Warm roof is a term that is associated with a modern approach to the construction of roofing structures. Because through the roof of the house there is a loss of thermal energy equal to 20-30% of the total heat loss. And this is a significant amount. Therefore, in the article we will tell you what materials are used today to insulate roofs, what technologies are used for their installation, and several technological solutions for insulating roof structures.
Warm attic roof Source yandex.com
Roof preparation
Insulation installation diagram.
When insulating a roof with your own hands, first of all you need to draw up a work plan and decide on thermal insulation materials. Any roof, regardless of the type of structure, consists of an external and an internal part. The roof from the outside (from the street) is called the roof, and the inside part is made up of a frame of rafters and floor slabs. In order for the roof to be warm and last a long time, before starting work, if necessary, you need to carry out repair work, get rid of moisture and all its manifestations on the roof structure: rust, mildew or mold. In this case, the metal parts are cleaned with a metal brush and coated with anti-corrosion agents, and areas affected by mold or mildew are treated with antiseptic compounds.
Regardless of the type of roof, if there is no insulation, the heat loss of the house can be 25%
Based on this, it is important to choose a suitable thermal insulation material. To simplify the installation of insulation with your own hands, the width of the slabs should correspond to the distance between the rafters
Otherwise, cold zones will form in unfilled areas, which will lead to a decrease in the quality of the insulating structure. If you use roll insulation (instead of slab insulation), you can set any width by cutting the roll with a regular wood saw. This will be relevant if the distance between the rafters is different. To keep the roof warm, today there is a wide selection of insulation materials. Each of them has its own pros and cons:
Scheme of a pitched roof with insulation.
- Glass wool is relatively cheap, easy to install, and has good thermal insulation characteristics. It must be used together with waterproofing, as it can lose up to 60% of its thermal insulation properties when wet. It is not a favorable environment for the life of rodents and insects.
- Mineral wool is similar in characteristics to glass wool, but has a long service life (up to 50 years). It is very convenient for DIY installation, as it is available in rolls or in the form of slabs.
- Basalt slabs - the main advantage of this insulation is its high fire resistance. When wet, it loses its thermal insulation properties, therefore, like other fiber insulation materials, it should be protected from moisture.
- Polystyrene foam is one of the cheapest, but no less effective insulation materials. The variety of slab sizes allows it to be used for any roof structure. The disadvantage is the fragility of the slabs, so you need to be careful during installation. In this case, the roof can become a habitat for rodents when using polystyrene foam as insulation.
- Expanded clay - the main advantage is the environmental friendliness and fire resistance of the material. At the same time, it is resistant to biological influences. But the application technology mainly applies to horizontal surfaces (roofs, ceilings), which limits its use. It is also heavier than mineral wool.
- Polyurethane foam is a liquid insulation with fairly low thermal conductivity. It is applied by spraying onto the prepared waterproofing layer. Suitable for cases where you need to quickly carry out insulation measures.
Icing on the roof
As practice shows, snow on the roof does not pose any danger, except for additional weight on the roof frame. The danger from snow appears when it begins to melt, resulting in the formation of ice.
Do-it-yourself insulation
And because of ice, icicles and ice plugs appear in drainage systems. In addition, ice has a negative impact on the quality of the roof covering. And this is not the only unpleasant moment for the roof.
The main reason for the formation of ice is the difference in air temperature between day and night. At the same time, snow melts due to heat transfer from the living space to the attic, and from there to the roof.
For this reason, a warm roof prevents all these problems. Although a lot depends on the material with which the roof is covered.
At this temperature, the air contains a small percentage of humidity, which completely eliminates the possibility of precipitation. And, if there is no precipitation, then there is nothing for ice to form from.
Algorithm for carrying out installation work
In order to insulate the roof from the inside with your own hands as efficiently , you need to carefully prepare - study topical articles and forums, watch training videos, consult with professionals. The work procedure itself can be divided into four stages:
You can do the work yourself
Roof lightning protection
When talking about roof insulation, one cannot help but touch upon such an aspect as lightning protection. No matter how durable the covering material with a super protective layer is, lightning is quite capable of burning through it. And since it is laid on a wooden sheathing, melting and burns can cause a fire. Therefore, creating protection to intercept a lightning discharge and redirect it to the ground is necessary.
