If the attic of the house is not supposed to be heated, there is no point in insulating the roof itself. Its function is to protect from precipitation and wind. But it is necessary to prevent heat loss, and insulating the ceiling in a house with a cold roof will help with this. By the way, thermal insulation effectively saves the room not only from cooling, but also from overheating by the sun. This makes it possible to survive the summer heat without much discomfort.
Types of insulation
Heat insulators can be classified according to different criteria:
- according to the shape of the products - rolled, slab, bulk, liquid;
- by installation method - for dry and wet installation, sprayed;
- composition - mineral, organic, mixed;
- by structure - fibrous, porous, cellular, film.
These materials not only retain heat, but also serve as sound insulation, which is quite important for ceilings. A cold roof is not always able to protect against external noise, and sometimes it itself becomes a source of noise (for example, a metal tile roof during rain).
How to choose insulation for a cold roof
Materials for thermal insulation of residential buildings must have:
- low thermal conductivity;
- light weight;
- environmental cleanliness;
- fire safety;
- ease of installation;
- at an affordable price.
Most modern insulation materials meet all requirements. And considering that savings on heating are noticeable in the first season, the costs of their purchase and installation quickly pay off.
Mineral wool
This is a large group of materials made from mineral raw materials - rocks, broken glass, waste from the metallurgical industry. For insulation of residential buildings, 2 types are used - basalt (stone) and glass wool. Slag wool is prone to strong shrinkage and water absorption, therefore it is used mainly for thermal insulation of outbuildings or industrial facilities.
Mineral wool is the most common insulation for frame wooden houses, since it does not burn and is close in technical characteristics to wood. It is produced in the form of rolls, slabs or stitched mats of standard sizes, suitable for laying between elements of the supporting frame. The loose fibrous structure retains heat well, and due to the elasticity of the fibers, cotton wool shrinks little under its own weight. The synthetic binder is present in a very small amount - up to 3.5%, which ensures harmlessness to health. For installation on the ceiling, roll material, soft or semi-rigid slabs are used. In the absence of load, they do not wrinkle and retain high thermal insulation qualities for a long time.
If you intend to walk on the floor, it is necessary to lay a flooring made of boards, OSB or plywood. This will protect the mineral wool from deformation. It is prohibited to step on it both during installation and operation. The disadvantage of fiber insulation is its high hygroscopicity. To protect the material from waterlogging, it is recommended to install a vapor barrier on the side of the warm room. It will prevent water vapor from penetrating the thermal insulation and deteriorating its properties.
During installation, mineral wool is laid out on a horizontal surface between the floor beams. The seams are filled with scraps to eliminate cold bridges. If there is a risk of leaks from above, waterproofing is spread over the insulation.
The thickness of the thermal insulation layer for reliable protection from cold is determined by thermal engineering calculations. Depending on the climatic zone, design and composition of the ceiling pie, from 150 to 300 mm of insulation thickness will be required.
Modern glass wool is somewhat cheaper than stone wool, but is not inferior to it in thermal conductivity and other indicators. Many people are afraid of the tiny glass dust that is released during installation. To protect yourself from its harmful effects, it is necessary to observe safety measures, as when laying basalt wool.
The better the roll materials
Rolled materials: mineral wool, glass wool and others retain heat in the house. It is difficult to work with such materials because the fibers fall off. Protective clothing and goggles should be worn during operation.
- When insulating the inside of a room, the ceiling is cleaned of old whitewash, the joints are sealed, unevenness is removed, and markings are made using a laser level.
- Drive the nails in so that the heads stick out.
- The threads are pulled between them in a zigzag manner.
- Then insulation is placed under the threads. Two people work: one pulls the threads, the other inserts rolled materials.
- Attach the film.
- The nails are driven in.
- Plasterboard is laid on top or a false ceiling is made.
“Lathing” of nylon threads on the ceiling
Foam insulation
This group includes foamed polymer materials manufactured using press, pressless, autoclave, extrusion and autoclave-extrusion technologies. The raw material for them is polystyrene and its derivatives. As a result of processing, slabs of different sizes and colors are obtained, which, by the way, does not mean anything; it is an indicator of the brand.
