Concrete floors are the most practical option for a private home, due to their strength, durability and low manufacturing costs. But concrete is a cold material, and without high-quality thermal insulation in the winter it is not very comfortable in the house. In addition to high heat loss, condensation, which forms due to the large temperature difference on the inside and outside of the concrete base, also creates problems. There are several ways to insulate a concrete floor in a private house, and even a novice master can do all of them.
How to insulate a concrete floor in a private house
Current budget insulation materials
The choice of insulation product for a wooden house is also influenced by the material factor. Therefore, if you decide to insulate the floor in your dacha yourself with a limited budget, then you can choose the following materials:
- clean dry sawdust;
- sawdust pellets;
- mineral wool;
- Styrofoam;
- expanded clay
Clean, dry sawdust or granules are most often used for the subfloor, but they require careful waterproofing from the ground, since the material quickly absorbs moisture, losing its unique performance qualities.
Clean dry sawdust
Mineral wool is laid both below the floor and in the interfloor ceiling, where it can flawlessly perform its functions for several decades.
Mineral wool
Polystyrene foam insulates almost all structures of a wooden house, from the basement to the roof, since its unique structure does not weigh down the structure. However, such material should first be protected from attacks by rodents, as well as protected from exposure to open flames, because polystyrene foam is the most dangerous in terms of instant fire.
Styrofoam
Expanded clay, as a rule, is used to fill the basement floor or the space under the joists, while the optimal layer thickness for our latitudes is considered to be 30–35 cm.
Expanded clay
Basic requirements for thermal insulation of industrial and administrative buildings
When we talk about thermal insulation of an industrial building, we immediately mean the presence of an aggressive environment, large areas, metal structures and, as a rule, short deadlines for completing work. Therefore, the materials that will be used to insulate an industrial building must:
- be installed quickly so as not to slow down production processes for a long time;
- do not be afraid of the alkaline and acidic effects that are present in the air;
- if possible, protect metal structures of walls and roofs from excess moisture and corrosion;
- inexpensive.
If there is a question about insulating an administrative building, then there are also some requirements:
- insulation should not spoil the overall aesthetic appearance of the building;
- be installed quickly, since the administrative building is constantly in sight;
- thermal insulation should have a low price;
- The service life of the insulation should be as long as possible in order to avoid costly repairs.
And in both cases, of course, we should not forget about EFFICIENCY. The building must maintain the required temperature conditions.
As we can see, there are many requirements for insulation of industrial and administrative buildings and all of them are quite serious. But for sprayed polyurethane foam insulation this is not a problem.
Choice of insulation
The first stage is the analysis of thermal insulation technology, which depends on the room. General requirements for the material are low thermal conductivity, resistance to moisture and temperature changes. The arrangement of the finished floor depends on the insulation.
For fibrous, sprayed and partly bulk materials, a hard finishing surface must be installed. If you need to choose how to insulate a concrete floor under a laminate, it is better to use monolithic sheets.
| Material | Thermal conductivity, W/m*K | Density, kg/m³ | View |
| Mineral wool | 0,034-0,05 | Up to 75 | Sheets, rolls |
| Styrofoam | 0,037 | Up to 16 | Sheets |
| Expanded polystyrene | 0,028 | Up to 45 | Sheets |
| Expanded clay | 0,16 | Up to 800 | Bulk |
Popular types of thermal insulation materials:
- Mineral wool. It is made by heat treatment of basalt rocks. The result is hollow fibers that are bound with a special compound. Advantages: non-flammable, retains heat well. Disadvantages - low density, installation of a finished floor is required.
- Styrofoam. Despite the good thermal insulation qualities, it is not recommended to insulate concrete floors with foam plastic in apartments and second floors of private houses. It has low mechanical strength; an additional screed or a system of wooden logs with a floor covering is needed on top of the sheets. This increases the load on the interfloor ceiling.
- Extruded polystyrene foam. Unlike polystyrene foam, it has an increased density (up to 75 kg/m³), which allows you to install a decorative coating on top of it - linoleum, parquet. Advantages: ease of installation, minimum heat losses at the joints. Disadvantages - flammable material.
- Expanded clay. After firing a mixture of clay and shale rock, small balls with a porous structure are obtained. There are a number of restrictions on use, granules absorb moisture well, and to create a good heat-insulating layer you need a large volume of material. You can insulate a concrete floor with expanded clay on the ground floor of a private house, garage or bathhouse.
The use of sprayed coatings (polyurethane foam, ecowool) for a relatively small volume of thermal insulation is impractical. To form a layer you need special equipment, which increases costs.
Advantages of using polyurethane foam as roof insulation
Roof insulation using polyurethane foam has many advantages over other insulation materials:
- there is no need to dismantle the old roof;
- polyurethane foam insulation has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient, which makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the thermal insulation layer;
- no special preparation of the roof surface is required;
- PPU material has great adhesion to most building materials;
- the ability of polyurethane foam to flow around surfaces of any shape and any bends;
- fill defects and cracks, forming a continuous, smooth, seamless coating;
- short deadlines for completing roof thermal insulation work using polyurethane foam (work speed is about 300 m2 per day);
- Icicles do not form on a roof insulated with polyurethane foam.
