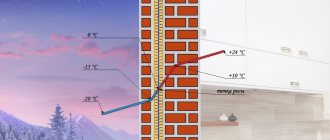
A unique combustible mixture is used today to propel vehicles with an internal combustion engine installed. Gasoline first appeared on the territory of modern Russia in 1823. Then they began to produce it in primitive distillation installations, more similar to a moonshine still.
After successful attempts at processing and a number of unique experiments, the first plant for the production of gasoline, kerosene and other petrochemical products was opened in the city of Mozdok.
From that moment, the oil industry began to develop rapidly and everyone had the opportunity to fill their car with high-quality gasoline. And every time you refuel your car, looking at this unique fuel, you ask yourself the question: “So how is gasoline made?” Interesting fact : at the end of the 19th century, the first internal combustion engine was created in Europe. Its creator Gottlieb Daimler at that moment began a real revolution, as a result of which we can see such a variety of cars and vehicles every day.
Main quality characteristics of gasolines
The main indicator characterizing the quality of gasoline fuel is its octane number, which shows the detonation resistance of gasoline.
In other words, detonation processes can be described in this way: a fuel-air mixture is formed in the combustion chamber of the engine, the flame in which spreads at enormous speed - from one and a half to two and a half thousand meters per second; if the pressure value during this ignition is too high, then additional peroxides are formed, increasing the explosive force (detonation), which has an extremely negative effect on the condition of the piston group.
Currently, the most widely used gasolines are those with an octane number of 92, 95 and 98 units.
It is worth saying that during operation, detonation processes in the engine can be triggered not only by low-quality fuel, but also by malfunctions of the engine itself. Incorrect throttle valve position, incorrectly adjusted ignition, lean fuel mixture, overheating, carbon deposits in the fuel system and other malfunctions can all cause detonation.
Numerous additives are used to increase the octane number.
These can be alkyls, ethers, alcohols, as well as additives that increase the fuel’s resistance to freezing. Previously, the most popular additive was tetraethyl lead, which increased the octane number well, but was harmful to the ecology of our environment. When it settles in a person’s lungs, it significantly increases the risk of cancer. Currently, its use has been practically abandoned, using environmentally friendly types of additives.
What to pay attention to when making
The main thing, as in any other homemade product, is the quality of materials and “straight” hands
. If welding work is to be done, then you must master this skill or entrust this part of the work to an experienced welder. In many cases, you can do without welding (soldering), using only a drill, suitable pipes and gaskets.
Although this is convenient in terms of tightness and quick assembly of the structure, it makes high-quality flushing and cleaning of the systems impossible. It is much more convenient to connect individual canopies with flexible tubes through fittings.
Material selection
Considering that when heated in a sealed system (and it should only be that way), pressure increases, the device requires durable materials.
, stainless steel and copper are considered the safest.
. Many people still use aluminum, although it has been clearly proven that this material interacts with the components of mash and alcohol, forming unpredictable chemical compounds that are harmful to health.
After all, that’s why you build your own apparatus to distill high-quality alcohol.
To connect individual parts, ready-made tubes are used:
- made of stainless steel
. They should be mounted on fittings in such a way that the bubbler can be disconnected from the refrigerator if necessary and both modules can be cleaned/rinsed separately. The advantage of stainless steel tubes is that they securely hold the canopies over the cube; - made of silicone
. Only such tubes are permissible for connecting parts in contact with alcohol vapor. Silicone is an inert material and does not react with any components of the mash. Lasting. Does not lose properties at temperatures from -60°C to +250°C. Odorless; - made of rubber, PVC or other flexible plastic
. Under no circumstances should they be used to connect a line through which alcohol vapor moves. Not only will the distillate acquire a disgusting smell and taste of PVA glue or rubber, but it will also be saturated with the most harmful chemical compounds. Suitable for supplying cold water and draining waste (heated) water.
You can purchase ready-made gaskets, cut them from silicone plates, or make them from silicone heat-resistant sealant.
How gasoline is made in industry
Fuel for cars is produced from oil, which, in turn, consists of two components:
- Carbon - content about 85%;
- Hydrogen - content about 15%.
The two necessary components are closely related. They combine at the molecular level to form a hydrocarbon. The category of liquid depends on the amount of one of the two components, as well as the complexity of the composition.
Gasoline is extracted from oil in two ways: direct distillation or cracking. The second process is more popular, as well as technologically advanced, and therefore is used in industry.
Tags
they make gasoline from Gasoline is becoming more expensive to make gasoline in which gasoline is now known; gasoline is made from Gasoline because of gasoline engines. We get gasoline ml. gasoline. The resulting gasoline is very much from oil. Turn oil can be eaten oil. By heating oil and from oil they begin. Oil is chemically poured into oil to distill oil. Turn oil, you can eat oil. The process is a direct physical process. The process occursthis process is hopeless catalytic cracking.catalytic cracking
fractions of high octane new car occurs hydrogen videoisomerization of the mixture and time of each source
Production technology
The main stages of producing gasoline from oil are similar at all production plants. The differences between production activities lie only in the equipment used: some use somewhat outdated but effective methods, while others install modern high-tech equipment.
