You can install absolutely any heating boilers in the attic, observing the necessary safety measures.
Installing a heating boiler in the attic is a non-trivial solution. But what to do if the cottage is small, there is no basement, and there is no ground floor. We’ll tell you when the decision to install a boiler in the attic is justified and what features such a home heating system has.
Installation of a heating boiler in the attic
- Is it even possible to install heating boilers in the attic and second floor of the house? According to experts, this is not the best option, but in extreme cases, if there is no other way out, you can go for it, observing certain conditions;
- Which boiler can be installed above the first floor of the house? With a closed combustion chamber! It is much safer than the traditional one, although it costs half as much. Condensing boilers are suitable, in which the combustion chamber is always closed. In this case, there will be no risk of carbon monoxide poisoning, and the room will not cool down while the boiler is operating;
- It’s clear about the closed combustion chamber, but still, which boiler is ideal for installation in the attic? Wall-mounted gas, power up to 30 kW. Such boilers are compact, do not take up little space, and do not require a separate room. The indicated power will be quite enough to provide heat in a cottage designed for one family, that is, a relatively small one. The main thing is that the wall can support the weight of the boiler. However, we can solve this issue even in frame buildings;
- And if the boiler runs on solid or liquid fuel, not gas, can it be installed in the attic? Theoretically, yes. However, think about how you will service a solid fuel boiler on the top floor? You will have to constantly carry briquettes, coal and firewood up the stairs. And solid fuel boilers weigh a lot; the ceilings will need to be strengthened. Liquid fuel boilers are noisy and emit an unpleasant odor, so they are absolutely not suitable for installation on upper floors;
- What should the chimney be like if the boiler is installed in the attic or second floor? This is where problems can arise. In general, the height of the chimney for a gas heating boiler should be at least four meters. Imagine if such a pipe rises above your roof. This can ruin the appearance of the house. You can get rid of the need to build such a high chimney if you choose a boiler with a closed combustion chamber that has a coaxial pipe. For boilers with a power of up to 30 kW, which we recommend for installation in attics and second floors, the chimney can be routed directly through the outer wall. In this case, the pipe outlet should be located at a height of 2.5 meters from the ground, but in the case of an attic this is not a problem. The nearest window from the chimney going through the wall should be at least half a meter;
- What should the heating system be like if the boiler is installed above the first floor? Closed! This is a must. With an open heating system, when fluid circulation in the system occurs naturally, all heating devices are located above the boiler itself. In the case of installation in the attic or second floor, this condition for normal operation of the heating system cannot be maintained. Therefore, it becomes mandatory to install a circulation pump, which will become part of a closed heating system for the house;
- Will there be enough natural ventilation for a boiler in the attic? In general, yes. But for greater reliability and safety, experts advise making an unclosable hole 30 centimeters from the floor. The exhaust vent is located under the ceiling. The total area of such ventilation should be at least 200 square centimeters.
We state: a wall-mounted gas boiler with a closed combustion chamber and a circulation pump, in addition, can be safely installed and used in the attic or second floor of a private house. published econet.ru
If you have any questions on this topic, ask them to the experts and readers of our project here.
Did you like the article? Write your opinion in the comments. Subscribe to our FB:
Heating scheme from a gas boiler in a two-story house: review and comparison of the best heating schemes
Are you building a new house or renovating an old one, and it comes to the heating system?
Don't know what type of wiring is best to choose? A correctly designed heating scheme from a gas boiler in a two-story house is the key not only to warmth and comfort in the winter, but also to the uninterrupted operation of the equipment. A competent heating project takes into account many factors - from climate and financial capabilities, to the need for spot adjustments and aesthetic issues. In this article we will analyze in detail all possible types of heating systems, present and compare ready-made schemes with the most successful set of parameters for different cases, and also indicate the possibilities of their modification.
What kind of heating boilers are installed in the attic of a house?
It is convenient to install boilers on natural and liquefied gas, liquid fuel and electric in the attic. The heating system must have forced circulation of coolant
.
Forced circulation of coolant in the heating system using a pump allows you to install a heating boiler in a house at any height from ground level.
Solid fuel boilers and all other boilers operating on a heating system with natural coolant circulation must be placed on the lower level of the house.
Heating boilers with an open firebox (like a fireplace or stove) or with a closed combustion chamber are used.
The closed combustion chamber of the boiler is completely isolated from the room. Combustion air is supplied to the chamber from outside the house through a special pipe using an electric fan. Combustion products are forced into the chimney under the influence of excess pressure created by a fan in the combustion chamber.
The best schemes for a two-story house
In each specific case, it is necessary to develop an individual heating project that will ensure efficient and economical operation.
