Do-it-yourself Kuznetsov stove: arrangement drawings and description of the stove laying
Since 1962, I.V. Kuznetsov has been designing, manufacturing and improving furnaces.
During this time, more than 150 different designs were invented, each of which strived for an absolute efficiency indicator - 95% efficiency. In this article we will tell you how to make a Kuznetsov stove with your own hands. Photo 1 Kuznetsov stove
The fundamental feature of the development is the system for separating gases into cold and hot flows. Due to the unique bell-shaped structure of the stove, hot air is retained inside, and cold air is discharged through a separate channel into the chimney pipe. Considering that a higher combustion temperature is maintained in the bell, and the heat is distributed evenly throughout the body, the efficiency reaches its peak. For comparison, the efficiency of conventional stoves is 30-35%, solid fuel boilers - 80%, pyrolysis boilers - 85%.
The low performance of most solid fuel units is explained by the fact that warm air exits along with combustion products into the chimney. In addition to the fact that the remaining volume is not always enough for full heating, quickly escaping flue gases further reduce the thermal threshold. In some designs, they try to solve this problem by increasing (lengthening) the chimney pipe, but then there is a risk of reducing draft and, as a consequence, reducing efficiency. The creation of such a unit that would provide full traction and increase heat transfer became the main goal of designer Kuznetsov.
Video 1 Construction of a heating furnace using the Kuznetsov system
We strengthen the structure with wire
https://youtube.com/watch?v=vXFx1VcDXKQ
Every third row should be laid with metal wire; this is a small but necessary detail that will make the structure reliable. Iron components must be inserted into the masonry with a gap of 0.5 cm, and the resulting void must be filled with fire-resistant wool.
To make a Kuznetsov sauna stove with your own hands, it is not necessary to have masonry skills. If you have a diagram and drawings, if you work carefully, everything will definitely work out. To find the scheme, just go to Kuznetsov’s website, there is information available to everyone that anyone can use.
If you have experience with masonry, then there will be no problems, the main thing is to follow the instructions.
Construction of a Kuznetsov furnace with your own hands
The sequence of actions is as follows:
First, they study the floor plan of the room where the heating device is planned to be installed. In the case when the house is not built, it is necessary to ensure uniform heating of all rooms. It is not advisable to install a heating unit into a finished building, but if necessary, you can
But at the same time, you should take into account the location of the supporting structures and beams when arranging the chimney. Then the foundation for the heating device is prepared. It is made of concrete, and the width should be 10 centimeters greater than the size of the device
It is advisable to design the foundation for the stove at the house planning stage.
Preparatory work before assembling the stove
Before you start building a stove, you need to study in detail the floor plan of the room where the stove will be located. Since it weighs quite a lot, the foundation must be well strengthened.
The following information will help you build the stove correctly and efficiently in order to avoid problems during its further operation.
- The cap and the hearth should be combined with a dry seam - the size is 2-3 centimeters. It is necessary for the correct movement of air flows. Heavy gases saturated with water vapor will move in the hearth and create a certain vibration, increasing the quality of firewood combustion.
- You cannot combine the furnace with a hood, since the firewood must burn in a certain volume. This is the only way to create the highest possible temperature.
- A catalyst made of refractory bricks in the form of a grate should be installed above the combustion chamber. Here they heat up to the maximum and burn out what was burned in the hearth.
If the stove is being built in a wooden house, then it is very important to protect the walls from severe overheating. To do this, it is recommended to install gaskets made of refractory material at the junctions of the walls and the stove itself.
Also, at the joints of the furnace, the gaps, which will be filled with refractory material, are needed for the free movement of expansion of the masonry during its heating. Otherwise, the mortar on the seams will crack and the stove will become deformed.
Useful tips for craftsmen before starting work
- The fireproof protection inside the furnace should be positioned as if it were suspended in the air. That is, it should not come into contact with the walls of the oven.
- The internal masonry must be installed on edge. External masonry is done at the discretion of the master.
- The wire is needed to strengthen the brick bond. Therefore, it is necessary to lay it every 2-3 rows to make the oven more durable and stable.
- After the solution has completely dried, the furnace walls must be treated with a special refractory substance.
- Test lighting should be carried out at the lowest possible temperature, with a gradual increase in heat.
Kinds
According to their purpose and design features, blacksmiths can be divided into several types:
- Heating. The devices are designed for efficient and safe heating of premises.
- Cooking. Used for cooking. This includes ovens for baking bread and bakery products.
- Bathhouses. The Kuznetsov bathhouse stove is designed for simultaneous heating of the main bathhouse premises. Such devices have high heat transfer with minimal fuel consumption.
- Street. A stove complex consisting of a grill or barbecue for outdoor cooking.
- Fireplace. The equipment is used as a decorative element of the interior or as an additional heating option. Some fireplace stoves are equipped with special loungers for a pleasant leisure time.
The most popular are complex devices that are distinguished by their multitasking. A striking example is the Kuznetsov heating and cooking stove, which is intended both for heating residential premises and for preparing food.
Despite their functional features, all stoves operate on the same principle - effective distribution of heated gases in the bell into separate streams.
It is noteworthy that stove hoods can be equipped with additional equipment - electric heaters, hot water tanks, steam generators, oven and stove.
A competently designed and constructed Kuznetsov sauna stove will provide reliable heating in all functional rooms: steam room, washing room, dressing room, rest room. In addition, it will allow you to quickly heat water, accumulate hot steam and purify the air.