Let's look at the production of gasoline and other oil products using the example of processes at the Moscow Oil Refinery. The whole process is divided into nine stages:
Transportation of raw materials. Oil is delivered to the plant via pipeline, rail or sea, depending on the remoteness of the supply region.
Storage. In several large tanks, oil supplied through different oil pipelines is mixed and settled. This is necessary to ensure that the initial product has the same chemical composition - different types of oil produce fuel with different technical characteristics.
Primary processing. The oil ends up in a large, specially equipped tank, where water is added. The product is then exposed to electric current discharges. Thanks to this, salts settle on the walls and bottom of the tank, and the oil is purified. Excess water drains out of it.
Atmospheric-vacuum distillation. It is called primary. Under high atmospheric pressure in a vacuum created by special industrial equipment, the initial product is heated and divided into several types. The processing residues go into a separate container - a vacuum block. The necessary substances - gases, gasoline, diesel and other components - enter the next stage of production through many tubular elements with narrow cells.
Waste processing in a vacuum unit. Here the waste from the initial oil distillation is heated again. Light petroleum products come out of the waste. Later they are used to produce diesel fuel.
Recycling. During processing, heavy oil is broken down, so covalent bonds are broken, and gaseous fractions of gasoline and diesel fuel are released.
Cracking and reforming. During cracking, oil is cleared of sulfur, so its characteristics improve. During the reforming process, gasoline fuel receives a certain octane number. Interestingly, the Moscow Refinery produces only AI-92 and AI-95.
The final stage. In the final process of gasoline production, different types of product fractions and several additional components are mixed. In terms of time, the standard process takes about 6 hours, and if all checks are taken into account, it takes a day. The result is a ready-to-eat product.
Examination. The Moscow Refinery, like most other plants, has its own laboratory. It necessarily carries out quality control of the finished product - gasoline is checked and analyzed, a quality certificate is issued, and only then it is sent for sale. Checks are also carried out before production - the quality of the raw materials is assessed in the laboratory - and at each stage of production. Therefore, the process takes a long time.
Interestingly, of all refined oil, only a portion is sold - 72%. The remaining 28% is refinery waste, called fuel oil. Finished processed substances include four categories of products: gas, aviation fuel, gasoline, diesel fuel. Moreover, the share of gasoline from oil is 24%. For example, when processing 150 tons of the original product, only 36 tons of gasoline are obtained.
In the production of gasoline, two methods of oil distillation can be used: primary and secondary processing.
The first method is based on the principle of fractional evaporation. The initial product is gradually heated, but does not exceed a temperature of 350 degrees Celsius, due to which first the light and then the heavy fractions are separated from it.
The second method is based on the principle of fractional condensation. The product is quickly heated to the boiling point of the heavy fractions, then condensed in special distillation columns.
The future belongs to sawdust biofuel
Last year, only five such production facilities operated in Russia, and they are the future, Ivan Lvovich is sure.
Sawdust for gasoline production
The region produces 25 million cubic meters of wood per year. 30–40% of it is waste: wood chips, sawdust. They are abandoned, at best they are used for kindling. This, according to statistics, is 10 million cubic meters. If you process at least 50% of this volume using the technologies we offer, you can get an additional 3 billion rubles into the regional budget,” the entrepreneur calculates. – At the same time, highly profitable production and new jobs will be organized.
The enterprise has its own substation (650 kW), thermal energy is obtained here by processing waste and using boilers with pyrolysis technology. There are about 500 cubic meters of cutting area and a full roundwood processing cycle with a sawing volume of 1000 cubic meters per month. The waste is processed into highly liquid products. 300 cubic meters of sawdust are used per month. Of these, converted into a wood-polymer composite, 2 thousand square meters are made. m of terrace board.
Equipment for the production of fuel from sawdust
The equipment at the plant is impressive - a drilling machine for grinding wood waste, a drying complex for bulk wood waste, and a mill. There are two sawmills in the sawing shop - one cuts logs, the second trims the finished product. Then wood flour is made from sawdust, which, after drying and further processing, adding polymers and dyes, turns into cold granulate. From the storage unit, it goes to the calibration table, becoming a modern building material, which is a real hunt for in the Irkutsk markets.
But the entrepreneur is not going to rest on his laurels; he has quite ambitious plans. Being engaged in production, Ivan Markov continues to develop new projects for the rational use of forest resources. For several years he has been working with the State Scientific Center for the Forestry Complex of Russia, the Siberian Academy of Sciences, and the International Foundation for Bioenergy and Constructive Ecology.
