In heating systems of residential buildings and apartments, systems based on electrode boilers are common. In terms of characteristics, this equipment is more efficient than standard heating elements and heats up the coolant faster, while its cost is low. And enthusiasts can assemble an inexpensive electrode boiler with their own hands.
Device
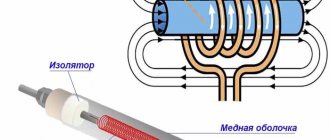
Structurally, the electrode boiler is an all-metal pipe with polyamide insulating coating. On the case there are power terminals and coolant input/output (water or other liquid). At one end of the cylinder, electrodes are inserted into the boiler, and the other has an outlet into the heating system.
On the picture:
- 1 - pipe for supplying hot coolant to the external system;
- 2 — steel body;
- 3 - layer of electrically insulating material;
- 4 - coolant heated by current;
- 5 — electrode block;
- 6 - pipe for introducing cold liquid for subsequent heating;
- 7 - insulation and seal;
- 8 - power input.
The composition also usually includes an electronic control unit. There are samples of ready-made automation units for factory boilers on the market; they can also be adapted to a homemade “water heater”.
These boilers received the name “electrode” precisely because of the two electrodes located inside - the anode and the cathode. “Minus” goes to the cathode, and “plus” goes to the anode. When current is applied to the electrodes, the heat-carrying medium heats up and enters external systems. The electrical charge passes directly through the liquid, causing it to quickly become hot.
In industrial boilers, the following device diagram is usually used:
- cylindrical body with a round electrode inside;
- “zero” is connected to this electrode;
- the second contact is the housing itself - the phase is connected to it.
With such a scheme, the case is certainly grounded, for which a ground contact is placed on it. Homemade samples also adhere to this method of manufacturing electrode boilers.
Average parameters of factory products:
- pipe length - up to 60 centimeters, diameter - up to 32 centimeters;
- power - from 2 to 50 kW. The most powerful ones heat rooms up to 1500 square meters. m.;
- the current used is three- or single-phase. The latter operates relatively low-power household appliances, and three-phase current powers productive high-power boilers in commercial buildings, workshops and industrial facilities;
- The ideal temperature of the working fluid is 75 degrees. At this level, optimal energy consumption is established. At a higher temperature, the boiler consumes too much current, and at a low temperature it drops, since as it cools, the thermal conductivity of the medium decreases.
Boilers are divided according to the method of supplying water or other liquid:
- open - the movement of the working fluid is carried out naturally: it leaves the heat generator, transfers heat to the environment and returns back;
- closed - equipped with an expansion pump and tank. The pump provides circulation, and the tank serves for initial heating of the coolant.
Interesting: modern industrial boilers not only have advanced control automation, but are also often equipped with remote control systems and GSM communication modules. Such a device can be controlled via an application from anywhere in the world with Internet access.
Difficulties in operation
During use, the consumer may encounter some problems characteristic of electrode heaters:
- The quality of the coolant plays an important role. The service life of the product and reliability of operation depend on this. The use of tap fluid can lead to increased corrosion of metal pipes and radiators and a decrease in efficiency. Manufacturers recommend that owners of electrode boilers use ready-made compositions that have the necessary physical and chemical characteristics. The liquid changes its properties over time, so after 3-4 years the system needs to be filled with fresh coolant.
- It is necessary to pay attention to ensuring the electrical safety of the unit. The body of the device is connected to the neutral cable, the phase is connected to the electrodes. During installation, grounding must be provided. Electric boilers create a large load on the network, so before installing the heating device you should make sure that the wiring is reliable throughout the room.
- Under the constant influence of current, the processes of electrocorrosion of steel and cast iron are accelerated, which reduces the service life of the system several times. Aluminum or bimetallic communications and radiators should be used with electrode units. To provide heat to a cottage or home, you need to make sure that the elements of the heating system are made of recommended materials.