Houses with a metal roof do not need to install lightning rods; for them, it is enough to provide a down conductor made of thin steel wire and its grounding
Lightning protection device
There are two types of lightning protection - internal and external. The internal one protects all electrical appliances in the house from overvoltage. The cheapest and easiest way of internal protection is to turn off electricity in the house or at least electrical appliances from energy sources during a thunderstorm. External lightning protection is designed to meet a lightning strike at the roof, conduct it along a safe path (down conductor) and neutralize it in the ground.
Internal lightning protection protects electrical appliances from overvoltage, and external protection protects the roof from lightning discharge and possible melting of the covering material
The external lightning insulation scheme is quite simple. It is easy to do it yourself using a gas apparatus and clamps for attaching the down conductor.
The lightning protection system is not a very complicated device, so you can easily and quickly do it yourself
This protection system consists of the following elements.
- Lightning rod (lightning rod) - “bait” for lightning in the form of a galvanized, copper or aluminum pin with a diameter of approximately 12 mm and a height of 0.2–1.5 m, installed at the highest point of the roof. You can replace the pin with a lightning mesh - important for flat roofs - or with a metal cable laid along the ridge ridge.
- A current conductor is a charge conductor from a lightning rod to a ground electrode, made of steel wire Ø 6 mm, descending from the roof along the walls of the building and secured with clamps or staples.
- Ground electrode is a device that ensures contact of the conductor with the ground. This can be a welded structure made of angle bars and pipes buried in the ground, a metal barrel, a sheet of iron, or steel reinforcement driven into the soil. For the ground electrode to work effectively, the soil around it must be moist. Therefore, it is recommended to periodically moisten it with water during drought, and even better, drain wastewater into this place.
Every year before the start of the rainy season, you need to inspect the lightning rod, checking all fastenings. Loose fasteners should be tightened. Once every 5 years it is necessary to open the grounding device and check it for the depth of corrosion. If rust has covered ⅓ of the ground electrode, it needs to be replaced.
Video: DIY lightning rod, budget option
In this article, we looked at the issues of roof insulation so that you can navigate the variety of materials available today to solve this problem. But you need to understand that even perfect insulation of the roof structure will not give the desired effect without suitable protection of the foundation, walls, floors and ceilings. Only a set of isolation measures will create truly comfortable living conditions in the house. Good luck to you.
The need for roof insulation
How to make the roof warmer to significantly reduce heat loss at home? First of all, you need to choose the right insulation materials and definitely adhere to the installation technology. A well-insulated roof increases the thermal efficiency of a house by 15%, making it possible to create an attic into a room suitable for year-round residence.
Especially great demands are placed on the heat insulator of the attic roof of residential buildings located in areas with cool winters
. The roofing layer of summer attics or used attics includes a thinner insulating layer. The roof, under which an unused attic is located, in most cases is not insulated - thermal insulation is installed on the attic floor or ceiling of residential premises. A warm, non-residential attic is well ventilated, which prevents rotting of the wood elements of the roof frame.
When installing pitched and flat roofs, various roof insulation options are used.
Cellulose
The cellulose in pellet form is blown under pressure to ensure that even the smallest nooks and crannies between rafters are insulated. In addition, the treatment can be carried out even through small openings, which in case of repair allows you to avoid confusion and disassembly of roof elements. Similar to spraying polyurethane foam, this process is quick and precise. The thermal conductivity coefficient is about 0.037 W/(m*K).
Blowing out the cellulose can also be an easy way to fix faulty insulation. This is a good option for insulating the roof from the inside.
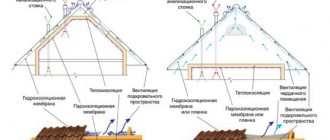
Thermal insulation of pitched roofs
The pitched roof pie is created with insulation along the rafters
It is important to understand how to properly insulate the roof of a house, so as not to allow mistakes that ultimately lead to damage to wooden structures
The most famous insulation material in private housing construction is mineral wool. This is an easy-to-install, non-flammable material that you can purchase at a low cost. But the design of the fleece itself helps the accumulation of moisture, which causes a significant decrease in the quality of the thermal insulation of the material, and after some time it incites rotting of the components of the rafter system
Likewise, when creating insulation, it is important to provide for proper ventilation and waterproofing and vapor barrier of the roofing pie
Installation of a pitched roof heat insulator is created from the attic side during construction work or roof repairs. If repair work is underway, before laying the insulation you need to check the condition of the rafters - rotting parts need to be replaced with new ones. It is also worth finishing all wooden structures with a fire-retardant composition.