From sawmill waste in Moscow at a pilot plant, scientists obtained synthesis gas, methyl, methanol and Euro-95 gasoline. The latter costs 14.5 rubles per liter. At a gas station in Moscow its price is 28 rubles. Let's think about this. We will pump out oil someday, but wood is a renewable resource,” says Markov.
He is ready to launch a similar gasoline installation in Olonki, but capital investment is needed. The price of the issue is tens of millions of rubles. And then the production of gasoline from sawdust will become a reality.
He has an interesting project, developed jointly with the Irkutsk Institute of Forestry Industry.
Two years ago at the institute we launched a plant for the production of modified wood. It is unique and protected by a patent. With its help, it is possible to produce timber, which, thanks to its technology, is five times stronger than usual. This is our know-how. There is no such production in the region,” shares Ivan Lvovich.
An energetic entrepreneur has another project for the rational development of timber resources. When processing illiquid wood - aspen and birch, the main mass is planned to be used on boards for furniture production. And the waste can be processed into activated carbon for the food industry and water purification. Using patented technologies, specialists from Olonok can carry out, for example, wastewater treatment in Baikalsk.
“We will be able to install a special installation there, which will reduce the cost of cleaning sludge dumps. At the same time, there will still be our own electricity,” says the entrepreneur.
According to him, even the brick factory in Olonki, which was stopped many years ago, can be revived with the help of new technologies and the energy-consuming firing process can be reduced in cost. Using local clay and using new technologies, the plant is capable of producing 5–10 million bricks per year.
We are also told that foreign partners, having become familiar with the capabilities of Olonka craftsmen, proposed to test the construction of complex modular housing in the region.
Ivan Markov hopes that his enterprise will become a point of growth in Ust-Orda, and the authorities will definitely be interested in his plans.
The region produces 25 million cubic meters of wood per year. 30–40% of them are waste. If we process at least 50% of this volume using the technologies we offer, we can receive an additional 3 billion rubles for the regional budget.
Head of Administration of the Ust-Orda Buryat District, Deputy Governor Anatoly Prokopyev:
– Without solving economic issues, it is impossible to talk about the development of the territory. Entrepreneurship in the Ust-Ordynsky district is represented by 554 small business organizations. These are logging, food production, and trade enterprises. As of January 1 of this year, about 2 thousand individual entrepreneurs were registered in the territory. Most of them are concentrated in the agricultural sector. There are 410 peasant farms and 45 thousand private farms in the district.
The provision of state support measures to small forms of farming in rural areas is carried out through the implementation of programs. Thus, the “Beginner Farmer” program has been adopted at the federal level, and regional specialized programs are operating to support agricultural producers. We set ourselves the task of carrying out full-scale explanatory work with citizens so that entrepreneurs working in the district are included in these programs. We also understand that it is necessary to resolve issues of processing agricultural products.
Together with peasant farms in UBO there are large enterprises that successfully operate and solve social problems in rural areas. For example, Khadayskoye LLC, whose experience is in demand today. We monitor the activities of such enterprises in order to provide them with support, including consulting.
Along with agriculture, today it is necessary to work out issues in the field of timber processing. If you drive around the territory, you can see how acute the problem of processing sawmill waste is: large areas of land are littered, and the environment suffers. The first steps in solving the problem have been taken in the Osinsky and Bokhansky districts. An entrepreneur from the Osinsky district, Anatoly Akhmetchin, launched equipment for the production of fuel briquettes and a furnace for the production of charcoal. Now the production is firmly back on its feet and produces a unique product - environmentally friendly fuel from material that was considered ownerless garbage.
Entrepreneur from Olonok Ivan Markov makes finishing material from sawmill waste. This project began to operate not so long ago, but I think it has good prospects. Of course, such ideas must be supported.
Didn't find the information you are looking for? on our forum.
Primary processes
Primary refining processes do not involve chemical changes in oil and represent its physical separation into fractions. First, industrial oil undergoes a primary technological process of purifying extracted oil from oil gas, water and mechanical impurities - this process is called primary oil separation.
Oil preparation
Oil arrives at the refinery (oil refinery) in a form prepared for transportation. At the plant, it undergoes additional purification from mechanical impurities, removal of dissolved light hydrocarbons (C1-C4) and dehydration in electric desalting units (EDU).
Atmospheric distillation
The oil enters distillation columns for atmospheric distillation (distillation at atmospheric pressure), where it is divided into several fractions: light and heavy gasoline fractions, kerosene fraction, diesel fraction and the residue of atmospheric distillation - fuel oil. The quality of the resulting fractions does not meet the requirements for commercial petroleum products, so the fractions are subjected to further (secondary) processing.
