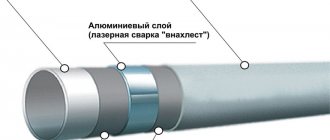
In order to connect heating pipes, various methods and materials are used. The method of connecting these building elements to each other directly depends on the raw materials from which such pipes were made. The most commonly used pipes for installation of pipelines are pipes made of polypropylene, steel, metal-plastic and copper.
In this article we will talk about which methods are most often used by installers when installing the types of heating elements listed above.
Each material has its own types of connection
Types of connections
Modern communications can be installed from metal, plastic, metal-plastic, PVC, HDPE and other pipes.
The material of manufacture determines the choice of method for connecting the risers into a single structure. Therefore, elements of the pipeline system can be of collapsible and non-demountable types. Among the many detachable joints, connections both with and without threads are equally popular. Threaded methods include connections using:
- bends, couplings, locknuts;
- American women with a union nut;
- bidirectional threads.
The threadless method includes jointing using:
- flanges;
- welding;
- compression fittings.
and other devices, depending on the material used to make the pipes.
We will talk about these types of connections in more detail later.
Variety of fittings depending on purpose
In addition to differences in parts based on material, there are different types of fittings for polypropylene pipes based on shape and purpose. Such elements are calculated in advance when a clear pipeline installation scheme is known.
Couplings, connectors and adapters
These elements have a cylindrical shape and are used for joining smooth sections of polypropylene pipe. Installation is carried out using an electric soldering iron or an open-end wrench, which depends on the modification of the fitting.
Fitting with transition to external thread
The element has a plastic solder coupling on one side and an external thread on the other. The latter is possible in all pitch sizes and diameters established by GOST 6357. The fitting is used for connecting polypropylene to metal engineering systems or connecting equipment, plumbing, etc.
There is a hex thread on the plastic to hold the pipe with a second wrench while tightening the counter nut. This will protect it from deformation.
Fitting with transition to internal thread
The fitting is similar to the one described above in application and configuration, only the outlet to the metal has an internal thread. The size of the turns and the pitch are possible in accordance with pipe GOST 6357. Through such a fitting, it is convenient to attach ball valves and other elements to the polypropylene wiring.
Polypropylene fitting - one-piece coupling
The part consists exclusively of polypropylene. The inlet and outlet have the same flow diameter. The cylindrical fitting is designed for joining two PP pipes by welding with a soldering iron.
Internal-external transition coupling
The PP fitting has a cylindrical shape with different end diameters. It is used in situations where it is necessary to expand or, conversely, narrow the subsequent part of the pipe. Can serve as an adapter for connecting to a tee or angle. Attached by socket welding.
The element can be of standard length or shortened. The latter option is relevant for limited areas, for example, if the pipe runs close to the radiator connection hole.
Turnkey conversion to internal thread
Cylindrical part made of polypropylene with embedded metal insert. It has an internal thread with dimensions in accordance with GOST 6357. For screwing, iron edges are provided for an open-end wrench.
This allows you to not only hold the fitting, but also tighten it with high force. Suitable for joining polypropylene to steel utilities.
Turnkey transition to external thread
A fitting with a solder coupling on one side and an external metal thread on the other. Contains iron edges for gripping with an open-end wrench. Suitable for connecting ball valves, equipment, and connecting to engineering systems. The thread diameter and pitch are selected depending on subsequent communications.
With union nut
Consists of a polypropylene coupling for soldering and a pressed-in stainless steel part with a union nut and internal thread. Additionally, there is a section on the plastic for a hex key to hold the fitting during the last turns of the key, preventing the pipe itself from turning.
The rubber seal is responsible for the tightness, so winding is not required. Used for transition from boiler, pump or metal pipe fitting.
With union nut for transition to Eurocone
The fitting consists of a socket welding coupling and a steel insert with a VT.708.E union nut and internal thread. Inside there is a metal nozzle with rubber seals. The element is used for fixing polypropylene pipes to shut-off valves or transition to metal-plastic pipes.
Installation is carried out with an open-end wrench, and additional edges on the plastic allow you to fix the fitting, protecting it from turning.
With union nut for transition to “cone”
A connector with a union nut allows you to directly, without any adapters, connect a polypropylene pipe to fittings with “cone” standard outlets.
Manifold fitting with conversion to PEX
Used to connect cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes to a polypropylene manifold.
Detachable coupling for soldering
The fitting is used on a section of a polypropylene pipe where it is necessary to create a detachable connection. It can be used for channel cleaning and other technical needs. The element consists of two mating parts - an external thread and a union nut.
The device is combined - partly from PP and partly from nickel-plated brass. A sealing insert made of synthetically produced rubber is used inside. The sides are joined using socket welding and then twisted together.
Detachable coupling with transition to internal thread
Another type of detachable threaded fitting, but here one end is soldered and the other is screwed. For this purpose, the metal has an additional internal thread. Suitable for connecting shut-off valves and equipment to a system made of PP pipes, as well as joining with communications made of other materials.
Fittings
These are elements for a mating nut or thread for connecting PP pipes with systems made of other materials, such as flexible hoses. Often used on straight sections. Here are some forms of fittings.
Union nut fitting
It has a metal fitting on a fragment of a polypropylene pipe. There is a plastic flange at the end for support. The thread rotates and attracts the plastic to the mating union nut. To prevent leaks, a rubber flat ring is used inside.
The hexagon on the metal part helps to secure the fitting well to withstand pressures up to 20 bar. Often used to connect a reinforced faucet hose.
