Do-it-yourself water heating: everything about water heating systems If a country house is actively used not only during the summer season, but also during the cold season, creating a high-quality heating system in it is an urgent need.
Different coolants can be used in heat supply lines: air heated to 60°C, water steam at 130°C and water at a temperature of 95°C. Water heating is most often used.
One of the main advantages of this coolant is the ability to install various water heating systems depending on the design features of the house, personal preferences and other factors.
Classification of water heating systems
Depending on the location of the place where heat is generated, water heating systems are divided into centralized and local. In a centralized manner, heat is supplied, for example, to apartment buildings, all kinds of institutions, enterprises and other objects.
In this case, heat is generated in CHP plants (combined heat and power plants) or boiler houses, and then delivered to consumers via pipelines.
Local (autonomous) systems provide heat, for example, to private homes. It is produced directly at the heat supply facilities themselves. For this purpose, furnaces or special units operating on electricity, natural gas, liquid or solid combustible materials are used.
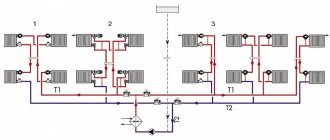
Depending on the method by which the movement of water masses is ensured, heating can be with forced (pumping) or natural (gravitational) movement of the coolant. Systems with forced circulation can be with ring circuits and with primary-secondary ring circuits.
Different water heating systems differ from each other in the type of wiring and the method of connecting devices. They are united by the type of coolant that transfers heat to heating devices (+)
In accordance with the direction of movement of water in supply and return lines, heat supply can be with associated or dead-end movement of the coolant. In the first case, water moves in the mains in one direction, and in the second - in different directions.
Based on the direction of coolant movement, systems are divided into dead-end and counter-current. In the first, the flow of heated water is directed in the direction opposite to the direction of the cooled water. In passing schemes, the movement of the heated and cooled coolant occurs in one direction (+)
Heating pipes can be connected to heating devices in different patterns. If heating devices are connected in series, such a circuit is called one-pipe, if in parallel - two-pipe.
There is also a bifilar scheme, in which all the first halves of the devices are first connected in series, and then, to ensure reverse outflow of water, their second halves are connected.
The location of the pipes connecting the heating devices gives the wiring its name: there are horizontal and vertical varieties. According to the assembly method, collector, tee and mixed pipelines are distinguished.
Schemes of heating systems with upper and lower wiring differ in the location of the supply line. In the first case, the supply pipe is laid above the devices that receive heated coolant from it; in the second case, the pipe is laid below the radiators (+)
In those residential buildings where there are no basements, but there is an attic, heating systems with overhead wiring are used. In them, the supply line is located above the heating devices.
For buildings with a technical basement and a flat roof, heating with bottom wiring is used, in which the water supply and drainage lines are located below the heating devices.
There is also a wiring with “inverted” coolant circulation. In this case, the return heat supply line is located below the devices.
According to the method of connecting the supply line to heating devices, systems with overhead wiring are divided into schemes with two-way, one-way and inverted movement of the coolant
Pumps
Additionally, when laying heating pipelines for a country house, circulation pumps are installed - they do an excellent job of circulating water in large houses with a long length of pipes, save fuel consumption, and also heat the room faster due to the rapid movement of water.
Experts recommend that for one-story houses with a steep roof and a basement, make a scheme with vertical risers and two-pipe wiring. When installing water heating with your own hands, it is important to think about where the exhaust gases will go. To ensure their exit, you need to install a special pipe.
Requirements for the operation of the heating system
With all the variety of water heating systems, there are a number of general requirements for their operation.
They have to:
- uniformly warm up all the air in the rooms;
- be repairable;
- do not create difficulties during operation;
- be linked to ventilation systems;
- be regulated.
The operating principle of the heating system itself is also common: water is heated, after which it circulates through the pipeline and releases the resulting heat, warming the rooms.