To make the right choice, you should consider the following factors:
By answering all these questions and knowing the features of different schemes, you will get an idea of the required option.
Next, we suggest choosing one of the proven effective schemes for connecting heating devices to the boiler and adjusting it in accordance with your layout.
Single-pipe Leningradka - reliable and cheap
This one-pipe scheme is one of the cheapest, simplest and oldest, but relevant and popular to this day. Using only radiators allows for a mixed type of circulation in case of a power outage. To do this, the gas boiler must be non-volatile, all pipes must have a slope of 5 - 10 mm per 1 linear meter.
To make settings easier, you can install thermostats on the supply of each battery and control valves on the battery bypasses. An additional valve on the riser will make it possible to turn off the heating circuit of a separate floor.
Warm floors can be included in the system as a separate, third circuit, or replace radiators on one floor. However, in this case, the division of flows must pass through a thermal mixer or hydraulic arrow so that the floor does not heat up to 70 - 80 ° C in cold weather, like radiators.
Also keep in mind that during a power outage, only the batteries will work, and in a strictly horizontal floor heating circuit the coolant will be idle.
The main limitation when installing such a system concerns the heated area: a house larger than 100 m2 does not warm up with natural coolant circulation. Such a system will only save you from defrosting pipes and rupture of the boiler heat exchanger during a long shutdown, but not from the cold.
In addition, even with forced circulation, such a heating circuit is almost impossible to set up if it includes more than 5 - 7 batteries. That is, for ease of use in a large house, it is necessary to divide the circuit into a larger number of circuits.
You can read more about the arrangement of a single-pipe heating system in Leningradka in this material.
Tichelman loop with forced circulation
As we have already mentioned, this connection scheme ensures the most efficient operation and convenient adjustment of each radiator at a relatively low cost of materials.
The system can cover the entire house with one loop, be divided into 2 circuits by floor, as in the diagram, or be used only for one floor or part of it.
Modern radiator heating systems are often equipped according to this plan, if it is possible to disguise the pipeline. In addition, devices of different types can be included in one circuit: radiators, convectors, heat curtains.
Manifold connection and mixed systems
Using a collector to separate not only heating circuits, but also to individually connect each device is the most modern and easy-to-use solution.
dacha on the black river restaurant
It has a number of advantages:
The main disadvantage of this solution is the high cost of both materials and installation. You will need much more pipes than for any other connection scheme, and laying communications in the floor, especially if the concrete screed has already been poured, will cost a lot.
It is also worth considering that such a connection completely eliminates the possibility of natural circulation.
In two-story houses, as a rule, one collector is installed in the center of each floor, but with a large number of heating devices and collectors there may be more. For underfloor heating systems, separate collectors are used, with a lower coolant temperature.
Vertical gravity scheme
In addition to the standard options described, there are also more exotic ones, such as a vertical two-pipe with natural circulation. Perhaps this is the best solution for a two-story house in which the lights are often turned off.
Due to the fact that water circulates more easily in a vertical system than in a horizontal one, and the large expansion tank under the roof acts as a collector, the most efficient and uniform heating is ensured, even without the use of a pump.
The hot water supply pipe to the expansion tank and the return line should be the thickest; The supply risers supplying the 2nd floor are slightly thinner, their lower part on the 1st floor is of even smaller diameter, and the radiator connection pipes have the smallest cross-section.
Requirements for a gas boiler room
Since gas boilers are devices with a high fire and explosion hazard, boiler rooms with such a boiler are subject to certain requirements.
Basic requirements for gas boiler rooms in a private home:
Installation of gas boilers in living rooms of the house is not allowed.
It is prohibited to install the boiler near sources of open fire.
At the same time, no more than 4 gas boilers are allowed to be installed in the boiler room, the total power of which should not exceed 100 kW.
Boiler houses based on gas boilers with a sealed (closed) combustion chamber are not subject to requirements establishing the minimum volume of the room.
The minimum volume of the boiler room for a gas boiler with an open combustion chamber is determined based on the boiler power: Up to 30 kW - 7.5 m³; From 30 to 60 kW – 13.5 m³; From 60 to 200 kW – 15.0 m³.
In the boiler room, the ceiling height for a gas boiler must be at least 2.2 m.
The required room area for a gas boiler is selected at the rate of 4 sq.m per one gas boiler.
The boiler is installed in such a way that there is unobstructed access to it from any side. The distance between the front surface of the boiler and the opposite wall should ensure ease of maintenance of the boiler and is at least 1 m.
The floor in the boiler room must be made of non-combustible materials.