Union fitting
A polypropylene pipe with a flange at the end, on top of which there is a union nut. The principle of the fitting is similar to the American one, but the metal here is not pressed in, but simply put on top.
The part is designed for screwing onto metal external threads. The rubber seal rests against the flange and ensures tightness.
Corners, elbows, bends, water sockets
A group of polypropylene devices for joining straight sections of pipe, changing its direction, connecting other equipment, and dividing the system. Parts can be made entirely of plastic or with metal inserts.
Square 90º
A fitting with the same inlet and outlet diameters to change the direction of the pipe by 90 degrees. The connection is made with a soldering iron.
Elbow with transition to internal thread
A part with a 90º bend that changes the direction of the PP pipe. The fitting has the same internal diameter, only one side is mounted into the system by soldering, and the other by a threaded connection.
To do this, a metal internal thread is soldered into the second end. The plastic casing around it has a hexagonal design for holding with a wrench.
Elbow with transition to external thread
Angle fitting with a 90º bend for connecting pipes at an angle. One part is soldered using socket welding, and the second is screwed. The metal threads are pressed and have plastic edges for holding with an open-end wrench.
Water inlet with internal thread
Polypropylene corner fitting with mounting plate. With its help, the part is screwed to the wall. The connection from below is carried out using soldering. A ball valve or mixer, as well as a flexible hose, can be attached to the side through the internal thread.
Water inlet with external thread
Polypropylene fitting with 90 degree bend and perpendicular mounting plate. Attached to a vertical base. One edge is soldered into the system, and the second is screwed using an external thread.
Angle with union nut
A variation of the American one, but the polypropylene pipe fragment is made at an angle of 90º. The element is designed for tying polypropylene pipes to metal pipes with external threads. To connect using a union nut, you will need a wrench.
Angle at 45º
The outlet is made of polypropylene with equal diameters at the inlet and outlet. Changes the direction of the pipe by 45 degrees. Fixed on the pipeline by welding plastic with a soldering iron. With its help, it is convenient to carefully bypass architectural structures or equipment located on the path, as well as bring the pipe to the connection point using a shorter route.
Plank with water sockets
Two water sockets with internal metal threads, connected to each other by a rigid polypropylene strip. It has two holes for fixing the device to a vertical surface. Due to the strip, a fixed distance of 150 mm is maintained between the centers of the fitting, intended for connecting a standard mixer.
Contours
The parts are used when two pipes intersect and it is necessary for one of the pipes to pass over the other. You can “jump” over the interfering pipe by using 45 or 90º bends, but more couplings and soldering will be required, which slows down the process. Therefore, it is better to use contours.
Long circuit with couplings
The long contour has a smooth deviation from the axis with a gradual rise and fall. At the ends there are already two couplings for joining with a straight pipe. The fitting allows you to bypass an obstacle in the way such as a riser, window sill protrusion, etc.
Short circuit with couplings
Polypropylene pipe with a short arched bend. Helps you get around a perpendicularly located pipe or other obstacle. The short length is convenient for installation in limited space. Installation is carried out with a soldering iron, and two couplings are already available at the ends, which makes the work easier.
Smooth outline
A section of pipe without couplings that is bent at the factory for installation in obstructed areas. Has a neat bend without loss of throughput. For installation you will need a soldering iron and two couplings, since the part does not have them.
Crosspieces
A type of fitting for attaching four pipes at once. Installation is carried out using socket welding. The element differs in form.
Regular cross
It has four identical outlet pipes located in the same plane with a step of 90º (directed in four directions). Branches the stream into 4 parts.
Coplanar spider
Performs the same role as the outlet, but looks more aesthetically pleasing due to the monolithic body. Inside, the intersecting channels do not mix, but pass over each other. The fitting does not reduce the throughput, since it has protruding walls that increase the diameter of the channel inside.
Two-plane cross
It also has four pipes, three of which are located in one plane, and one in another. The exits are mutually perpendicular. Used to divert polypropylene pipe to the side.
Tees
The device is used to branch a pipe from the main line. It can only be made of polypropylene or combined with metal. Designed for horizontal wiring from vertical risers, for example when connecting radiators.
Tee with transition to internal thread
The main pipe has a flat part, and the side inlet is equipped with a metal internal thread. The outside of the branch is equipped with edges for fixing with a key. The fitting is optimal when you need to add a part with a threaded connection to the system.
Tee with transition to external thread
A plastic element with three outlets, where the side one is equipped with a pressed-in steel part with an external thread. The fitting is soldered in a straight section, and the branch continues with a threaded connection.
Triple adapter
All pipes of the part are plastic, but one has a larger diameter than the other two. Used to narrow or expand the system capacity and branch it.
Two-plane tee
Element for directing communications in two planes. Often used in corners where you need to simultaneously extend the horizontal line with a turn and make an exit to the radiator.
Collectors
Fitting with a number of bends from 2 to 6 or more. It is used to supply liquid and maintain the same pressure in different circuits or uniform distribution of coolant.
Manifold tee
A polypropylene part with a coupling and a small flat area for welding. The upper pipe is equipped with an external metal thread without a hexagonal shell. If an element is welded in series with similar ones, then a manifold of any length can be created, depending on the needs and availability of free space. This type of fitting is relevant for organizing a water heated floor.
Manifold tee with ball valve
An element similar to the one described above, only a ball valve is provided in front of the external thread. Sequential soldering of such parts makes it possible to create a manifold of the required length. If necessary, part of the heated floor can be turned off to reduce the volume of heated coolant.
