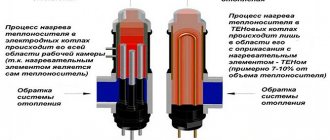
In fact, there are no problems associated with what units of measurement to calculate consumed heat, but for the average consumer, not everything is so simple. Difficulties arise only due to the fact that it is necessary to pay for thermal energy consumption in Gcal
, but at the same time, many users have metering devices that produce measurements in
kW
. Accordingly, everything needs to be correctly translated from one unit of measurement to another, that is, in essence, this is a mathematical problem, but many consumers are wondering why such difficulties arise and how to avoid them.
Watt and kilowatt - what is it?
A watt is a unit of measurement of power, as well as heat flux in physics, sound electrical flux, direct electric current power, active and apparent electric current power, radiation flux and ionizing radiation energy flux in the international measurement system. It should be noted that this is a scalar measurable quantity, that is, measured and calculated.
Description from link
To make the use of watts convenient, the international system has adopted the use of prefixes that define a decimal multiple of the original indicator. Typically one kilowatt is used for this. Translated from Greek, the prefix kilogram means thousand. Using a prefix means increasing the original value by 103 times.
Note! KWh is a non-systemic unit of measurement that shows when energy is produced or consumed and in what quantity. It also shows the mechanical work performed and the temperature. Used to measure household electricity consumption or to measure electricity production in the energy sector.
What else needs to be taken into account when calculating
Previous calculations do not provide an accurate estimate of the power of the boiler room; it is necessary to take into account the preparation of hot water. The power of the boilers needs to be increased by about 20% - that much heat is spent heating the water. For a private home, it is better to purchase automatic double-circuit heating systems - they save fuel consumption, work to heat the room and prepare hot water.
It is better to measure the operation of gas boilers in m³/h or kg/h, so as not to confuse electrical energy with thermal energy. It should be remembered that the combustion of 0.112 m³ of gas is equal to 1 kW of heat.
The geographical location of the heated room is also taken into account. For this purpose, there are maps indicating average temperatures at different times of the year for different areas. The coefficient taken from the map is added to the calculated figure set earlier. For the climate of central Russia it is equal to 1, for the northern regions - from 1.5 to 2. The figure obtained by measuring the area and volume of the heated room is multiplied by this coefficient. The result will be the boiler power required for the given region.
An example of calculating heat consumption in a brick house in Syktyvkar:
- house 3 m high;
- area 100 m².
We calculate the volume: multiply 100 m² by 3 m, we get 300 m³. We multiply 34 W by 300 m³, we get 10.2 kW. The settlement is located in the northern zone, so the last number is multiplied by a factor of 2. The result is 20.4. To this number is added another 20% for water heating and 25% of reserve power. To prevent premature wear of the equipment, add another 10% of power. As a result, the full power of the boiler room is obtained.
If several houses are heated, you need to calculate the energy expended for each of them and add up the resulting values. This amount will indicate the required thermal power.
For more accurate calculations, experts use formulas that include:
- heat loss coefficients;
- number of people in the room;
- types of thermal insulation materials;
- difference between external and internal temperatures.
The larger the heated objects, the more factors are taken into account.
— systems for the production and use of thermal energy
How to correctly convert these units
A watt is equal to a kilogram per square meter divided by cubic seconds. The prefix kilo means multiply by 1000. The same principle applies to power indicators, that is, 1 kW equals 1000 watts and 1000 volts. This means that 1 unit = 0.001 subunits. That is, if you make a power transfer, a 3 kW electrical appliance will be equal to 3000 W.
You will be wondering what power the 16a machine is designed for
Conversion formula
In electricity
To simplify measurements in electricity, a subblock is used. You can find out how many watts are in kilowatts and convert the units by multiplying watts by 103 and dividing by 1000. To do the reverse conversion, you need to multiply kilowatts by 103 or multiply the known values by 1000.
Amount in electricity
In heating
Joules must be used to measure thermal power. This is the work done by 1 newton per 1 meter. To convert joules to kilowatts, you need to use the joules subunit. 1 kJ contains 0.239 kcal. There are 4.1868 kJ in 1 kcal. 1 kW contains 860 kcal. This means that 1000 kcal is 1163 kW per hour.
Thermal measures
Energy units
1.1. Units of energy measurement used in the energy sector
- Joule – J – SI unit, and derivatives – kJ, MJ, GJ
- Calorie - cal - non-systemic unit, and derivatives kcal, Mcal, Gcal
- kWh is an off-system unit that is usually (but not always!) used to measure the amount of electricity.
- ton of steam is a specific value that corresponds to the amount of thermal energy required to produce steam from 1 ton of water. It does not have the status of a unit of measurement, however, it is practically used in the energy sector.