The most common in construction are pressless PSB and extruded EPS. The first type is better known as household foam. It is more fragile and loose than EPS, but is cheaper. Polymer insulation is characterized by low density and thermal conductivity, sufficient strength under compressive loads and durability. The service life with UV protection can reach 50 years.
A common drawback of all materials is flammability. When burning, particularly dangerous substances are released. To reduce flammability, the addition of fire retardants is introduced. The result is self-extinguishing grades, which are more preferable for residential construction. But even insulation with fire retardants is recommended to be protected with a layer of non-combustible material of at least 30 mm. This means that the thermal insulation must be laid on a concrete slab and filled with screed.
If the ceiling is made of wooden beams and sheathed with wood materials, the use of foam insulation is not recommended. Wooden structures are classified as fire hazards, so the risk of fire is very high. The slabs are laid in several layers with overlapping joints. The seams are carefully filled with polyurethane foam. No vapor barrier required. Expanded polystyrene has zero vapor permeability, that is, in fact it is itself a vapor barrier.
He feels good surrounded by concrete. But wood doesn’t like polystyrene foam. In the place where wooden structures are tightly adjacent to polymer materials, a zone of high humidity is formed. Wood is not ventilated and rots quickly, so this proximity reduces the service life of the load-bearing beams.
Communications Contact
What to do if a ventilation pipeline or chimney passes through a ceiling made of wooden beams? If a beam is located on the path of a vertically oriented highway, it is cut, and the load is transferred by transverse elements to adjacent beams. In this case, the distance from the outer surface to the strapping of jumpers must be at least 100 mm.
Connection of pipes with insulated ceiling
The chimney is lined with expanded polystyrene slabs 40 - 50 mm thick, not only in the intersection area, but also along the entire length of the structure exiting the roof. The membranes are folded up (the vapor barrier is down, the water barrier is up) and covered with bitumen tape for a tight fit to the polystyrene foam sleeve of the pipe. The gate areas are then crimped with a frame made of wooden blocks using dowels passing into the walls of the chimney.
The same should be done with ventilation ducts, with one exception: in most cases they are not sleeved. Electric cables are attracted by clamps to the beams, and in places where they pass through the membranes, the places where the films are folded are sealed with foil tape and fixed with plastic clamps.
Expanded clay, vermiculite, perlite
These bulk insulation materials are made from mineral raw materials - clay, shale, volcanic rocks. High-temperature swelling results in the formation of porous granules with low thermal conductivity.
Mineral materials do not burn, tolerate waterlogging well, and shrink little. But there is a significant drawback - it is quite heavy in comparison with fibrous or polymer heat insulators.
A higher load may not be critical for load-bearing structures if they are calculated with a margin. But bringing, pouring out and leveling several dozen cubes of expanded clay in the attic is not such an easy task. For comparison, the weight of 1 cubic meter of mineral wool weighs 50 kg, foam plastic - 35 kg, and expanded clay of fractions 5-40 mm - 300-400 kg. In terms of an attic area of 100 sq.m and a layer height of 25 cm, the result is 7.5-10 tons.
The second drawback is that a fairly thick layer is required. Its thickness should be determined by calculation. On average, it is 25-30 cm. In the southern regions, it is allowed to reduce the thickness of the insulation to 15-20 cm. In the northern regions, it should be increased to 35 and even 40 cm.
Bulk materials must be protected from moisture from steam. To do this, a vapor barrier made of dense film is spread on the base under the insulation layer. There is no need to cover the top with anything; moisture evaporation should occur naturally.
Spray polyurethane foam
The advantage of this type of insulation is the creation of a seamless coating and high installation speed. PPU is sprayed using a compressor unit or a hand-held spray can with a gun. The polymer hardens very quickly, and the surface shape can be any.
The vapor permeability of polyurethane foam is close to that of wood. Unlike the foam shell, which does not allow the wood to breathe, polyurethane foam does not retain moisture, so it freely migrates between layers and evaporates into the atmosphere.
Spraying is done in one layer. One can is enough for 1.2 square meters with a coating thickness of 50 mm. But this is not enough for the middle zone. According to the standards, floors under a cold roof in a temperate climate zone must be insulated to a thickness of at least 81 mm, that is, the cylinder will be consumed for 0.74 sq.m.
Polyurethane foam, like any polymer, is afraid of ultraviolet radiation, so leaving it unprotected in direct sunlight is not recommended. It is also necessary to take into account that polyurethane foam is low-flammable, so it is advisable to spray it on a non-flammable substrate.
