appears on the agenda, there are many who nostalgically recall Soviet cast-iron “accordions” - although bulky, they are hot and warm the room well. Indeed, at one time such batteries worked “excellently,” but now they are deteriorating and are considered obsolete. They have already been replaced by new, more efficient, convenient and cost-effective models.
But the main problem is that there are many diametrically opposed opinions regarding new radiators. And in practice it’s the same: you go to neighbors who have installed modern radiators at home - some are warm, while others are cold. At the same time, both places have almost identical heating batteries - that is, which of them is better for a private home does not always depend on the specific model.
Heating a house with radiators
Classes of heating radiators and their types and features
The principle of operation of a radiator is to transfer heat to the surrounding space from the coolant fluid circulating in this heating device.
The autonomous heating system (AHS) consists of:
- boiler;
- pipelines;
- thermal elements.
The table shows the main types of thermal appliances:
| Device | Operating principle | Example |
| Radiator | Heat is radiated | ceiling radiant panels, sectional cast iron, tubular radiators |
| Battery | Heat is radiated and also transferred by convection | sectional aluminum, sectional steel, bimetallic, tubular |
| Convector | Heat is mainly transferred by convection | plate, tubular convectors, finned tubes |
Heating a house with radiators
In addition, heating devices are divided into the following classes, let's consider a unique rating of heating radiators from this side:
Sectional
They consist of heating sections that are connected to each other. The more sections, the more heat they will transfer to the surrounding space. To prevent the room from overheating, special thermostats are installed on the radiators to regulate the temperature.
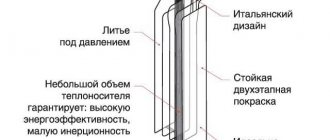
Standard cast iron radiators are also sectional: heat from them is transferred in the form of infrared radiation, evenly distributed throughout the room - top, bottom and middle. Such batteries have large dimensions and thick walls, which accumulate enough heat so that it is emitted in the infrared spectrum. It is this method of heating that is considered optimal for human health, although it must be borne in mind that part of the heating also occurs through convection.
In the middle of the content
If you need to order high-quality installation of engineering systems (heating, water supply), please contact DESIGN PRESTIGE by phone +7 , and we will install the system at a professional level in accordance with high quality standards.
Thanks to the thick walls, such batteries have high thermal inertia - therefore, after turning off the AOS, the radiators remain hot for a long time. Cast iron is not very susceptible to corrosion and is not afraid of harmful impurities in the coolant - the service life of such devices reaches 50 years. One of the disadvantages is the heavy weight.
Aluminum radiators have good heat transfer (1/2 radiation + 1/2 convection) and quickly warm up the room. Compared to cast iron, they are more lightweight, and in general, the ability to transfer heat into the room is several times higher than that of cast iron and steel.
An additional advantage of modern models is the ability to regulate the temperature using a valve with a thermal head. The metal surface is coated with a protective coating, which increases its service life. The cost of aluminum radiators is low, and therefore the prices are more affordable.
Aluminum radiators cannot withstand high overloads, so they are not used in central heating systems (CHS). They break due to pressure surges, the presence of rust or sand particles in the coolant. Chemical additives are not allowed in liquids.
Bimetallic heating radiators consist of external aluminum plates and steel pipes located inside the sections. They are valued for their reliability and durability, but are not cheap. Equally well suited for centralized and autonomous heating systems.
Radiators are also produced that have only steel-reinforced vertical pipes. These are no longer completely bimetallic devices; they are less corrosion resistant. Among their advantages, it is worth noting their high thermal conductivity, which is higher than that of real bimetallic radiators.
Tubular
Steel tubular heating devices give off heat well, are economical in terms of energy consumption, and heat up quickly. Their disadvantage is that they are sensitive to oxidative processes. If the coolant fluid does not fill the steel radiator reservoirs, it will begin to corrode. Another weakness of a steel radiator is its hypersensitivity to water quality. Even if the water is considered good by usual standards and can be drunk, it is recommended to install filters to minimize the formation of scale.
The sizes of steel tubular radiators are from 30 cm to 3 m. The number of rows of tubes is 1–9. They are considered very reliable - the permissible operating pressure for devices from a number of Russian manufacturers reaches 15 atm. Radiator reservoirs are designed to hold a large volume of liquid, so they quickly reach the required temperature levels when it is necessary to increase or decrease power. The method of heat transfer is radiation and convection.