Thanks to the unique properties of polyurethane foam, the roof can be insulated both from the outside and from the inside. When applying polyurethane foam to the outer surface of the roof, the PPU coating must be protected from sunlight. For these purposes, you can use liquid rubber or urethane mastic. Coatings made from these materials will protect the thermal insulation layer of polyurethane foam from ultraviolet rays, create additional waterproofing of the roof and increase its service life.
When using sprayed rigid polyurethane foam to insulate a roof, compared to traditional thermal insulation methods, the time savings is 80% and the money savings are 50%. In terms of quality and durability, PU foam insulation technologies are many times superior to other insulation methods.
When repairing roofs with polyurethane foam, there is no need to remove the worn-out coating; in addition, all structures present on the roof are additionally sealed, and the absence of thermal bridges prevents the formation of condensation. During roof thermal insulation work using polyurethane foam, there is no need to stop the activity of the entire room, which is also an important advantage of using polyurethane foam.
Polyurethane foam is applied to the surface with a special high-pressure spraying unit and within a few minutes the polyurethane foam becomes rigid.
How to insulate a concrete floor using chipboards?
This option for arranging floor thermal insulation, using the heat-retaining properties of shavings, involves creating a structure from three layers of different coatings, which are laid on a ready-made concrete base.
In this case, a sufficiently thick layer (several thin layers) of polyethylene film is placed on the hardened concrete. It will serve as a waterproofing protection.
Scheme of insulating a concrete floor with polystyrene foam.
Then a layer of particle boards is installed. In this case, you should definitely leave a thermal gap of approximately 15 mm between the walls and the edges of the chipboard panels. It is necessary so that if the slabs expand or swell due to moisture, they do not rest against the walls and become deformed, which leads to damage to the floors.
When laying particleboard material, you should pay attention to the tightness of the joints of the boards with each other. To prevent the formation of cracks in the joints, these places are covered with construction mesh and then thoroughly rubbed with putty, which is mixed with oil paint.
The slabs themselves are attached to the concrete base using powerful dowels.
After the wood insulation layer has been fixed, the floor is equipped with a finishing coating. It can be any of the modern floor coverings that the customer chooses according to his taste. Decorative skirting boards are attached along the walls.
Horizontal heating
Some people believe that for a comfortable life it is enough to install a warm floor, any of the possible systems. But before installing water, electric or infrared heated floors, the concrete slab or screed must be insulated and properly insulated. Otherwise, half the power of your heated floor will simply go down, which will significantly increase the cost of using such a system.
Therefore, before installing horizontal heating, all measures for thermal insulation of concrete should be carried out, and before the finishing coating, the system itself should be installed. Concrete allows for all kinds of possible devices. Only the installation methods differ.
Before installing a floor heating system, it is necessary to lay thermal insulation
Insulation of concrete floor
In most cases, the floors in apartments in city high-rise buildings are reinforced concrete slabs. The concrete floor itself is very cold, but if you add to this the gaps between the slabs and insufficiently tight joints between the walls and the floor, then it becomes truly icy. Therefore, insulation of concrete surfaces is a top priority for residents of multi-storey buildings who seek to increase comfort in their apartments.
Each master involved in insulation develops his own formula for the ideal insulation “pie” on concrete slabs. Let's look at the most popular possible options.
Option No. 1 - insulation + screed
The thermal insulation properties of a concrete floor can be significantly improved by laying insulation between the floor slab and the cement leveling screed. In this case, floor insulation in the apartment is performed as follows. The first step is to remove the old floor covering and remove the screed. The surface of the slab is cleaned of debris, dust, and unevenness from cement screed residues is eliminated.
Insulating the floor in an apartment using thermal insulation material and reinforced screed
Then a vapor barrier is performed. A polyethylene or polypropylene film is laid on the concrete base, laying the strips overlapping by 15-20 cm and extending 3-5 cm onto the walls. The overlap joints are insulated with special tape. Foam plastic with a minimum thickness of 50 mm and a density of 25 mm is laid on the vapor barrier film. Instead of polystyrene foam, you can use polystyrene foam, mineral wool, etc. The insulation sheets are laid as closely as possible to each other so that cold bridges do not form in the seams. After this, another layer of vapor barrier is laid. If polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene were used as insulation, then this step can be skipped.
Now lay a metal mesh with square cells (cell side – 50-100 mm). The mesh will act as a frame for the cement screed, making it more durable. A cement screed with a minimum thickness of 50 mm is poured over the mesh. A thinner screed will be unreliable - after a while it will begin to crack and crumble. The cement screed must dry, this will take about two weeks. After which, to strengthen the top layer, it is necessary to cover it with a primer. After all this, any decorative covering is laid on the screed.
Option No. 2 - insulation along joists, without the use of wet processes
This option is similar to insulating a wooden floor. The difference is that the thickness of the wooden floor initially contains logs, between which it is convenient to lay any type of insulation. In the case of concrete floors, these logs will have to be constructed independently.
Insulation of the concrete floor along the joists eliminates wet processes and does not burden the ceiling
Technology for insulating concrete floors using joists:
1. First of all, clean the concrete slab from old screed, debris and dust.
2. Arrange waterproofing. It is convenient to use ready-made waterproofing polymer-bitumen solutions, which are applied to the concrete surface with a roller or brush. Another option is to use a vapor barrier film for these purposes, which is laid out overlapping on the floor, extending onto the adjacent walls. If you want to save money, then the most suitable material for hydro- and vapor barrier would be ordinary polyethylene film.
