Published
06/26/2018 |
Author: kmveg 0
What creates comfort, an atmosphere of convenience and relaxation in our home. Of course, a modern heating system. In a city apartment or house, installing a heating system is not difficult.
In a country house, and especially if it is located in an area where there is no gas supply, the issue of heating requires the selection of different options.
If we take into account all the wishes of the household so that the premises heat up quickly in winter, that heating does not require carrying a lot of coal, and that a fireplace is required, then the only solution is to install Kuznetsov bell-type stoves.
There is another option - a channel oven. This stove, as it is called with history, is also called the “Russian stove”.
What is a bell furnace
This is one of the modified designs of a conventional stove. At first, this operating principle was used to operate industrial units. Since the middle of the last century, bell-type heating began to spread in private homes.
Now bell-type furnaces are considered the most suitable option for operation. During construction, they do not require complex calculations of the chimney height to create artificial draft. The process of kindling and heating is carried out much faster than, for example, with a channel stove.
The main difference from the latter is in the method of removing smoke: a duct stove pulls exhaust gases out through the chimney, while a bell-type stove, on the contrary, pushes out smoke. Due to this, the speed of its movement in the chimney is reduced and, accordingly, the efficiency increases (up to approximately 93%). It also reduces the risk of flames being blown out and carbon monoxide poisoning.
Russian builders have always been famous for their skill in laying stoves. The best existing option for such a furnace is the design proposed by Kuznetsov. The secret lies in the use of smooth bricks, clay mortar and a special arrangement in which the bricks divide the space into several cavities, which are caps.
Features of Kuznetsov furnaces
In addition to high efficiency, these devices have the following advantages:
- Easy cleaning - due to the high temperatures in the combustion chamber, even ash burns, reducing the number of necessary cleaning operations.
- Multifunctionality - blacksmiths are often equipped with a hob, oven, and boiler for heating water.
- The design allows you to build stoves of various shapes and sizes, this ensures their more convenient location in the house, and also expands the choice of decorative design of appliances.
- Uniform heating of the furnace walls has a positive effect on the strength of the masonry, so blacksmiths are durable.
The construction of such a furnace will be quite possible for an experienced craftsman - if there is not enough experience, it is recommended to contact a specialist to calculate the drawing. When working independently using a finished scheme, you must carefully follow the recommendations without changing the order of the selected project at your discretion.
Advantages and disadvantages
The dome stove has many positive aspects:
- Savings during construction. During construction, a large amount of materials will not be required. In addition, almost all of them are at hand.
- Simplicity. The installation process is easily carried out if you have a drawing or masonry diagram. There are no complex mechanisms in the design.
- Convenience and ease of use. It is unpretentious to fuel and does not require special care.
- Fast and efficient heating. Design features significantly reduce the time spent heating the stove itself.
- Many options for execution and design. For example, one of the design variations is a two-bell heating stove with a water circuit.
In addition to the positive, there are also negative aspects of using this type of stove:
- Despite the heating efficiency, not all parts of the oven are heated evenly.
- The design limits the possibility of introducing an additional volume of air for blowing with poor draft and low heating.
- Higher fuel consumption compared to other types. This is the biggest drawback, but with a correctly calculated heating scheme, this is compensated for.
Counterflow heating furnace
Air enters these ovens from below. After heating in the combustion chamber, it rises through the lifting channel, where it cools and descends through a pair of lowering channels. This convective system is capable of providing high efficiency due to high-quality heat transfer into the room. The body of such a heating stove heats up quickly and evenly. The outside of the wood-burning stove is finished with facing brick or stone, which gives the structure an aesthetic appearance and allows it to retain heat.
Counterflow oven
The Finnish counterflow wood heating stove removes smoke through the main pipe, and there are additional channels. Thanks to this, a hob is installed on the stove. The only drawback of counterflow furnaces is their complex design. Only an experienced craftsman can build such a furnace.
Operating principle
Before the bell-type system began to be used for heating a house, ducted structures were most in demand. The heated air along with the exhaust gases rose up the channel, heating its walls. Next, the smoke entered the chimney and was discharged outside due to the action of artificial draft.
Note! The system heated unevenly and cooled quickly, which after some time caused the integrity of the masonry to be compromised. Another disadvantage of this method was the large amount of soot formed.
When a bell-type stove operates, the hot air moves on its own: it is pushed out by a new portion of gas. In fact, any such system is a two-bell furnace, since it always contains two bells, which are either next to each other or above each other. Hot gases are retained in them. Both cavities are connected by a jumper through which hot air circulates.