Polypropylene manifold with taps
It is made in a single body made of polypropylene and, in addition to the main line, has three outlets. Each channel is equipped with its own tap. The subsequent system is mounted by soldering. For reliable fixation of the fitting, mounting eyes are provided. The part is used for distribution of water supply or heating systems.
Plugs, stoppers, caps
The parts are used when testing part of the system when not all taps, radiators or mixers are yet connected. Such fittings may also be required at the end of the pipeline. This is relevant if you plan to continue the system in the future.
End cap
Blind end fitting. Molded entirely from polypropylene. Attached by heating and soldering. To remove it you will need to cut off the pipe.
Polypropylene plug
A plastic fitting with a thread, a stop flange and a hexagonal head for a socket or open-end wrench. The plug is installed in couplings with internal threads and tightened. A rubber gasket is used for tightness.
Filters
A branch on a flat section of pipe where there is an internal metal thread. A mesh cylinder is inserted into it, blocking the passage channel. From the outside, the hole is closed with a bolt with a copper or rubber washer. The filter collects rust, plaque and dirt, which protects the subsequent system from clogging.
Check valves
The fitting is in a plastic case and contains a valve inside that prevents the reverse flow of liquid. Used in private home water supply systems.
It is installed after the pump and prevents water from flowing back into the well if the pump stops. It is also relevant for the supply in front of the boiler, so that the heated volume does not escape through the riser to the neighbors. The screw plug allows you to service (clean) the mechanism.
Compensators
Sections of pipe with a loop that are installed on long pipelines in a vertical or horizontal position. Compensates for linear expansion and contraction during heating and cooling. Help maintain the integrity of the system and extend the life of communications.
Fastenings
They come in the form of clamps, crimping semicircular grips, brackets, and clips. Used for fixing polypropylene pipes and fittings to the wall and floor. Prevents deformation and vibration of the system and promotes a neat appearance.
Ball Valves
The outer casing is made entirely of polypropylene. There is a lever on top that controls the internal flap that closes the passage channel. With its help, you can regulate the flow rate of the coolant or temporarily cut off part of the heating and water supply system circuit (annex, garage, room).
The fitting is mounted using soldering, where the pipes are inserted inside it. Some space is required to turn the lever, so there should be some free space on one side of the element.
Valves
Designed to adjust the throughput of a node or block a channel. A crane axle box or a ground axle box is used inside. The difference from a ball valve is the mechanism that closes the channel.
Connection in heating system
The industry produces pipes from various materials. These products are used for laying water pipes, sewers, gas pipelines, and other pipeline communications.
When laying heating systems, pipes from:
- become;
- copper;
- plastic.
Depending on this, risers in heating structures can be connected using:
- welding;
- threaded fittings;
- flanges;
- press connections;
- compression and push-on fittings,
- and other ways using innovative modern technologies.
Rules for choosing the diameter of heating pipes
The cross-sectional size affects the circulation rate of the coolant. If the diameter is chosen incorrectly, the transportation of the heated liquid will be slow, and the devices will heat up unevenly. Coolant fluid flow speed standards are 0.4–0.6 m/sec. Reducing movement to 0.2 m/sec. causes water stagnation and air pockets form. Provided the coolant circulates at a speed of 0.7 m/sec. Energy consumption increases and noise is heard. The optimal parameter for the speed of water movement in the system is 0.3–0.7 m/sec. From this calculation, the diameter of the heating pipe is selected.
Recommendations from experts on product selection:
- if no more than 2 radiators are connected in the network, the cross-sectional size is up to 16 mm;
- when integrating 1 battery with a capacity of 7 kW or several radiators with a capacity of up to 2 kW (in total, the total power should not exceed 7 kW) - the permissible circuit cross-section is 20 mm;
- with a total power of a group of radiators in the main line of 11 kW, a pipe with a diameter of 25 mm is needed;
- supplying heat to a dead-end distribution, for example, to a distant wing of a house, requires the installation of elements with a cross-section of 25 mm;
- parts with a diameter of 32 mm are mounted into a network with 12 batteries with a total power rating of up to 19 kW;
- if the house system has more than 20 radiators, the total power of which is not higher than 30 kW, products measuring 40 mm will be required.
It is also important to consider the capacity of the pipeline. If the water speed in the main line is no more than 0.4 m/sec, the polypropylene circuit ensures the transfer of the required amount of heat
Table of thermal energy release depending on the pipe cross-section:
| Thermal energy (kW) | Outer diameter (mm) | Inner diameter (mm) |
| 4,1 | 13,2 | 20 |
| 6,3 | 16,6 | 25 |
| 11,5 | 21,2 | 32 |
| 17 | 26,6 | 40 |
Threaded fastening of copper pipes
Steel pipes have long dominated the installation of heating systems. Gradually they began to be replaced with products made from other materials.
Today is the time for copper and plastic pipes. They are connected using soldering, compression and press fittings. But the threaded connection in the heating system of metal pipes practically remains a priority among all types of joints.
Threaded connections are used not only when laying heating pipes, but also when fastening steel, including galvanized water risers.
In gas pipelines and especially in high-pressure pipelines, welding is used as a connection.
Articulation using threaded fittings is characterized by:
- speed of assembly;
- high quality, reliable connections;
- Possibility of installation in hard-to-reach places.
Important! Using a threaded coupling, bends, locknuts, elbows, and taps, you can not only quickly dismantle, but also assemble the pipeline.