What you need to know before starting work
Where to start?.. The topic is quite extensive, and work related to insulation requires, if not professional, then at least basic knowledge about the materials available on the market, their properties and methods of their use.
If you do the work without having this knowledge, you can, at best, waste time, effort and money, so to speak, in the wind, which is what makes it cold, and at worst, provoke a fire due to neglect of fire safety rules and improper installation of insulation material. Yes, insulation is needed to keep warm, but a fire is clearly too much in every sense.
Now we will look at the most popular materials, and also learn how to insulate a ceiling with a cold attic using common types of insulation. We'll find out what the advantages and possibly disadvantages of each are.
Polyethylene foam films
Most often used as a vapor barrier. They retain heat to a small extent, so they are practically not used as the main insulation. The metallized coating increases the amount of infrared rays reflected into the room. But during installation you need to follow some rules:
- the foil layer should be directed downwards;
- the distance from it to the nearest surface is at least 20-25 mm.
If these conditions are met, the foil will actually work. Otherwise, the reflection effect is practically absent.
Important. Multilayer thermal insulation effectively retains heat. The main thing is that it is safe to use.
Other insulation materials
To insulate ceilings in a house with a cold roof, you can use:
- Linen, straw, reed mats treated with fire retardants and antiseptics are laid outside on the ceiling spaced between the joists. The seams are filled with straw or sawdust.
- OSB boards, moisture-resistant chipboard, plywood - are usually used for internal and external cladding of ceiling beams. They also play the role of additional thermal insulation.
- Sprayed ecowool is a mixture of crushed waste paper, boric acid and borax. It is spread dry or wet by a compressor unit. Manual installation possible.
- Cork is a roll or sheet material that is glued to the ceiling from the inside. It is quite decorative, has good soundproofing properties, is not afraid of moisture and does not contribute to the spread of fire.
- Sintepon or felt are non-woven materials made from synthetic fibers. They have low thermal conductivity, vapor permeability, moisture resistance and environmental safety. There is no dust during installation, so installation can be carried out without gloves, goggles or respirators.
The need for ceiling insulation
A cold roof is a budget and practical option for organizing the roof of a house for seasonal living. This design significantly saves construction costs, but does not contribute to heat conservation.
It is advisable to resolve the issue of thermal insulation of the ceiling zone at the stage of building a house. However, insulation is often used in the used premises.
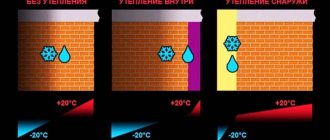
The warm air of the heated room rises and, in contact with the cold ceiling, quickly cools. Thermal energy losses through an uninsulated roof and ceiling reach 25-40%
Thermal insulation of the ceiling solves a number of problems:
- Reduces the cooling intensity of heated air, helping to save home heating costs.
- Increases sound insulation in the room, muffling the rumble from the wind or noise from heavy rain.
- In summer, insulating material helps keep the room cool by keeping heated air from outside in.
Insulating the ceiling increases the comfort of a private home and optimizes the microclimate of the room. If the installation technology is followed, thermal insulation prevents the appearance of condensation on structural elements.
How to insulate the ceiling in a house with a cold roof: 2 simple effective ways
Thermal insulation can be installed on both the upper and lower sides of the ceiling. Before starting work, the frame beams must be installed. Electrical communications are carried out in protective non-flammable casings.
Insulating the ceiling from the outside
It is very convenient to carry out thermal insulation from the upper side of the ceiling. The material is laid on a horizontal surface without the need to hold it suspended. The rough filing of the ceiling should already be ready.
Laying vapor barrier
This is the most important issue in the entire insulation process. If mineral wool or other material with high moisture absorption is used, it is necessary to use a vapor barrier film with a thickness of at least 200 microns.
The panels are connected to each other with an overlap and glued with tape. It is important not to leave even the slightest gaps for the penetration of warm air from the room into the insulation.
The vapor barrier can be attached either from below to the sheathing or laid on top along the joists. The edges of the film should be 30-40 cm higher than the ceiling and wrapped up onto mineral wool. This way there will be no way for warm air to get into the insulation layer.
