The choice of heating devices for a water system always remains the prerogative of the homeowner, even when the installation is carried out by hired craftsmen. But choosing batteries based on the advice of sellers or reviews of Internet users is not easy - the former often do not understand the topic and repeat advertising slogans, the latter “praise their swamp,” which is understandable. To find out which heating radiators are best to choose for an apartment or private house, we suggest using a simple and understandable algorithm.
Instructions for choosing batteries - a simplified approach
Before you buy or order new heating radiators, you should quickly study the catalogs of large online stores. This will allow you to find out the price order and see the existing types of batteries. All convection water heating devices are divided into 4 groups:
- aluminum sectional;
- bimetallic - sectional and monolithic;
- cast iron;
- steel – panel and tubular.
Lyrical digression. You can read reviews and articles on resources that publish ratings of products from various brands. But the information will not bring much benefit - there are endless debates on forums and fake responses are written, and ratings are often compiled based on the TOP 10 manufacturers from the first pages of the search.
To select the power of heating radiators, you must first calculate the amount of heat consumed to heat each room. Calculation methods - by area, volume or heat losses of the building - are published in a separate article. How to choose the right batteries:
- Estimate the cost of a future purchase, weed out more expensive and too cheap heater options.
- Select models that you like in appearance, shape and color that fit well into your home interior. Pay attention to the height of the batteries so that they fit into the niches.
- If you live in an apartment in a high-rise building (9 floors or more), open the page with the technical characteristics of the selected radiators and find out the maximum operating water pressure - the device must withstand at least 12 Bar.
- For owners of private cottages, the pressure parameter is not of interest - models with any characteristics are suitable. If the house is heated with a wood or coal boiler, it is worth checking the maximum temperature of the coolant - the higher the figure, the better.
- Find out what connection methods are provided by the manufacturers of the selected batteries. The bottom line allows you to better hide the heating lines; with the side option, the pipes will have to be walled in the wall or left in plain sight.
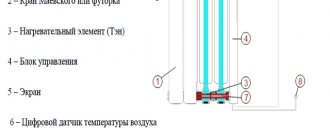
- Find out the weight of the product and the installation method - floor or wall. Find out if the radiator comes with mounting brackets and liners, otherwise there will be additional costs. Radiator valves and Mayevsky tap are usually purchased separately.
To install the devices you will need footers, a Mayevsky tap with a key and hanging brackets - Make the final choice of model and determine the size of radiators by power. We will tell you how the actual heat transfer of 1 section (panel) is calculated at the end of this instruction.
Please note that we did not mention materials of manufacture and types of devices. In reality, this factor does not play a big role. Modern radiators differ little in technical parameters; only the heat transfer indicator remains important. The lower threshold of working pressure is only relevant in multi-storey buildings.
Next we will look at the design and characteristics of various batteries, comparing their advantages and disadvantages. But first, let’s dispel popular myths invented by advertisers.
Myths about heating radiators
In order to promote a particular product, three common fables were invented about heating appliances made from various materials:
- the heat transfer of aluminum radiators is significantly higher than that of steel and cast iron;
- radiators made of cast iron are massive, so they take a long time to heat up and cool down, supposedly storing heat;
- In the central heating network, water hammer and pressure occur, which only bimetallic heaters can withstand.
Note. The main established myths are listed here; we will tell you about others in the process of describing radiators.
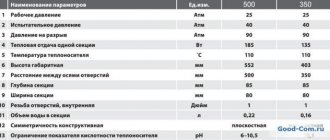
Compared to ferrous metals - steel and cast iron - aluminum conducts heat much better. Let’s confirm with numbers: the thermal conductivity coefficient λ of aluminum products is 209 W/(m•°C), steel – 47 W/(m•°C), cast iron – only 42 W/(m•°C). Here’s the catch: heating devices are made not from pure aluminum, but from an alloy of the AK12 group - silumin, which contains 11-13% silicon and other impurities indicated in the table above.
The purpose of adding silicon is to increase the strength and corrosion resistance of the alloy. The physical properties of silumin are different, the thermal conductivity is noticeably lower - 168 W/(m•°C). Considering the thickness of the battery walls is 4-5 mm, the difference in heat transfer between aluminum and iron devices is invisible in practice. Place 2 of these radiators of the same power in a room - you will not be able to determine which one works more efficiently.
The best conductor of heat is copper. Plate baseboard heaters and copper-aluminum water convectors are made from it.
The stumbling block is the prices of copper products. The right photo shows the Thermia heater costing 70 USD. e., dimensions - 400 x 400 x 90 mm, heat flow - only 430 W.
The transfer of thermal energy from any metal battery is greatly influenced by the following factors:
- temperature and coolant flow;
- surface area of the device;
- temperature difference between the air in the room and the water in the pipes.