Temperature conditions for different types of poultry
Suitable temperature is one of the most important conditions for incubation, without which hatching of chicks is simply impossible.
For each type of bird, these indicators are purely individual, so when laying eggs from chickens, ducks, geese or turkeys, you should focus on the following values:
| Type of eggs | Required temperature in the first days of incubation, °C | Required temperature in the last days of incubation, °C |
| Chicken | 37,9 | 37,6 |
| Goose | 38,4 | 37,4 |
| Duck | 38,0 | 37,1 |
| Turkeys | 37,6 | 37,1 |
| Quail | 37,8 | 37,5 |
In general, a homemade incubator is a good solution both for those who are just trying their hand at poultry farming, and for experienced farmers who do not want to spend extra money on purchasing ready-made equipment. By equipping the structure with automatic egg turning, you can achieve 80–90% hatchability of chicks.
Operating principle of Kuznetsov bell furnaces: ordering
The operating principle of Kuznetsov furnaces is not complicated. When building a furnace, it is necessary to carry out all work according to drawings, diagrams and, of course, use procedures.
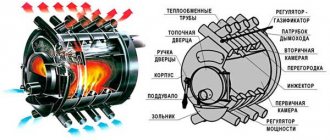
All Kuznetsov bell furnaces operate on the principle of separating combustion products. This principle lies in the fact that the gas generated as a result of fuel combustion is divided into two streams: cold and hot. The movement of gases inside the furnace design is very well thought out. Hot air is retained in the oven and retains heat for a long time. Cold air quickly flies into the chimney through a specially made recess. A furnace operating on this principle is called a bell-type (dome) furnace. Inside such a furnace, the hearth is combined with its lower part and forms something like a hood. It then acts as a gas separator into two streams. The flow of hot air rises and is retained in the hood, thus concentrating heat.
Advantages of Kuznetsov stoves:
- Cost-effective;
- Long-term heat retention;
- Slight soot formation;
- No need for frequent cleaning;
- A choice of different shapes and designs is possible.
The high efficiency rate (95%) of Kuznetsov furnaces is the result of a fundamentally new development and design features. For comparison, a traditional Russian stove has an efficiency of 25-40%. If Kuznetsov stoves have disadvantages, then they are few, and they are lost against the background of their advantages.
Podgorodnikov’s stove and the Swede A. Batsulina
There are 2 types of Podgorodnikov’s two-bell OVP: IP-1 and IP-2 with an oven.
The IP-1 oven has a height of 210 cm, a depth of 77 cm and a width of 115 cm. It consists of 30 rows. Just like the Kuznetsov stove, this one has a valve for summer mode so that the gases go immediately into the pipe. In winter, this valve must be closed all the time. In Podgorodnikov ovens, the cooking chamber is equipped with doors so that the heat is retained inside even longer and does not allow the food to cool down. The holes for cleaning the channels are covered with bricks, without pushing them in completely.
Podgorodnikov stove
Podgorodnikov's stove IP-2 has the same dimensions as IP-1, but slightly narrower - width 102 cm. The oven is mounted under the hob. Even when the two-bell ORP is running in summer mode, the oven still heats up, since hot gases pass right past it.
Podgorodnikov furnaces have a built-in ventilation valve. When the stove is heating, it is closed or slightly open. If you open it completely, the traction will noticeably deteriorate. Podgorodnikov stoves can be heated with wood and coal.
The two-bell Swedish A. Batsulina works on the same principle, but has a slightly different masonry. Its design allows, in addition to the hob, to build in an oven, the temperature of which can be regulated by a summer slide. The oven is installed in the second hood, as a result it will be heated from all sides.
To prevent the pipe from condensing, a direct-flow valve is provided. Thanks to it, you can heat the pipe to a high temperature (+150°C) in a short time. As a result, the possibility of condensation is completely eliminated. Also, unlike Kuznetsov’s stoves, this one has a regular brick ceiling instead of an arch.
Swede Batsulina stove
Recommendations for self-construction
If you decide to build a stove according to one of Kuznetsov’s plans with your own hands, get ready for careful and scrupulous work. On the diagrams you will find a graphic representation of each row, but before starting laying you need to become familiar with the features of the technique, in particular:
- selection and pre-processing of bricks;
- purchase of metal parts (plates, dampers, doors, valves);
- determining the most suitable location;
- preparation of the base and foundation;
- possibility of installing a chimney, etc.
Fireclay refractory brick (Sh-5, ShB-8) is recognized as the best material for the internal masonry of “smiths”, and ceramics (M-150) for external decoration. To strengthen brick walls, metal elements (rebar, wire) are used. In order for the stove to function with maximum heat output, experienced craftsmen hone not only their skills, but also every brick - literally. They polish every detail, which is why projects completed by professionals look flawless.
Fireclay brick masonry
Having the author's order in hand, we recommend not to experiment, but to follow the designated order. Deviations from the diagram do not guarantee complete heat transfer.
What will be needed for construction
Let us immediately note that it is better not to use used bricks to build a furnace. Constant temperature changes are not the most suitable conditions for its operation, and if you take a material with fatigue stresses, it is possible that after a couple of years the walls of the furnace will simply begin to crumble into dust. So, what will you need to prepare to implement our project:
- solid red clay brick M 150 in the amount of 754 pcs. – for laying the body of the heating device and chimney;
- sand, 150 kg;
- fine clay, 130 kg;
- refractory brick - 63 pcs., which will be needed to equip the core of the furnace; Fireclay bricks of the Sh-5 and ShB-8 brands are most often found on sale. In our case, it is better to take the latter, since its dimensions fully correspond to the dimensions of the red brick.