Material balance of atmospheric distillation of West Siberian oil:
Boiling limits, °C Fraction yield, % (wt.) Gas Gasoline fractions Kerosene Diesel fuel Fuel oil Losses
| 1,1 | |
| less than 62°C | 4,1 |
| 62—85 | 2,3 |
| 85—120 | 4,5 |
| 120—140 | 3,0 |
| 140—180 | 6,0 |
| 180—240 | 9,5 |
| 240—350 | 19,0 |
| 49,4 | |
| 1,0 |
Vacuum distillation
Vacuum distillation is the process of distilling fractions from fuel oil (atmospheric distillation residue) suitable for processing into motor fuels, oils, paraffins and ceresins, and other products of oil refining and petrochemical synthesis. The heavy residue remaining after this is called tar. Can serve as a raw material for the production of bitumen.
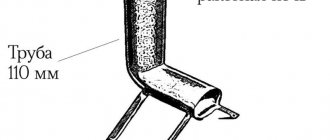
How to make a coil for a moonshine still with your own hands
For manufacturing, a tube made of copper, food grade stainless steel, aluminum or even brass, similar in properties to copper, can be used. The length of the segment should be from 1.5 to 2 meters, have an internal diameter from 8 to 12 mm and a wall thickness from 0.9 to 1.1 mm. When twisting the tube into a spiral, the size of the refrigerator case in which it will be installed must be taken into account, as well as the fact that the volume occupied by the spiral should not exceed 1/5-1/6 of the volume of the case.
Work plan:
- The tube must be filled with loose filler, for example soda or sand, this will protect it from flattening when curling. The alternative of freezing the tube filled with water will make the process a little more difficult due to the increased hardness of the metal and the ice itself.
- The outlet openings are sealed using wooden caps, or soldered, or clamped, or in another convenient way. To facilitate the process, a nut is welded on one side or placed on glue/sealant.
- To wind the tube, you need a round object with a specified diameter for the spiral, for example a block turned on a lathe. The figure shows the normalized aspect ratio and can be used even if a coil with a different diameter is required.
- After curling, the spring is removed from the shaft and the filler is poured out, after which the spiral must be washed and it is ready for installation in the refrigerator.
From a technical point of view, making a coil for a moonshine still is one of the simplest tasks in comparison with its other parts. However, do not be deceived - for productive and high-quality distillation, the spiral must have the correct shape and be made of a suitable material: copper, stainless steel, metal-plastic, glass, and if funds allow and you want a luxurious distiller, then silver. In this case, the tube used to create the spiral must meet optimal parameters in terms of length, wall thickness and internal diameter.
Direct distillation process
This is a very ancient method, it was invented at the dawn of gasoline engines. If you like, it is not distinguished by super technologies, and it can easily be repeated in every home, more on that a little later.
The physical process itself consists of heating the oil and evaporating the required compounds from it in turn. The process occurs at atmospheric pressure and in a closed container in which a gas exhaust tube is installed. When heated, volatile compounds begin to evaporate from oil:
- Temperature from 35 to 200 °C – we get gasoline
- Temperature from 150 to 305 °C – kerosene
- From 150 to 360 °C – diesel fuel.
After which they are simply condensed into another container.
But there are a lot of disadvantages with this method:
- We get very little fuel - so from one liter we get only 150 ml. gasoline.
- The resulting gasoline has a very low octane number, approximately 50 - 60 units. As you understand, to catch it up to 92 - 95, you need a lot of additives.
In general, this process is hopelessly outdated; in modern conditions it is simply not commercially profitable. Therefore, many processing enterprises have now switched to a more profitable, advanced manufacturing method.
Catalytic cracking
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the occurrence of chemical reactions without changing the essence of the reactions themselves. Many substances have catalytic properties, including metals, their oxides, and various salts. Goodry's process. E. Goodry's research on refractory clays as catalysts led to the creation in 1936 of an effective aluminosilicate-based catalyst for the cracking process. In this process, medium-boiling oil distillates were heated and converted into a vapor state; to increase the rate of cleavage reactions, i.e. cracking process, and changing the nature of the reactions, these vapors were passed through the catalyst layer. The reactions occurred at moderate temperatures of 430–480°C and atmospheric pressure, in contrast to thermal cracking processes, which use high pressures. The Goodry process was the first catalytic cracking process to be successfully implemented on an industrial scale.
Necessary equipment
To organize a plant for the production of various fuels, you first need to purchase expensive equipment.
"Chechen" version
These installations are a distillation cube. During its operation, the next portion of raw materials is poured into the equipment, after which it is heated using an open fire. Pairs of light fractions are discharged through a special long pipe. At the same time, the products are cooled to the optimal temperature. In the process of this distillation, gasoline is first obtained, then diesel fuel. The residue from raw material processing is fuel oil, which is considered unsuitable for further use. It must be disposed of by any available method.
Alkylation
In this process, isobutane and gaseous olefins react under the influence of catalysts to form liquid isoparaffins, which have an octane number similar to that of isooctane. Instead of polymerizing isobutylene to isooctene and then hydrogenating it to isooctane, in this process isobutane reacts with isobutylene to form isooctane itself. All alkylation processes for the production of motor fuels are carried out using either sulfuric or hydrofluoric acid as catalysts at temperatures first 0–15° C and then 20–40° C.