Reference. The difference between the average temperature of the coolant and the heated air of the room is called temperature difference (DT). The value will be useful later when calculating the power of devices.
Let's dispel the remaining myths point by point:
- When heating/cooling, the massiveness of cast iron does not matter, since its heat capacity is 9 times lower than that of the water inside (0.54 kJ/kg •°C versus 4.18 kJ/kg •°C). Therefore, the cast iron battery will cool down simultaneously with the coolant, and not longer. Silumin and steel will cool faster because they hold a much smaller volume of water.
- Water hammers simply do not happen inside district heating networks. Maximum operating pressure is 10 Bar, test pressure is 12 Bar. Modern aluminum appliances can easily withstand such pressure.
Trench convectors
Trench convectors come in two varieties - water and electric heating devices. Heaters built into the floor draw in cold air masses and release them into the room already warmed up. Typically, convectors are built into the floor under panoramic glazed walls or large display cases. Just like with baseboard heaters, warm air rises in a vertical curtain, cutting off the penetration of cold through the glass from outside the house.
Electrical devices built into the floor are similar in their technical characteristics to warm baseboards with heating elements. Water convectors operate from an individual boiler or boiler installed in a private house.
Technical characteristics of water trench convectors
| Heat dissipation | 200 – 300 watt/rm |
| Maximum heating | 1000 C |
| Operating temperature | 450 C |
| Coolant | Water, antifreeze or glycol |
| Life time | 15 – 20 years |
Well-known manufacturers of thermal equipment of this type in Russia are Techno Board, Turbo-Tech, Charley, Orion and Mr. Tektum. The average cost of an in-floor convector for water supply is approximately 6 - 7 thousand rubles. per linear meter
Design and advantages of aluminum appliances
Radiators of this type are manufactured by injection molding or extrusion. The finished product is a vertical single section or a solid, non-separable battery (both varieties are produced by the well-known company Rifar). A heater of the required power is assembled from individual sections; the connection method is a threaded nipple with a gasket.
Inside the silumin radiator section, shown in section in the photo, there are 2 horizontal collectors, between them there is a vertical connecting channel of oval cross-section. The outer heat exchange part consists of convection fins coated with heat-resistant powder paint. The shape of the fins and the number of plates are determined by the manufacturer.
Reference. The height of the battery is calculated by the distance between the centers of the horizontal collectors. Aluminum products are offered in 3 standard versions - 35, 50 and 80 cm. Permissible pressure in radiators is 14...16 Bar, heat transfer of a section with an interaxial distance of 500 mm is about 190 W according to the Italian brand Global.
Advantages of aluminum alloy batteries:
- light weight;
- attractive appearance;
- efficient heat transfer is facilitated by a large surface area;
- small water capacity - 0.2...1 l depending on size;
- relatively low price 7...10 cu. e. per section, Chinese models - from 5 USD. e.
A disadvantage of aluminum is considered to be low corrosion resistance, although in practice heaters serve in apartments with central heating for 20 years. The statement should apply to private houses, where too hard water, saturated with magnesium and calcium salts, is used as a coolant.
Method of assembling a sectional heater on threaded nipples with EPDM rubber gaskets
The second disadvantage is inherent in any sectional batteries - when pouring non-freezing coolant, leaks occur at the joints. Solid modifications, for example, Rifar Monolith, do not experience such problems.
Pros and cons of bimetal
As you can easily guess from the name, heating devices are made of 2 metals - silumin and steel. Externally, the batteries are indistinguishable from aluminum sections, but inside the collectors and vertical channels there are iron tubes welded together. The steel frame is designed to solve 2 problems:
- protection of the silumin part from the chemical effects of the coolant in old centralized systems;
- increasing the reliability of the radiator by increasing the operating pressure threshold to 20...30 Atm.
For reference. There are bimetallic models with double vertical channels made to improve water flow and heat transfer. An example is the Rifar SUPReMO line of non-separable batteries, shown in the photo below.
In terms of other technical characteristics, bimetal differs little from aluminum - the power of 1 section, weight and capacity are almost the same. The operational advantages of radiators also remain, but a couple of disadvantages appear:
- the price of batteries is 30-50% higher, for example, the original bimetallic section from Global Style Plus with an axial spacing of 500 mm costs about 15 USD. e. (970 rub.);
- due to different coefficients of thermal expansion of silumin and steel, the pipe core can burst at the welded joints, making repairs and sealing the leak is unrealistic.
In a monolithic structure, the collectors of adjacent sections are connected by welding. Feature of Rifar products - 2 vertical channels
Important addition. Sometimes on sale there are defective bimetallic radiators with steel tubes embedded only inside the collectors. The vertical channel of the section remains unprotected.
Features of cast iron accordions
The structure of batteries made by casting from gray cast iron is well known to most homeowners. Like its aluminum “brother,” the heater is assembled from separate sections, twisted with nipples through gaskets (a long socket wrench is needed).