The coolant in winter can be a non-freezing liquid - antifreeze. So that the ethylene glycol contained in its composition does not cause corrosion of pipelines
Principle of operation
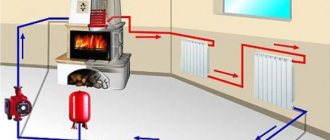
This system has gained popularity for its simplicity. Heating uses the following operating principle: the boiler heats water (or antifreeze) to the required temperature, it flows through pipes to radiators or radiators in the rooms, giving off heat, and returns to the boiler.
Diagram of a system with gravity flow of water.
Also, a water heating scheme may include:
- expansion tank - excess water generated during heating is discharged into it, and it also ensures the absence of oxygen in the system;
- the circulation pump maintains a constant circulation of water in the system, with its help the rate of heating of the room increases due to faster movement of water;
- pressure gauge;
- thermostats;
- air vent - automatic or shut-off;
- safety valves.
Equipment power calculations
The indoor temperature depends on the following factors:
- air temperature outside the building;
- the thickness of the walls of the house and the quality of its individual elements;
- heat capacity of the materials from which the house is built.
When calculating your home's heating needs, you need to take into account all factors, including heat loss through windows and doors, walls and floors with ceilings. Special standards required in the calculation process must be applied taking into account the climatic conditions of the area in which the residential property is located and the degree of existing thermal insulation.
The general meaning of the calculation is to calculate the total heat losses corresponding to the minimum air temperature in your region in order to purchase equipment that can more than compensate for these losses
The greatest heat loss occurs through the outer walls of the house. As the temperature difference between inside and outside the building increases, heat loss also increases.
If we take into account the material from which the external walls were built and the thickness of these walls, then for an external air temperature of – 30°C, the heat loss will be different and amount to:
- brick with internal plaster - 89 W/m² (2.5 bricks), 104 W/m² (2 bricks);
- chopped with internal lining (250 mm) - 70 W/m²;
- from timber with internal lining - 89 W/m² (180 mm), 101 W/m² (100 mm);
- frame with expanded clay inside (200 mm) – 71 W/m²;
- foam concrete with internal plaster (200 mm) – 105 W/m².
However, heat loss occurs not only through external walls, but also through other enclosing structures.
At the same – 30°С they will be for:
- wooden attic floors - 35 W/m²;
- wooden basement floors – 26 W/m²;
- double wooden doors without insulation – 234 W/m²;
- windows with double frame made of wood – 135 W/m².
To calculate the total heat loss of a building, you need to calculate the area of all enclosing structures in square meters, multiply by the standard heat loss by type of structure, taking into account the materials from which they are made, and summarize the results.
The calculation should be made based on the minimum seasonal temperature of a particular area. Heat losses through the walls are calculated separately, because it is necessary to take into account the area of glazing and doorways.
Losses through floors without hatches into the attic or underground are calculated for the entire area as for single structural elements.
The heating boiler is chosen taking into account the fact that its power should be enough to compensate for heat loss with a 20-30 percent margin.
On our website there is a block of articles devoted to the calculation of water heating, we recommend that you read:
- Hydraulic calculation of a heating system using a specific example
- Calculation of water heating: formulas, rules, examples of implementation
- Thermal calculation of a heating system: how to correctly calculate the load on the system
Boiler selection
When purchasing a boiler, as a rule, they take the value of 1 kW of power per 10 sq. m of heated living space, taking into account that the ceiling height is no more than 3 meters. They also take into account the volume of the room, the degree of insulation of a private house, the size of windows, and the presence of additional heat consumers.
With heated area: from 60 to 200 sq. m – boiler power up to 25 kW, from 200 to 300 sq. m – 25-35 kW, from 300 to 600 sq. m – 35-60 kW, from 600 to 1200 sq. m – up to 100 kW.
You can choose an electric boiler - with an area of a private house from 30 to 1000 square meters. m, you can use boilers with a power of 3 to 105 kW, respectively. The disadvantages of electric boilers are the high cost of electricity, power outages or insufficient power.