3. Install the logs at a distance of no more than 0.9 m from each other; if you take a step larger, the floors will sag. Instead of logs, if you plan to use bulk material for insulation, metal beacons are attached to the floor.
Installation of wooden joists on a concrete floor
4. Lay the selected insulation. Both mineral wool and polystyrene foam, and any type of bulk thermal insulation materials are suitable. Insulation in the form of sheets or rolls is laid out tightly, without gaps between the joists. Bulk material (for example, expanded clay) is poured between the beacons and leveled to one level using a metal rule.
Insulation is placed in the space between the joists
5. Lay the floor. To do this, you can use sheets of plywood, gypsum fiber board, OSB, chipboard with a thickness of 10-15 mm. It is safer to lay them in two layers so that the seams of the lower sheets overlap the panels of the upper sheets. Thus, the floor covering will be seamless, which will eliminate the possibility of cold bridges. After laying, the layers of sheets are connected to each other and to the joists (beacons) using self-tapping screws.
Laying sheets of dense material (plywood, gypsum fiber board, etc.) on joists
6. Suitable for any finishing floor covering.
Laying laminate flooring on an insulated floor
This short video will clearly demonstrate the process of insulation using joists:
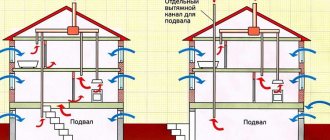
Roof structure
The construction of roof structures is divided into attic and non-attic.
Industrial buildings are made at a slight slope to drain precipitation; they are usually roofless. Attic roof types are mainly pitched structures with a slope angle of about 30-70° and load-bearing elements in the form of rafters, large panels and trusses. The rafters and trusses are covered with sheathing, usually made of wooden beams, or plank flooring. It serves as the basis for a roof made of rolled waterproofing materials. Additionally, before laying the rolled carpet, if there is such a need, vapor and heat insulation is made with special materials.
For spans of 10-12 m, they are built as a system with hanging rafters. It is a structure, the main load-bearing part of which is roof trusses resting on the walls of the building. A vertical headstock (suspension) is installed in the center of the truss. It is connected to the walls by rafter legs, which serve as a supporting base for the roof. To give the structure rigidity, struts running from the base of the beam rest against them.
The following materials are most often used for this design:
- for hanging rafters - boards or beams;
- for the lower chord and tensile racks - steel profile or pipes;
- for farms - reinforced concrete or steel.
Single- or gable roofs made of large ribbed reinforced concrete panels are built with a central support, which can serve as an internal wall. The panels rest on it and the outer walls of the structure. The span of the structure, as a rule, is 6-6.4 m. Fastening is steel anchors. An asphalt or cement screed is applied to the panels and a roll carpet is glued. Nowadays, panels are predominantly made from waterproof concrete, which does not require waterproofing, so there is no need for it.
Industrial roofs of buildings with a height of more than two floors are protected with brick parapets.
Industrial roofing without purlins is formed by reinforced concrete slabs, which are both a load-bearing element and the base of the roof. A cold roof is built from heavy concrete; after laying, the surface is leveled with asphalt mastic or cement mortar, followed by gluing of rolled carpet.
For insulation, foam concrete and mineral insulation are used, a screed is made on top of them and roll waterproofing is glued.
Sometimes flat roofs are made without a slope. To avoid overheating, in some cases they are protected by filling them with 5-15 cm of water; before the onset of winter, the water is drained.
Chimneys and ventilation outlets require a special device for connecting the roof to them. To do this, collars are made of tin, closely adjacent to the pipe; the collar is placed above the plane of the roof. If the covering is asbestos-cement slate, then the collar on the ridge side is inserted under the roof, and on the overhang side it is placed on top of the slate sheets.
Industrial buildings with a height of more than two floors are fenced with brick parapets or gratings according to MRTU 20-4-65.
Choice of insulation
Many materials are used to insulate the floors of a wooden house. The simplest and most inexpensive is expanded clay or sand, which is poured between the rough and finishing coating. They are hygroscopic and protect the boards from rotting, the spread of fungus and provide ventilation. However, bulk non-metallic insulation has its own drawback - over time, their hygroscopicity decreases.
Today on the market you can find many materials for insulating a wooden house. In addition to good thermal insulation, it must meet basic requirements:
- ecologically pure;
- be safe for the residents of the house;
- long service life.
For insulation, fiberglass, mineral wool, penoplex, expanded polystyrene, etc. are used. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages:
o Mineral wool. It can be slag, stone and glass. The form of release is also varied - plate, roll, mat. Mineral wool has a high density, does not burn, conducts heat poorly and is quite economical. The main disadvantage is considered to be low moisture resistance.
When using mineral wool, you should carefully consider the vapor barrier system and ventilation. The side of the stove that is not covered with foil should be on the bottom.
When purchasing mineral wool, carefully read the composition, since the impregnation often contains substances hazardous to the body. The more saturated the yellow color of the material, the more dangerous it is.
The following are more in demand in construction stores:
- Izovol is a mineral fiber product. A distinctive feature is its high hydrophobic efficiency in comparison with conventional mineral wool. Additionally, it has low thermal conductivity, is non-flammable, biologically and chemically resistant.