Without fittings with internal and external threads, it is impossible to properly install a pipeline from copper risers. To install these system parts, it is necessary to have threads not only on the connecting elements, but also on the ends of the risers. All measuring instruments are connected using fittings.
When installing copper pipes, American pipes are often used, which is rightly considered one of the types of threaded connections.
Important! When using copper pipes for hydraulic systems, remember that copper does not combine well with other metals and alloys, since upon contact a chemical reaction occurs that can destroy the elements of the heating circuit.
Twisted compression fittings
Features of screw clamp couplings used in the installation of multilayer pipes are the ability to install them in walls and the speed of connection. There is no need to use specialized pressing tools, and for installation work you only need an open-end or adjustable wrench.
- Using threaded compression fittings for metal heating pipes, plumbers are able to repeatedly disconnect and connect individual elements of the installation without the use of seals.
- We should also pay attention to the aesthetic value of the connectors, which is provided by the nickel material. This feature is especially important if the connection is placed in a visible location.
The most important property is the reliability of the connection and thus the elimination of even the smallest leaks.
Compression fittings are available in several types. You can buy Euroconus couplings that crimp on a cut-out brass ring. Elements of this type are usually nickel plated fittings with NBR/FKM O-rings.
Screw couplings are offered in the Vestol version, where the brass sleeve placed on the body is corrugated. In this connection, a ring with a lock nut is put on a calibrated pipe and then tightened onto the fitting.
When tightened, the ring is pulled onto the pipe, ensuring a tight connection. Fittings of the Vestol type are produced in the ZBK version. Most often, these connectors are used to connect to radiators and manifolds.
Gas
For decades, gas lines were installed using seamless metal pipes. Under the influence of corrosion, their service life is significantly reduced. This factor was one of the reasons for replacing metal pipes with products made from other materials
:
- polyethylene;
- copper;
- of stainless steel.
Each type of pipe can be joined in different ways. Is it possible to connect gas pipes with a threaded connection?
and if so, what materials are the risers fastened with threads from? Yes, you can. For example, threads are used to connect steel and copper products.
When joining gas pipes, a threadless method is also used.
In particular:
- soldering can be used to joint copper or polyethylene pipeline parts;
- welding is successfully used when laying steel and copper lines. For example, steel elements can be welded with an autogen or arc welding machine;
- Main pipelines are installed using flange fastenings. In addition, flanges are installed at those points of the pipeline system at which there is a branch from the main gas pipeline to the house or apartment.
Quick tips for connection and operation
- When using various fittings , it is advisable not to save much, since most often they are inexpensive and have a short service life.
- Be responsible when applying sealant to threaded connections, because most leaks occur precisely because of poor-quality winding.
- When starting the system for the first time , be sure to check all connections for leaks.
- Pipes connected in different ways must be painted to avoid rusting.
- When installing a water supply network , install a filter that will avoid contamination of the entire system.
- on the mounted elements as possible, do not place heavy things.
Metal
Metal pipelines transport gas, water, steam, household waste, and other working media.
When laying individual sections, permanent connections are used:
- welding;
- carving;
- soldering
Detachable joints include
flanges, bends, union nuts. They are used in systems that are frequently dismantled.
Metal risers are used when laying water and gas pipelines. To connect using a thread, you must use a drive, a coupling, or a lock nut.
Copper pipes are connected using soldering. Such joints are characterized by increased reliability.
Both threadless and threaded types of pipe connections come in collapsible and non-separable types.
Can a threaded device be non-separable, you say?
Yes maybe. There are situations when 2 pipes are connected with threads and then welded to fixed structures. This is an example of a permanent type thread fastening.
Threaded coupling
An interesting type of joint was joining using a bidirectional thread
. Such a connection is made with a threaded coupling by simultaneously screwing it onto both risers, if the pipes being connected have multi-directional threads. Therefore, before making a threaded connection of such pipes, you need to once again make sure that there are different thread directions on the risers.
The main thing is to choose a good seal. Can be sealed with silicone. Although many people use the old proven method, using FUM tape or sealing thread and oil paint.
Stainless steel pipes
These products are divided into two varieties: smooth and corrugated.
- Smooth ones are used less often due to their high cost. Supplied in the form of long rods, which are cut and connected with corners.
- Corrugated ones are produced in the form of coils; they are highly flexible - no pipe bender is required to give the desired shape.
Connection methods
- Welding is used only for smooth pipes.
- The compression fitting is suitable for both corrugated and smooth pipes. Tightening is carried out using a regular wrench. However, these types of connections cannot be installed in a hidden way.
When considering the durability of stainless steel pipes, it must be taken into account that compression fittings have their own service life.
Advantages of stainless steel pipes
- Corrugated pipes are suitable for integral installation without fittings, since they need to be bent along the desired path.
- Withstands freezing of the coolant.
- Resistant to sun and precipitation, does not corrode when exposed to moisture. This makes stainless corrugated pipes a good option when laying outdoors.
- Suitable for local use: heat exchangers in buffer tanks, solar collectors, etc.
- Gas tightness - the material does not allow steam to pass through, thanks to this, air does not accumulate in the heating system.
Disadvantages of stainless steel pipes
- There is no way to collect it in a hidden way. If in the case of a copper pipe hidden installation is allowed, but it is not very convenient, then a stainless steel pipe does not have fittings suitable for this.
- Grounding is required to prevent eddy currents.
- Corrugated pipes look unsightly and are inferior to smooth pipes from a visual point of view.
- The high hydraulic resistance of corrugated pipes with a long coil length will lead to loss of pressure.
- High cost of the heating system.