Water heating systems
Despite all the external differences and different connection schemes, the basic operating principle of water heating systems is the same. The coolant heated in the boiler is transported through a pipeline to the heating devices.
As the water cools, it transfers heat to the environment and then returns to the place where it will be heated. This cycle repeats itself over and over again.
Natural and forced circulation
The following types of heating systems are used in private homes:
Natural circulation . Its performance is based on the difference in density between hot and cold. The upper positions of such a system are occupied by warm water, and the lower positions by cold water. When warm water cools down, it moves down, and when it warms up, it moves up.
The second factor that ensures the natural circulation of water masses is the slope at which the pipes are installed.
This is how the sources of circulation pressure are graphically represented. Firstly, its appearance is due to different water temperatures, and secondly, the inclined position of the pipes (+)
The advantage of the natural circulation scheme is its complete independence from the power supply.
It has many more disadvantages:
- small radius of action , not exceeding 30 m in the horizontal dimension;
- warm-up duration - a long period of reaching operating temperatures at all points of the system when starting after a long break;
- risk of work stoppage due to ice formation in the open expansion tank.
The diameter of the pipeline must be large enough due to the low circulation pressure in the circuit. This factor also influences the choice of batteries, because modern radiators have a too narrow cross-section, which creates additional resistance that counteracts circulation by gravity.
In order to further stimulate the movement of the coolant, the pipeline is constructed with a slope so that there is an average of 3 mm per 1 linear meter. Correct installation of pipes at the right angle is not an easy task, but without solving it, the system will function much slower and more efficiently.
Due to the fact that the coolant sequentially moves through the devices to those closest to the battery supply line, it arrives at a higher temperature (+)
The coolant flows to the distant radiators of gravity systems when it has already cooled down significantly. To maintain the heating temperature, cast iron radiators should be used. To balance the temperature difference, the furthest batteries must have more sections than those closest to the boiler.
Forced circulation is provided by a pump. The circuit may contain one or several pumps. Using several pumps is preferable: an emergency shutdown of one of them will not damage the entire heating system.
The coolant moves cyclically along a closed circuit, which includes an expansion tank, which eliminates the evaporation of water.
A distinctive feature of a water heating system with forced circulation of coolant is the presence in the circuit of a pump, which promotes the movement of water
Advantages of a forced circulation system:
- for heating installation you will need more pipes, but of a smaller diameter;
- you can use different types of radiators and heat pipes with small diameters;
- the temperature of heating devices is easier to regulate;
- the range of action has been significantly expanded due to artificial stimulation of coolant movement;
- the possibility of using heating units with increased coolant characteristics.
The disadvantage of forced systems is their dependence on energy supply. In order to avoid incidents with complete heating inactivity, it is recommended to stock up on a diesel or gasoline generator.
In addition, the disadvantages include:
- the need to accurately calculate the diameter of the pipeline, because too narrow channels will sharply increase the hydraulic resistance, and when circulating through excessively wide pipes, the coolant will “noise”;
- considerable cost of construction due to the almost double length of the pipeline, the inclusion of one or two circulation pumps in the circuit, and, if necessary, a booster pump;
- mandatory use of expensive regulators of coolant flow, its temperature and pressure in the system.
The correct choice of the type of circulation depends on the individual characteristics and location of the building in which the water heating will be installed. However, recently they have begun to resort to schemes with natural movement less and less, using them mainly in buildings for temporary residence.
Most often, private houses are equipped with systems with artificially forced coolant movement due to significantly greater capabilities.
Combined circulation systems
The combined system can operate in both natural and forced modes. This means that when installing it, it is necessary, as in the case of using natural circulation, to provide for a pipe slope of 3-5 mm per linear meter, as well as installing a pump, as for forced circulation.
Typically, such a heating scheme includes a solid fuel boiler.
The circuit includes: 1- electric boiler, 2- solid fuel boiler, 3- pump. This is a diagram of a combined heating system, in which, in addition to the pump, there is an inclined pipeline system, and the electric boiler is duplicated with a solid fuel one, so that the system can operate without electricity (+)
The point of using a combined system is that it will continue to operate even in the event of a power outage. But a sudden cessation of heating in winter threatens not only a decrease in the temperature in the room.