The pitched roof pie includes
:
- final roof covering;
- hydrobarrier (layer of material for waterproofing work);
- heat insulator;
- vapor barrier;
- interior finishing (optional).
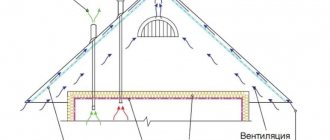
Proper thermal insulation of a roof requires a good exchange of air, for which it is necessary to create layers of air between
:
- under-roof waterproofing and roof covering;
- insulation and water barrier;
- vapor barrier and internal lining (if provided).
Air circulation (removal and free inflow) is provided thanks to specialized vents, one of which must be located in the roof overhang, and the second - under the ridge.
What else to consider
Mineral wool should not be pressed against the foil, even if it may come into contact with it. This can have negative consequences.
In areas where such padding may cause swelling, there is a risk of damage to the foil underneath the covering of easily heated materials (such as metal shingles). Then all your efforts will be wasted, and you will have to insulate the attic from scratch.
Types of roof insulation for a modern house
The final stage in the construction of the frame of any building is the installation of the roof, the quality of installation of which determines the comfort and coziness of the premises, as well as the durability of the entire building. A reliable roof over your head means preventing up to 30% of all heat loss in a building, insulating it from internal condensation and precipitation. Important aspects of the durability and efficiency of roofs are considered to be correctly selected and laid protective layers - waterproofing, thermal insulation and vapor barrier.
In a roofing pie, each layer performs its assigned function, provided that they are placed in the correct order
Each of them is located strictly in its designated place and carries a certain functional load, on which the performance characteristics of the roof depend.
- The waterproofing layer protects the under-roof space from the penetration of atmospheric moisture. It is laid along the outer edge of the rafters, fixed with counter-rails and sheathing. A significant condition for proper installation is the presence of a ventilation gap between the waterproofing and insulation.
- The thermal insulation layer is designed to protect interior spaces from the summer heat and eliminate heat loss through the roof during the cold season. The insulation is laid between the rafter legs in such a way that its inner surface does not slightly reach the upper edge of the rafters, thereby creating a ventilation duct necessary for good ventilation of the roof.
- Vapor barrier membranes or films protect the insulation from warm and moist steam from the room below. They are hemmed along the inner edge of the rafters and secured with slats or finishing materials, for example, clapboard, drywall, etc.
Rafter system
The rafter system forms the frame of the pitched roof; it consists of rafter legs, tie rods (crossbars) and vertical posts. The rafters can rest on a wall, a reinforcing belt or on a mauerlat.
Mauerlat is a beam that runs along the perimeter of the “box” of the house. This element of the pitched roof is attached to the wall with studs. The Mauerlat is needed to evenly distribute the thrust loads from the rafter legs.
The thickness and width of the insulation depends on the parameters of the rafter legs. The material must completely occupy the space between the wooden elements.
Installation options
Insulation of an unheated attic
The simplest type of roof insulation device is thermal insulation of an unheated attic, since insulation of roof slopes is irrational. The most reasonable thing in this case is to insulate the attic floor. Structurally, it is performed as follows:
- by attaching a vapor barrier to the joists with an overlap from below, they create an obstacle to moving steam;
- insulation is placed between the joists;
- so that you can move on the thermal insulation, it is either covered with a continuous flooring, or “paths” are laid from boards.
Thermal insulation must be constantly dried, so ventilation holes are provided in the gables, and waterproofing is installed under the roofing material to protect against possible leaks.
Insulation of a warm pitched roof
Thermal insulation of a used attic or residential attic is somewhat more complicated. The insulation design, which also includes thermal insulation of slopes, is as follows:
Vapor barrier
Necessary to minimize the penetration of vapors from residential premises into the thermal insulation. The vapor barrier film consists of several layers of polyethylene in several layers and a reinforcing grid made of polyethylene or polypropylene. Fastening is carried out either using a stapler or strips.
It is important to always glue the joints with construction butyl tape.
When installing a vapor barrier, special attention is required to the junction units. They are also glued with butyl tape
Roof insulation
The space between the rafters is filled with insulation of the calculated thickness.
The calculations take into account the thermal conductivity coefficient and operating conditions of the pitched roof. Quite often, mineral wool acts as insulation (density - 30-50 kg/cube
m) and staple fiberglass. For additional fastening of fibrous materials, stretchers made of fishing line or rope are also used. If the height of the rafters is not enough to lay insulation of the required thickness, it is increased by adding timber to the rafters.