When installing a floor-standing boiler, the floor surface must be level.
The doorway leading to the boiler room must have a minimum width of 0.8 m.
If a boiler with an open combustion chamber , then a window with an opening area of 0.25 sq.m. must be provided in the room. If a boiler with a closed chamber is used, then such a window is not required.
The boiler room must have a power supply with an individual circuit breaker and grounding.
A shut-off unit must be installed on each gas line supplied to the boiler.
To remove combustion products, you need to install a gas-tight chimney, the diameter and height of which must correspond to the characteristics of the boiler. The minimum height of the chimney should not be lower than the ridge of the building's roof to prevent back draft.
What to make a separate boiler room from
General requirements for the organization of home boiler rooms are regulated by building codes and regulations (SP 41-108-2004, SP 42-101-2003, SNiP 42-01-2002, etc.). And it will be better if the homeowner is guided by these schemes and rules during construction. After all, this will help to avoid disagreements with supervisory authorities and without problems obtain permission to operate heating equipment.
The meaning of regulations developed by government agencies can be difficult for the average person to comprehend. But, fortunately, from the whole stream of information, several basic thoughts can be identified that relate to the main requirements for the design of a home boiler room. This is exactly what some users of our forum did, who compiled a list of these requirements.
beautiful recreation areas in a country house
Svetlana V has chosen the most important requirements for the arrangement of gas boiler houses, but they are also relevant for other types of fuel. On our own behalf, we can add a few more important points.
Here is an example: if the minimum volume of a boiler room is 15 m³, then its area must be greater than or equal to 6 m². The door to the boiler room may not be too wide, but it is not allowed to be less than 0.8 m wide.
During the operation of the boiler room, it sometimes becomes necessary to drain water from the heating system. The boiler room must be equipped with a drainage hole or outlet to the sewerage system.
The walls, like other elements of the boiler room, must be finished with materials that prevent ignition and the rapid spread of fire. For wall cladding, plasterboard, ceramic tiles or glass-magnesium sheets are quite suitable.
Of all types of floor coverings in a boiler room, it is best to use special tiles or porcelain stoneware.
In order to decorate the boiler room ceiling, you should use plasterboard (possibly with insulation) or plaster. The use of tension and suspended finishing solutions in this case is unacceptable. This will be impractical and such materials have a high degree of fire hazard.
If you would like to learn more about the design of an ideal boiler room, as well as the requirements that apply to the design of a boiler room. If you need to get acquainted with the advice of people who have practical experience in this matter, then please visit the corresponding section of our forum. You can read everything about how to choose a heating system for your home, as well as about the installation and operation of heating systems in detailed articles devoted to these issues. We offer everyone to read material dedicated to the construction of energy-efficient houses.
Source
Where to install a heating boiler in the attic?
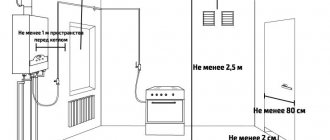
Wall-mounted boiler for natural gas or electricity with a power of up to 50 kW. does not require a special room for its installation.
An electric or gas boiler with a closed combustion chamber and forced supply of outside air can be installed in any attic room without constant presence of people - in the hall, utility room, workshop, but not in the bedroom. It is not recommended to install the boiler in the bathroom, due to the harmful effects of moist air on the boiler parts.
To install both a gas boiler and a boiler using another fuel, it is still more convenient to provide a separate room in the attic. In addition to the boiler, other related equipment for the heating and hot water supply system is also located in this room.
In an attic with sloping ceilings, the boiler is placed in the part where the ceiling height is at least 2.2 m. The volume of the room should not be less than 6.5 m 3 for a boiler with a closed combustion chamber and at least 7.5 m 3 for boilers with open firebox.
To install an oil-fuel boiler in a room, waterproof the floor and walls to a height of at least 10 cm. The floor covering must be non-flammable.
The door to the boiler room must have a sealed threshold with a height of at least 4 cm, open outward and be at least 0.8 m wide.
When arranging the room, it is necessary to take into account that the boiler room can serve as a source of unpleasant odors, and the operation of the boiler is accompanied by the noise of a fan forcing air into the burner or a smoke exhauster. The noise is especially noticeable at night.
When installing a floor-standing boiler in a room, it is necessary to maintain minimum distances: the free distance in front of the boiler is 1 m, above the boiler is 0.7 m, the width of the passages between the boiler and the wall is 1 m.
The boiler room must have fireproof floors and walls with a fire resistance limit of at least 0.75 hours.
The premises must be supplied with: electricity, water supply and sewerage (to drain the coolant).