Elements of the heating system may simply fail because water, expanding when freezing, will break their tightness.
Water temperature and pressure in heating networks
The normalized temperature in water heating systems depends on the air temperature outside the building:
- If outside the window it is not below zero degrees, then the temperature of the coolant in the supply pipeline is maintained within 40-45 degrees. In this case, the return water will be at a temperature of 35°C.
- If the temperature outside is 20 degrees below zero, then water with a temperature of 67-77°C circulates in the supply line. Then the coolant in the return will be no colder than 53 degrees.
- When the outside temperature drops to -40°C, the hottest coolant (+95°C) is supplied to the heating devices. In this case, the return temperature can reach 70 degrees.
In networks with natural circulation, the pressure inside the circuit is slightly higher than the static pressure. In one-story buildings with forced coolant flow, the pressure in the heating pipeline is maintained in the region of 1.5-2.5 bar. As the number of floors increases, the pressure in the network increases. So, in five-story buildings it reaches 4 bar, in nine-story buildings - 7 bar, and in high-rise buildings it reaches 10 bar.
Methods for installing water heating systems
Let's consider two main installation schemes for heating systems.
Single pipe heating system
The design of the pipeline in the single-pipe version is characterized by a direct sequence of supplying coolant to the radiators. The coolant fills and warms up the first battery, then the next, and so on.
Two pipes are connected from one pipe to each radiator: the first is needed to supply coolant, and the second is to drain partially cooled water.
A single-pipe heating system is characterized by a sequential connection of all radiators, in which the coolant, having passed through the first heating device, enters the next one.
The peculiarity of this scheme is the relatively low heating of the last battery compared to the first, since the water “reaches” it, having already given up part of its heat.
Another disadvantage of the single-pipe heating option is that it is impossible to stop the supply of coolant to one specific radiator in case it breaks down. You'll have to shut down the entire system.
Two-pipe system and its varieties
In a two-pipe heating scheme, as is already clear from the name, not one, but two pipes are involved. In this case, each of the batteries is connected by one pipe to the main line through which the coolant is supplied, and by the second to the return pipe. It turns out that separate pipes are provided for hot and cooled coolant.
This system involves two pipes: one carries hot water, entering the radiators through pipes, and the second carries coolant (+) from the batteries.
Thanks to this heating design, the water in all radiators has almost the same temperature. The operation of such a system is easier to control, adjust and automate.
The two-pipe system, in turn, is divided into two types:
- with the upper gasket of the supply pipe, i.e. with top wiring;
- with the bottom gasket of the supply pipeline, i.e. with bottom wiring.
Systems with overhead wiring are built mainly in multi-storey buildings with an attic space. Schemes with bottom routing are a priority in private low-rise construction, because they make it possible to hide the laying of the pipeline to the maximum and eliminate or reduce the number of risers.
A two-pipe heating system for a private house is often made according to a collector circuit, although the latter can also be single-pipe. The radial arrangement of pipeline sections allows to significantly reduce the cost of heating the coolant (+)
Pipe layout diagrams
Pipe routing involves various options for connecting heating devices to sources of thermal energy. There are serial (one-pipe), parallel (two-pipe), collector (radial) wiring.
Single-pipe
The hot coolant passes through all the heating devices in a sequential manner and transfers a certain percentage of thermal energy to each. This type of water heating is considered the simplest. It requires few components and time. It is worth noting that single-pipe wiring is characterized by disadvantages: there is no possibility of isolated regulation of the heat transfer of any device, the amount of thermal energy decreases with distance from the central heating unit.
Single-pipe (single-circuit) heating system diagram
The diagram shows a single-pipe system, which includes a heating boiler, heating devices, pipes and an expansion tank. In addition, this circuit contains taps that regulate the supply of coolant. The red color shows the movement of the hot coolant, and the blue color shows the cooled coolant. The cooled coolant flows back into the heating boiler.