- Noise when operating a water supply system in corrugated pipes.
- Flexible corrugated pipes have poor resistance to mechanical damage.
Galvanized
Zinc is one of those metals that do not corrode. Therefore, you cannot think of better protection for steel pipes from moisture.
The galvanizing process involves coating the internal and external surfaces of the riser with zinc. The service life of such a pipeline is determined by the quality of the coating and the thickness of the applied metal layer.
Galvanized risers are connected by threading or welding. Many people believe that galvanized pipes are generally prohibited from being used for laying water pipes. But that's not true. The fact is that such risers are not recommended for transporting hot water.
But the use of products to supply the home with cold water does not pose any danger to the human body. The main thing is that the drinking pipeline is used constantly, and the water does not stagnate in the pipes. Then the presence of zinc in such a liquid will be about 5 mg/l, which is below the maximum permissible concentration per day (the norm is 12-15 mg/l).
Important! The degree of zinc concentration can be determined independently: if the presence of zinc is elevated, then the water has an astringent taste.
Galvanized riser
Galvanized risers are used to lay an autonomous water supply system. They are used to construct wells, although GOST does not foresee the use of such risers as casing pipes.
The fact is that the water exchange in the well is small, which does not exclude the possibility of deterioration in the chemical composition of the water. Plus, under the influence of the soil environment, if the joints are not reliably sealed, electrochemical corrosion is possible.
Therefore, when asked whether it is necessary to seal the threaded connection of the casing pipe
The answer is clear: yes, it is necessary.
When screwing a joint, thread sealants are used. The highest quality seals include the RUSMA series seals, which reliably seal and protect threaded connections.
Steel pipes
This variety was previously widely used; in modern construction of private houses, steel pipes are rarely found. In most cases, you can find products made of black steel or galvanized. The latter are not suitable for drinking water supply systems, since the zinc coating is toxic to humans.
Advantages of steel pipes
- High thermal conductivity and good heat transfer - the pipes quickly heat up and begin to give off heat.
- Gas-tight - the material does not allow air to pass through.
Disadvantages of steel pipes
- Corrosion – steel pipes are susceptible to rust, its particles clog the heating system and can damage equipment. On galvanized pipes, the protective layer also wears off over time and they begin to corrode.
- The need for maintenance - systems with steel pipes are demanding on the quality of the coolant. Repair of connections and cleaning of circuits are often necessary.
- Low reliability - steel pipes are often destroyed under the influence of various factors, as a result of which the walls become thinner, and fistulas can form in some places.
Metal-plastic
Old metal pipes that have served for a long time are usually replaced with metal-plastic ones. This replacement is due to the presence of a number of positive characteristics that metal-plastic has in comparison with other materials.
It is different:
- long service life;
- ease of installation;
- reliability and durability;
- low cost;
- the ability to function in a wide temperature range: from -8⁰С to +95⁰С, which makes it possible to use it for heating systems.
Metal-plastic risers can be articulated:
- using compression fittings;
- using press fittings.
Before connecting, it is necessary to draw a drawing of the placement of risers, plumbing fixtures, and control devices.
Then you need to take accurate measurements and cut off the necessary pieces of pipe and lay them out along the future pipeline. To prevent burrs and roughness from remaining on the ends, clean the ends with a sharpened drill or round file. Use a calibrator to straighten the deformed edges and the pipe is ready for installation.
Heating pipe material
An important parameter when choosing pipes is the material; it affects how the products behave in certain conditions. There are three main varieties.
- Metal ones are represented by copper and stainless steel pipes. Until recently, they occupied the main share of the market, but now they have been replaced by polymer products
- Polymers are made from cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) or polypropylene (PP).
- Combined - the most advanced type is made of metal-plastic. Combines the properties of the other two groups.
Pvc
Statistics say that when repairing utility networks, about 75% of old risers are replaced with PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipes. The laying of new communications is also most often carried out using PVC risers. Why is their popularity growing so much?
The fact is that:
- The installation of the main line can be done by yourself. This fact distinguishes risers from similar products made from other materials;
- their cost is quite affordable, which helps save significant money;
- products are durable and reliable;
- the structures are resistant to corrosion processes, which contributes to a long service life.
You can join PVC pipes using:
- bells In this way, sewer risers are connected, and rubber rings act as a seal. They can be lubricated with anaerobic sealant, which will significantly enhance the sealing process;
- flanges Such fastening is indispensable in the presence of pipelines that are subject to disassembly associated with frequent periodic maintenance work. This applies to temporary mains, to pipelines that are often moved;
- thermistor type welding, which is used when joining pipes with diameters of 20 mm or more. In addition, cold welding (adhesive bonding) is often used. The procedure is carried out using a special glue, which should be applied with a brush along the entire length of the inner surface of the fitting and along the circumference of the pipe.
Important! Before cold welding, it is necessary to chamfer the ends of the bonded risers at an angle of 15 degrees. To carry out the procedure, chamfered incisors are used.
Press fittings
Press fittings are indispensable when connecting pipes to elements and installation devices.
- The most popular option is pressed brass couplings with a self-aligning sleeve with a diameter of 16 to 32 mm.
- Additionally, they are coated with a layer of nickel. Plastic extruded couplings with a polyphenylene sulfone (PPSU) body with a diameter of 16 to 25 mm can be used.
- Manufacturers offer coupling models with a self-aligning sleeve, which is separated from the body.
- The outer ring plays an important role. It is thanks to him that you can control the depth of insertion of the pipe. The connection is sealed when the sleeve is pressed against the pipe.