- blower door, 1 pc.;
- combustion door, 1 piece;
- doors for cleaning channels, 6 pcs.;
- grate, 1 piece (minimum size 250x375 mm, which can be assembled from separate grates);
- steel wire for tying rows;
- metal corner;
- chimney damper, 1 piece;
- asbestos cord or basalt sealant - for sealing the installation sites of cast iron castings.
If you have ever done brickwork, you should know what you will need:
- trowel (trowel);
- container for preparing the solution;
- building level;
- plumb line and cord;
- bushhammer;
- mixer for mixing the mixture (you can use an attachment for an electric drill or prepare the solution manually);
- roulette;
- pencil.
If during the construction process it is necessary to trim bricks for the front side of the stove, then this work is best done using a grinder with an installed cutting disc for stone and concrete.
Date: September 25, 2022
What is the difference
The main feature of the group of stoves invented by Kuznetsov is the absence of extended smoke channels with many turns and bends. To make the most of the heat from burning fuel, duct stoves have a system of passages through which hot smoke heats the bricks. In this case, the oven heats up unevenly at different levels, which can lead to cracking of the masonry. In addition, there is a need for regular cleaning of narrow places and corners.
Kuznetsov's stoves for home and bathhouses do not have this drawback. In them, hot gases from the firebox enter the so-called hood - an internal space limited at the top by the ceiling and having an outlet at the bottom. The heated smoke rises to the very top of the hood, where it lingers until it begins to cool. As they cool, they gradually fall down along the walls of the bell, and a new portion of smoke takes their place.
The cooled smoke exits through the channel into the chimney or into another hood, depending on the design and purpose of the stove. Gradually, as it passes through cascades of hoods, the flue gases cool to a temperature of 120-150 degrees. The temperature of the gases at one level of each cap is the same, which avoids uneven expansion of the brick.
Basics
Most of the advantages of Kuznetsov furnaces come from the principle of free passage of gases. Let us explain again with an example.
Let's imagine a stove with a complex system of smoke ducts: an ethermark, a four-five-turn Dutch oven. In this cramped labyrinth, strong turbulence will inevitably arise. Have you heard the furnace humming? This is only a minor manifestation of the vortex energy raging within her. And there’s nowhere to get it from except from the fuel stash. If the channels are long and narrow enough, then at first glance there is nothing terrible here: the vortices, by the time they reach the pipe, will dissipate, cooling, and will still give their energy to the body of the furnace, and it to the room. But in reality, nuances appear, which will be discussed later in the text. Because of them, the efficiency of a channel furnace over 60% is an exceptional rarity.
In a channel stove, while it is being heated, a huge flow of energy rushes about, and only a small part of it can be used for heating or heating water without disturbing its operation. Such a furnace is somewhat similar to a nuclear reactor. Don’t be alarmed, just because of the synergy, i.e. along the paths of energy circulation in it. A nuclear reactor has to be loaded with tens of times more fuel than is necessary to ensure the design energy output. Otherwise, the neutrons will simply fly out without having time to meet the uranium atoms ready to receive them. In a channel furnace, hot vortices, without having time to cool, will fly out into the chimney or, conversely, will cool down immediately, producing smoke and soot.
But the Kuznetsovkas (details below) are closer in synergy to the thermonuclear reactors of the future. “Thermonylus” sounds scary, but this is only due to its association with the hydrogen bomb. In fact, fusion reactors are quite safe.
Why? Because they generate exactly as much energy as the consumer needs, and the technological power reserve required for rarefied plasma is scanty. If suddenly the chamber of a tokamak or stellarator suddenly completely collapses, the plasma will be completely emitted (there are no heavy atoms in it) and will cool down before it reaches the walls of the room. The repairmen will curse - maybe the duty department is sharpening their laces - but after 5 minutes. will be able to blunt to elimination without protective equipment.
So what do Kuznetsov furnaces have in common with thermonuclear reactors? The fact that the energy of the flue gases, thanks to the principle of free passage, does not rotate many times in the flow until it is pushed into the body of the furnace, but saturates it immediately. And now she has nowhere to go from there except into the room and/or the water heating register.
Design and operating principle
Bell furnace design
The stove with a hood was developed by engineer Igor Kuznetsov in the early 60s of the last century. Subsequently, Russian metallurgist Leonid Kotlyar improved the design so that it retains heat for up to 19 hours. The peculiarity of the “blacksmith” is that the heated air does not leave the pipe, but is collected under a hood. Slowly it cools down and is forced out by rising hot streams. Saving heat is the advantageous difference between a bell-type stove used for heating a house and a channel stove, where hot air, under the influence of draft, freely escapes to the street.
A two-meter-high structure with a base of 1m*1m can reach a thermal power of 3.5–4.5 kW. Such a bell-type stove is enough to heat a house of 50 square meters in a temperate climate zone, if you heat it twice a day.
The inventor improved the design by adding another cap. In Kuznetsov’s two-bell heating stove, the first covering element is connected to the combustion compartment and separates the cold and heated flows. The second cap is located in the upper part of the stove, trapping hot air, which, before entering the chimney, gives off heat to the bricks for a long time.
A two-bell stove uses fuel more economically and is usually equipped with a hob. This allows you to cook delicious meals without consuming electricity or gas. The design of the stove already includes an exhaust hood - there is no need to install an additional ventilation system.