The first hood extends directly from the firebox. The air entering it is retained and cannot move upward. After this, depending on the degree of heating of the bell walls, the gas either gives up heat and, cooled, enters the furnace again, where it is reheated, or enters the second bell. The second cavity serves to create draft and more uniform heating.
This system thus regulates the temperature and combustion mode itself, increasing or decreasing the flame depending on whether the gas movement is directed into the second bell or into the firebox.
Note! Thanks to the hot air constantly present in the circuit, which does not leave it until it gives off maximum heat, the efficiency of the stove increases to 93%.
Distinctive features and principle of operation
People call Kuznetsov’s bell-type heating stove simply “kuznetsovka” or “kolpakovka”. It received its name in honor of its creator - I.V. Kuznetsov, who began developing a new heating technology back in the 60s of the twentieth century.
Compared to conventional units operating on solid fuel, this design is characterized by greater heat transfer and higher efficiency.
If the efficiency of a conventional furnace does not exceed 60%, then the productivity of Kuznetsov bell furnaces reaches 80%.
This is achieved due to the unique principle that underlies the operation of such devices, which is the movement of gases inside the furnace.
Due to its own gravity, heated gases move through the pipe, warm air masses are directed upward and displace cold ones. Unlike conventional stoves, which operate on the principle of “forced air movement through the chimney,” in blacksmiths the air does not come out of the chimney, but accumulates under the hood. Over time, it cools down there, and is then displaced by a hot stream of air.
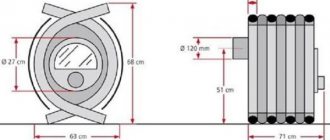
Schematic diagram of the Kuznetsov bell furnace
The design of the cap and the principle underlying its functioning are more complex. However, it is precisely due to the fact that the air moves naturally that greater fuel economy and high heat transfer are achieved. Based on their functional features, such units are divided into:
- bell-type stove for a bath;
- stove for cooking (with a hob, oven, cauldron, grill, etc.);
- bell-type stove with fireplace;
- stove for heating the house;
- combined type.
The most popular are “blacksmiths” of a combined type, on which you can cook food and heat the entire house.
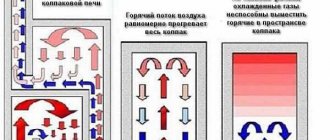
To better understand the operating principle of the Kuznetsov stove, imagine a fire lit in the open air. Since a large amount of air constantly enters it, it gives off a little heat. If you cover this fire with a metal cap, leaving a small gap at the bottom so as not to completely extinguish the flame. Thus, the hot air will move upward and begin to give off heat to the walls. After it cools, it will begin to sink down, and a new stream of hot air masses will take its place. This is the principle of circulation of hot gases, which was developed by Kuznetsov.
The figure shows a diagram of the movement of gases in a bell-type furnace.
Movement of gases in Kuznetsov furnaces
DIY installation
Installation of the furnace is carried out in three main stages:
- Preparatory;
- First level masonry;
- Second level masonry.
Preparatory stage
First you need to collect all the necessary tools and materials to build the stove system. For this you will need:
- Shovels (scoop and bayonet).
- Reinforcing rod made of metal.
- Formwork.
- Polyethylene film.
- Cement mortar (consists of a mixture of sand and cement in a ratio of 3:1, water as required).
- Sand.
Next, all actions are performed step by step:
- First, use a bayonet shovel to dig a hole measuring 1.5 × 1 m, depth approximately 0.8 m. You should try to make the edges as smooth as possible.
- The bottom of the pit is covered with a layer of sand 15 cm thick. So the pit should be left for up to 2 days. This is necessary for the sand layer to settle. This method helps to give additional stability to the oven.
- Formwork can be made from old waste boards, ideally from plywood.
- Reinforcement is performed with a steel rod of average or slightly less than average thickness (this is not critical, since the loads are small).
- Next, the solution is poured slowly and evenly. An important point is to “stir” the already poured solution to prevent the formation of air bubbles in it. This event will maximize the reliability and durability of the foundation.
What materials and tools are used?
Construction work will be impossible without the use of appropriate equipment and necessary materials. Before starting construction, you need to make sure that ready-made components are available. For a bell furnace you will need the following material:
- red and fireclay brick;
- waterproofing sheet for the foundation;
- metal corner;
- mortar kit (sand, clay, cement);
- combustion door, cleanout door, ash door;
- grates;
- cooking surface (presumably cast iron);
- oven;
- chimney valves of different sizes;
- reinforcing mesh.