- The advantage of press fittings is that they always use the same pressure force. The speed of connection and the possibility of applying insulation are also important.
The outer diameter of the couplings is not much larger than the diameter of the pipe. Couplings also serve as mounting fittings, i.e. tees, elbows, flares, etc.
Polyphenylene sulfone (PPSU) couplings offer additional benefits. We are talking about resistance to loads and impacts, as well as the absence of corrosion. This type of fittings is lighter compared to brass models.
Some fittings have a leak control feature. To protect the sealing element from damage, a cylindrical pipe guide is provided, which additionally provides double pressing.
Polypropylene
Risers with a diameter of less than 63 mm are fastened using socket or socket welding. To do this, use an additional element - a coupling. For threaded or other joining of risers, fittings with sockets are used.
In the case of joining risers 63 mm in diameter and above, butt welding is used. If the appropriate fittings are available, then you can use sleeve welding. When it is necessary for the fastening to be dismountable, flanges are used.
Using a special welding machine and attachments for it, you can reliably and quickly connect polypropylene or polyethylene pipes. Using such a device, risers with a diameter of 16-40 mm are fastened. Non-stick Tiflon is used to cover the nozzles, which makes it possible to make connections of the highest quality.
Features of installation of couplings for various types of pipes
To install most couplings, no special tool is required; one or two adjustable wrenches are enough; to seal joints in metal products, you will need flax tow or plumbing thread, fum tape for plastic threads. To fasten polypropylene pipes or install press fittings, you will need a special tool and some skills; if you do the work yourself, it is easier to rent the necessary equipment from a construction tool rental.
Rice. 12 Installation of plastic sewer pipes
Sleeve compression connection
Crimp compression couplings are dismountable connections; their installation does not require specialized tools (except for two wrenches); the process of joining with a metal-plastic pipe includes the following operations:
- Prepare the end of the pipe for installation of the coupling fitting; to do this, cut it at an angle of 90 degrees to the axis with scissors and insert a calibrator inside, turning it slightly to expand the seat.
- Place a nut and a ring with a slot on the pipe, insert the fitting body fitting inside it, and move the ring with the clamping nut to the end of the body.
- One wrench holds the fitting body, the other screws the clamping nut.
Plastic
Electrofusion welding
Docking of plastic pipes is carried out using:
- diffuse welding;
- carving;
- flanges;
- glue;
- fittings;
- electrofusion welding.
When installing sewerage from plastic pipes, they can be connected into a socket. The connection is quite effective when used in low pressure pipelines, such as the above sewer system.
An excellent option for fastening plastic pipes is cold welding. The essence of its effect on connecting risers is that the glue dissolves the upper part of the plastic of the pipe, thus ensuring adhesion of the risers at the molecular level. Simple, high quality, reliable.
An effective and relatively inexpensive way to connect plastic pipes is a fitting connection. If you need to fasten plastic pipes to metal ones, the easiest way to do this is to use a fitting joint.
For collet fastening, crimp-type fittings are used. The joint is formed in the place where the teeth of the metal riser cut into the main element.
Heating installation
The heating system is installed in the following sequence:
Radiator installation
First of all, you should determine and prepare a place for their placement . Typically, heat exchangers are mounted under window openings, this is due to high-quality air flow circulation. It is important to accurately calculate the distance from the support base where the battery will be located.
Upon completion of the preparatory work, for hanging the batteries, markings are made for the consoles. To do this, the heat exchanger is centered along the window opening at a distance of 11-12 cm from the floor covering and window sill.
Then, at the marks, using a hammer drill, holes are drilled for fasteners, which are subsequently screwed in so that there is a gap of 3-3.5 cm between the wall and the back side of the heat exchanger. For 1 radiator mounting, you will need 4 brackets, for installing a cast iron battery - 6.
Installing plugs for piping the mounted heat exchanger
Almost all heating batteries have 2 open inlet holes on both sides, some of them are closed with plugs during the installation process, and others are closed with threaded passage plugs.
Most often, in the process of installing a heating system, they use the connection of batteries on one side, which provides for the supply of thermal mass from above the heat exchanger, and the return is carried out from below the same side of the battery. On the other hand, in the upper part of the battery, a Mayevsky valve is mounted to remove air, and the lower hole is closed with a plug.
Installation of taps on a heat exchanger
Upon completion of the installation of the plugs, a regulatory element is installed in them, which can serve as valves with a spherical lock . To carry out manual regulation of the movement of thermal mass, you can use conventional radiator taps; for automatic regulation, taps with thermostatic heads can be used.
Typically, American ball valves are used, which ensure quick shut-off of water. To install such a faucet into the battery plug, you will need a special key that is placed in the faucet connecting adapter.
The joint between the passage plug and the tap should be sealed with elastic sealing paste or flax fiber. To do this, check the tap threads in advance by connecting them without a sealing agent. After densely filling the entire depth of the thread with fiber, paste must be applied to the winding and the element must be screwed in.
In the case of using metal shut-off valves, in order to switch to plastic, it is necessary to screw in threaded couplings. As in the previous case, winding is also used here.
Installation of the Mayevsky tap (due to the presence of a rubber gasket) does not require tightness.
Upon completion of work, the heat exchanger can be installed in the designated location.
Pipeline laying and assembly
In the process of installing a heating system, the primary thing is to groove grooves in the floor and walls. When using a two-pipe system, the best solution is to lay it in the floor, and connect the heat exchangers from the walls. The layout can be carried out in a cement base, by cutting a groove, or laid before the screed is poured. It is advisable to place the supply and return pipes in isolated channels, at a distance of at least 10 cm from each other.