Advantages and disadvantages
The principle of hot air movement in a bell furnace
Kuznetsov’s designs have many advantages. One of them is increased efficiency - 93 percent. For comparison, in Russian furnaces it is about 80. At the same time, “blacksmiths” have uniform heat transfer and less temperature fluctuations.
Other advantages of the design:
- There is no soot left behind, so the stove and smoke duct can be left uncleaned for several years, making maintenance much easier.
- The device can be erected anywhere - in a corner area, in the middle of a room, near a wall. Often, a two-bell stove heats several floors of a house on one floor.
- The stove chimney can be shortened to save bricks.
- “Kuznetsovka” can be easily combined with a stove, fireplace, or stove bench, featuring a variety of modifications.
- It is easy to connect a water circuit to the stove and pipe heated water for bathing or heating.
- Thanks to the increased level of pyrolysis, fuel, which can be of any kind, is saved.
- The masonry will last longer and there is less risk of cracks.
- When the valve is open for a short time, it is almost impossible to cool the stove, because the cap is always filled with warm air, and the cold air is pressed downwards.
“Kuznetsovkas” have few disadvantages, most of them are related to construction: stove makers who are ready to carry out such a project inexpensively are not easy to find. In addition, the units are quite large in size, but are slightly inferior to Russian stoves.
Double bell oven
The most common option for high-quality heating of a private home is the Kuznetsov device with two hoods.
Its efficiency is significantly higher due to longer retention of hot air.
The heat-resistant brick hoods are located one above the other with a slight offset - the air displaced from the first hood immediately enters the second, from which it goes into the exhaust pipe.
The size of such a stove is directly dependent on the area of the house; it is even possible to build with an internal volume of up to 5 cubic meters. m. The firebox usually occupies the entire base area, this helps to increase the heating power of the air in the furnace.
d79996939d6d9526a6f20a7cb2b08264.jpe
18ae580d3f50fc0040ae71d956f18099.jpe
Reference. In the design of a two-bell furnace, special valves are often installed to insulate the second bell and reduce the heat transfer of the device. This is necessary in warmer times of the year, when high heating power is no longer required.
When using dampers, hot air from the first hood is directed directly into the chimney.
Kuznetsov's fireplace stove: ordering
Kuznetsov's fireplace stove is a large heat storage device. A brick structure that looks like a fireplace and is as warm as a stove. Due to its mass, the fireplace stove heats the room in a unique way.
The construction of fireplace stoves is a complex matter, but if you wish, you can do everything yourself. To begin such a complex process, you must have the procedures at hand. Kuznetsov's fireplace stove has a lot of advantages.
Advantages of fireplace stoves:
- The beauty and grace of stonework;
- Efficiency of brick heater;
- Low carbon monoxide and soot emissions;
- Long-term maintenance of a comfortable temperature in the house;
- Economical.
Some fireplace lovers make them look like works of art by decorating them with grates and decorative elements, using the services of a blacksmith. You can feel a pleasant feeling of radiant heat if you equip your country house or cottage with such a fireplace stove.
Basic rules for creating a heating stove
- To make Kuznetsov stoves, the ordering (masonry diagrams) should be printed in advance.
- The refractory shell located inside the furnace must be free on all sides, since the brick expands during the heating process.
- Internal refractory masonry when using fireclay bricks is always done on edge. If the bricks are made of clay, on the inner walls and on the posts, they are laid at the discretion of the stove-maker.
- To strengthen the bond, a wire is laid every two brick rows.
- When a Kuznetsov stove is created, the ordering of brick stoves for a home provides that various elements (for example, doors) are installed in such a way that there is room for expansion. A special gasket is placed between the brick and the metal element.
- After completing the construction of a brick structure, it should be treated with a fire-resistant compound.
- The first kindling begins at a minimum temperature and is then gradually increased.
Building a foundation for a furnace: universal instructions
Regardless of the stove model, it needs a reliable and durable base. This foundation is suitable for both the Swede and the two-bell model.
The sequence of arranging the support is as follows.
We dig a pit about half a meter deep.
Foundation pit
Second step
We compact the bottom of the hole and fill it with a 15-20 cm layer of sand. Pour water over the sand and compact it thoroughly.
Fifth step
We prepare a solution from part cement, five parts crushed stone, three parts sifted river sand and water. Fill approximately half of the free horizontal space of the pit with this solution. Let the fill dry.
Sixth step
We prepare a solution from part cement and three parts sand. Fill the remaining space of the pit with the mixture. Carefully level the upper part of the fill using a rule.
Poured foundation for laying a brick stove
Types of designs with an oven
Kuznetsov furnace
It is installed in rooms with minimal space possibilities, while the design and decoration are selected individually. A special feature of this type of furnace system is its high efficiency, which for such devices is more than 80% along with a small amount of soot formed during operation. The design is suitable for placement in any area of the room; it is possible to place several similar stoves at once. Any type of solid fuel is suitable for the firebox.
Bykov's device
The thick-walled structure has a simple laying pattern and a rectangular shape. This type of stove provides for placing the device in 2 rooms at the same time. Nevertheless, the Bykov design has significant differences in its structure from bell-type structures. The lower region includes 2 gas channels: ascending and descending. The upper part has the shape of a sieve, the cap of which is divided by 5 channels.
How to build a structure?