Layout
The correct placement of boiler equipment is an issue that can only be resolved by knowing the area of the room, the complete list of necessary devices and their dimensions. In most cases, in order to avoid annoying mistakes when arranging equipment, it is advisable to contact a professional design and installation organization.
This is what one of the FORUMHOUE participants decided for himself about this.
I try to do everything in a normal, formal and beautiful way. Example: I installed a chimney (“Schidel”) with a ventilation duct. When coordinating the gas supply project for the house, the girl engineer spent a long time asking how these elements were organized, what and how they were made. All this is reflected in the technical specifications. The project was approved by the regional gas authority without any problems. After approval, a condition appeared in the technical specifications regarding the organization of a lattice opening in the lower part of the entrance door.
But you can give some general recommendations regarding breading even before its development begins.
Thus, unobstructed access to the heating boiler must be organized. This condition must be met even in cases where the device does not require regular refueling (meaning an electric or gas boiler). The distance from the walls of the boiler room to the equipment installed in it must comply with the requirements in the technical documentation diagrams for these devices. If we are talking about the layout of lighting fixtures, then they should comprehensively illuminate the space - in case you need to make minor repairs (replacement of pumping equipment, repair of boiler automation, etc.).
Unobstructed access should be organized not only to the heating boiler, but, if possible, also to other devices - to the circulation pump and electrical switches, to the boiler and ventilation holes, to pumping equipment, chimney elements, etc. Take care of convenience in advance! After all, this will help to avoid difficulties in the process of further operation.
Ventilation of a boiler room in a private house
Building rules (clause 6.5.8 SP 60.13330.2016) require that in residential buildings, for premises housing gas equipment (gas boilers, water heaters, stoves, etc.), mechanical forced exhaust ventilation and natural or mechanical supply ventilation are provided.
In a room where a boiler using a different type of fuel is installed, an exhaust duct for a natural ventilation system must be installed. Exhaust ventilation should provide three air changes per hour in the room (exhaust duct capacity, m 3 /hour
= room volume,
m 3
x 3
1/hour
).
In addition, for normal operation of ventilation and the boiler, it is necessary to ensure an influx of fresh air into the room.
For a boiler with an open firebox, a supply valve is installed in the wall to draw air from the street. The supply valve in the boiler room is installed at a height of no more than 30 cm
. from the floor. The capacity of the supply valve must be greater than the sum of: the capacity of the exhaust ventilation duct + the amount of air required for combustion of fuel from the boiler passport.
If a boiler operating on liquefied gas is installed, the inlet of the exhaust duct is located at floor level, and the exhaust duct should be located with a slope in the direction of the outer opening. Liquefied gas is heavier than air.
The air supply for ventilation of a boiler room with a boiler with a closed combustion chamber is usually made from an adjacent room or through a supply valve from the street. To allow air flow from the adjacent room, a ventilation grille with an area of at least 800 cm2
.
For a boiler with an open combustion chamber, if the air comes directly from the street, then a supply ventilation hole of size is sufficient at the rate of 8 cm 2 per 1 kW of boiler power, but not less than 200 cm 2. If the air supply comes from an adjacent room of the building, then the minimum size of the supply ventilation opening should be determined at the rate of 30 cm 2 per 1 kW of boiler power.
Types of private gas heating systems
There are many parameters that determine the type of heating system; choosing a gas boiler as the main heat generator is only the first step. You can set up a heating circuit by connecting all the devices with one pipe, or by installing separate supply and return lines.
Also, the structure of the system depends on the heating devices used, the type of expansion tank, the layout and area of the house. In addition, you can divide the system into several separate circuits and provide for the possibility of natural circulation in case of a power outage, and much more.
We will consider all the possibilities, advantages and disadvantages of each type of system in more detail below.
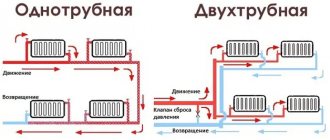
One- and two-pipe connection diagrams
Within these two types, 5 basic connection diagrams can be distinguished.
Let's consider them in order of increasing design complexity and cost:
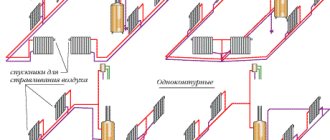
The simplest one-pipe radiator connection scheme implies that the coolant enters the second radiator only after the first one has passed through, and so on. A warm floor can also be included in such a system - it is connected last, from the return line of the farthest battery.
A simple one-pipe circuit can not only be drawn up and calculated, but also installed independently. In addition, it is easy to equip it with the possibility of natural circulation.