Two-pipe
Such a layout of the heating circuit implies the possibility of connecting two pipes suitable for the batteries. The upper pipe provides forward current, and the lower pipe provides reverse current. It is possible to regulate heat transfer for any heating device by controlling the passage of heated coolant through it. The two-pipe scheme for organizing space heating can be horizontal or vertical.
Two-pipe (double-circuit) heating system diagram
The diagram shows a two-pipe heating system, which includes a heating boiler, batteries, pipes and an expansion tank. It is worth noting that two pipes are suitable for each battery: one is necessary for the entry of hot coolant into the system (its movement is marked in red) and provides forward current, and the second is required for the removal of cooled coolant (its movement is shown in blue) and provides reverse current.
Collector (radial)
Such a connection scheme is characterized by the extension of a pair of pipes individually from the boiler to each heating device to implement the autonomous nature of the reverse and forward flow of water. Next, the pipes are connected next to the boiler on combs. The total length of pipes in such a room heating system exceeds their length even if a two-pipe system is used. But there are also advantages, namely the absence of connections between pipes. In order to distribute thermal energy evenly, preliminary balancing is required before start-up. The balance is leveled by adjusting the flow of coolant in the loops.
Leningradka
The “Leningrad” scheme for organizing space heating involves solving the problem of independent regulation of heat transfer for any radiator in the case of connecting a single-pipe system. Any battery is equipped with shut-off valves, which allow you to regulate the flow of coolant. In addition, shunting occurs using a bypass pipe with smaller dimensions in order to ensure correct circulation of liquid along the circuit when the taps on the batteries are closed.
Heating scheme “Leningradka”
This diagram shows how the Leningradka system is implemented. Each battery is equipped with shut-off valves, which are necessary to regulate coolant flow. The diagram also shows: heating boiler, pipes, security system, expansion tank. Red indicates the movement of hot coolant, and blue indicates coolant.
Open and closed heating systems
In addition to the types of water heating systems we have already discussed, there is a division into open and closed structures.
An open heating system consists of a boiler (any type except an electric one is used), pipelines, heating radiators and an expansion tank, into which excess water flows as it expands during the heating process.
The tank is not sealed, water from the system can evaporate, so its level must be monitored and topped up if necessary.
In order for an open heating system with overhead wiring and natural coolant circulation to work more efficiently in winter, it is recommended to insulate the supply riser. This measure will prevent the coolant from cooling and, as a result, slowing down its movement (+)
The pump is not used in an open heating system. The heating boiler is located at its lowest point, and the expansion tank is located at its highest point.
The closed design is airtight . It includes all the same elements as the open one. But since the movement of coolant in it is forced, the mandatory list of elements is supplemented by a circulation pump.
The expansion tank, which is part of a closed structure, consists of two rolled parts, separated by a diaphragm. When an excess of expanded liquid occurs in the system, it enters one of the chambers of the tank, pushing the diaphragm into the second chamber filled with nitrogen or air.
As the coolant expands, the pressure in the system increases, and the part of the tank filled with water tends to displace and compress the gas mixture. When the pressure limit in the tank is exceeded, a safety valve is activated, releasing excess coolant.
A closed heating system is characterized by forced movement of coolant and the presence of a closed expansion tank with a membrane; this system is more complex than an open one
Each heating system has its own advantages and disadvantages. They differ in a number of characteristics and are suitable for various objects. If you need to heat a small private house or cottage, use a simple and reliable open design.
A closed heating system, which is more complex to install and operate, is more often used in large cottages and multi-storey buildings.
Two-pipe heating scheme
This heating scheme is the best option for a private home. For a small family, the boiler can heat the required volume of water. It is advisable to use softened or tap water. Well water is not suitable for this system.
You can use one circuit for heating and the second for heating water. This system is beneficial because in the warm season you do not need to heat the house. Therefore, you can only use the water heating circuit. For such a circuit, a small part of the boiler power is wasted. Approximately 25% of total capacity.