The ordering of the Kuznetsov or Podgorodnikov two-bell furnace is carried out in accordance with the operating diagram. Before taking any measures to arrange the facility, you need to study all the main points that the drawings contain. Half of the mistakes that a brick structure will have in the future are related precisely to the incorrect implementation of the project. After the foundation is ready, the process of laying out the furnace begins. Brick rows are laid in strict order, each subsequent row is measured at the building level for errors in work. The final stage of the work is the construction of the chimney structure. After all the oven elements are ready, you should start the device for the first time. The test run should not be carried out at full power, so it is not recommended to use large amounts of fuel.
Second thermal load
Nothing works on bare principles. In order for a theoretically absolutely correct stove to heat, dry and cook well, it must also be made correctly in the material. In relation to bell-type furnaces (and especially double-bell furnaces), this means that the thermal load on the material must be high. Making a bell furnace massive, with thick walls, is like lighting a fire in a cave. To feel the warmth, you need to sit next to the fire, and there will be soot...
c309b8141378ec4433e1fa6a65105e41.jpe
eb9a96611664c70a0b926656370364e4.jpe
Take a look at fig. On it are drawings and orders of some Kuznetsov stoves: a bathhouse. heating and cooking. a double-circuit hot water boiler and an improved Russian stove with a stove bench. Not being an experienced stove maker, it is clear that the material per unit of output power (500 W * sq. m of outer surface) in the Kuznetsov stove uses one and a half to two times less than in traditional ones. In general, any bell-type oven is “emptier” inside than a channel oven of equal power.
Orders of some Kuznetsov furnaces
On the one hand, this is good; bricks and mortar cost money. But on the other hand, it requires careful development and adherence to construction technology (see below). The heat load, which would not cause a pile of cobblestones to move, would destroy a thin brick wall even during the accelerating fire.
Structural mechanics are also important for Kuznetsov furnaces. The strength of the wall with clay mortar decreases much faster when its thickness decreases than with cement-sand mortar. Therefore, the foundation for these furnaces must be done especially carefully in strict accordance with the author’s recommendations. They must be strictly followed during construction.
Note: I.V. Kuznetsov allows freely copying his materials for himself, for construction, but objects to republications. However, the pictures in Fig. small. An amateur cannot build anything using them, but a master knows where to get full-fledged drawings. Therefore, we hope that Igor Viktorovich will forgive us this small borrowing for the benefit of the cause.
Features of masonry: materials and recommendations
It is recommended to use ordinary clay solid bricks for laying the body and chimney. Brand M150 and higher, size 250*120*65 mm. It is not difficult to calculate the amount of bricks for Kuznetsov stoves: you need to multiply the number of rows of the model you have chosen by 0.8. This amount is enough to lay the hull (taking into account the battle and rejection). For the chimney you need to count separately. The calculation scheme is slightly different: you know how many bricks are in one row, multiply by the number of rows (each is different depending on the dimensions of the stove and the height of the building), add 10% for the battle and get the required number.
For the fireclay core (if any), Sh-5 (230*114*40 mm) or ShB-8 (250*123*65 mm) is recommended. Its quantity is calculated individually according to the scheme. The core in Kuznetsov furnaces is not connected to the body, that is, there are no common points of contact between them. Between the two parallel walls, the body and the fireclay core, there should be a gap of 5-6 mm. To make it easier to withstand, you can wrap the finished core (usually it is placed first) with ordinary packaging cardboard of the appropriate thickness. Instead, for better thermal insulation of the firebox, you can lay a heat insulator, basalt cardboard, for example.
Barbecues can also be built according to the principle of bell-type stoves
The height of the rows of ceramic bricks does not coincide with the height of the rows of fireclay. They do not need to be adjusted one after the other
It is important to maintain verticality and horizontality, monitor angles, as well as the recommended seam width. And then everything will be as it should be
In reality, the dimensions of ceramic bricks differ from the standard 250*120*65 mm. If the deviations are not critical, they can be corrected with a seam. Therefore, when calculating stoves and their heights, they take the height of the brick with the seam. It should be 70 mm. But you cannot make a seam larger than 7 mm, so look for a brick of suitable quality and size.
At the top, in the places where the fireclay laying ends, there are compensation gaps that take into account the different expansion coefficients of the materials. It is imperative to observe them: the expansion of fireclay bricks is greater than that of ceramic bricks, and if there is no such gap, the core will after some time break the masonry on top due to the fact that it expands more strongly.
Cutting from the order of the Kuznetsov stove with a mark
The size of the gap must be calculated according to the marks in order. The height of the last row of fireclay is marked on the drawings. Calculate the height of the ceramic brick wall yourself: multiply the number of rows by the height of the row with the seam (70mm) and get the required value. It should be 10-15 mm greater than the height of the fireclay. This gap is compensatory and it must be present. The resulting void is filled with stone basalt wool (not glass wool, but one that has a use temperature above 1200°C).
If there are columns and internal walls inside (usually a quarter thick), the brick can be laid flat or on edge in them. There is no difference, do what is more convenient. There are places in the drawings where in one row there is a brick placed flat and on its edge. In this case, it needs to be adjusted to size (cut).
There are also nuances in the installation locations of furnace castings. Due to the specifics of the program, the drawings above the firebox door show ceramic bricks, but fireclay needs to be placed there on edge. When there is a difference in height, the voids are filled with cut fireclay plates. There remains a gap of 5 mm between the metal parts and the masonry - again due to different temperature expansions. A suitable heat insulator (with an operating temperature of 1200°C or more) is placed in this gap.