Steel radiators are also used as heated towel rails, which, in addition to drying clothes, provide additional heating in bathrooms
Floor radiators-benches with support legs are steel tubular heating devices with a seat in the form of a wooden board on top. They are connected to the heating system in the same way as conventional radiators. They can also serve as the main heating device in rooms such as the kitchen, bathroom, hallway.
Panel
These steel radiators are a rectangular panel that acts as a heating device. The panel consists of 2 ribbed sheets welded to each other; plates with a U-shaped relief are placed inside.
Operating pressure is 6–8 atm, high sensitivity to pressure changes, therefore they are used only in autonomous heating systems for residential and commercial premises. Such radiators can consist of 1, 2, 3 heating plates. React quickly to temperature changes. The main method of heat transfer is convection. The choice of sizes of such devices is wide enough so that they can be selected for a room of any size.
Ceiling thermal panels consist of steel plates to which pipes intended for coolant are welded. Their use is advisable in rooms with high ceilings from 3 to 20 m. Heat transfer is carried out by radiation.
Lamellar
Plate heating devices consist of horizontally arranged pipes to which metal plates are welded, thereby increasing the surface area for heat transfer. Heat transferrs can additionally be covered with protective covers. The advantage of such radiators is their reliability - they can be used for centralized and autonomous heating. The main method of heat transfer is convective, so the space is heated unevenly: it is much warmer on top. They are mainly used for offices, corridors, garages and utility rooms, but there are also models for residential premises.
Types of thermal media
To transfer heat from the generator to the heated room, water is most often used, which has been heated to a certain temperature and circulates through a pipeline.
Today this is the most affordable and simple solution. By correctly calculating the number of radiators and the power of the boiler, you can organize a high-performance system that does not require any special care.
In addition to water heating, in a private wooden house the following is used:
- air;
- oven;
- electric.
A combination option is also often used. A well-designed scheme makes it possible, without spending a lot of money, to build a system that will completely warm up the house in a matter of hours.
If water is used as a heat transfer agent, it must first be filtered. This will significantly increase the service life of heating equipment
Rules for the location of batteries in the house
In order for the system to work properly, installation rules must be strictly followed. Although the installation technology is not complicated, it has its own nuances, so the work must be carried out by specialists.
Important! If radiators are installed incorrectly, they are not covered by the warranty.
In order to avoid heat loss and uneven heating of the room, when installing devices it is necessary to observe indentations and choose the correct location:
- The most suitable option for the battery is considered to be a place under the window, i.e. where the heat loss is the most significant. The radiator width must be at least 70% of the window width. Mounted clearly in the middle.
- Leave at least 10 cm from the battery to the windowsill, as well as to the floor. The optimal distance between the floor and the radiator is 12 cm. It is not recommended to leave more than 15 cm.
- The battery is fixed at a distance of 5 cm from the wall.
- You can stick heat-reflecting material behind the radiator - then some of the heat will not go into the wall, but will return to the room.
- If the radiator is planned to be placed not under the window sill, but on the wall, then the distance between them should be at least 20 mm.
Calculation of the number of sections
It is not necessary to look for the most expensive heating devices to make the room comfortable. The main thing is to correctly calculate the number of sections. If the rooms are standard, then this greatly simplifies the calculations.
Often they resort to calculations based on the volume of space because they are simple, but at the same time give fairly accurate results.
- 1 m³ requires 41 W of power. If good double-glazed windows are installed and heat loss is minimal, then the indicator drops to 34 W.
- Room volume (m³) = area (m²) × height (m).
- Required heating power for the entire room (W) = room volume (m³) × 41 W (or 34 W).
- In the technical data sheets of devices, manufacturers indicate the heat transfer of one section.
- The total power (the value calculated in point 3) must be divided by the heat transfer of one section. The resulting number is the number of sections.
For example, the required thermal power is 2890 W, and the heat output of one section is 170 W. Then for this room you need to purchase 17 sections.
If the room is non-standard, the calculations become more complicated. To calculate the total power, the features of double-glazed windows (double or triple), thermal insulation parameters of the walls, the ratio of the sizes of windows and floors, ceiling heights and other parameters are taken into account. Designers calculate all this using specialized software.
Principles for calculating battery power
To choose heating radiators for a country or private house, you need to perform calculations based on the fact that to heat one square meter. m of living space requires approximately 95–125 kW.