In a frame house, the vapor barrier should form a continuous closed loop. Ceiling insulation is combined with wall insulation and this must be considered during construction. The film on the top of the walls is laid with a margin of 20-30 cm in order to glue it with the vapor barrier of the ceiling. You can overlap from the ceiling side.
To protect mineral wool from moisture, vapor barrier diffuse membranes are also used, which differ from polyethylene films in their breathable structure. The smallest conical holes ensure the movement of steam in only one direction - out of the insulation. When installing, it is important not to mix it up and turn the membrane the correct way. Usually the manufacturer's logo is on the surface facing the room.
Installation of insulation
Plates or rolls are laid between the joists. It is advisable to break the large thickness into several thinner layers. At the same time, overlaps of at least 20-30 cm must be made in adjacent rows to avoid the formation of through seams.
When laying, it is recommended to avoid strong compaction of the material. This worsens its thermal insulation properties and provokes early shrinkage. The distance between the lags should be only 2 cm less than the width of the slab, then a slight expansion will be provided without excessive compression.
To fill the gaps, pieces of appropriate sizes are cut out. They are installed in the slots also with slight pressing.
If you plan to walk on top, a flooring made of boards or OSB is installed. When installing a continuous floor, it is necessary to leave a ventilation gap between it and the surface of the mineral wool to ventilate moisture.
Insulation of the ceiling from the inside
If there is no easy access to the attic or there are already subfloors there, you can insulate the floor from the bottom side. The ceiling pie will be the same, and this will not affect the performance of the thermal insulation in any way.
Mineral wool slabs are laid between the beams with a slight spacer (the width of the strip of material should be 10-20 mm greater than the lag pitch). To prevent the insulation from falling, it is secured from below with stretched lines or thin slats. As a vapor barrier, you can use foil film or aluminum foil. They are applied from below and secured to the beams with a stapler. The seams are sealed with metallized tape.
For the air gap, slats with a thickness of 20-25 mm are installed. They are nailed at such a pitch that it is then convenient to attach the sheathing to them - lining, drywall, OSB, etc. When installing suspended ceilings, such lathing is not done.
Important. A suspended ceiling does not work as a vapor barrier. In the openings for lamps or communications, warm air with vapor penetrates into the ceiling, so it is necessary to install a full vapor barrier layer.
Peculiarities
Most of the warm air masses escape through the roof. Therefore, when building a house with an uninsulated attic, you need to carefully approach the topic of insulating the attic floor with wooden beams. After all, it creates a certain barrier between warm rooms and a cold attic.
Let's consider the special criteria for attic insulation that affect the maintenance of temperature in the house:
- Purpose of the room.
The attic is a kind of buffer between the environment and the living rooms. Its task is to regulate the temperature difference between the external environment and the house. - Temperature regime.
In any season and on any day, the temperature of the air masses in the attic will always be higher than outside the window. This is why the attic is very cold in winter, and unbearably hot and stuffy in summer. - Heat loss in winter.
The more a substance heats up, the less dense it becomes. This is a physical phenomenon. This is why in residential premises with a heating system, warm air from household appliances is concentrated in the ceiling area. That is, if you do not insulate the ceiling, then in winter all the warm air will warm the attic.
- Excessive heat in summer.
In summer, the reverse process can be observed. The roof, heated by the rays of the sun, will warm up the attic air, which, in turn, will penetrate into the room through the attic floors. - Reverse circulation of air masses.
In contact with the ceiling without thermal insulation, warm air becomes cold, more dense and, as a result, sinks to the floor. This is reflected in the living space in the form of circulating drafts that cause harm to human health.
- The appearance of excess moisture.
When it comes into contact with an uninsulated attic, hot, humid air turns into condensation. The overall level of humidity in the house increases, which leads to mold growth in the corners. - Saving
. The heat lost through the roof without insulation is about 30%. This means that with proper insulation of the attic floor, you can save 30% of the fuel used. Using air conditioning in the summer will also cost less.
The entry of warm air masses into a technical attic (non-residential) leads to negative consequences:
- Due to the mixing of warm and cold masses, condensation may appear in the attic. Water falling on the surface can lead to rotting of wood on load-bearing beams.
- If the attic is warm, the snow collected on the roof will begin to melt. The water dripping at the same time will begin to turn into icicles. Ice forms on the drainage system.