For thermal insulation of furnace castings, asbestos cord was previously used. Now they recommend basalt wool or cardboard
Now about the mortar: for laying the body (made of ceramic bricks), clay or clay-sand mortar is used. For laying fire-resistant fireclay, purchased compounds (fire-resistant mastics) are used. Kuznetsov does not recommend soaking the brick before laying it. If you need to do this, then only with secondary raw materials. Immediately after completion, the oven must be dried, even if you do not put it into operation immediately. If this is not done, then during the first few fires there will be a smell of fumes.
How to make Kuznetsov brick stoves with your own hands
IN AND. Kuznetsov developed a large number of furnace designs. Some types of stoves can be made with your own hands. To do this, you will need the order of the furnaces and their drawings.
Many, knowing about the positive reviews about Kuznetsov’s stoves, and also in order to save money, begin to build them themselves. Everything will work out, of course, but for this you need to use the appropriate materials and strictly follow the procedures.
Materials used for the construction of the Kuznetsov furnace:
- Fireclay brick;
- Clay brick brand M150;
- Good quality clay;
- Cleaned sand;
- Metal fittings.
For the construction of internal masonry, fireclay bricks are used. According to the order, you can calculate its quantity. For the construction of external masonry, clay bricks are used, preferably grade M 150. Its quantity is also calculated using the same order. It is recommended to use only good quality clay for mortar. Purified sand for masonry is used twice as much as clay. You can use commercially available clay-sand mixtures. For 500 bricks you will need about 0.2 cubic meters. m of clay-sand mixture. In addition, you will need grate bars, two doors (blower and furnace), two steel corners and five meters of wire. Kuznetsov’s book “Building stoves and fireplaces: a practical guide” will help you build the structure you need. It presents all types and designs of stoves and fireplaces.
What materials and tools are used?
Construction work will be impossible without the use of appropriate equipment and necessary materials. Before starting construction, you need to make sure that ready-made components are available. For a bell furnace you will need the following material:
- red and fireclay brick;
- waterproofing sheet for the foundation;
- metal corner;
- mortar kit (sand, clay, cement);
- combustion door, cleanout door, ash door;
- grates;
- cooking surface (presumably cast iron);
- oven;
- chimney valves of different sizes;
- reinforcing mesh.
In addition, the work will not be ensured if the following tools are not available:
To do the job you need to acquire a rule.
- trowels of different sizes;
- building level and rule;
- tape measure for measurements;
- pickaxe hammer;
- equipment for sewing seams;
- shovels;
- container for mixing the solution;
- mop and rags.
Kuznetsov furnaces design and principles of operation, advantages, variations, drawings
Kuznetsov's stoves are well known not only to stove makers - they heat many homes in Russia and abroad. I.V. Kuznetsov has been working on improving furnaces since 1962 and has gathered around him a strong team of like-minded people. The team has more than one and a half hundred developments to its credit, covering almost the entire range of household stoves, see fig.
Some of the furnaces of I.V. Kuznetsov
Many would like to build one of Kuznetsov’s stoves with their own hands, and this article will help them. But we are not going to reveal some hidden secrets of the “blacksmiths” - they simply do not exist. On Igor Viktorovich’s website stove.ru, those interested will find a huge array of stove information for free: from information on the design and construction of stoves to detailed drawings and recommendations for installing a stove in a house and constructing a blind area around a building with stove heating. We also do not intend to criticize or correct anything in this home-stove encyclopedia: we are, to put it mildly, far from I.V. Kuznetsov in the oven business.
The purpose of this article is to provide a kind of introduction to Kuznetsov’s body of information, allowing one to more freely navigate the source material. Let us explain with an example why this is necessary.
Let's say I'm a generalist auto mechanic with extensive experience and want to pass it on to others who are interested. A car is a complicated thing. If I begin to get distracted along the way, explaining in detail that how running and caster (let’s assume that readers are not exactly dummies, now everyone drives) affect the handling and directional stability of the car, and the valve timing diagram affects fuel consumption depending on road conditions. conditions, and so on, I will eventually become confused to the point that I myself will no longer understand how the car I drive works. Willy-nilly, I will have to present the material, albeit “on the fingers,” but in a professional, fluent manner.
189e53d9f8ccba456843c21464a99fef.jpe
However, it will be a little difficult to read even for specialists like me, but for an amateur it will make his head spin. Therefore, I will need someone to help me, who can be called a “half-teapot”. In fact, he is not a kettle at all; he can adjust the suspension and set the valve lifters himself. But in this case, his task is to describe how the entire filling of the car is assembled into one whole, controlled according to the principle: “steer with the steering wheel, gas with the gas, brake with the brake.”
In the automotive industry of the USSR, a similar situation arose in the late 50s and early 60s, when the industry began producing cars for wide sale to the public. Then the super bestseller of that time, “How a Car Works,” was published. Edited by none other than the most important designer of the legendary “Victory”, A. A. Lipgart.
Information “from the recipient” will not yet allow you to start working: it does not provide deep knowledge that will allow you to at least intuitively estimate the required values of numerical parameters along the way. But it is essentially fundamental: mastering it, a professional text can be read with understanding and faster. And, if somewhere in it something is still unclear, it no longer causes loss and wandering, but simply a mark in the mind: this is what you need to find out in more detail.
The government has not yet adopted any landmark resolutions on stoves and stove heating. But their role in household heat and power engineering in times of energy shortage is undeniable: already a heating stove with an efficiency of 70%, when used on a large scale, will provide fuel savings on a national scale, because The designs of new heating plants include heat losses in the mains of 35%, and it is not yet possible to reduce them. So, with the popularization of stove knowledge, you have to figure it out yourself, without being either Lipgart or Kuznetsov. Well, let's try.
Why blacksmiths?