- Rockwool is a basalt tile. Its peculiarity is that it does not cake, does not lend itself to deformation and shrinkage, like mineral wool. Rockwool resists mechanical stress well. The material is additionally used for sound insulation, since the porous structure absorbs noise well at any frequency. Like Izovol, Rockwool conducts heat poorly, does not burn and is resistant to biological and chemical influences.
- Expanded polystyrene - has a high thermal insulation rate. It is resistant to moisture and does not absorb water, holds its shape well under temperature changes, is durable, environmentally friendly, durable and is not subject to the destructive effects of microorganisms. Expanded polystyrene is easy to process and use.
- Penofol is a modern heat insulator. Sold in rolls, it is insulation with a layer of foil. The thickness and weight are small. The base may vary, but in most cases it is penofol (foamed polyethylene). Thermal insulation properties are maintained under high mechanical load. Laying occurs overlapping or butt. The seams must be taped with metallized adhesive tape. Penofol does not require an additional layer of hydro- and vapor barrier, since the foil already performs these functions.
- Ecowool is a natural heat insulator made from cellulose. The fibers are bound with boric acid and lagnin (an organic antiseptic). The uniqueness of the material is that it does not absorb water and removes it outside. The composition contains no components hazardous to health. Ecowool is fire- and bio-resistant, absorbs sound well and does not conduct heat. A special sprayer is used for application, but the material consumption then increases by 40%.
- Isolon is a new material in construction. With a thickness of 2-10 mm, it insulates well heat and sound, has high moisture resistance, is not subject to rotting and is durable.
For insulation, ordinary sawdust can be used. This heat insulator has been used for many centuries. The natural material is quite cheap and completely safe for the body. Sawdust is often left behind after building a house. This is the most affordable insulation for a wooden house.
Sawdust is added to some building materials:
- sawdust concrete consists of sawdust, cement, sand and water;
- granular heat insulator - sawdust, glue and antiseptic-fire retardant;
- wood concrete – sawdust with cement and chemical additives;
- wood blocks - sawdust, cement and copper sulfate.
Materials for insulation of industrial buildings
It is important to remember that the specifics of thermal insulation of industrial buildings are determined, first of all, by their purpose and location. In all cases, comprehensive work is required to improve the overall thermal protection of the building
It is therefore logical that for each individual part of the structure a different material should be used, suitable for a specific purpose. You can read more about ways to insulate buildings here. For example, mineral wool slabs with combined insulation are best suited for roofing.
In general, the process of insulating an industrial roof includes several stages:
- Laying galvanized steel profile sheet.
- Installation of vapor barrier (polyethylene film).
- Installation of insulation (mineral wool).
- Installation of polystyrene foam boards followed by installation of the roofing system.
Stages of thermal insulation of walls of industrial buildings
The load-bearing walls of the structure must be made of brick, concrete and its varieties (foam concrete, aerated concrete). The structure of these materials has specific features that prevent the passage of cold air.
When using cement or bitumen glue, PPS boards are installed. It is necessary to use only varieties that are designed specifically for the facades of premises. For greater safety, you can install fireproof cutouts made of mineral wool.
The final stage is giving the walls the desired appearance using decorative plaster. To do this, a reinforcing mesh is applied over the slabs, and then a layer of plaster.
This method of insulating the walls of industrial buildings is very popular in Europe. Its peculiarity is that after using this technology there is no need to update the insulation itself. It is enough just to change the outer decorative layer from time to time, which can crumble over the years.
Speaking about industrial insulation, it is worth taking into account the fact that the thermal insulation of industrial buildings must be comprehensive. In this regard, we must not forget about floor insulation.
Stages of floor insulation
Installation of floor slabs to provide stability to the future insulated structure.
Laying PPS slabs. Their size depends on the area of the room and is selected individually in each specific case.
Installation of the waterproofing layer.
The final stage is screed. Laying plywood and gypsum fiber to increase the thermal insulation properties of the floor, as well as the stability of the entire structure.
This insulation technology is usually used specifically for reinforced concrete coverings of premises (industrial buildings). It has the best characteristics and is designed to increase the thermal stability coefficient of the building as a whole.
Features of industrial thermal insulation using polyurethane foam
The methods described above are classic and provide good performance in terms of thermal protection. However, technology does not stand still, and the thermal insulation of industrial buildings is also taking on new forms. In particular, this applies to the use of polyurethane foam (PPU), applied by spraying.
The following qualities can be considered its undeniable advantages:
- Long service life. If technology is followed using modern equipment, polyurethane foam can last more than 50 years.
- Safety for human health.
- It withstands negative environmental influences and is resistant to fungi and mold.
- No technological seams. Thanks to this, the thermal insulation characteristics of industrial buildings are significantly increased.
- The process of spraying polyurethane foam can be carried out in the shortest possible time, which is also a plus for the entire production rhythm.
Of course, when insulating industrial facilities, many nuances always arise. This applies to both the choice of materials and the method of application (which in turn depends on the purpose of the object and its location).
Ignoring at least one of the points can significantly reduce the thermal protection of production premises, which will inevitably lead to additional costs in the future. The second mandatory condition is an integrated approach to the entire industrial facility. If these conditions are met, the best effect is achieved. And the process of insulating an industrial building will be practical and effective.