In addition, the work will not be ensured if the following tools are not available:
To do the job you need to acquire a rule.
- trowels of different sizes;
- building level and rule;
- tape measure for measurements;
- pickaxe hammer;
- equipment for sewing seams;
- shovels;
- container for mixing the solution;
- mop and rags.
User reviews about bell furnaces
Alexander, Moscow: “For many years now, at our summer cottage, a two-bell heating and cooking stove has been a source of heat and food. Easy to maintain and very effective. A minor drawback is uneven heating.”
Tatyana, Vologda: “I ordered the construction of a stove in a private house from a local craftsman. I'm happy with everything. Correct calculations and construction strictly according to the drawings led to the fact that the stove itself heats up perfectly evenly and warms the house.”
Bell-type heating is a universal solution that can replace heating in places where this is not possible. It can also perform the functions of a stove and hot water supply.
Choose which stove is better - channel or bell-type
Not all types of stoves were originally intended for heating residential premises. So, for example, the bell structure was first developed and used in metallurgy. Due to its high efficiency and rapid heating of the surface, it was successfully used for ore smelting.
Channel structures were initially adapted for domestic needs and satisfied the human need for warmth and cooking. In this regard, the consumer may have a question, which stove is better, duct or bell-type? A traditional classic option that has been used in homes for centuries or one that has been converted for domestic use relatively recently?
Advantages and disadvantages of channel and bell-type designs
In order to choose a duct or bell-type stove, it is worth taking into account the technical features of their design, as well as the advantages and disadvantages that each system has.
- Channel furnace. The traditional device is used in a classic Russian oven. The principle of its operation is that warm air from the combustion chamber enters the smoke exhaust system or duct and is released using draft. The disadvantage of this solution is the large amount of smoke during kindling. This is due to the fact that thrust is generated due to a well-heated channel. Another disadvantage of such a device is that the chimney pipe must be quite high. In this case, special skill is required from the stove maker in order to correctly calculate this coefficient with the number of channel revolutions.
- Bell furnace. In this case, the principle of natural circulation of warm air is used. The heated masses rise up and enter the top of a kind of bell (hood), after they have given off heat, they fall down and enter the smoke removal system through the undersides. Some models use several hoods at once, thus increasing the productivity of the furnace several times. The advantage of such a device is that it does not need to be warmed up to ensure normal operation. The chimney pipe may be lower, heating the surface faster, but usually less uniformly than in a duct stove.
A little theory
When designing a homemade “induction”, you need to firmly remember: the minimum power consumption does not correspond to the maximum efficiency, and vice versa. The stove will take the minimum power from the network when operating at the main resonant frequency, Pos. 1 in Fig. In this case, the blank/charge (and at lower, pre-resonant frequencies) operates as one short-circuited turn, and only one convective cell is observed in the melt.
Operating modes of crucible induction furnace
In the main resonance mode, up to 0.5 kg of steel can be melted in a 2-3 kW furnace, but heating the charge/workpiece will take up to an hour or more. Accordingly, the total electricity consumption from the network will be high, and the overall efficiency will be low. At pre-resonant frequencies it is even lower.
As a result, induction furnaces for melting metal most often operate at the 2nd, 3rd, and other higher harmonics (Pos. 2 in the figure). The power required for heating/melting increases in this case; for the same half a kilo of steel, the 2nd one will need 7-8 kW, and the 3rd one 10-12 kW. But warming up occurs very quickly, in minutes or fractions of minutes. Therefore, the efficiency is high: the stove does not have time to “eat” much before the melt can be poured.
Furnaces using harmonics have the most important, even unique advantage: several convective cells appear in the melt, instantly and thoroughly mixing it. Therefore, it is possible to conduct melting in the so-called mode. rapid charge, producing alloys that are fundamentally impossible to smelt in any other melting furnaces.
If you “raise” the frequency 5-6 or more times higher than the main one, then the efficiency drops somewhat (not much), but another remarkable property of harmonic induction appears: surface heating due to the skin effect, displacing EMF to the surface of the workpiece, Pos. 3 in Fig. This mode is rarely used for melting, but for heating workpieces for surface cementation and hardening it is a nice thing. Modern technology would be simply impossible without this method of heat treatment.