When laying plastic products, they should be separated with polyethylene foam to ensure thermal expansion. The space around the connecting elements is also filled.
It is not recommended to use rigid fasteners for fastening, which will prevent linear expansion. For these purposes, elastic clamps or plastic brackets are used. In this case, the pipes must be firmly fixed at the point where they exit the wall.
Laying should be carried out vertically or horizontally on the walls, bends should only be made at right angles.
Installation should be carried out in the direction from the risers to the installed heat exchangers. The place of the last welding is preliminarily determined; it should be convenient for working with a soldering iron (as a rule, this is the area between the radiator and the wall).
The material is prepared based on the number of straight zones determined by the diagram. Their sizes are determined by measurements using a centimeter tape. Please note that about 1.5 cm of the pipe length extends into the connecting element.
Drilling and high pressure pipelines
Using drill pipes:
- lift the rock cutting tool;
- rotation is transmitted;
- axial loads are transferred to the tool;
- flushing liquid is supplied.
Therefore, the load on such a structure is quite large. The connection of drill risers is carried out using drill joints, which have a special locking thread.
To make the structure more durable and operate for a long time, anti-corrosion grease is used to protect the lock threads. The threads are also protected by applying metal safety elements to the connecting points.
One of the most complex technological operations is the process of designing and installing high-pressure pipelines. The specifics of operation do not allow the possibility of interruptions in the operation of the pipeline. Otherwise, an emergency situation may arise. Therefore, the risers must be securely fastened using high-quality sealing of threaded connections.
High-pressure pipelines can transport gas, steam, and liquids over long distances. The pressure in the transport system can reach 25 atm and higher.
To lay pipelines, pipes made of steel (carbon and alloy), copper, and plastic (mainly polyethylene) are used. The fastening of pipes to each other can be of detachable and permanent types.
Important!
When installing a high-pressure pipeline, you need to strive for a minimum number of detachable-type connections. This is due to the need for increased safety when transporting the working environment. The following are rightfully considered to be fairly reliable permanent fastenings:
- seam welding;
- fusion welding;
- soldering.
Cast iron and copper couplings
There are special fittings for connecting this type of pipeline, but installation in this case is quite complicated. Firstly, it is imperative to be able to get close to the pipe from each side, otherwise it is impossible to ensure the tightness of the joint. If the pipeline is laid near a wall, you will have to hollow out part of it near the connection point. Secondly, all work must be done very carefully and focused. It is highly advisable that the installation be carried out by an experienced person, since such work may not be possible for a beginner.
Installation is carried out as follows.
- First, the joint is sealed with bonding.
- The pipe is inserted into the fitting until it stops. This is necessary so that the seal does not fail.
- The bondage is being minted. This must be done in several turns and each turn must be minted around the entire circumference.
- After embossing, it is necessary to cover the joint with cement mortar.
You can also mint it with a simple screwdriver.
Important! Do not neglect the embossing of the seal. If you limit yourself to cement mortar, the connection will not last long. After some time it may leak.
Thread sealant and sealing
In places where pipeline elements are connected, liquid can flow and gas can escape. To protect yourself from such situations, seal the threaded connections of pipes with thread sealant. The product may look different, but its purpose is the same - to seal joints.
Teflon tape
Among the many sealing materials we can highlight:
- Teflon tape, which is the simplest sealant;
- mastic or red lead paint in combination with tow. This seal has been used for several decades, and is still relevant today;
- sealants containing special solvents.
Important! Choose a high-quality seal that will provide a reliable threaded connection, which is especially important when laying gas pipes.
A one-component paste is also used, with which you can easily achieve reliable sealing of not only threaded, but also other types of fittings and risers.
Important! Work with this sealant is accompanied by quick installation and maximum accuracy. The substance does not shrink and does not pollute the internal cavity of risers.
The great advantage of the material compared to Teflon or tow is that with the help of paste, minimal gaps or cracks in the system are ideally filled, which ensures absolute tightness. This cannot be said about Teflon tape, which can collapse under dynamic loads and contaminate the internal pipe space.
Working with tow is accompanied by some inconveniences in the form of contamination of risers and floors. In addition, it is characterized by strong creep and shrinkage.
Advantages and disadvantages of each method
Thread
Advantages:
- reliability;
- ease of assembly, possibility of disassembly;
- low cost.
Flaws:
- tension in the thread cavities increases material fatigue, reducing its strength;
- the need to use locking means to prevent the working element from unscrewing.
Flanges
Advantages:
simplicity and convenience of reusable connection and disconnection.
Negative properties:
- high labor intensity in manufacturing, therefore, high price;
- with prolonged use, the location of its connection decreases, loss of tightness.
Bonding
The advantages of this method include its not labor-intensive process, which does not require much skill and effort.
But the wait for gluing sometimes reaches three days, which is not always convenient.
This type of connection cannot be considered a reliable method.
Welding
Advantages:
- reliability;
- durability;
- tightness;
- the ability to connect parts of any shape.
Flaws:
- the occurrence of residual stresses;
- possibility of changing geometry;
- risk of destruction under vibration and shock loads.
Trumpet
In comparison with all types, socket pipes have the advantage of low cost, the possibility of small axial and lateral movements of the pipe, which is very useful during temperature changes and soil shrinkage.
The negative indicator lies in the difficulty of connecting the connector and insufficient reliability at high pressure.