To warm up a room with average parameters (one window, one door, ceiling height up to 3 meters), it is necessary to heat the coolant to 70 °C.
If actual parameters differ from those indicated, adjustments must be made. For example, with a ceiling height of more than 3 meters, it is necessary to increase the calculated power of the batteries as many times as the actual height exceeds the conditional one. For low ceilings, recalculation is carried out in the opposite direction.
A decrease in coolant temperature for every 10 °C relative to the specified average level forces a corresponding increase in the design power of heating devices by 15–20%. If the room is corner and has two windows, the average calculated power of the batteries is increased by 1.5 times.
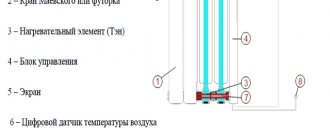
The heat transfer of radiators largely depends on their connection diagram. The average calculation is based on the fact that the heated coolant is supplied to the upper side inlet, and the return is connected to the lower inlet diagonally. Other connection options are less efficient and reduce the heat dissipation of batteries by 5–10%.
Note! The number of sections for radiator models of this type should not exceed 10 pieces - further expansion will not help increase power, since the coolant will not be able to fully warm up such a battery.
Calculating radiator parameters
Particular care should be taken when choosing panel and tubular batteries. Manufacturers include in their product line models of the same power, but with different geometric parameters.
When choosing, take into account the features of the installation location - the height from the floor to the window sill, the length of the wall in an elongated room, etc.
Homeowners choosing heating devices and wanting to purchase the best options at a reasonable price opt for steel or aluminum models.
The cost of the most reliable, imported bimetallic radiator is prohibitively high, and cast iron batteries have many serious disadvantages.
According to statistics, those who are thinking about which radiators to choose for a private home or country house choose aluminum sectional or steel panel models based on the ratio of price and practicality.
Source: https://profiteplo.com/radiatory/111-kak-vybrat-dlya-chastnogo-doma.html
Which radiators to choose for a wooden house
Heating a wooden house (we are talking primarily about log houses) indeed has its own characteristics, since the thermal conductivity of wood is low and depends on its species. In addition, it is necessary to ensure maximum fire safety. But in general, the issue of providing heat, as well as safety, rests primarily on the correct installation of the heating system, the choice of boiler and the number of radiators. There are no restrictions on the type of radiators here: steel, cast iron, bimetallic, aluminum - all of them can be used in a wooden frame.
Radiator connection diagrams
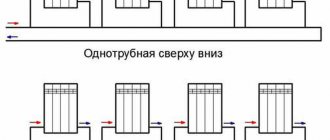
Depending on the method of supplying coolant, heating systems can be single-pipe or double-pipe. They are presented in several connection options, which differ in their operating principles and design features.
Among single-pipe schemes for one-story and two-story buildings with a small number of rooms, the most optimal is the “Leningradka” with forced circulation. To balance the system, radiators are equipped with bypasses, and the installation of shut-off valves and thermostats allows for repair work and temperature control.
The two-pipe scheme is more difficult to install and requires more materials and components during assembly. A popular option are networks with associated coolant movement, since they do not require additional balancing. When installing a circuit with forced circulation, it is possible to combine radiators with a “warm floor” system. Additional heating pipes are laid in separate rooms of the building or placed on one of the floors.
Which heating batteries to choose for a private home and cottage
It is not difficult to select batteries for a private home, because the autonomous heating system operates without significant overloads, which a centralized system experiences. Here you can connect any radiators, focusing on the required power, quality, efficiency, and cost of the device.
Many owners of private houses prefer aluminum radiators. They are cheaper than cast iron, more economical to operate and have higher heat transfer rates, and the sensitivity of aluminum devices to water hammer in an autonomous heating system can be neglected.
If you want to choose batteries based on the brand name, then you can take into account the unspoken rating of aluminum heating radiators for a private home. The top positions here belong to the brands Calidor, Global, Rifar, STI, which are well suited for operation in Russian climatic conditions.
Steel radiators are no less common, which is not surprising, because they are reliable, affordable, able to warm up quickly and have good heat dissipation. Here, in the ranking of steel heating radiators for a private home, the leading places are occupied by Kermi, Purmo, Zehnder, Sunerzha.
Among the worthy brands producing bimetallic radiators are the Russian Rifar and the Italian Global. Those who decide to purchase cast iron heaters should pay attention to Konner (Russia), Guratec (Germany), Retro Style (Russia).