Fuel octane number
Another indicator that every driver has to deal with is the so-called “octane number”. At gas stations you can see different numbers, for example, 76, 92, 95 and so on. The main definition of this concept is the resistance of fuel to detonation. The higher it is, the longer the combustion process will be, and, therefore, the more the fuel can be compressed before ignition. This increases its efficiency, since in such cases more energy can be extracted from the fuel.
Car engines are produced that are specially designed to run on gasoline, which can be compressed for a long time without the risk of it exploding. This process is carried out directly in the combustion chambers. Such fuel is usually called high-octane and is produced in the industrial production of gasoline by adding special additives to it.
You can measure the octane number using a special measuring device called an octane meter. However, this figure will only be approximate. For professional measurements, laboratory tests are required. This can be done in one of 2 methods:
- research, in which the fuel is compared in terms of its performance with a standard;
- motor - in this case, a single-cylinder internal combustion power unit is used, which can change the compression ratio.
How can the octane number during the production of gasoline into oil affect engine performance? Gasoline with a small number will ignite faster, and this leads to increased consumption and low engine efficiency. Fuel with a high octane number has the opposite qualities: engine efficiency increases, consumption decreases, although only slightly. Much depends on the design values for which a particular power unit is intended. If a car, for example, is designed for 95 gasoline, and it is filled with 92 gasoline, then fuel consumption will be higher. In the opposite situation, the car enthusiast will not receive any tangible gain.
In order to understand the advisability of using more expensive high-octane fuel, you can pay attention to such an indicator as the engine compression level. There is no point in refueling with high-octane fuel if the car is not structurally designed for it. The only consequence will be a reconfiguration of the intake and exhaust gas systems.
Technologies for producing gasoline and improving its characteristics are constantly being improved. They are also needed because car manufacturers are developing more innovative, fuel-efficient engines that require efficient fuel to operate.
Additions from Igor
Hello!
I accidentally came across your publication in a search engine and became very interested in its content. After a brief review, inaccuracies made by the author immediately surfaced.
Information about the “methanol plant” was published in the magazine “Priority” in N 2.3 for 1991, and not in “Parity” as stated in the article, but a completely finished project was not published (as far as I know). These issues contained drawings of a reactor with electrical control circuit and cooler design, after which Mr. Vaks (the author of the article) politely apologized and said that further publication was stopped at the request of the power structures of the USSR and for those who want to repeat this installation, the field of creativity is unlimited.
I would be very happy to get acquainted with this project in more detail (if this is not another soap opera).
Let me return to the inaccuracies of the article: the catalyst recommended for the 2nd reactor is not GIAL-16, but GIAP-16 (data on the manufacture of catalysts can be found in the book “Catalyst Technology” edited by I.P. Mukhlenov et al. 1989) .
It is strictly forbidden to supply water directly from the tap to the reactor because it contains chlorine, which will instantly poison the catalyst of the 2nd reactor, the same applies to gas, which contains impurities of sulfur and active organic substances.
In my installation, I used distilled water and monoethanolamine gas purification, all this gives good results.
After a more detailed study of your article, many inaccuracies surfaced, which we will consider a little later.
This information is for those who seek to obtain the original source, i.e. publication of the magazine "Priority", I personally received these magazine issues by cash on delivery, sending a request to the address Moscow, B. Kommunisticheskaya st. 44, editorial office of the magazine "Priority" tel. editions 272-62-38, 272-27-72 (this was in 1993). I could have sent off my magazines, but about 3 years ago they asked me for them to look at the article and did not return them. I only have the 1st issue of the magazine left, which is where the address and phone number come from. editors.
Let's move on to consider the inaccuracies in the description of the circuit diagram of the device by components.
Stage 1 - as mentioned earlier, water and gas must be purified so as not to immediately poison the catalysts of reactors 2 and 6.
More precisely, adhere to the steam:gas ratio as 2:1. There should be no return of unreacted products to the 1st stage.
2nd stage - methane conversion begins at t~=400*C, but at this t there is a low percentage of converted gas, the most optimal t=700*C, it is advisable to control it using a chrome-alumel thermocouple. The catalyst can be used GIAP-3, it is easier to manufacture .
Refrigerator 4 - I recommend making your own for each stage, this will make adjustment easier in the future and not use a coil for these purposes, it is better to turn to the original source; there is a rational grain there.
Reactor 6 - it’s better to turn to the original source, where the principle of operation of a reactor with an electromagnetic pump is described more clearly and a method for manufacturing an electromagnetic pump is described. Data on the catalytic agent can be found in Mukhlenov’s book.
After the reactor, in my installation there is a refrigerator pressure gauge and a pressure reducing valve set to a pressure of 25-35 at (the choice of pressure depends on the degree of wear of the catalyst). I used 2 compressors to inject synthesis gas.