Concrete floor insulation technologies
It is necessary to take into account the operational properties of the room. For example, before insulating a concrete floor in a bathhouse, you should make good waterproofing. Otherwise, moisture will enter the concrete structure, which will lead to its partial destruction.
An exception is the use of heat insulators with low or zero moisture absorption. These include polymer materials - polystyrene foam or extruded polystyrene foam.
The preparatory stage is common for all types of technologies. Large cracks in concrete are sealed, grease stains and residues of other substances and compounds are removed. It is recommended to level the surface if bulk heat insulators are not used. The height difference in the room should not exceed 1.5 cm per 1 m. The solution is the use of leveling mixtures.
It will help remove excess moisture from the concrete, but at the same time reduce the likelihood of water affecting the insulation. For the kitchen and bathroom (wet areas) only waterproofing is needed. You can use polymer materials or special mastic.
Continuous layer
You can use polystyrene foam for this method. It is recommended to choose extruded one, as it has better rigidity. There is no need for additional load-bearing structures - joists, lathing.
The problem with sheet materials is the formation of cold “bridges” at the joints. This will increase heat loss. The solution is to install sheets with special grooves. They are mounted with overlap. But in order to properly insulate a concrete floor with penoplex, preliminary cutting is done.
Stages of work.
- Preparing the base.
- Laying waterproofing. The layers should overlap and be secured to each other using construction tape.
- Damper tapes are installed near the walls. They minimize the influence of thermal expansion of polystyrene foam.
- Checking the level.
- Installation of finished floor.
If installed correctly, there is no need to attach polystyrene foam to the floor with dowels. The sheets should fit snugly at the ends (locks). This method is convenient for insulating a concrete floor in an apartment under laminate or parquet. It is not suitable for linoleum, as it will not provide the required surface rigidity.
Frame method
This method is chosen for soft insulation, for example, basalt wool. The idea is to install an additional structure on the concrete surface - a log system. A finishing base made of sheets of chipboard, OSB or similar materials is mounted on top of them. A heat insulator is placed between the joists.
Before insulating a concrete floor under linoleum, the logs need to be dried and then their dimensions checked.
Stages of installation of a frame structure.
- Marking the base for the logs. The distance between them is 0.5-0.7 m.
- Installation of a wooden structure. The logs are located along the length of the room, and wooden jumpers are installed between them for rigidity. Under the base there is waterproofing. Contact between concrete and wood must not be allowed.
- Laying insulation. Its height should be 1.5-2 cm less than the log level. This is necessary to form a ventilation gap.
- Installation of steam-waterproofing film.
- Spacer strips are attached on top of the joists.
- Installation of finished floor.
Under the screed
Convenient if you plan to place a large load on the surface. This way you can insulate a concrete floor in a garage or utility room. A screed is poured over the insulation layer. The method is relevant for arranging heating for warm water or electric floors. The screed will reduce the thermal effect on the heat insulator.
For this method, you can use all materials - expanded clay, basalt wool, expanded polystyrene. But for cotton wool, it is recommended to install a metal frame on top of the insulation layer. It will evenly distribute the load of concrete and reduce compression.
How to make thermal insulation under a screed.
- Laying waterproofing.
- Installation of damper tape around the perimeter of the walls. Its height should be 2-3 cm greater than the thickness of the screed. After the surface has dried, the remainder can be cut off.
- Installation of insulation, sealing of joints.
- Laying vapor-waterproofing.
- Installation of metal mesh (frame).
- Pouring concrete.
The last layer must be uniform, the thickness does not exceed 3-4 cm. Otherwise, the load on the heat insulator will increase, which will lead to a decrease in thickness due to compression. This does not happen only with polymer sheet materials, for example, expanded polystyrene.
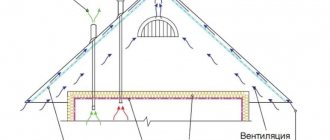
Standards for insulating attic reinforced concrete slabs
To produce high-quality insulation of the attic floor and extend the service life of the roof covering and rafters, you need to use a vapor barrier. It is worth knowing how to install a vapor barrier correctly. The vapor barrier is laid on the slab, and the thermal insulation is on top. This will prevent moisture from forming on the wood and metal parts of the attic. If the vapor barrier layer is damaged, as a result, the thermal insulation properties of the insulation deteriorate.
Thickness of the insulating layer of the attic floor
Nuances of arranging a “warm floor” system
The water system is more complex to arrange. It requires not only the installation of pipes under the screed, but also the installation of special equipment designed to heat and ensure forced circulation of water.
Nuances of arranging a “warm floor” system
The heating system is installed directly on top of the thermal insulation material
It is important that the insulation has a foil coating, due to which more heat will be reflected into the room. If there is no foil barrier, it is recommended to lay it manually
The system is installed according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer. After checking its performance, you can lay a reinforcing mesh to strengthen the structure and begin arranging the screed. When using a “warm floor” system, the solution can be prepared without crushed stone, expanded clay and other fillers.
Coating structures
The coverings of industrial buildings, as a rule, are designed without attics. They consist of load-bearing and enclosing structures.
Load-bearing rafter structures are trusses, beams, arches and frames. They support the enclosing part, giving it the required slope corresponding to the roofing material.