As a result, all radiators are universal, which means posing the question of which heating radiators are best for a private house with a gas boiler is not entirely correct, because when choosing, they are mainly guided by the required power, the features of the room and the possibilities of the budget.
Premises and frequency of operation
Unlike an apartment with a central heating system, a private house has an autonomous or closed heating system. In practice this has its advantages:
- full control over system management,
- individual selection of coolant for the heating system,
as well as its disadvantages:
- the design and maintenance of the entire heating system falls on the shoulders of the home owner.
The most common mistake that owners of private houses make is completely trusting builders in matters of organizing a heating system. Unfortunately, not all of them have the highest level of competence, and often builders have only superficial knowledge about heating.
The design and installation of a heating system should be carried out by special engineering companies that are professionals in this matter and are aware of current trends in the market.
If you decide to delve into the essence of the matter yourself, this article will tell you how to choose heating radiators for a private home.
A little about the coolant in radiators
There are two types of coolant for radiators: water and antifreeze. By water, as a rule, we mean distilled water, purified from various impurities. Antifreeze coolant also differs in composition: based on glycerin, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol.
If you rarely live in your house, do not visit it in winter and turn off the electricity, then you cannot use water as a coolant. Otherwise, at the very first frost, your radiators and the entire heating system will fail with very sad consequences. Therefore it is necessary to use antifreeze.
If you plan to live in the house permanently and you do not have critical power outages, then use distilled water: this will ensure the maximum service life of any radiators. There is no need to drain the water during the entire service life of the radiators.
Progress does not stand still and manufacturers of heating equipment today have taken care of those who want to use water, but do not live in the house permanently. It is enough to install a GSM device that allows you to control the heating remotely via SMS commands or an application on your phone. This is already in the field of smart home technology. There are simple devices that inform you that the system is defrosting, and there are advanced ones that allow you to directly change the temperature, pressure and other parameters of the system. True, in the event of a power outage, you will still have to drop everything and quickly go to the house to start the generator and connect the heating system to it until the electricity comes back on.
Radiator prices
The cost of heating devices varies significantly depending on the following factors:
- brand and country of origin;
- material and production technology;
- design.
Italian, German, Finnish, and Czech batteries are more expensive than Russian ones, but in terms of their technical and operational characteristics, products from domestic manufacturers are not much inferior and even superior to many foreign analogues.
Buying heating radiators for a private home is quite expensive. But if you make the right calculations and select cost-effective devices, then costs can be significantly reduced.
The average cost of aluminum radiators per section is in the range of 1227–8200 rubles, bimetallic devices – 3000–11900 rubles. The cheapest of them can be purchased at a price of 1100 rubles. The range of prices for steel radiators is also quite wide: from 830 to 60,000 rubles. Steel models costing from 3,500 to 26,000 rubles are popular. Inexpensive cast iron batteries can be purchased for 500–1000 rubles. Cast iron appliances are in demand for RUR 3,000–8,000.
Retro-style batteries can be found from 8,000 rubles.
If batteries are needed for an entire house, then even inexpensive devices cost a pretty penny. In addition, costs will be added for related products: valves, thermostat heads, brackets and other parts.
How to correctly calculate the number of sections
Calculating the power of heating radiators in a country house depends on several factors. The calculations look like this:
- The thermal power of the radiator section is determined. For cast iron appliances, the performance is 100-150 W, aluminum and bimetallic – 150-180 W. You can check the power of the battery section in the technical documentation.
The heated area is calculated. Calculations are performed as follows: the length of the room is multiplied by the width. The result obtained will be the total heated area.
Calculation formula - there is a simple rule that allows you to perform the calculations yourself. For every 1 m² of heated area, a thermal power of 100 W is required.
Calculate the heating radiators of a private house. Calculation of total battery power. Calculations are performed not based on the total area of the house, but individually, for each room, based on the location of the batteries in the house. For example, you can calculate how much thermal energy is needed to warm a room with an area of 20 m², taking into account that for 1 m², 100 W of energy is required, heating a room with a ceiling height of no higher than 2.7 m is performed by a 2 kW heater. Approximately 10-15% should be added to the result obtained for possible heat loss. It turns out 2.3 kW. If there is excess heat, you can reduce heat transfer by adjusting the radiators. A thermostat, in the form of a faucet or thermostat, is installed on bimetallic and aluminum batteries.