But is it worth focusing specifically on Kuznetsov’s stoves? Worth it because they are worth it. From the very beginning, Igor Viktorovich viewed Russian-style stoves not as a protected relic of the past or an expensive luxury item, but as an indispensable attribute of the economical energy sector of the future, which is now the present. The rest realized, as they say, when the roast rooster pecked.
As a result, a 4 kW blacksmith heats a house of 100 square meters. m. the same as a 12 kW firebox. Which, by the way, does not speak about the invention of a perpetual motion machine, but about the fact that branded advertisers are creating their prospectuses, perhaps, sniffing out the “path of happiness.” In any case, it is a fact that Kuznetsov constantly receives orders from the USA, Canada, Sweden, Finland, which themselves are not trailing behind the furnaces. Specifically, the advantages of blacksmiths are as follows:
- High efficiency - 80% is not surprising for Kuznetsov furnaces.
- High temperature of fuel combustion without the use of technologies and materials that require industrial production.
- As the first consequence of the previous one - omnivorousness. In blacksmiths, any fuel burns to ash, and soot deposition is minimal.
- The second consequence is easy care: because. Soot also burns, Kuznetsov stoves may not be cleaned for years.
- Lower material consumption combined with uniform heat transfer between fireboxes: in a city apartment with central heating, the temperature fluctuates more during the day than in a house heated by a blacksmith with 2 fireboxes per day.
- Wide possibilities for integrating a water heating circuit without compromising the technical parameters of the furnace.
- Good draft with a short chimney, which reduces the cost and simplifies construction and installation work during its construction.
- The plasticity of the design and appearance as a consequence of the two-bell design (see below): without deteriorating the stove, it can be designed to suit almost any room and design requirements.
- Automatic redistribution of thrust among the channels during the transition from heating to cooling, which guarantees against waste: the view almost never needs to be closed; it is intended more for emergency operating modes.
Note: the method of thrust redistribution invented by I.V. Kuznetsov is fundamentally different from the well-known gas view. Through it, the flow created by the draft is passed past the heated parts of the furnace body by special downstream channels, and when the flame burns in the firebox, convection from it pulls the air flow towards itself. As a result, a separate room ventilation system is not required. In addition, a gas tube can be blown out by reverse draft when blowing into a pipe, or, conversely, pulled out in a strong wind, and in a blacksmith any air flow will pass by everything that it could blow out.
More about round ones
Round stoves theoretically have a lot of advantages, but they are not very convenient in the house. However, there is also a significant demand for compact mobile ovens, and here the extremely high efficiency of round multi-caps can be a decisive factor, because when the size of the oven decreases, its efficiency drops sharply due to the square-cube law.
Such furnaces, of course, would have to be made of metal. This solves the problem of cleaning; the stove can be made collapsible. But the choice of metals suitable for the ratio of heat capacity and thermal conductivity is extremely limited. The only inexpensive ones are cast iron, but it is heavy and fragile.
However, there is a lighter and stronger metal material with similar properties. These are products of powder metallurgy. In relation to scissor knives, “powdered crap” is quite justified, but for a stove in which nothing works for shear, powdered parts can be a godsend.
The second problem, which has already been mentioned, is the heat-resistant lining on the arch of the first cap. If it can be solved, then perhaps the works and efforts of Igor Viktorovich Kuznetsov will bear fruit that is more extensive and significant than it now seems.
Duct or bell-type?
Duct or bell-type?
Which is better: a time-tested average or a new promising upper limit? This dilemma has been going on for over 45 years among stove makers across the country! How to choose between a pie in the sky and a bird in the hand, who can tell you which is better and how not to end up with nothing? If we turn the conversation to the topic of brick kilns, then all these questions can be reduced to one thing - which type of brick kiln is better, channel or bell-type?
From all the variety of options for brick stoves, several varieties can be distinguished, differing from each other in their functionality; there are stoves only for heating, only for cooking, there are combined and highly specialized ones. However, according to their technical data, all of them are divided into two types of hot gas removal, and, accordingly, into their heating method. These two methods of removing gases have long been known to everyone - the channel system and the bell-type method. Debates about which method is better and which type of furnace gives the greatest return have been going on since the middle of the last century, because it was then that a model of a brick furnace was first created, in which the bell-type method of heating and removing combustion products was used.
Operating principle of ovens with two hoods
The secret to the efficiency of this stove lies in its original design, which allows it to accumulate and save heat for a long time. To understand the operating principle of a two-bell furnace, let’s consider its design diagram.
After kindling in winter, hot flue gases rise under the arch of the lower hood, transferring heat to the surrounding walls and hob. But new air enters the combustion chamber, the combustion process continues and the release of hot combustion products continues, displacing cooled gases under the top of the bell. Those, in turn, descend and fall into a vertical channel leading to the upper bell, where the two-bell design of the furnace provides for the repetition of the previous process with the release of gases out through the chimney.
The temperature of the exhaust flue gases is lower than any other stove with a stove, since they intensively transfer their heat to the walls of the stove. For this reason, chimneys of heat sources of this design must be protected from the destructive effects of condensation. After heating is completed, the heat remains for a long time at the top of both hoods, even if the main valve remains open. Cold air entering through the ashpit cannot rise under the hood arch and passes into the chimney along the path indicated in the diagram by blue arrows.
A two-bell cooking stove with a stove allows you to cook food in the summer thanks to an additional valve, the opening of which allows gases to pass directly into the chimney pipe. If the valve is not opened completely, then the flow of combustion products will be divided into two, going along different paths. In this way, in the autumn-spring period, you can regulate the intensity of heating of the hoods, that is, the thermal power of the stove.