Waterproofing insulation
The main function of this layer is protective: firstly, against leaks of the roof covering, and secondly, against condensation that forms on some of its types. For waterproofing use:
- a hydrobarrier made similarly to a vapor barrier made of PE layers with a reinforcing lattice, with the difference that to remove steam, it has additional micro-perforations and cone-shaped punctures. During installation, a gap of several centimeters is maintained between the thermal insulation and the hydrobarrier.
- a superdiffusion membrane, the vapor permeability of which is very high compared to a film hydrobarrier. It is laid without any gaps directly on the heat-insulating layer.
Ventilated gap
An air gap must be provided above the waterproofing layer for ventilation, through which steam that escapes from the insulation through the waterproofing is removed. The vents are located on the roof eaves and ridge.
Substructure for roof covering
As a rule, laying the roofing requires the installation of sheathing - solid or lattice with a certain pitch.
Expanded polystyrene
Another popular insulation material is cheaper than mineral wool. However, it is a less flexible material, which makes it difficult to fill the entire space between the rafters. Therefore, you should be especially careful when choosing the sizes of polystyrene foam boards and their exact location.
There are two main types of polystyrene:
- EPS - polystyrene foam boards with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.030 - 0.042 W/(m*K),
- XPS – extruded polystyrene with a coefficient from 0.029 to 0.034 W/(m*K).
A steel grid is installed under the laid polystyrene foam slabs, and a second layer of expanded polystyrene is installed under the rafters to avoid thermal bridges.
Choosing a material for a cold roof
However, it is impossible to mount insulation closely to such a film. The fact is that when it comes into contact with the insulation, the film loses its insulating properties and the insulation actually gets wet. So, if in the future you plan to equip and insulate an attic or attic, it is better to use a waterproofing membrane.
When installing a cold roof, you can use all traditional materials as a covering, which do not require a solid base. However, the optimal solution, according to experts, is profiled sheets or metal tiles, which are technologically advanced, durable and reliable roofing materials.
Steel profiled sheet
The simplest solution for a cold roof in the case of a non-residential building is the use of profiled steel sheets equipped with an anti-condensation coating. This material, which has the structure of synthetic felt, is applied to the back side of the corrugated sheet directly during the manufacturing process.
Between the interwoven fibers of synthetic felt there are many tiny air cavities, due to which the coating accumulates and retains a certain amount of moisture (up to 1 l/sq.m.). As the air temperature rises, it begins to evaporate intensely. In this case, there is virtually no need to install a counter-lattice or lay a waterproofing film.
Installation of a roof made of profiled sheets with an anti-condensation coating is carried out similarly to the installation of conventional corrugated sheets. For installation work, neither specialized tools nor additional devices are needed. When using this material, a 30% cost savings is achieved according to the estimate.
The anti-condensation coating reduces the noise of wind, hail and rain, prevents the formation of mold and mildew, and is easily cleaned under pressure using water to remove contaminants.
2019stylekrov.ru
Construction of a roofing pie ↑
It is recommended to carry out work from inside the room.
- The first layer of waterproofing is laid. It is secured over the sheathing and secured to the counter-lattice bars using staples. The material is laid with a slight sag, but not more than 10 cm.
- Next, insulation is placed on top of the waterproofing. Thermal insulation is installed between the rafters, without gaps.
- Depending on climatic conditions, another layer of thermal insulation can be laid. In this case, the seams of both layers should not coincide with each other.
- The insulation on top is covered with a vapor barrier film and secured to the sheathing using a construction stapler. Sheets of film should be overlapped and taped.
- When laying layers, keep small distances between them.
- The top of the roofing “pie” is covered, for example, with sheets of plywood.
© 2022 stylekrov.ru
Vapor barrier
In any living space there is always water vapor that rises from the bottom up, ending up in the under-roof space where the roof insulation is located. which should not be exposed to these vapors.
Therefore, a vapor barrier is a mandatory element that a roof and roof insulation must have. Finishing the walls of an attic or attic space with a material that does not allow vapors to pass through can sometimes prevent their penetration into the insulation, but most often it is necessary to use special films for vapor barriers, which are laid between the thermal insulation and the ceiling, usually adjacent directly to the insulation material.
The most important quality of such films is their vapor permeability, determined by the density of its material and expressed in g/m2 (the higher the density, the more effective the vapor barrier).