The fencing includes flooring (reinforced concrete slabs, asbestos-cement or metal sheets, etc.), vapor barrier, insulation, leveling screed and waterproofing.
Non-insulated (“cold”) coatings lack vapor barrier and insulation.
In one-story industrial buildings, the most common coatings are large-sized slabs laid along the upper chords of rafter structures. When using decking made from small-sized elements, the latter are supported on purlins laid on the rafter structures.
How to insulate reinforced concrete slabs
To lay the insulation on the slabs, a wooden beam is attached. Between the logs, insulation is placed in the form of loose material or overhead heat-insulating boards of various types. Loose insulation is poured in a layer of 20–30 cm onto the roofing material glued to the slabs and filled with a thin layer of mortar.
The most expensive and effective rigid insulation is foam glass. To obtain the desired effect from using foam concrete, the thickness of its laying layer should be about 0.4 m. It does not require a screed.
The rule for any type of roll and tile insulation is that in order to avoid the formation of cracks in the insulated layer, it is necessary to follow a checkerboard pattern and correctly place the material in several layers.
Note The thickness of the insulation should be selected in accordance with the region where the private house is located, but not less than 15 cm. Saving on 5 cm and laying only 10 cm in a house with an attic is not worth it for the simple reason that insulation costs are one-time, and the effect of reducing heating costs will be noticeable over time.
And if, suppose, the total thickness of the material used is taken to be 15 cm, then it would be rational to use insulation 5 cm thick, laying the joints overlapping. Because if you lay slabs 15 cm thick, the joints between them will release some of the heat, so it is better to avoid this. The cost of thermal insulation is calculated per cubic meter, so the price will not have any impact.
In order to use ecowool in the attic of a house, first lay a vapor barrier on the floor. This insulation is made from cellulose with fluffed fibers. It is not allergenic. Packed in bags. Fills up between prepared joists. A special property is non-flammability, which is achieved by using special impregnations. The cost of such material is quite high in comparison with similar insulation materials.
Insulation of a cottage attic with ecowool
What material should you choose for warehouse thermal insulation?
If you decide to insulate your warehouse, then it is best to choose polyurethane foam for these purposes. It has a lot of advantages:
Easy to install. Insulation work using this material will take no more than 1 day. Agree that such terms are quite attractive;
Saving. In addition to the fact that your goods will always be safe, you can save on heating. Insulating warehouses with polyurethane foam reduces energy costs by 50%. A one-time investment in insulation will help you save for years to come;
Durability. Polyurethane foam as insulation can last for several decades.
Why is it worth using our help to insulate a warehouse?
Have you decided to insulate your own warehouses, but don’t know who to entrust this work to? Contact .
We have been providing insulation services using polyurethane foam for more than 7 years. Our specialists have extensive experience in this field and use modern equipment.
takes on objects of any complexity. And the result of its work and the materials used are guaranteed for up to 50 years. We use only certified polyurethane foam.
All work is completed as quickly as possible - up to 1 day. At the same time, the cost of our work is very affordable. In fact, you only need to pay for the material itself. Its delivery, installation and calculation of the cost of all work are carried out absolutely free.
Warehouses are designed to store various materials and goods. Often, the storage of certain groups of goods requires special conditions, including a certain temperature, humidity, and generally microclimate. To create these conditions, the room must be insulated as much as possible from the influence of external environmental conditions, that is, sealed and thermally insulated. In cold climates, house facades are not able to retain heat indoors on their own. The result is high heating costs, the low efficiency of which is due to the high thermal conductivity of building materials.
POLYURETHANE FOAM – THE BEST SOLUTION FOR WAREHOUSES
Today, for thermal insulation of premises of any type, many modern insulation materials are used, which are designed to solve various problems. However, polyurethane foam, or PPU, is best suited for insulating warehouses. This heat insulator has unique characteristics that are still unattainable for other materials. In particular, polyurethane foam has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient, which allows you to recoup investments in thermal insulation in just two seasons, and subsequently save up to 50% on energy resources for a long time.
Preparatory work
Insulation of a concrete floor in a private house or apartment begins in the same way - with preparing the base:
- We remove the old flooring and subfloor, exposing the concrete slab.
- We carry out inspection of the concrete surface. We carefully clean all detected defects, embroider them using a grinder or a hammer drill, and fill them with repair solution.
- Large irregularities (sagging, protruding fragments of reinforcement, etc.) are removed, leaving a flat surface.
Waterproofing with film
- For any insulation it is necessary to install a waterproofing layer. The base can be covered with a thick plastic film, or a water-repellent paint composition can be applied to the concrete. The price of painted waterproofing is slightly higher, but it also has a longer service life.
- When performing waterproofing work, it is necessary to provide protection from moisture not only to the floor, but also to the adjacent walls to a height of at least 150 mm.
Having completed waterproofing, it is fashionable to move directly to insulation. Below we will tell you how to properly insulate a concrete floor.
Advantages of polyurethane foam insulation of buildings
Firstly, the thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam is quite low, so even with a small thickness of this insulation on the roof or walls of a building, we can always talk about high efficiency (30 mm polyurethane foam with a coefficient of 0.019 W/m*K).