Calculation of dome heating devices
Design includes methods for selecting internal fittings and equipment to obtain effective draft and increase heat transfer without loss. The heat loss of the room is calculated by volume, then the resulting value is multiplied by 21. This is the average loss for 1 cubic meter. The stove power should exceed the value by 15%.
If the projects do not suit the user, he can make the project himself, taking as a basis the general rules for the construction of bell-shaped structures. Determines the external dimensions of the heating structure, dividing the result by 300. The number means the heat power that the square of the external wall of the stove can give off. The required square footage of the walls located above the grate is obtained.
Features of the Kuznetsov furnace
Since the main goal of Kuznetsov’s developments was efficiency and productivity (he worked to increase the efficiency value), this required a fundamentally new and improved approach.
From the above, the conclusion follows: the system of free movement of gases created by this master is more natural, it optimizes the operation of the device and uniform heating. In addition, soot formation is minimized.
In addition to these advantages, Kuznetsov furnaces have other positive aspects:
- combustion occurs without soot and smoke;
- heating is more uniform;
- better heat transfer;
- the need for cleaning is ten times less;
- efficiency;
- there is more space to place the steel heating element;
- low level of heat loss;
- resistance to cracks;
- the ability to change the shape and design of the structure.
Kuznetsovka: drawings and their variety
Thanks to the basic principles used in the design, it is possible to add additional functions without increasing the overall dimensions of the oven. The main advantages and disadvantages can be described as follows:
- heating and heat transfer occurs evenly - the lower part of the furnace unit is heated in the same way as the upper part;
- The dimensions of the hob can be different - there is no rigid connection with the design;
- the injection of heat in the bell structure leads to complete combustion of hydrocarbons, so soot and smoke are practically not observed;
- very high efficiency, up to 95%;
- uniform heating protects the brick from cracking and the masonry from deformation;
- the shapes can be varied - stove makers are happy to help you select and develop a suitable design;
- many equip stoves with water circuits for local heating of their home.
The ability to design various shapes and equip these structures with heating circuits has made it possible to expand their functionality.
Kuznetsovka in section
- Heating options provide narrowly targeted application for effective heating of houses of various sizes and floors.
- Cooking options - use a minimum amount of firewood to quickly prepare a full lunch or dinner.
- Bath structures are characterized by high efficiency, rapid heating of washing rooms, as well as heating of water.
- Fireplace stoves, barbecues, grills and smokehouses can be reflected in stoves of this type.
- Combined options - the ability to combine multiple functions in one place.
Construction of the Kuznetsov furnace
In most models that were invented earlier, hot gases always moved through channels. During their movement, the structure heated up and then cooled down. This movement of gases was created by draft. At the same time, the body was heated unevenly, which ultimately led to cracks. The heat exchanger was placed in the firebox because there was no more room for it. There it came into direct contact with fire and its service life quickly expired.
d929e2742175cf2fa25982de10eadaee.jpe
Kuznetsov used a completely different principle of gas movement for his model. The stove has hoods turned upside down. The caps can be mounted on top of each other and tied together with a dry seam, as a result of which gas begins to pass through them from one cap to another. It is because of this principle of operation that the Kuznetsov furnace is also called a bell furnace.
Improve your designs I.V. Kuznetsov started in 1962, and a large number of like-minded people gathered around him. Many summer residents also want to create a Kuznetsov stove with their own hands. Let’s say right away that you can build a Kuznetsov bell furnace with your own hands, but like-minded masters did not reveal many of the hidden secrets, or maybe they simply don’t exist.
It is worth noting that, thanks to the operating principle of the Kuznetsov stove, it is possible not only to create separate heating in the house, but also to obtain a supply of hot water. To do this, the rear side of the hood must be equipped with a steel heat exchanger.
Advantages of the Kuznetsov bell furnace:
- Smoke gases are stratified throughout the entire structure equally after the combustion chamber.
- One building may have not one, but several hoods. They will help achieve more warmth.
- The hood is located near the firebox and all carbon monoxides enter it. Therefore, ash, carbon monoxide and volatile hydrocarbons, which in other furnaces exit through the chimney, in this case burn out under the hood. This will increase heat transfer and minimize soot production.
- With the help of their convection, all products formed as a result of combustion cannot escape from the oven, so they give up their heat to it.
- The heat exchanger in this building is located in the hood or outside the combustion chamber, so it does not affect the temperature of the fire and cannot reduce efficiency.
Mechanical removal
How to remove super glue from laminate flooring mechanically? The most important thing is never try to pick super glue from the laminate; it is bound to the substrate at the molecular level. You will simply tear off a drop along with a piece of laminate, thereby irreversibly damaging the surface.
But there is a way, and with the help of a file, a needle file, a sharpening stone or just a nail file, you can achieve good results.
Due to the transparency of cyanoacrylate, you can gradually remove the top layers to the base, however, the main thing is not to overdo it. A thin layer of glue will remain on the floor, which will not be very noticeable, and if the stain is located where the inhabitants of the house constantly walk, it will be erased over time.
Let's summarize. The best and relatively safe way to remove glue from laminate flooring, and indeed from any other surface, is naturally specialized means - debonders, preferably using the same brand.
In any case, no matter what method you use, you need to clean the surface carefully and slowly. You should not make excessive efforts; in addition, you should scrub surfaces using cleaning agents or solvents without using abrasive materials.