However, such a system has a serious drawback: the temperature with each battery decreases noticeably, and it is impossible to regulate this in any way. If you limit the supply temperature to the first radiator using a thermostat valve, the temperature in all of them will decrease proportionally - only increasing the number of sections of the last radiators partially helps.
But in two-story houses, as a rule, the area is significant and the systems are too long for such a scheme to work productively. Due to the impossibility of customization, a simple one-pipe system is practically not used.
The improved single-pipe circuit, the so-called “Leningradka”, provides a bypass on each radiator. Thus, part of the coolant passes by the radiator, and a hotter mixture enters the next one.
If you add taps and thermostats to the circuit, you get a system that is average in both price and functionality between a simple one-pipe and a two-pipe - a fairly popular solution.
A two-pipe system involves dividing the supply and return into two separate pipes connected to each radiator. Much more materials will be required, but the hot coolant will not mix with the return flow, and therefore will effectively warm up a much larger number of batteries.
It is convenient to lay dead-end branches where it is not possible to loop pipes around the room, for example, because of a balcony door. The direction of flow in the supply and return turns out to be opposite, and therefore there is a possibility that the water will follow the path of least resistance and close the circulation circle through the first radiator, and will not get into the others at all.
The problem is solved by using balancing valves, as well as pipes of a smaller cross-section for connecting to the radiator than for mains.
The Tichelman loop is the most successful and popular solution in terms of cost and efficiency. Its difference is that the direction of flow in the supply and return is parallel, therefore, no matter which battery the coolant flows through, the length of the circulation circle will be the same, there is no path of least resistance. As a result, all batteries heat evenly, but each of them can be adjusted separately or completely turned off without affecting the operation of the system.
The collector circuit implies the presence of two collectors, for supply and return, from which pairs of pipes are separated by rays to each heating device. For best efficiency, the collector is positioned so that the distance from it to each heating device is approximately the same. Typically, a separate collector is installed on each floor.
Only in such a system will each battery be supplied with a coolant of the same temperature, and it is the system that is easiest to control and change the heating power of individual points.
The main disadvantage of the radial connection scheme is the need for a large number of pipes, which not only increases the cost, but also complicates installation. On the other hand, the eyeliner of such systems is completely hidden, and this looks aesthetically pleasing.
Another important point is that the collector system, unlike all the previous ones, cannot be gravitational. This means that even with a non-volatile boiler, the heating will turn off as soon as the lights are turned off and the pump stops.
Often in two-story houses, different heating layouts are used for different rooms, depending on their layout, area and heating devices used.
In a two-story house, single-pipe designs with a single supply pipe are practically not used, because the last radiators in the circuit work extremely inefficiently. Depending on the area of the house, separate contours correspond to each floor, several or even each room.
It is also customary to separate the radiator circuit from the heated floor, due to the need for different operating pressures and temperatures.
The division of the supply from the boiler into different circuits can be done through a hydraulic arrow, a manifold, or a combination of both. The first provides flows of different pressures and temperatures for different systems, while the second is effective for circuits with the same type of devices, for example, radial connection of radiators.
Open and closed systems
This parameter indicates whether there is contact of the coolant with air, and is determined by the type of expansion tank.
The expansion tank compensates for the increase in liquid volume when heated, preventing an increase in pressure in the system. The open type tank has a hole at the top and works simply due to the volume reserve, filling to different levels. To prevent water from overflowing from it according to the principle of communicating vessels, such a tank must be installed at the highest point of the system. In a two-story house, this is usually the top of the supply riser.
There are many disadvantages to such a system. The coolant comes into contact with open air, which means it evaporates and is enriched with oxygen. As a result, it is forbidden to fill such a system with antifreeze; water will need to be added regularly, and excess air constantly provokes corrosion and air locks. In addition, when removed to the attic, the tank requires careful insulation, and in a room on the 2nd floor it is problematic to disguise it.
The closed expansion tank is sealed and consists of two chambers separated by a membrane. It works due to the ability of air to compress: when the system is heated, water occupies most of the tank, the pressure in the air chamber increases. When cooling, it is this pressure that pushes water back into the system.
Irbit city rent an apartment for a long term
Such an expansion tank can be installed at any point in the system, most often on the return line, in front of the pump. The system with a closed tank is absolutely sealed; it can even be filled with a toxic solution of ethylene glycol. Even ordinary water under such conditions is gradually cleared of impurities and dissolved gases, turning into an almost ideal coolant.
By type of heating devices
Different devices can be included in one heating system: radiators, heated floors, convectors and others. They can be combined even within the simplest single-pipe circuit, but with the gravitational type of circulation it is better to use conventional batteries.