About levitation in an inductor
Now let’s do a trick: wind the first 1-3 turns of the inductor, then bend the tube/bus 180 degrees, and wind the rest of the winding in the opposite direction (Pos. 4 in the figure). Connect it to the generator, insert a crucible in the charge into the inductor, and give current. Let's wait until it melts and remove the crucible. The melt in the inductor will gather into a sphere, which will remain hanging there until we turn off the generator. Then it will fall down.
The effect of electromagnetic levitation of the melt is used to purify metals by zone melting, to obtain high-precision metal balls and microspheres, etc. But for a proper result, melting must be carried out in a high vacuum, so here levitation in the inductor is mentioned only for information.
Duct or bell-type?
Duct or bell-type?
Which is better: a time-tested average or a new promising upper limit? This dilemma has been going on for over 45 years among stove makers across the country! How to choose between a pie in the sky and a bird in the hand, who can tell you which is better and how not to end up with nothing? If we turn the conversation to the topic of brick kilns, then all these questions can be reduced to one thing - which type of brick kiln is better, channel or bell-type?
From all the variety of options for brick stoves, several varieties can be distinguished, differing from each other in their functionality; there are stoves only for heating, only for cooking, there are combined and highly specialized ones. However, according to their technical data, all of them are divided into two types of hot gas removal, and, accordingly, into their heating method. These two methods of removing gases have long been known to everyone - the channel system and the bell-type method. Debates about which method is better and which type of furnace gives the greatest return have been going on since the middle of the last century, because it was then that a model of a brick furnace was first created, in which the bell-type method of heating and removing combustion products was used.
Announcements on NN.RU – Construction
Bathhouse log 6*3 planed. The cutting method is at the request of the customer (into the bowl, down into the bowl, into the paw, etc.). Price with a set of lumber 98. Price: 77,000 rub.
Smarty owlets chest of drawers ?dimensions: w720*d466*h750 ?material: made of white chipboard + photo printing ?ball guides - full. Price: 3,690 rub.
Technical supervision services in Nizhny Novgorod and the region. Technical supervision of the construction of public, industrial, residential buildings. Price: 3,000 rub.
We will always buy anion resin AN 31, AB 17-8 and their import taxes. Trilon B, graphite GL 1, Aminat KO 2. We purchase spent cation exchanger KU. Price: 50 rub.
An explosion occurred on the territory of a military unit in Achinsk near Krasnoyarsk: a storage facility for gunpowder charges for artillery caught fire.
Imagine, you wake up in the morning, open the curtains, bright sunlight bursts into your apartment, and outside the window is a stunningly beautiful landscape.
In the Nizhny Novgorod Kremlin, bones recovered from the ground by archaeologists are stored right in the open air. The townspeople were concerned: historical.
Residents of the Ankudinovsky Park residential complex are frightened by announcements that the gas may be turned off. Supposedly from the management company.
Which stove is better, duct or bell-type?
Let me clarify right away that we will be talking specifically about Kuznetsov’s brick kilns. We will not consider modern potbelly stoves - slow-burning metal stoves - for now.
The rich variety of stoves found in our country and beyond can be divided into two categories: duct
(revolving) and
bell-type
. There are, of course, intermediate options. But these two are the most typical, and in their design they are based on two principles that differ from each other.
Channel (recirculating) furnaces
Bell furnaces
Dry seam in the oven
Thus, the hood turns out to be a more efficient design that better removes heat from the exhaust flue gases, and does not require a long chimney
. Which provides better opportunities for designing a greater variety of furnace designs. Well, if we place a second one above the first hood, we will further improve the thermal characteristics of the stove. And with a very slight lengthening of the chimney, we get a serious increase in the preservation of the body inside the stove.
What do we get in the end?
Heating stove: types and design
Structurally, heating stoves can vary greatly, but their basic elements remain unchanged:
- base;
- frame;
- chimney.
The difference between channel heating stoves is the presence of smoke channels. In ductless systems, their function is performed by separate cameras.
Heating stove base
The foundation (base) of a heating furnace is designed to protect the structure from soil movements and the penetration of groundwater. Heavy, large-sized stoves require a strong foundation, which greatly increases the cost and complexity of the installation process.
The structure of the wood-burning stove body is also standard:
- firebox;
- blower chamber;
- roof;
- doors;
- valves
Combustion products are discharged through the chimney of a heating stove. It also creates additional thrust, increasing the flow of oxygen into the combustion chamber.
Heating stoves are:
- countercurrent;
- straight-through;
Direct flow heating furnaces
- bell-shaped;
Bell furnace
- duct.
Each model has its own operating features, disadvantages and advantages.