Secondly, the closed cellular structure of polyurethane foam does not allow water or steam to pass through, so the water absorption rates of polyurethane foam are also low. And this speaks not only about the preservation of the insulation properties
throughout the entire service life, but also about the anti-corrosion protection of metal structures.
Thirdly, polyurethane foam is installed using a foam generator using the spraying method
, which implies the absence of fasteners, guides, as well as acceleration and simplification of the installation process. In addition, sprayed polyurethane foam is held so tightly that its dismantling is possible only by crude physical methods.
Fourthly, polyurethane foam is not afraid of exposure to any chemical reagents (except concentrated alkalis and acids).
Fifthly, polyurethane foam is applied to the surface in a seamless layer that completely repeats its structure and shape, so you don’t have to worry about a damaged facade. When insulating the facade of a building, you can always paint it with polyurethane foam, apply plaster over it, or use a ventilated facade system.
Methods for insulating concrete floors and their features
There are several main methods of thermal insulation of a concrete floor. Each of these methods can be used at a strictly defined stage of floor installation.
Methods for insulating concrete floors and their features
So, when creating a floor “from scratch,” the heat-insulating material is laid under the screed
If the floor in your home is already finished, you can turn your attention to a system called “warm floor”. It makes it possible to provide high-quality heating of the surface over its entire area
An excellent solution is to replace the crushed stone in the mixture with perlite or expanded clay with similar properties. But this option, like the first, is relevant only when arranging a floor structure from scratch.
A very popular thermal insulation option is the construction of the so-called. "raised floor". This technique is based on the construction of wooden logs, the free space between which is filled with a heat insulator.
For additional insulation of the floor, you can use a special “warm” covering, for example, carpet. However, this method should not be considered as an independent, full-fledged thermal insulation.
For additional insulation of the floor, you can use carpet
Why insulate the floor
Among the total heat losses, the floor occupies a prominent place - up to 15%. A cold floor not only “steals” kilocalories of heat - it significantly reduces the comfort for those living in the house. If your feet are cold, the general feeling of cold intensifies. Cold floors are especially dangerous for young children, who often play sitting and lying down, and for older people.
The cold coming from the floor harms pets and indoor plants. Large heat losses have a number of other unpleasant consequences: moisture can condense on cold surfaces and the relative humidity will increase. This will lead to the appearance of mold and mildew, which are extremely harmful to human health. Therefore, in addition to thermal insulation, it will be necessary to take care of the vapor and waterproofing of the ceiling.
Determining heat leakage paths
Heat leaves rooms in two ways - by heat transfer through concrete and with drafts through joints with walls. Accordingly, when insulating the floor, you need to block both of these paths by selecting and installing suitable thermal insulation materials.
Popular thermal insulation materials and their features
The modern construction market offers a large selection of materials, the characteristics and properties of which allow them to be used for insulating the floor of the first floor. Each insulator has both a number of advantages and a certain list of weak qualities.
Mineral wool
Types of mineral wool by density
| Those. characteristics of mineral wool | Indicators |
| Density | 115 kg/m3 |
| Water absorption at full immersion, no more | 1% |
| Average fiber diameter, no more | 0.2 µm |
| Content of non-fibrous inclusions in the mass, no more | 4,5% |
| Thermal conductivity at 283+1 K, no more | 0.044 W/m*K |
| Shear strength, not less | 50 kPa |
| Compressive strength, not less | 100 kPa |
| Tensile strength, not less | 150 kPa |
The most popular material for insulating various structures is mineral wool. Among its main advantages are:
- high thermal insulation properties;
- fire resistance;
- good sound insulation;
- relatively low cost.
The main disadvantage is poor resistance to moisture, against which there is a need to install a high-quality waterproofing layer, otherwise the insulation will collapse very quickly.
Comparative characteristics of different types of mineral wool
Mineral wool is produced in the form of slabs and mats, which makes it possible to choose the most convenient option for a particular situation.
Styrofoam
Physical characteristics of foam plastics
No less popular thermal insulation material. Advantages:
- low thermal conductivity;
- small thickness and relatively light weight;
- strength;
- durability;
- resistance to mechanical damage.
Unlike mineral wool, polystyrene foam does not require such serious moisture protection.
Foam plastic PSB-S-15
If you have a sufficient budget, you can even buy foamed polyethylene. During the production process of this material, its surface is covered with aluminum foil, eliminating the need for additional waterproofing.
Foil foam
Ecowool
Ecowool
It is a cellulose-based insulation with various additives that help improve its fire-resistant and environmentally friendly characteristics. The structure is a bulk material. Ecowool is very easy to install - just pour it into a pre-assembled sheathing and cover it with flooring.
Comparative assessment of some types of insulation
A significant disadvantage of ecowool is its low resistance to moisture. Under its influence, the material very quickly loses its performance properties and collapses.
Ecowool does not burnInsulating floors with ecowool
Fiberglass
Fiberglass
This insulation is rapidly gaining popularity. The basic performance characteristics of fiberglass are beyond praise. The material is excellent for insulating the floors of rooms located on the ground floor. Also among the advantages of fiberglass is its affordable price.
Calculation of the roof covering of an industrial building
Required heat transfer resistance.