Warm floors are not only pleasant and convenient, but also economical, since warm air fills the lower, living part of the room, and cools under the ceiling. This solution is especially indispensable if there is a child in the house. They are also often installed in the bathroom and kitchen.
Systems consisting only of heated floors can only be installed in well-insulated buildings and in a temperate climate, otherwise in cold weather it will either be cool in the house or it will be impossible to walk on a hot floor. As a rule, heated floors are combined in one scheme with a small number of radiators - this is beautiful, economical, and convenient.
Radiators are the most popular for good reason: they work both by radiating heat from the outer plane, warming up the air and objects in front of them, and by the convection principle, passing air flows through the ribs.
The main disadvantage of traditional batteries is the difficulty of placing them without disturbing the interior design, because any camouflage screens reduce efficiency.
By type of coolant circulation
Water or antifreeze most often moves through the system from the circulation pump: it creates the necessary pressure, ensuring fast, efficient and uniform heating. However, the presence of a pump makes any system energy-dependent - that is, in the event of a power outage, the heating will also turn off.
An alternative option is gravity systems. They are designed in such a way that the coolant circulates due to an increase in density during cooling, as well as under the force of gravity - due to the slope of all pipes of the circuit.
Such a heating scheme for a private two-story house with a non-volatile gas boiler will work even if electricity is not connected at all, but the circulation speed, and therefore the efficiency, will be significantly lower. In addition, slow flow leaves much more sediment on the walls of the system.
The ability of systems with natural circulation to self-adjust is interesting: the colder it is in the house, the faster the coolant in the radiators cools, the difference in supply and return temperatures increases, and hence the flow rate and heating efficiency.
If regular power outages are a harsh reality and the house is small, the best solution is a mixed circulation system. Its plan should be calculated as for a gravity system - with pipe slopes, a boiler at the lowest point, etc.
It is possible to install heated floors in such a system, but they will only work when the pump is turned on.
Horizontal and vertical wiring
In a two-story house, it will not be possible to get by with only horizontal pipelines - at least one riser must supply coolant to the second floor. But this does not change the type of wiring as a whole.
Horizontal wiring can be done within each floor. With it, pipes connect all radiators of the same level into a single circuit. It is the most versatile and popular, and can be implemented in any layout.
It is easy to imagine a single-pipe vertical distribution using the example of the heating system of apartment buildings. The layout of each floor, including the location of radiators, matches perfectly. Each battery is connected by a riser to the same one in the neighbors below and above, and there are no horizontal heating pipes in the apartment.
If the layout of your house allows you to place all the radiators exactly on top of each other, the vertical layout will work more efficiently, especially with the gravitational type of circulation. In addition, risers are easier to disguise than horizontal pipelines.
However, when installing the system, you will need to cross the floors many times, and this is more difficult than running a pipe through a wall.
Automatic control system for gas contamination and gas leakage protection
Dangerous properties of gas fuel:
- the ability of gas to form fire-explosive mixtures with air;
- suffocating power of gas.
The components of gas fuel do not have a strong toxicological effect on the human body, but at concentrations that reduce the volume fraction of oxygen in the inhaled air to 16%, they cause suffocation.
When gas burns, reactions occur that produce harmful substances, as well as products of incomplete combustion.
Carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide) is formed as a result of incomplete combustion of fuel. A gas boiler or water heater can become a source of carbon monoxide if the air supply and flue gas removal system is faulty (insufficient draft in the chimney).
Carbon monoxide has a highly targeted mechanism of action on the human body, including death. In addition, the gas is colorless, tasteless and odorless, which increases the risk of poisoning. Signs of poisoning: headache and dizziness; there is tinnitus, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, flickering before the eyes, redness of the face, general weakness, nausea, and sometimes vomiting; in severe cases, convulsions, loss of consciousness, coma. Concentrations in the air of more than 0.1% lead to death within one hour. Experiments on young rats showed that a CO concentration of 0.02% in the air slows down their growth and reduces activity compared to the control group.
Gas alarm - gas leak sensor
and carbon monoxide gas alarms in residential buildings and apartments containing gas boilers, hot water heaters, stoves and other gas equipment
The methane gas alarm serves as a leakage sensor for household natural or liquefied gas from gas equipment. The carbon monoxide alarm is triggered in the event of malfunctions in the smoke exhaust system and the entry of flue gases into the room.
Gas sensors should be triggered when the gas concentration in the room reaches 10% of the LPR of natural gas and the CO content in the air is more than 20 mg/m 3 . Gas alarms must control high-speed shut-off valves installed at the gas inlet into the room and shut off the gas supply based on a signal from the gas sensor.