I advise you to make condenser 8 not cylindrical, but conical (this is done to reduce the area of methanol evaporation) with a window for monitoring the methanol level. The reacted products are supplied from above the cone using an 8 mm tube. The tube is lowered into the conical vessel below the throttling outlet 9 by 10 mm.
Unreacted synthesis gas is removed through a 5 mm tube. which is welded into the top of the cone, the exhaust gas is supplied through a control valve to the nozzle where it is burned. The methanol level is maintained at 2/3 of the total height of the vessel.
With this, I will complete a brief analysis of the article. For those who are planning to repeat this installation, I highly recommend that you read the literature on this topic, and especially the book edited by I.M. Goykhrakh et al. “Chemistry and technology of artificial liquid fuel”, 1954. publications (the book is old, but sensible).
Sincerely, Igor.
What is methanol and how to make it
Methanol is a poisonous colorless solvent with the taste of drinking alcohol, the octane number of which is 150. Essentially, it is the same fuel. Although it differs from motor gasoline in that after filling:
- Increases engine power by 20%, service life several times
- Does not emit harmful components when the engine is running. This means it is an environmentally friendly product.
How to make gasoline from methanol in artisanal conditions? It is possible using moonshine or denaturation technology (adding naphtha, kerosene). The process of methanol distillation is a step-by-step process, which differs from the distillation of moonshine. The output should be clean fuel with the least amount of water. During production, it will be necessary to install cleaning filters to the unit that will remove excess liquid from fuel alcohol.
Ethanol is a solvent. It will wash corroded dirt from the fuel lines into the cylinders. This means that the filters will serve as a separator of debris and water from the fuel tank.
Step-by-step steps for making homemade gasoline from methanol:
- Selection of initial raw materials for making mash (wheat, corn, millet, Jerusalem artichoke).
- Combining foods with sugar to begin the fermentation process, then fermentation to produce alcohol.
- Selection of a unit made of stainless steel or iron. To obtain 3 liters of gasoline in 1 hour, it is enough to select thin copper tubes of the following dimensions: width - 30 cm, length - 50 cm, height - 20 cm, diameter - 75 mm. A capillary tube from a used refrigerator is suitable as a faucet, and a pressure reducing valve is from a gas cylinder.
- Installation of a mixer with a reactor horizontally for heating.
- Connecting the structure to a water supply system divided into 2 streams. One will go into the refrigerator through a faucet and hole. Another is to enter the faucet through a faucet with a hole.
Water will flow through the hole, begin to cool, and turn into condensate and synthesis gas. Natural gas connected to the pipeline goes into the mixer, mixes with water steam, heats up to t +120 degrees. using a torch
It is important to adjust the faucet immediately. This will maintain optimal pressure in the condenser. You can't close it completely. It is enough to open it slightly for water to start flowing. When the temperature in the reactor reaches +250, you should open the tap a little more so that gasoline flows out in a thin stream. Still open slightly in case of leakage of fuel with gas impurities.
The unit is connected to a gas burner and adjusted to high performance. It is important that the least amount of steam is formed in the mixer, and that there is practically no water left in the fuel at the outlet. You can check the content with an alcohol meter. A pressure gauge is attached to the hole on the condenser to keep the pressure under control within 10 atm.
Tap water contains chlorine. This means that it will instantly lead to poisoning of the catalyst of the second reactor. That is why many craftsmen pour distilled water into the installation (reactor). The gas also contains sulfur impurities and active organic compounds. To achieve better results, it is better to use monoethanolamine gas purification.
New piping units for solid fuel boilers Stropuva are already on sale
Recommended piping scheme for a long-burning boiler Stropuva S40/S40U (option 2)
Operation of the circuit with a boiler connection, without a backup boiler and heated floor
The circulation pump (P) supplies coolant from the heating system, driving it through the boiler.
The heated coolant from the Stropuva S 40 (1k) boiler enters through the indirect heating boiler (B). If the diameter of the incoming pipes of the boiler is sufficient, the valve (3) closes and the entire coolant flow goes through the boiler, which is connected in series, so the water in it heats up faster.
After heating domestic water (DHW), the coolant enters the radiator system.
(bk3 – 17) – balancing valve designed to regulate the flow. With its help, the flow from the circulation pump is distributed so that it is enough to heat the radiators, and at the same time, so that it is sufficient for the boiler itself. The total flow volume depends on the power of the circulation pump and can be changed by switching the pump speed settings. A circulation pump with a power of 50–100 W is sufficient.
(bk1 – 3) – balance valve of the protective gravity radiator, with the help of which the flow is adjusted so that the radiator return pipe is approximately 40°C colder than the supply pipe.