Principle of operation
Many people are familiar with the simplest boiler circuit - two safety razor blades connected to wires. Such a “heater”, constructed from scrap materials, is dangerous, but is still capable of quickly boiling, for example, a mug of water. It uses the phenomenon of electrolysis: water contains various substances and metal salts, and if current is applied to contacts immersed in water, charged particles will begin to move from one contact to another. In household electrical networks in the Russian Federation, the current frequency is 50 Hertz, therefore, the ions will change direction 50 times per second. This causes heating. The same principle is used by an electrode heating boiler.
The speed at which the operating temperature is reached is affected by the composition of the water: the more salts it contains, the lower the resistance and the faster the movement of charged particles. And Ohm's law states that at a constant voltage, a decrease in resistance causes an increase in current. The conductive properties of water are worse than those of metals used in electrical engineering (aluminum, copper), therefore, as the current increases, it actively heats up. Due to this, the efficiency of electrode boilers is very high: they convert a significant part of the energy supplied to them into heat.
The boiler power is calculated by the formula P=UI, where P is the power in watts, U is the mains voltage (220 V in single-phase networks and 380 in three-phase networks), I is the current in amperes.
Myths about outstanding efficiency
Promotional materials claim that electrode-based boiler equipment extracts thermal energy from the void. Indicators - 120-150% of the applied electrical power. But they completely ignore the laws of physics and heat engineering.
Myth - the conversion of electrical energy by an electrode boiler is many times greater. We focused on the promotion of thermal equipment that was powered by a heat pump with a positive COP coefficient.
You should not believe the statement that electrical energy is 100% converted into heat. Losses are inevitable.
Pros and cons of ion boilers
An important advantage of an electrode heater is its resistance to voltage drops. Ionization will be carried out even if the voltage drops to 180 V. This is very important in places with unstable power supply.
Another plus is compactness. Electrode boilers can be very small, suitable even for small homes.
The third advantage is safety. It is based on the principle of operation: if water/other coolant suddenly disappears from the system, the electrode electric heating boiler will simply stop working, which cannot be said about solid fuel or gas options. Emergency situations are excluded - which also excludes the introduction of expensive control and measuring automation into the circuit.
In addition, electrode equipment is free from the standard problem of devices based on heating elements - scale. Thanks to this, they have a long service life. And it works almost silently, which cannot be said, for example, about induction options.
Other benefits include:
- the ability to remotely control the device, if such functionality is provided and supported;
- speed of work. Thanks to minimal thermal inertia, water heats up very quickly;
- ease of installation;
- the ion boiler does not require a separate room;
- on its basis you can make a full-fledged efficient hot water supply system in a house or apartment;
- environmental friendliness - the complex does not produce exhaust emissions, does not emit combustion products and does not burn any fuel;
- installation does not require special permits or permits;
- high efficiency - up to 98%.
But there are also some disadvantages. Among them:
- specific requirements for the quality of the working fluid. In pure water without impurities, ionization is impossible. Therefore, distilled water diluted with salt or soda is poured into the system, which you have to buy or prepare yourself. The additive is mixed with water in an amount of approximately 6–8 mg per 100 liters;
- It is possible that current leaks to metal parts of the heating system - for example, radiators. This is due to the principle of operation, because the current flows directly through the coolant. If installed incorrectly, the device poses a great danger, therefore, the installer of such equipment must strictly follow the grounding rules and provide protection against the occurrence of dangerous differential leakage currents. A residual current device in a circuit by itself will not provide sufficient reliability and safety due to the large length of the heating route;
- Although scale does not form on the electrodes, over time they decrease in size as particles are constantly “knocked out” of them. Therefore, the elements need to be periodically replaced. The service interval is different for each boiler, but on average it is about five years;
- the need for constant power supply. In regions where electricity is expensive, this may become inconvenient or unacceptable;
- if the circuit is not closed, it is necessary to use containers and pipes with a special anti-corrosion coating to protect against air oxygen.
Economical
The ion boiler has low inertia both during startup and while maintaining the set temperature. There are no intermediate carriers - incoming electricity is immediately transferred to the liquid. The process begins instantly, while a classic heating element takes up to several minutes to reach operating temperature. The same goes for turning off: after interrupting the current supply, heating stops, energy is not wasted. Thanks to this, the device is significantly less energy-consuming compared to a heating element boiler: reviews give figures of up to 30% less electricity consumption.