In addition, the film must be sufficiently tensile for two reasons:
- When the insulation loses its elasticity, the rafters no longer hold it, as a result of which the weight of the material falls on the vapor barrier, which must withstand such a load;
- High tensile strength allows the film to keep the vapor barrier intact even when mechanical stress occurs in the roof structure.
The following hydro- and vapor barrier materials are used in modern construction:
- Polyethylene films used as hydro- and vapor barriers;
- Polypropylene films, often used for waterproofing;
- Breathable non-woven membranes, usually used as waterproofing.
The main purpose of materials for vapor and waterproofing is to protect the roof from moisture penetration, as well as to maintain the required operating conditions of the insulation under the roof.
Their main functions are:
- Preventing the penetration of moisture into the thermal insulation material, which sharply reduces its properties and often leads to its destruction;
- Participation in the operation of the roof ventilation system. preventing the accumulation of moisture in the thermal insulation material and facilitating the removal of its vapors to the outside.
Waterproofing films should be used when constructing pitched roofs, the covering of which does not form a continuous carpet, such coatings include:
- Tiles of all types;
- Metal roofing;
- Slate.
These films also protect against moisture penetrating from outside during strong winds or slanting downpours.
Vapor barrier films must be used in the construction of both pitched and flat roofs, regardless of the type of coating. They protect the thermal insulation layer of the roof from water vapor penetrating from the interior, formed during human activity and rising into the under-roof space as a result of convection and diffusion.
Insulation
We will list the layers not in order of the roof, but in order of importance. The presence of insulation distinguishes a “cold” roof from a “warm” one. All other layers are auxiliary - they are needed to protect the thermal insulation material from moisture and condensation.
In most cases, mineral insulation materials (basalt wool, glass wool) are used to insulate pitched roofs. These materials are very vulnerable to water; humidity increases their thermal conductivity and reduces efficiency.
Thermal conductivity is the property of a material to transfer thermal energy. The higher it is, the worse the material retains heat. Humidification causes the pores to be filled with water and thermal conductivity increases.
In the context of construction, they often talk not about thermal conductivity, but about the resistance to heat transfer of the entire structure. This parameter is set by building regulations for each region. For example, in the Central region of Russia, the resistance for a roof must be at least 4.7 m2*S/W.
Calculation of roof thermal insulation, how many materials are required
The thickness of the thermal insulation of the roof, according to SNiP, must compensate for the energy losses of the building, so it is determined on the basis of the thermal conductivity coefficient of the selected material, but not less than 20 cm. If the thickness of the supporting structure is not enough to organize appropriate insulation, then a more efficient material with a low degree of thermal conductivity is used for thermal insulation.
To calculate the amount of insulation, it is necessary to measure the roof and determine its total area. Then it all comes down to simple arithmetic operations: divide the roof area by the total area of insulation in one package and multiply by the required number of layers. An additional 10% for cutting is added to the rounded number of packages.
Let's look at an example of how many packages of 6 m of insulation are needed to thermally insulate a roof of 80 m2.
80/6 x 3=40 packs +10%= 44 packs.
Thus, with these initial data, 44 packages of thermal insulation material will be needed to insulate the roof.
Polyurethane foam
The use of polyurethane foam is undoubtedly a newer technology than the use of polystyrene and mineral wool. This is one of the reasons why it is so much more expensive.
- There are two types of polyurethane foam - closed cell foam with coefficients from 0.021 to 0.024 W/(m*K) and open cell foam with coefficients from 0.036 to 0.040 W/(m*K).
- To insulate the roof, open-cell foam is used - the thickness of such insulation should be at least 18-20 cm.
PUR foam is sprayed or applied using a special gun. For an experienced team, this insulation option is very fast and reliable - you can create a layer of any thickness that will perfectly cover the insulated surface.
The sprayed foam begins to expand almost immediately, penetrating even the smallest cracks, ensuring the seal of the insulation.
Roof insulation
One of the stages in the construction of wooden houses is the installation of roof insulation. Why is this necessary? The answer here will be unambiguous, roof insulation is, first of all, the protection of its structural elements from unfavorable factors, such as: – moisture; – wood rotting; – formation and reproduction of fungal diseases of wood; – evaporation (condensate).
Wood is a fairly strong and durable material, and in this it is perhaps the leader among its analogues. However, all its unsurpassed quality properties are preserved only in the complete absence of moisture. This means that in order for the wooden structures from which the roof is constructed to last a long time and be structurally indestructible, it is necessary to ensure the most favorable conditions - waterproofing the roof, as protection from moisture of the structure from all sides.