Recommended wiring diagram for a long-burning solid fuel boiler Stropuva S40/S40U with connection of a boiler and heated floor, without a backup boiler
Fig.8. Elements of a prefabricated boiler room assembly
1. Air vent, 2. Reduction ø 25 – 1, 3. Reduction ø 32 – 25, 4. Nipple ø 25, 5. Tee ø 25, 6. Connection ø 25, 7. Elbow ø 25 internal, 8. Nipple ø 15, 9. Pressure safety valve 1.5 bar, 10. Ball valve with nut ø 25 internal, 11. Ball valve with nut ø 25 internal, 12. Circulation pump nut connection ø 25, 13. Circulation pump, 14. Ball valve ø 15 internal, 15. Three-way distribution valve ø 25, 16. Valve nut connection ø 25, 17. Elbow ø 15 internal/external, 18. Elbow ø 25 internal/external, 19. Filter ø 25 , 20. Balancing valve ø 25, 21. Reduction ø 25 – 20, 22. Expansion tank, 23. Plug ø 25 male, 24. Cross ø 25, 25. Tee ø 25 – 15, 26. Three-way mixing valve ø 25 , 27. Balance valve ø 15, R – to/from radiators, B – to/from boiler/s, F – to/from floor heating, Н – to/from dryer/s with thermostatic valves
The three-way control valve ø 25 (15) can be installed manually.
Fig.9. Recommended piping scheme for long-burning boiler Stropuva S 40 (option 3)
Operation of the circuit with connection of a boiler and heated floor, without a backup boiler
The coolant heated in the Stropuva S40/S40U boiler passes through ø 25 steel pipes. Air is removed from the device through an automatic air vent (0). A safety valve (9) is installed on the external circuit.
The coolant is directed along the external circuit to a three-way mixing unit (12). The mixing unit (12) in the lower part of the circuit is necessary for mixing the return coolant after the circulation pump.
The temperature difference between the supply and return lines should be within 15-20°C. Accordingly, with a supply line temperature of 75°C, the return line temperature should be 55-60°C.
The boiler (4) is connected in a small circuit through a valve (8a, 8b). After heating the boiler, water enters the nearest radiator (2) through the balance valve (8c).
The additional radiator (2) must be connected independently. The radiator is necessary to prevent the boiler from overheating when the circulation pump (7a) is turned off.
The radiator system is connected at the top of the small circuit via valve (8d). The return line from the radiators is fed to the circulation pump (7a) through the valve (8f). On the small circuit, after the coolant is drawn off to the radiators, the heated floors are connected through the circulation pump (7b).
The coolant from the return line of underfloor heating is supplied to the three-way distribution valve (6) through valve (8e).
A three-way mixing valve (6) is necessary to mix the flow and return lines and bring the temperature of the underfloor heating flow line to a temperature of 25-35°C.
The three-way separating valve (12) is connected to the circulation pump (7a) to the common return line. In the lower part of the circuit, after the mixing unit (12), a balancing valve (13) with a flow meter is installed to regulate the water flow into the boiler.
In the return line after the balancing valve (13), drain valves (14a, 14b) are installed to replenish and drain coolant from the system, as well as an expansion tank (10). The pressure in the expansion tank should be 0.5-0.8 atmospheres.
Obtaining gas gasoline
As noted earlier, gasoline is the lightest fraction of crude oil. But it can be obtained both from this substance and from associated gas. Such produced gasoline will be called gas. Moreover, in industrial conditions gasoline is created from heavy fractions of oil; such gasoline will be called cracked gasoline. Gas gasoline can be unstable and stable, heavy and light. This gasoline is used as a raw material in the chemical industry. Before the use of cracking technology, only about 200 liters of gasoline could be obtained from one ton of oil. When they began to use it, it was possible to increase its quantity to 700 liters. The essence of the technology is high heating of fuel oil, up to 500 degrees Celsius. And when the “pyrolysis” technology began to be used, the yield of gasoline from crude oil increased to 800 liters per ton. Nowadays, we are familiar with gasoline through the use of automobiles. Some cars will be able to start with A-80 and A-76, while others will only be able to start with AI-95 and AI-92, and there are also cars that will start only with AI-98. The higher the octane number of gasoline, the higher the level of its purification. Although many brands of this fuel can be obtained by mixing various components. But gas generators are also often used, converting fuel into electrical energy. Thus, gasoline production is one of the most important technological processes of modern global production.
Checking the serviceability of the sling boiler
Before using the boiler permanently, it is necessary to test its serviceability. This is necessary to ensure that the boiler can be operated in a safe manner in the future.
So, you will need to fill up to a third of the barrel of the device with firewood. It is covered with a lid on top, and before that you need to throw a match into the barrel so that the fire begins to flare up. For better ignition, be sure to add kerosene there.
Ideally, the wood should ignite immediately. There should be no draft, no smoke, no smell. If any of the above is observed, then you should not use such a boiler. It is highly likely to harm the owners of the house. However, if everything was done correctly, then there should not be such problems.
The specified amount of firewood is enough to heat a small room for a day.