Important: to achieve this result you need specialized control automation.
But over time, power can decrease. This happens for reasons:
- wear of electrodes;
- incorrect composition of the prepared mixture for pouring into the circuit;
- degradation of the components of the control electronic unit, and so on.
Practice shows that after approximately 2.5–3 years of operation, the efficiency of the heating system begins to decline. This is usually due to wear of the electrodes or failures in the control automation, but sometimes it is possible to adjust the power by changing the composition of the heat-carrying mixture.
The best known manufacturers and models: characteristics and prices
Galan
The most common Russian manufacturer of electrode boilers. It has the widest model range and power options: from low-power 2-3 kW models for heating small rooms to powerful 36 kW ion boilers. Electric boilers have some of the most affordable prices, fast heating, and silent operation. Among the disadvantages are stepwise power adjustment and an expensive coolant recommended by the manufacturer (about 2,200 rubles for 20 liters).
The model range is represented not only by the compact “Ochag”, “Geyser” and “Vulcan”, but also by the monoblock “Galax”, the body of which is already equipped with an expansion tank, a circulation pump, a safety valve, an air vent and a pressure gauge.
Cost: 4,000-13,000 rubles. for compact and 29,000-30,000 for monoblock models.
EOU
Another Russian manufacturer, the abbreviation stands for “Energy-saving heating installations.”
The model range is represented by electric boilers with a power from 1 to 36 kW. Electrode EOUs are distinguished by their durability (the service life declared by the manufacturer is 30 years) and function better than ordinary tap water. The disadvantages are mediocre automation, higher prices and mediocre availability, since the manufacturer is represented in the smallest part of the heating equipment market stores.
Cost: 4,600-15,000 rubles.
Beril
Well-known Latvian manufacturer SIA “BERIL”. Despite their higher cost, Beril electrode boilers are among the best for heating a private home, as they are characterized by high reliability, build quality and, most importantly, multifunctional, economical automation. There is a smooth degree-by-degree power adjustment, several economical operating modes, the ability to connect external temperature sensors or a GSM module, and electricity consumption statistics.
There are also protection against overheating and a frost prevention mode typical for heating elements.
Cost: 4,450-25,000 rubles.
Coterm
Another Russian manufacturer of heating equipment. The most successful model is considered to be the Coterm “Dachnik M”, characterized by its most compact dimensions, build quality, reliability, and fast heating of the coolant. Known disadvantages are mediocre automation with only 3-step power control and limited functionality, as well as the need to use exclusively branded Coterm Eco coolant.
Cost: 8,800-11,000 rubles.
Reviews
“I retired, took up dacha chores, and it’s cool in the spring and autumn. I wondered how to heat the dacha. I recently purchased an electrode boiler. My house is insulated, protected from wind blowing, the option suited me. The boiler doesn’t work all the time, everything is fine.”
Nadezhda, Stary Oskol.
“My wife and I purchased the device specifically for our summer cottage. Guys, the boiler is working well. I have not tried it in large rooms. You can install it in a room without bothering with allocating a separate room for a boiler room. I advise."
Vladimir, Krasnodar.
Maintenance of the heating system using electrode equipment
Electrode boilers are a technical development for heating cottages with a small area. A feature that distinguishes it from a device operating on a heating element is the impossibility of breakdown from a voltage drop.
During operation of a device operating at the limit, high temperature and pressure are formed inside the housing, circulation of low-quality coolant occurs, and the device wears out very quickly. Under such conditions, wear of the electrodes and insulators occurs, and the tightness of the connections will become unusable.
In case of poor-quality heating of the coolant or leakage, urgent equipment repair is required. Before starting work, the device must be de-energized.
Cleaning the device
- To carry out maintenance, you need to dismantle the device. Unscrew the threaded connection on the flange and pull out the electrode.
- Assess how worn the electrodes are. Make sure the insulators are intact. There are no cracks on the body. If the electrodes are worn out by more than 40%, equipment replacement is required.
- Clean the surface of the electrodes and holders.
- Clean the inside of the case.
- You can reassemble the device in reverse order.
- Degrease the surfaces and apply sealant. You will need a high temperature substance.
Repair kit