Heating system elements
Since we are going to install water heating in the house with our own hands, we need to have an idea of the components of the proposed design.
Determining the right boiler
The boiler is the heart of the heating system. It is very important to choose it correctly, since the reliability of heat supply largely depends on it.
Heating boilers can be used either singly or in pairs, for example, in addition to an electric boiler, a solid fuel boiler can be included in the circuit in case of a power outage
Depending on the fuel used in the boiler, the following types of these devices are distinguished:
- Gas . This boiler is most popular among consumers. It is easy to install and works without unnecessary noise. Gas is relatively inexpensive and produces a lot of heat when burned. But to use it, you need to obtain permission, order the installation of a supply line and organize exhaust ventilation in the boiler room.
- Electrical . These boilers are the safest. Their installation location does not require any additional equipment. Their operation does not produce open flames or combustion products that could cause poisoning. But the efficiency of this device is relatively low, electricity is expensive, and the energy-intensive boiler requires a reliable power grid.
- Liquid fuel . Unlike gas boilers, these boilers are equipped with a special type of burner. This equipment requires a special boiler room. Liquid fuel quickly pollutes the boiler.
- Solid fuel . These devices burn coal briquettes and other types of solid fuel. If you are ready to prepare firewood or coal for the entire cold season, then you can use this option.
Combination boilers are considered the most reliable, in which different types of fuel can be used. There is only one drawback to such equipment - such boilers are expensive.
What are heating radiators?
In order not to be disappointed with the results of the work performed, you need to take a responsible approach to the choice of radiators. In this case, you should focus not so much on aesthetic qualities, but on the technical characteristics of the batteries. And the technical properties largely depend on the material used to make these products.
Modern cast iron radiators can look very attractive, especially if the interior of the room as a whole is designed in the same style.
Radiators are:
- Steel . These inexpensive products are too susceptible to corrosion. If the water is drained from the system in the summer when heating is not used, the service life of steel radiators can be significantly reduced.
- Aluminum . These attractive looking radiators heat up fairly quickly. Only significant pressure drops have a negative effect on them. In private homes this danger does not threaten them.
- Bimetallic . Such batteries are resistant to corrosion from aluminum, and high heat dissipation from steel.
- Cast iron . These products are expensive, but they will last a very long time. They take a long time to heat up, but they also take a long time to cool down. The significant weight of cast iron products is not a hindrance during their operation, but can slow down the installation process.
There are new models of radiators, the inner surface of which has a protective coating applied. These batteries are a little more expensive, but the money spent on them is more than worth it.
How not to make a mistake with pipes
Installing a heating system will require a lot of pipes.
Which one should you prefer:
- Metal . The service life of such pipes is not very long. Over time, metal products can rust. They are mounted using threaded connections.
- Polymer . This is an inexpensive but fairly reliable material that is resistant to corrosion. Even a non-professional can install these pipes. A pipeline made of polymer pipes will last a very long time.
- Metal-plastic . These pipes contain aluminum and plastic. The pipeline from them is assembled using threaded or press connections. As a byproduct of the high coefficient of thermal expansion of these pipes, they can crack if the water temperature changes suddenly.
If the home owners have no budget restrictions, it makes sense to install heating systems using copper pipes. This is a very expensive material, but the costs are worth it. Such pipes are reliable and durable.
They tolerate increases in temperature and pressure well. For their installation, soldering is used - silver-containing high-temperature solder.
Everything we told you above concerned the radiator water supply. But water can also be used as a coolant in other heating systems.
When installing a water heating system, you may need quite a lot of pipes, so you need to calculate the feasibility of purchasing expensive products and focus on your real capabilities
Elements of shut-off and control valves, safety and control
The complete set of the water heating circuit must include:
- taps and valves - to start/stop the flow of liquid;
- valves and taps - to regulate coolant flow;
- thermostats – for setting temperature conditions;
- filters – to clean the circulating coolant from impurities;
- air vents and Mayevsky taps - for relieving gas-air plugs.