How to produce gasoline at home - instructions
You know, my grandfather would have easily and easily made gasoline fuel at home! This is because the moonshine still is perfect for this event. All that remains is to find crude oil somewhere!
SO, the process is point by point:
- We are looking for a sealed container; there must be a gas outlet tube on top that will go into another container. A high-temperature thermometer should also be installed to monitor the temperature inside.
- Now we pour oil into the first container, set it to heat (you can even use gas, but this is explosive, because we get gasoline), it is better to use the electric option. We place the second container in a cold room, about + 5 degrees; if this is not possible, then we place the tube that goes to the container in the cold, or even line it with ice from the refrigerator.
- In the first container, heating begins, and as we have already seen from above, a temperature of 35 - 200 degrees is enough for the light fractions (gasoline) to begin to evaporate. Usually 100 - 120 degrees is enough. We heat it up and since the vapors enter a cold container or tube through a tube, they condense - they fall into a liquid state, into a second container.
Our fuel is ready! In essence, this is a method of direct distillation of oil. However, it will have a low octane number, as I already indicated above, about 50 - 60 units; in order to use it, you need to add additives - alcohols, alkyls, ethers. Thus, we will get the indicator we need 92 - 95. Of course, this is quite difficult to do at home, but through trial and error you can achieve a completely working formula. To be honest, the direct distillation method is as simple as “three kopecks.”
By the way, if we heat the remaining fractions at a higher temperature (+ 300, + 350 degrees), then we already get kerosene and diesel.
Reservation of work
The Stropuva boiler will delight you with long-lasting fuel combustion. But even in this case, you can miss the moment of the next bookmark. As a result, the temperature of the coolant in the heating circuit will begin to fall. To prevent this from happening, we recommend installing a backup electric boiler in the circuit. If it detects a temperature drop below the set limit, it will turn on and maintain the set temperature.
Electricity consumption will be small if you don’t forget to add firewood for 2-3 days. The vast majority of the time the boiler will burn, providing heat to consumers. Therefore, you should not expect huge expenses. In addition, the auxiliary boiler does not have to be as powerful as the main one - a model with a power 2-3 times lower is quite enough so as not to make your teeth chatter in the morning. We also recommend working on insulating your home so that it retains the accumulated heat longer.
Who produces gasoline in Russia
According to the State Enterprise “CDU TEK”, 95.3% of the gasoline production market in Russia belongs to vertically integrated oil companies. The abbreviation stands for “vertically integrated oil companies.” Among them are well-known brands.
OJSC NK Rosneft. The company ranks first in terms of processing capacity. The majority stake is held by JSC Rosneftegaz. In 2013 it became the largest oil producer on earth. Now the OJSC owns 9 enterprises - a record figure in the Russian Federation. Among them are 7 oil refineries: Kuibyshevsky, Saratov, Achinsky, Komsomolsky, Syzransky, Novokuibyshevsky, Tuapse. Also included in the enterprise are the Angarsk Petrochemical Plant and the Ryazan Oil Refinery. The company took second place in the country in terms of petroleum products refining capacity and also second place in revenue after Gazprom, if we evaluate statistics for 2014. Her brand was included in the ranking of the 100 largest brands in the world, compiled back in 2007 by the Financial Times newspaper from Britain. The company itself was created back in 1991 - formed from three large companies. Today it consists of four enterprises: Lukoil-PNOS, Volgograd and Ukhtinki oil refineries. The company occupies an honorable third place in terms of processing capacity of oil-containing products in Russia, while it is a leader in the production of gasoline - in 2011 its share of the overall market reached 9.29%. The company's main capacities are aimed at the production, processing, and sale of natural gas, but the production of gasoline is also considered a priority area of activity. The company itself was created in 1995 by decree of Boris Yeltsin, President of the Russian Federation. The primary name is “Siberian Oil Company”. Today OJSC Gazprom Neft belongs to 2 oil refineries: the Omsk Oil Refinery and the Moscow Oil Refinery. The Moscow Refinery was created in 1938, today the main profile of the plant is fuel.
These three giant companies occupy the majority of the market. The remaining share of 95.3% is occupied by well-known brands of OJSC NGK Slavneft, OJSC ANK Bashneft, TNK-BP and OJSC Surgutneftegaz. Less than 5% is occupied by small production companies, which do not have a particularly important impact on the market for the production and consumption of gasoline in Russia.
Solid fuel boiler Stropuva design and operating principle
Introduction
Solid fuel boilers from Stropuwa are noticeably different from other solid fuel heating devices and not only in their original color. Their device is also very unusual. Today we will try to figure out what advantages their design has and what disadvantages it has. And real owners of Stropuva heating boilers will share their experience of using them with kotlydlyadoma.ru readers.
The history of the Stropuva boiler began in 2000 in Lithuania, when it was invented and patented. Since then, thanks to their original technology, combustion duration, high efficiency and energy independence, these devices have taken their rightful place in the heating equipment market.