Types and methods of roof insulation
Roof insulation
The modern construction market offers a huge range of waterproofing materials for roofing. However, those of them that perfectly cope with their functions in one region will be absolutely useless in another. Therefore, when choosing materials, it is necessary to correlate their technological characteristics and climate characteristics in the place where the structure is being built. Roof insulation during the construction of wooden houses can be divided into several main types:
– Waterproofing with rolled materials (roofing felt, glass insulation, etc.). This is the most common method of roof insulation and is used on all types of roofs. The material is unwound, sections equal to the length of the roof are formed, which are overlapped layer by layer; – Waterproofing the roof with liquid solutions (bitumen mastic, paint, polyurea, etc.). They are applied using a specialized sprayer over the entire surface of the roof. This method of insulation is used on roofs with a large area, mainly industrial enterprises; – Roof waterproofing with sheet materials – consists in the fact that the entire roof area is covered with sheet materials, for example steel, forming a monolithic covering; – Waterproofing with membrane films. This insulation method is used for flat roofs. Membranes are monolithic rolled products that, due to their unique structure, are capable of allowing air to pass through, but prevent the penetration of moisture and steam, which helps protect the roof from leaking, but at the same time provides the possibility of its ventilation and prevents the formation of condensation.
All house designs presented in the catalog have already been developed taking into account a certain type of roof insulation and corresponding calculations of material costs.
Roof insulation device
When building houses from timber, experts strongly recommend that you take the utmost responsibility when installing roof insulation, observing the sequence of actions, standards and recommendations of design and technical documentation and SNiP. Only with this attitude can we talk about a reliable and durable roof. Professionals will help you not only with choosing the optimal waterproofing material, but will also calculate the required material for construction.
Arrangement of insulating layers
The design of a warm roof provides for a certain sequence of laying insulating layers to achieve the best result. The order of their location is reflected in the design documentation, drawings and diagrams:
waterproofing layers are laid at the very top and bottom of the roof structure. At the same time, the upper waterproofing protects against the adverse effects of precipitation, and the lower one traps fumes rising to the ceiling of the room; a vapor barrier layer requires installation only if there is a possibility of increased air humidity. For example, if a bathhouse roof is being built, then a vapor barrier will protect vulnerable structural elements from fumes, and the insulation of the bathhouse roof will not be affected; When a warm roof is built, the thermal insulation layer is located in the middle of the roof structure - in this way it is protected from possible damage
This is one of the most important components of the roof and for this reason, special attention is paid to it during installation;
parts made of natural wood ensure the reliability and strength of the rafter structure and create the necessary level of ventilation of some roofing layers in order to prevent the formation of condensation; rafters are an integral element of the roof frame and the basis for the installation of insulating layers; Concrete inserts and stone embankments on the roof are necessary to strengthen individual parts of the roof; they protect it from possible mechanical influences. They should be used only when appropriate, since they significantly increase the load on the rafter system, which can ultimately lead to roof collapse; the roofing covering is the final layer when creating the ceiling of a building, which reliably covers the interior of it
The material for the roof surface gives the building a complete appearance, while one should not forget about the aesthetic component.
Roof insulation, detailed video:
Lightning protection of a building with a metal roof
The topic of protection against lightning strikes should be discussed separately. It is relevant for buildings where the roofing material is metal.
A lightning protection device on the roof involves equipping the roof with a steel mesh, which is mounted on top of the finishing materials, or under them, provided that the waterproofing and thermal insulation are non-flammable. This mesh performs one function - grounding the roof and does not carry any technical load other than ensuring the safety of people in the building. Lightning protection mesh is installed on a flat roof, on a gable roof, and on roofs of any other structure.
- Residential building and rigid roofing - the advantages of such a roof
- Sandwich panel roofing: technology and installation
- Combined roofing: types and advantages
- Different types of roofing and their features
- How to draw up a roof plan for an industrial building?
- Metal roofing and its classification
- How to calculate the roof slope in percentages and degrees?
Answers on questions
The main classification of roofing coverings distinguishes two types of roofing - soft and hard. Due to their novelty, more attention is paid to soft roofing materials such as.
Another creation of engineering thought recently is a roof made of sandwich panels. If you use sandwich panels on the roof, this will reduce the time required for roofing work.