According to the type of control, shut-off and control valves can be mechanical or with a servo drive, and according to the method of fixation - coupling, flange or welding. When installing heating circuits in a private house, fittings with a threaded connection are often installed.
A mandatory element of the system is the security group. It is located after the heat generator on the supply line. The group consists of a pressure gauge, a safety valve and an air vent. Its task is to automatically relieve excess pressure and gas-air mixture. If the boiler design is already equipped with a safety group, then its additional installation is not required.
Comfort of use and automation of the heating system are provided by controllers and programmers. To connect heated floors, pumping and mixing units and manifold distributors are used.
Make-up system
When using water heating, a gradual decrease in the volume of coolant is observed. It occurs due to leaks, evaporation or discharge through an emergency valve. Other reasons for fluid loss include removing air through a Mayevsky valve or automatic air vent, and carrying out repair and maintenance measures.
To replenish the coolant volume, a make-up system is used. Its functions in a closed circuit are performed by a special valve. And in an open-type heating network, liquid can also be added through an expansion tank.
Coolants
When choosing a coolant, pay attention to its heat capacity, viscosity, chemical inertness and safety of use.
Water. The most accessible and inexpensive option. It has a high heat transfer coefficient, low chemical activity, and makes it easy to regulate the temperature. However, water has a relatively narrow operating temperature range, boiling at +100°C and crystallizing at +100°C. Both threshold states of the coolant water can lead to damage to the heating system.
Antifreeze. They have a low freezing temperature (from -10...15°C and below). Almost no salt deposits form. Antifreezes are produced on the basis of ethylene glycol or polypropylene glycol, so they are more expensive than water. Ethylene glycol-based mixtures are toxic and therefore are not used in open systems.
Water system "Warm floor"
The air is heated unevenly along the height of the room: in the upper part of the rooms it is colder, and in the lower part it is warmer.
Warm floors are a wonderful invention that allows you to warm up a room in height in full compliance with the sanitary and hygienic standards required for it (+)
The system temperature is only 55°C, which meets design standards. The installation of heated floors is carried out over the entire area of each room. This is quite a complex job that can only be done efficiently at the stage of building a house. Operating the system also poses a number of difficulties.
Installation features
Before you start installing water heating with your own hands, it is worth considering the most popular and practical systems, advantages and disadvantages, installation principles, as well as suitable types of radiators.
Homemade house construction is always associated with the organization of space heating. This issue is thought through long before the start of the relevant work. There are many options. They are considered by any person who is going to provide heating for a country house with their own hands. Quite often there are cases when no one can help with advice. Company specialists charge a fee for this, which makes their services not the most profitable option. You have to think through everything yourself.
Baseboard heating system
If installing a “Warm House” is difficult, and radiators spoil the interior of the room, you can use a baseboard heating system.
With this type of heating, the pipes are installed behind the baseboard, that is, slightly above the floor level. In this case, the room, as in the case of “Warm Floor,” warms up in the correct sequence.
Thanks to baseboard heating, there is no need to rack your brains over how to fit pipelines, manifolds and radiators into the interior of a country house so that they are not conspicuous (+)
At the same time, the floor is heated, which creates favorable conditions at any time of the year. Heating under the baseboard is becoming more and more popular and is gradually becoming fashionable.
The house you plan to live in all year round needs heating during the cold season. To make your living conditions comfortable, you need to choose a water heating system that is most suitable for your individual conditions.
Nuances of operation
When using a furnace, to improve the operation of the system, the difference between the lower point of cold water (return) and the upper point of hot water is maximized. The riser is brought to the ceiling. In any case, water heating is calculated. If a heating boiler is used, it is recommended to lower it lower, if possible, for example, into the basement. This arrangement allows you to increase the height of the riser and give the water a greater impulse of movement. Consequently, efficiency will increase and the house will warm up more evenly.