Cast iron batteries on the market are divided into 2 groups:
- Soviet-style products of the MS-140 brand, the center spacing is standard - 300 and 500 mm.
- Designer models cast in modern, retro style and so on. The distance between the plugs is arbitrary.
Inexpensive “accordions” of the MC series are significantly inferior to any radiators in appearance; they are used mainly in industrial premises. The heat output of the 50 cm section is 160 W, the operating pressure is up to 9 Bar, the water capacity is 1.45 liters. Cost - from 6 USD. e. (420 rub.).
The appearance of modern retro batteries (left) is strikingly different from the Soviet “accordion” MS-140 (right)
Beautiful designer batteries from different brands differ greatly in size, power and other parameters. The table below shows the characteristics and prices of decorative heaters from Czech, Turkish and Russian brands (excluding the cost of decorative shut-off valves).
Note. The numbers after the product names indicate the center distance and thickness of the heater in millimeters.
Cast iron “accordions” are reliable in operation, durable and completely resistant to corrosion. In appearance, retro radiators confidently occupy the first position among all heating devices. Now let's reveal the negative points:
- the exorbitant price of designer sections is noticeable in the table;
- cast iron is brittle and cracks under impact loads;
- solid weight of the product;
- the battery holds 2-4 times more coolant than other types of radiators.
Heating devices in the Art Nouveau style from the Czech brand Viadrus
The so-called inertia of cast iron sections is explained precisely by their increased capacity. Two liters of water cools down significantly longer than 0.2-0.6 liters in the aluminum section. Particularly heavy modifications, for example, Retro Style Anerli, are produced in a floor-standing version and are equipped with legs.
Electrical
Sometimes the use of centralized heating is impossible for a number of reasons - it could be a break in the heating main, economic disadvantage, etc. In such a situation, many consumers pay attention to electric batteries . And not without reason, they have a lot of advantages - they are easy to use, economical, can be easily adjusted, both mechanically and remotely, and also have an affordable price. In many Western European countries, residents have long moved away from central heating systems in favor of individual electric heating networks. Today the market is represented by a variety of heating devices that use electricity, the most popular of which are fan heaters, oil and infrared radiators, as well as convectors.
Electric batteries
Advantages of steel radiators
Manufacturers offer 2 options for iron batteries:
- panel - flat and profile;
- vertical tubular (sectional).
The design of a standard panel (left) and a vertical design model (right)
Comment. Both varieties are available in a designer vertical design (see photo above). Well-known brands in the post-Soviet space: Kermi, Korado, Purmo, Arbonia and others.
Heating panels are welded from stamped steel plates with a thickness of 1.2…1.5 mm. Fittings for connecting connections are installed on the side or bottom of the radiator. Convective fins are attached between the panels. Batteries are divided into types depending on the number of heating panels and profile fins, as shown in the table.
Performance indicators of panel heaters (taken according to the German radiator “Kermi” type 22, installation size 100 x 50 cm):
- permissible pressure – up to 10 bar;
- thermal power 1550 W at supply water temperature 75 °C, return water temperature - 65 °C;
- coolant volume – 5.4 l;
- unit weight – 28 kg, price – 95 USD. e. (6300 rub.).
The characteristics of tubular radiators are not too different from panel radiators. If we take a double-row Arbonia 3050/22 device, comparable in size to the Kermi option under consideration (500 x 1014 mm), we get a power of 1481 W with the same operating pressure and a weight of 25.9 kg. Only the price of the product is different - 430 USD. e.
Tubular radiators "Arbonia" in horizontal and vertical versions
Since we are considering affordable options, we will list the advantages of panel batteries:
- steel panels are the most budget option among all radiators;
- resistance to chemical corrosion;
- acceptable design and appearance;
- the one-piece design allows you to pour antifreeze into the system and not be afraid of leaks;
- the ability to select power without changing dimensions - by adding heating panels and fins (from 1 for Type 10 to 3 pieces for Type 33).
The disadvantage of radiators is the low operating pressure threshold - 6...10 Bar. We will not refute this, but we will suggest watching a video from our expert, where an inexpensive steel panel is inflated with a pressure testing pump until the weld breaks (pressure over 20 Bar):
Design differences
Steel tubular radiator
Classification of heating batteries according to design characteristics:
- Sectional. Assembled from identical sections with channels for coolant inside. They have increased heat transfer and efficiency. It is possible to install a thermostat. However, the connections between sections may begin to leak. Another disadvantage of sectional type heating radiators is their tendency to quickly become dirty and clogged.
- Panel. They consist of two sheets of metal coated with anti-corrosion protection and welded to each other. The coolant moves in vertical channels, and ribs are installed on the back side, increasing the area of the heated surface. Such devices are light, cheap and compact. But they are afraid of increased pressure and water hammer, and they require clean coolant.