Energy units are used to measure the total amount of energy (thermal or electrical). In this case, the value can indicate generated, consumed, transmitted or lost energy (over a certain period of time).
1.2. Examples of correct use of energy units
- Annual demand for thermal energy for heating, ventilation, hot water supply.
- Required amount of thermal energy to heat ... m3 of water from ... to ... °C
- Thermal energy in ... thousand m3 of natural gas (in the form of calorific value).
- Annual demand for electricity to power the boiler room's electrical receivers.
- Annual boiler room steam production program.
1.3. Conversion between energy units
1 GJ = 0.23885 Gcal = 3600 million kWh = 0.4432 t (steam)
1 Gcal = 4.1868 GJ = 15072 million kWh = 1.8555 t (steam)
1 million kWh = 1/3600 GJ = 1/15072 Gcal = 1/8123 t (steam)
1 t (steam) = 2.256 GJ = 0.5389 Gcal = 8123 million kWh
Note: When calculating 1 ton of steam, the enthalpy of the source water and water vapor at the saturation line at t=100 °C was taken
Converter
You can use an easy to use converter to calculate the values. A converter is a system that converts source data into a given value. All that is required from the user is to enter existing data in the field and click the start button on the service being used.
Note! There are various system converters. Some convert these watts, others directly into kilowatts.
Convector
Conversion table for watt to kilowatt
The measurement values presented in the table below will help you calculate the energy used by a particular device and perform other mathematical calculations in electrical engineering.
Table
In general, kilowatt is a subset of watt, a symbol representing power. You can correctly convert Watts to kW into electricity and heat using the conversion formula, table and special online calculator.
The difference between kilowatt and kilowatt∙hour
In electrical engineering there is a quantity called kilowatt-hour, which is measured by electric meters. Many people substitute concepts, not seeing the difference between the definitions of “kilowatt” and “kilowatt ∙ hour”, considering the values as a parameter.
Despite the similarity of names, these are completely different values. Kilowatt ∙ hour is used to measure the amount of electricity produced or consumed per unit of time. Specifically, the electricity consumption of a 1 kW ∙ hour user indicates the energy consumed by a 1 kW user in 1 hour. Conversely, a kilowatt is a unit of power that indicates the rate at which electricity is produced or consumed.
Example: A recessed LED luminaire is equipped with a 35W LED lamp. For 1 hour of operation it consumes 35 W ∙ hour of electricity, for 2 hours, respectively, 2x35 = 70 W ∙ hour. With continuous operation for 5 days / 120 hours, the power consumption of the lamp will be 35×120 = 4200 W ∙ hour or 4.2 kW ∙ hour.
Relation to base and multiple units of power
Watt refers to a derived unit of power, so in practice it is sometimes necessary to determine the value of a parameter in relation to the basic units of the international SI system. In technical calculations, the following correspondences to the basic values are used:
- W = kgm²/s³;
- L = Hm/s;
- W=VA
The parameter has universal application and is equally used in technical developments in various fields of activity.
Thermal engineering uses non-SI units to measure heat output in 1 cal/hour. Our considered value is related to it by the ratio: 1 W = 859.85 cal/hour.
Often, for the convenience of working with large power values of power plants and power groups, the word watt can be used with the prefixes “mega” or “giga”:
- megawatt is designated MW/MW and corresponds to 106 W;
- gigawatt (abbreviated GW/GW) is equal to 109 watts.
On the contrary, in low-current information networks, electronic devices and modern electronic equipment, power is measured in fractions of watts:
- milliwatts (mW, mW) – 10-3 W;
- microwatts (μW, μW) are equal to 10-6 W.
Using these ratios, it is always possible to convert most parameters into the required power units.
Calculation of boiler room thermal power
Consumers are served by the following types of boiler houses:
- local (for one or more houses);
- block (for houses of an entire block);
- regional (large structures).
All boiler rooms can be heated with the following types of fuel:
- hard (wood, peat, coal);
- gaseous;
- liquid (fuel oil, oil, oil, diesel fuel);
- combined.
When burned, solid fuel releases gases and leaves ash. Pellet boiler houses use pellets, which are produced from the remains of lumber (branches, sawdust) and sunflower husks.
The use of solid fuel requires equipping boiler houses with special grates that allow ash to pass through. The wood must be dry; sheds are used to dry firewood. It is better to use hardwood firewood, because... pine logs clog chimneys with combustion products.
Thermal energy for this type of fuel is calculated as follows: per 1 m² of building area there should be 100 W/h. For a house with an area of 100 m², the power is 10 kW. Knowing the number of days on which heating is produced, the total thermal output can be calculated.