Collector (beam) system
It consists of supply and return collectors, to which two pipes go from each radiator. The collectors are equipped with flow meters to control each heating device connected to the collector. Inlet and outlet pipes are laid under the floor and there is no need to think about how to hide them. The disadvantages include the large length of the pipeline and, consequently, increased cost of work. In addition, the collector system cannot operate without an electric pump, and when installing it, it is worth providing an autonomous power source (battery, electric generator).
Central heating of apartment buildings
Through main pipelines, coolant from the central boiler room is supplied to the heating unit of an apartment building and is further distributed among the apartments. In this case, additional adjustment of the degree of hot water supply is carried out directly at the heating point, for which circular pumps are used. This method of supplying coolant to the end consumer is called independent (more details: “Central heating is both pros and cons”).
In addition, dependent heating systems are used in apartment buildings. In this case, the coolant is transported to apartment radiators without additional distribution directly from the thermal power plant. In this case, the water temperature is determined regardless of whether it is supplied through a distribution point or directly to consumers.
Replacing water with antifreeze
If the system has already used water, and you want to switch to antifreeze, then two circumstances should be taken into account.
Secondly
. It is never possible to completely remove water from the heating system. Some of the water remains. If you simply pour prepared diluted antifreeze, its concentration will be insufficient for reliable protection against freezing. Thus, a concentrate must be used. I usually mix concentrate with diluted antifreeze in a 1:1 ratio. After filling the system, you need to start the circulation pump (for a system with forced circulation) or turn on the boiler (for a system with natural circulation) so that the coolant is thoroughly mixed. Then you need to pour out some coolant and measure its density. There is a device for measuring density that is sold in most car dealerships. This device is used to prepare a car for winter (checking the properties of antifreeze in the engine cooling system), but it is also perfect for our purposes. If the device shows a freezing temperature lower than necessary, for example -50 degrees, it’s okay, but if the temperature is higher than we need, then we will have to drain part of the coolant and replace it with concentrate. The drained coolant must be disposed of carefully; it is poisonous and should not be poured into septic tanks or ditches.
I would also like to draw your attention to the fact that different antifreezes may be incompatible with each other. There is an opinion that red composition should not be mixed with a composition of another color.
This is true, but in fact there are other undesirable combinations. Supplements from different brands may react with each other or simply reduce each other's effectiveness. Unfortunately, manufacturers do not indicate what other antifreezes their product can be mixed with. My advice is to pick one brand and stick with it. If you still need to mix, then mix liquids of the same color and before pouring, pour out a little coolant from the heating system, mix it in a jar with a new composition and see if a sediment forms, if the liquid becomes cloudy, or loses its homogeneity.
Best answers
Konstantin Sukhorukov:
Only the heating engineer did not say what would happen to the boiler heat exchanger from the effects of antifreeze. If you want to use anti-freeze, then use liquids based on propylene glycol. And you can pump it without using a water pump, using a regular car pump and a lockable container with two fittings.
Larisa:
pump and hose
Alexander Bakushev:
open the emergency light and fill it until it runs out!
Andrey:
Pump a small container in the usual way and into it a cheap submersible pump, through a hose to the make-up tap, control the pressure using a standard pressure gauge, bleed air, pump and pump. Pre-pressurize the system with network water, check its operation under temperature changes. Evaporation of antifreeze and antifreeze inside a living space is goodbye to health and vision. for these reasons, fill it with an aqueous solution of drinking alcohol (vodka). Moreover, if the system is new and its volume is not very large, get a supply of the strategic product.
Bely Oleg:
Make two fittings in the canister, pour in anti-freeze, one hose goes to the boiler, and pump air into the other with a compressor from the refrigerator. The compressor from the refrigerator presses up to 8 bar - this is definitely enough for you. Productivity is just low. But they cannot pump any electrically conductive liquids - the windings there are not protected in any way...
Denisochka:
Where did the need for glycol coolant come from? When using it, heat transfer is reduced and boiler maintenance becomes more difficult, especially if the boiler is double-circuit with one heat exchanger. For almost any heating system, the best coolant is water.