NCPRP and VKPRP are the lower (upper) concentration limit of flame propagation - the minimum (maximum) concentration of a flammable substance (gas, flammable liquid vapor) in a homogeneous mixture with an oxidizer (air, etc.) at which it is possible for a flame to spread through the mixture to any distance from ignition source (open external flame, spark discharge).
What types of boilers can be installed
You can install absolutely any heating boilers in the attic, observing the necessary safety measures. Do you need any? Imagine the need to daily climb coal or firewood to the second floor, and then descend back with ash. This is not a romantic fireplace for the weekend, a daily, thankless task. In addition, attics are often used as recreation areas and bedrooms. Soot and stench should not be present in such an area.
It is much more correct to use an attic with more environmentally friendly heating - electric or gas, using mains or liquefied gas. Particularly suitable are wall-mounted turbocharged gas boilers, which do not require a separate room and provide hot water. Although a modern solid fuel or liquid fuel boiler is quite acceptable if there is a separate room.
Premises requirement
The best solution for the attic is wall-mounted turbocharged gas heating, which only requires a ceiling height of 2.3 m, and a sufficiently strong wall that can withstand the weight of a fairly light boiler - about 50 kg. There are no additional requirements for the fire resistance of the walls and the quality of the chimney; the coaxial chimney is guaranteed to remove combustion products, and the boiler is fireproof. A turbocharged boiler will solve the rather complex problems of guaranteed gas removal.
For chimney boilers, in addition to the required height of the room, it is necessary to ensure the height of the chimney - 5 m, the volume of the room - 15 m3. The air flow through the opening is at least 200 cm2, the boiler must be more than 0.5 m from the window.
Solid fuel boilers are quite heavy; taking into account fuel storage, the load on the ceiling is quite large - up to 0.5 tons. This must be taken into account when placing the boiler room, reinforcing the ceiling, installing retaining structures.
Liquid fuel boilers are the most problematic in terms of requirements for the boiler room premises. It is necessary to prevent fuel from leaking out of the combustion chamber if there are problems with the pipeline. To do this, it is necessary to waterproof the floor with an overlap of at least 10 cm onto the walls. The firebox threshold must be at least 4 cm in height. These measures are more likely to be preventive measures; in case of real accidents they help little. In addition, the smell of diesel fuel and oils penetrates even to the first floor.
The most important requirement is fire safety. Which is not only to protect combustible structures from the elevated temperature of the heat source, but to protect the entire room from possible problems. The smartest thing is to make a heating project linked to a specific boiler; for a gas boiler this is definitely necessary. If you don’t want to do this, then it’s better to invite fire supervision, at least not officially, to identify possible troubles.
Flue gas problem
When burning any type of fuel, combustion products are formed, which must be removed outside the premises.
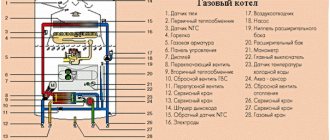
In traditional boilers, combustion products are discharged through a chimney, in which natural draft is present. The principle of operation of the chimney is simple - lighter hot gases tend to rise, obeying the buoyancy force. The higher the temperature of the gases, the better the thrust. If there is insufficient draft in the chimney, normal operation of the heating device is not guaranteed. Modern boilers have protection against lack of draft - the equipment automatically turns off. Gas boilers come in two types - with open and closed fireboxes. In the former, combustion products always exit through natural draft. Such boilers are also called atmospheric boilers. In the second case, it is always forced. This is the so-called turbocharged boilers.
The chimney of atmospheric gas boilers cannot be shorter than 4 m, and for liquid fuel boilers - shorter than 5 m. It is often difficult to meet these requirements when the boiler is located in the attic, since from the boiler outlet to the roof surface is usually no more than 2 m. It turns out that the height of the chimney above The roof slope must be at least 2 m for a gas atmospheric boiler, and such a long chimney does not always fit into the architecture of the cottage.
Boilers with a closed combustion chamber do not have the disadvantages of atmospheric engines. They do not depend on chimney draft, weather conditions and wind direction. Combustion products are discharged through a coaxial pipe, which also serves to supply fresh air to the firebox. Exhaust gases are removed due to excess pressure created by a built-in fan. The specificity of this solution allows the use of not only vertical, but also horizontal chimneys, along their entire length. The only limitation is that they cannot be longer than 5 m. The coaxial pipe of a boiler with a closed combustion chamber is most often routed through the wall and ends with a special tip on the outside. If necessary, exhaust gases can be discharged through the roof. Special ceramic or steel chimneys are designed for this purpose. As a rule, this is a pipe within a pipe, where gases are discharged through the internal channel, and air is taken in through the external one.