Pressing
A common positive factor is excellent self-centering of the joined parts and stable state under shock loads. A simple and non-labor-intensive process.
Cannot be disassembled or dislodged from each other. Here are a few disadvantages of this method.
Methods for connecting metal pipes
Couplings
When repairing gas and water supply systems or laying new ones, the question arises: what is the best way to connect risers and seal the resulting joints.
If we are talking about detachable connections, then it is best to connect the risers using couplings. They can be used both in the form of connecting parts and as adapters if the linear dimensions, including the diameters of threaded pipe connections, are different.
Important!
When choosing a fitting, remember that pipes and couplings must be made of the same material. The couplings differ:
- reliability;
- availability and breadth of assortment;
- speed, ease of assembly and disassembly;
- low cost.
Depending on the types of risers, similar connecting fittings are produced. The sealant is selected in the same way. If metal fittings are most often sealed with tow and oil paint, then for plastic parts FUM tape and synthetic sealant, in particular anaerobic sealant, are best suited.
Pipeline assembly technology
To assemble the pipeline, you must perform the following sequence of actions:
- First, screw the coupling onto the pipe.
- Then the side with the short thread is screwed into the coupling (sometimes it is connected directly). The parts should be screwed all the way, then the connection will be reliable.
- A locknut is screwed onto the long side of the drive.
- Next comes the connecting fitting.
- Then the end of the drive is applied to the pipe and the coupling is screwed together so that it goes onto the pipe. The connection will be easier to complete if the axes of the parts coincide as much as possible.
- The fitting must then be secured with a locknut. To do this, it should be screwed to the coupling so that there is a distance of 2-3 cm between the parts. This space must be filled with strands of flax. They should be wound in the direction of rotation of the nut. Then the locknut should be tightened until it stops. This must be done to seal the connection and prevent water leakage through it. You should use a wrench to tighten the locknut because its edges are narrow.
Which fittings are best for connecting a heating radiator?
For steel batteries the set includes:
- Traffic jams.
- Flushing tap.
- Lock nut.
- Sgony.
On the upper floors of high-rise buildings you will need a Mayevsky crane.
Currently, American ones are used instead of radiators: two are enough for one radiator. It is more profitable to purchase these fittings combined with taps and throttles.
The fittings in the radiator piping include ball valves, chokes, and a thermal head.
For a heating system, it is better to select connecting elements made of bronze or brass.
Ready-made sets of fittings are produced for radiators in polypropylene networks. They include 4 adapters from one thread size to another, a Mayevsky tap, a key for it, and fasteners. Threaded connectors are equipped with seals.
Classification of fittings and adapters
Assembling pipelines using special nozzles is the most popular method of wiring engineering systems. In order to select the necessary types of fittings for polypropylene pipes, you should familiarize yourself with their detailed classification.
For the manufacture, release and supply of technical polypropylene products, the provisions of state standard No. 52134 of 2003 are used.
Types of fittings for polypropylene pipes Source ecomont.ru
Installation technologies and rules
First, let's look at the general rules regarding the installation of copper pipelines. As you know, metal is an excellent conductor. To provide protection from stray currents, as well as reduce the risk of corrosion, you can use products in a polymer shell.
Image gallery
Photo from
Possibility of using lead solder
Connecting copper and aluminum parts
Use of brass fittings and adapters
Which radiators are best for copper systems?
In private practice it is quite rare, but in industry the assembly of pipelines made of steel and copper is still used. In this case, it is recommended to use steel for risers, and copper for wiring, that is, steel products should be in the first position in terms of coolant current. Magnesium connectors are required.
There are several ways to connect products, the choice of each of them depends on the specific situation:
- capillary soldering with solder;
- compression fittings;
- pressed fittings;
- threaded installation.
The last method is practically not used because it has lost its relevance. Soldering and crimping differ in the degree of labor intensity, execution technique, and the presence of different tools, but are equally in demand. Let's look at three popular pipeline construction technologies.
Fastening methods used in everyday life
Each apartment owner independently determines the level of installation quality he requires. Some people use soldering, while others use adapters or other alternatives.
"Hot" soldering of pipes
Considering soldering as the most reliable and durable method of fastening, some private property owners use this method of pipeline installation. In the absence of special equipment, they use a gas burner. In this case, you can save on purchasing a soldering iron and work with pipes of any diameter.
Workflow Features:
- The gas burner must be selected according to the type of fuel used. The gas with the highest combustion temperature is suitable for thicker pipes.
- It is best to select pipe sections of the same diameter. This will ensure an aesthetic appearance of the engineering system, preservation of operating parameters in all sections of the pipeline and the absence of difficulties during soldering.
- Before starting installation, it is recommended to mark (cut) the entire contour, clean the ends of the joints, and degrease them with a special compound.
Installation of polypropylene pipes using a gas burner Source ytimg.com
Installation and replacement rules
Features:
- Draw up a wiring drawing, mark the locations of fittings, determine the number of crosses and tees. Make a list of all necessary fittings. Squares, for example, can be taken with a reserve.
- Installation of the system begins from the risers towards the already tied and hung radiators. Threaded connections are sealed with flax. Fum tapes do not react well to elevated temperatures.
- Features of welding polypropylene bends lie in their proper preparation. The ends are cut off at right angles, then cleaned of burrs and crumbs. The diameter of the nozzle in the soldering iron must be equal to the cross-section of the element being welded.
- When replacing the heating system, the management company is informed about the upcoming work, and the replacement of the riser is coordinated with the neighbors above and below. An employee of the management company closes the riser while it is being replaced.