- Tubular. Externally they look like two collectors, top and bottom, between which vertical tubes are inserted. They heat well and are resistant to high pressure. The rounded edges and shape of the tubes prevent dust and dirt from accumulating on the surface. Strong welded joints eliminate leaks. But they are afraid of rust and are expensive.
There are also plate types of heating radiators. They are made in the form of a bent water pipe with steel plates mounted on it to enhance air convection. The devices are simple in design and inexpensive. But at the same time, they heat the room unevenly and collect dust well.
How to find out the real heat transfer
When selecting heating devices in an online store, it is difficult to find real power indicators for a panel or one section. It is more profitable for sellers to declare maximum heat transfer, which is practically unattainable when heating a country cottage or apartment. According to the passport, the water temperature in the supply pipeline should reach 90 degrees, the return line - 70 °C, room air - 20 °C.
Reference. In modern household heat generators, the heating temperature is limited to 80...85 degrees.
We recommend selecting sections based on heat transfer as follows:
- Open the official website of the manufacturer of the battery you like and download the operating instructions for the device. It indicates exactly at what temperature difference DT the radiator produces the nominal amount of heat. Focus on the 70/50 °C mode.
Power of Kermi steel panels depending on size and temperature conditions - example table - If there are no instructions, take the manufacturer's data as truth and multiply the heat transfer by an increasing factor of 1.5-1.8. If you make a one and a half supply, you definitely won’t go wrong.
- Select the latest radiators of a single-pipe system with a double reserve, since they receive the least amount of thermal energy.
The most accurate selection method is to calculate heat transfer at a given temperature pressure. The calculation algorithm is described in detail in the corresponding material.
What threats does centralized heating pose?
On the one hand, supplying heat from outside is more convenient than autonomous heating - you don’t have to bother with installing the boiler and setting it up. Autumn will come, and hot water will happily run through your radiators, warming your apartment.
But not everything is so smooth in the centralized heating system:
- Water that has traveled a long way contains many chemically active impurities that can cause corrosion of pipes and radiators.
- And small particles of sludge, which inevitably fall into the coolant, scratch the batteries from the inside, wiping them to holes after a few years.
- And the water temperature is not always stable - sometimes the batteries are at room temperature, or sometimes it’s impossible to touch them.
- And the most important danger is a sudden huge surge in pressure in the heating system, the so-called water hammer. It happens, for example, for the reason that the mechanic closed the tap of the pumping station too abruptly.
Previously, they used smooth-running valves, but with the advent of ball valves, it became possible to turn off the water instantly. Water hammer also occurs when excess air gets into the pipes. A second surge in pressure can cause a lot of trouble. Weak batteries cannot withstand enormous pressure and burst, splashing boiling water, ruining furnishings and causing damage to neighbors below.
Conclusions and recommendations
We hope the previous description helped you figure out which heating batteries are best for an apartment in terms of price and technical indicators. Finally, here are some practical tips:
- Please use the instructions at the beginning of this publication. Choose radiators that best suit your design and budget.
- The operating pressure of the coolant is important only for apartments in high-rise buildings; only bimetallic and aluminum batteries can withstand pressure above 10 bar. Any water heating devices are suitable for dachas and private cottages.
- If you are on a limited budget, feel free to buy steel panels - their heat output is not inferior to other heaters or convectors.
- For a gravity-flow system, you need to take radiators with a large cross-section of internal channels. It is better not to install stamped steel heaters, only tubular ones.
- In terms of price-quality ratio and set of operating parameters, the first place is occupied by sectional batteries made of light aluminum alloy.
- It is worth paying for bimetal when there is no confidence in the parameters of the coolant - the pressure is unknown, hard water is used.
- Try not to purchase frankly cheap radiators made from unknown material in China. They will warm, but probably not for long.
Characteristics of heaters of the same size, made of different materials - comparison table
Conclusion regarding cast iron. Heating radiators of the old type MS-90 and MS-140 are cheap, but they look unsightly. Beautifully designed models are incredibly expensive, and therefore beyond the reach of average homeowners. Cast iron is becoming rare, and the outdated “accordions” of the MC series are becoming a thing of the past.
If your budget allows you to install designer heaters, carefully select each battery according to its dimensions. It is better to place a vertical steel heating radiator in a narrow wall niche, and stylish cast iron products under the windows. It is advisable to additionally attach heavy floor-standing versions to the wall using a pair of brackets.
Results
When choosing new batteries for your apartment, you should not save too much , as this can lead to big troubles in the future, such as a flood. Therefore, approach the problem of selecting heating equipment of this type with all responsibility , collect all the necessary information, and consult with specialists. Buy products only from well-known and trusted brands that can reliably provide warmth to you and your loved ones.