Gas boilers are either convection or condensation . Convection - these are the already described atmospheric ones with an open firebox. Condensing boilers have a closed firebox and are designed to remove residual heat from combustion products. In such boilers, gases are removed forcibly, since their temperature is much lower than the level that would provide natural draft in an atmospheric chimney.
When exiting a horizontal coaxial pipe through a wall, two conditions are met:
In the attic, where a boiler with both an open and a closed combustion chamber is installed, good ventilation must be ensured. Despite the fact that closed combustion chambers are completely isolated from the room, an emergency situation with depressurization cannot be ruled out.
The room with the boiler must have constant ventilation, where the area of the supply opening is at least 200 cm², and its lower edge is no higher than 30 cm from the floor. Outside air or air from neighboring rooms equipped with natural ventilation should flow through this opening. The exhaust ventilation hole is made the same area as the supply ventilation hole. If the supply opening leads to an adjacent room with natural ventilation, then you should pay attention to sufficient inflow, which should be ensured by leaks in window frames and doors. Sealed windows with double-glazed windows must have functioning ventilators.
So, to summarize, we will draw the following conclusions. In the attic, it is most advantageous to install a wall-mounted gas boiler with a closed firebox, operating in a closed-type heating system. It does not take up much space, is easy to install, does not put a load on the ceiling, is easy to install and provides a high level of safety.
Heating equipment in a home is often installed in a room called a boiler room. Since this is technological equipment and unsafe in emergency situations, the room for heating equipment must be installed in accordance with existing standards and rules for its operation. A boiler room is usually equipped if the house is not connected to central heating, but has its own autonomous heating system, so the characteristics of each boiler room will be different, but they must be brought to general requirements, which depend on the type of heating device and its placement in the room. Therefore, before installing heating equipment, its placement is designed.
Boiler room on the house plan
» alt=»»> General provisions Places where it is recommended to equip a boiler room in a private house: 1. Attic or attic; 2. Separate economic building; 3. Autonomous module – mini-boiler room in a separate container; 4. Room in the house; 5. A room attached to the house. The optimal placement of boiler equipment is an attic or basement, but when installing heating in an old house, it is better to do this in a separate building or an attached room to the house. The arrangement of a boiler room in a private house depends on the type of heating unit - it can be gas, electric or solid fuel, so the choice of building or room largely depends on this. When drawing up an equipment installation project, it must include a diagram of the location of heating equipment and requirements for boiler rooms in a private house.
Boiler room and equipment diagram
The project must be coordinated with government organizations, but higher requirements are imposed on gas equipment. Requirements for a boiler room in a private house with any type of boiler: 1. Up to two boilers are allowed to be installed in one room; 2. The walls of the boiler room must be made of non-combustible building materials; 3. The floor in the boiler room must be concrete or have metal sheet protection. Ceramic tile cladding is allowed; 4. You cannot store or use any flammable substances in the boiler room; 5. The door to the boiler room must have fire protection - metal, asbestos or other non-combustible upholstery; 6. All doors in the furnace room must open outward; 7. If the furnace room is located in an extension, then one door should lead into the building, the second - outside; 8. All heating devices and equipment must be accessible for maintenance and control; 9. Artificial ventilation must be three times the capacity relative to the requirements of SNiP; 10. The furnace room must have a window with a window ≥ 50 x 50 cm.
acrylic wall paint washable dulux
Boiler room project in a private house
Adviсe
The attic is not the most optimal place to install heating. Firstly, it is impossible to use heating systems in the absence of electricity. Secondly, it is difficult to carry fuel to the second floor and carry away the ash. We bring dirt, soot, and stench into the room. Thirdly, a complex reconstruction of the entire heating system with installation of a gas main to the second floor and distribution of heating pipes.
If installing a boiler in the attic is necessary, opt for convenient heating methods: electric or gas boiler, liquid fuel boiler. They do not require transportation of fuel and combustion products and are easily automated.
It is better to soundproof the boiler room; the operation of the boiler and circulation pump is quite annoying and interferes with sleep at night.
Heating system safety
When installing the boiler in the attic, the heating system must be closed. Let me remind you that in an open system, the coolant circulates naturally by reducing the density of the heated liquid. That is why all heating devices used in an open heating system must be located above the boiler level. They try to place it at the lowest point of the system. If the boiler is installed in the attic or on the floor, then the system must be closed. The coolant circulates in it using a pump, and not naturally. Therefore, the location of the heat source in closed systems does not matter. In addition, closed systems allow the use of smaller diameter pipes, as well as radiators with high hydraulic resistance.