Boiler houses can operate on liquefied and main gas. For gas boiler houses, there are special requirements for laying pipes to ensure the operation of boilers (piping). The simplest option for calculating the power of gas heating equipment is 1 kW of energy per 10 m² of area. In addition, the area of the room, its location in a particular climate zone, and the heat loss of the heated building are taken into account. Accurate calculations can be performed by heating engineers. They will also help determine fuel consumption over the required period of time.
In remote areas, liquid boiler houses are installed. Fuel consumption for them is measured as follows: 1 kg of diesel fuel gives 10 kW.
The thermal energy released is calculated in megawatts (mW) or gigacalories (Gcal).
In combined boiler houses the following is used as fuel:
- gas and diesel fuel;
- gas and fuel oil;
- gas and oil;
- gas and waste oil.
The priority and secondary fuel is determined by the owner of the boiler house. The type of boiler depends on the type of coolant chosen.
When constructing and operating low-power heating boiler houses, several factors are taken into account to calculate thermal energy:
- wear and tear of heated buildings;
- the degree of their insulation;
- sizes of windows and doors.
How to calculate the total power of household appliances
The installed power of a house or cottage is important when calculating and choosing electrical wiring and machines. Without this parameter it is impossible to design the power supply of the house.
To find out the installed power, you need to select energy consumption data from the equipment data sheets. For example, as indicated on the license plate.
| Name | Power, W |
| A television | 150 |
| Water heater | 1,500 |
| Electric oven | 2 000 |
| Fixtures (total number of light bulbs throughout the house) | 1,000 |
| Computer | 100 |
| GENERAL: | 3.750 W or 3.75 kW |
To correctly calculate the power supply to a home, the combination coefficient is taken into account. Indicates how many consumers are running at the same time.
For installed power in a house, cottage, apartment up to 14 kW, a coefficient of 0.8 is used in the calculations. That is, the total value of the loads is taken and multiplied by 0.8. For our example, the calculations require a power of 3.75 * 0.8 = 3 kW.
Gcal and Gcal/h: what is the difference
If it is necessary to calculate the consumer's payment for state heat and power services (house heating, hot water), the value Gcal/h is used. It denotes a reference to time - how many Gigacalories are consumed during heating for a given period of time. Sometimes it is also replaced by Gcal/m3 (how much energy is needed to transfer heat to a cubic meter of water).
The value of Gcal/h can be calculated independently using this formula:
Q=V*(T1 – T2)/1000, where
- Q – amount of thermal energy;
- V – volume of liquid consumption in cubic meters/tons;
- T1 is the temperature of the incoming hot liquid, which is measured in degrees Celsius;
- T2 – temperature of the incoming cold liquid, similar to the previous indicator;
- 1000 is an auxiliary coefficient that simplifies calculations by eliminating numbers in the tenth digit (automatically converts kcal to Gcal).
This formula is often used to construct the operating principle of heat meters in private apartments, houses or enterprises. This measure is necessary when the cost of this utility service sharply increases, especially when calculations are generalized based on the area/volume of the room that is heated.
If a closed type system is installed in the room (hot liquid is poured into it once without additional water), the formula is modified:
Q= (( V1* (T1 – T2)) – (V2* (T2 – T)))/ 1000, where
- Q – amount of thermal energy;
- V1 – volume of consumed thermal substance (water/gas) in the pipeline through which it enters the system;
- V2 is the volume of thermal substance in the pipeline through which it returns;
- T1 – temperature in degrees Celsius in the inlet pipeline;
- T2 – temperature in degrees Aim in the outlet pipeline;
- T – cold water temperature;
- 1000 – auxiliary coefficient.
This formula is based on the difference between the inlet and outlet values of the coolant in the room.
Depending on the use of a particular energy source, as well as the type of thermal substance (water, gas), alternative calculation formulas are also used:
- Q= (( V1* (T1 – T2)) + (V1 – V2)*( T2 – T))/1000
- Q= (( V2* (T1 – T2)) + (V1 – V2)*(T1 – T))/1000
In addition, the formula changes if electrical devices are included in the system (for example, heated floors).
Converting watts to kW
For example, the iron says 2000 watts (W), this means 2 kW, another example with a 100 W light bulb, when converted to kW we get 0.1 kW, so:
1 kW = 1000 W
By analogy, other meanings can be translated:
You can also convert 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 kW, etc. In watts:
Power (W) Power (kW)
| 1000 | 1 |
| 2000 g | 2 |
| 3000 | 3 |
| 4000 | 4 |
| 5000 | 5 |
| 6000 | 6 |
| 7000 | 7 |
| 8000 | eight |
Calculation by area
Heat consumption is calculated based on the area of heated premises. It is considered normal to consume 1 kW of heat per 10 m² of a room up to 2.7 m high. To calculate the consumption of all thermal energy, you need to know the total area of the building.
In this way, the productivity of boilers is calculated depending on the area of the building.