The parameters of the enclosing structure are selected based on the required heat transfer resistance, calculated by the formula:
Where
— heat transfer resistance of the enclosing structure; — estimated indoor air temperature (); — minimum outside air temperature (); n
— the coefficient taking into account the location of the enclosing structure is adopted according to the SNiP -3-79 table (we accept
n = 1
);
— heat transfer coefficient, depends on the smoothness of the inner surface of walls and ceilings and takes values according to SNiP (smooth ceilings); — heat transfer coefficient, determined according to SNiP (for roofing); - the standard temperature difference between the air temperature in the room and the temperature of the internal surfaces of the enclosing structures is accepted according to SNiP (based on the condition “industrial buildings with normal operation” we accept); R
is the thermal resistance of the construction material, determined by the formula
,
Where
- thickness of the total layer,
-thermal conductivity for normal mode and normal climate, i.e. mode A:
Knowing , we derive from formula (*) the thickness of the roofing materials:
where is the thickness of the insulation, hence,
For roof insulation we use mineral wool mats, and for waterproofing - three layers of roofing felt on a bitumen base with a total thickness of 15 mm.
Thermal characteristics of roof insulation materials.
Table No. 2.
| Material. | Volume weight, | Heat absorption S, W/ (m2*C) | Thermal conductivity l, |
| Mineral wool mats | 75 | 0,46 | 0,05 |
| Bitumen | 1400 | 5,79 | 0,23 |
| Ruberoid | 600 | 3,06 | 0,15 |
Then,
— mineral wool mats with a density of .
As waterproofing:
- roofing material at density and -bitumen at density . From here we find the average thermal conductivity value for waterproofing: .
We substitute these values into the formula (**):
We round the resulting value to a multiple of 50 mm. Then, the thickness of the mineral wool layer should be at least 0.05 m
Examination.
Because — the condition for heat transfer of the enclosing structure is met, therefore, the calculation is correct.
Thermal inertia:
, Where
— thermal resistance of the i-th layer.
S1= 0.46 - heat absorption of mineral wool, W/ (m2*C);
S2= 4.425 - average heat absorption of roofing felt and bitumen, W/ (m2*C);
d1= 0.05 - thickness of the mineral wool layer, m;
d2= 0.015 - thickness of three layers of roofing material on a bitumen base, m.
l1= 0.05 - thermal conductivity of mineral wool, W/ (m*C;
l2 = 0.19 - average thermal conductivity of roofing felt and bitumen, W/ (m*C).
,
, Then,
Conclusion: for roof insulation we use mineral wool mats, and for waterproofing - three layers of roofing felt on a bitumen base with a total thickness of 15 mm.
To fill the window openings, we choose double glazing in metal frames.
Primer and marking
After preparatory treatment of the base, it is cleaned from dust and debris. If necessary, the boards are sanded. A primer is applied to the cleaned surface. This treatment will create a protective layer that prevents the appearance of bubbles, the absorption of moisture from the cement mixture, and the appearance of fungus and mold.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with decorating a bathhouse with your own hands: how to decorate the walls of a washing room, shower room, washroom, options, video, photo
Marking is carried out with a regular or laser level. The zero mark can be at any height. It is recommended to place several marks on each wall at a distance of 35 to 70 cm from the floor, taking into account the thickness of the future screed. Then the marking is carried out in the reverse order - from points on the wall to the floor.
It is important to take into account that the standard thickness of the screed should be ±5 cm. Moreover, every 1 cm of concrete exerts a pressure of 100-110 kg/m2
Therefore, the logs need to be reinforced with beams or metal channels.
Insulation of reinforced concrete attic slabs with Penoplex
Insulation of attic floors with Penoplex slabs
Penoplex slabs are used to insulate reinforced concrete slabs in the house, as well as wooden beams for attic floors. They are used both in new construction and for arranging an attic in a private house or when repairing buildings. List of advantages of penoplex slabs:
- Consistently high performance properties throughout the entire period of operation.
- Does not absorb moisture.
- Low thermal conductivity, does not release heat.
- Environmentally friendly, does not affect the health of surrounding people.
- Designed for laying in a continuous layer, eliminating heat loss through the joints between the slabs.
- High sound-absorbing properties.
Scheme of attic floor insulation with PENOPLEX slabs on a reinforced concrete base
The most reliable way to fill heated floors
Classic heating systems that use radiators are gradually losing popularity. They are being replaced by new concepts, including warm floors, which not only heat the room, but also create additional coziness and comfort. Manufacturers offer water or electric designs, constantly improve them and promote them in every possible way on the market. But, regardless of the principle of heat generation, for all heated floors it is necessary to make a screed. It forms a smooth surface, ensures long-term operation of floor coverings, success and ease of further repairs.
Pouring a heated floor has no fundamental differences from a conventional screed. But its organization is more complex and time-consuming. The most reliable method of pouring heated floors involves arranging a screed in several layers:
- Rough floor. The bottom layer for leveling the surface, which is poured in all rooms. If an apartment or private house uses a solid slab as a floor, the subfloor does not need to be poured.
- Thermal insulation. The insulation is placed on a rough screed so that the heating elements heat the room, and not the lower floor or foundation. Additionally, this layer will serve as sound insulation.
- Reinforcing mesh. The metal frame will give the main screed greater strength; it will not crack or collapse.
- Heating elements. They are placed evenly with a given step on top of the laid mesh.
- Clean screed. Pouring concrete hides thermal insulation and heaters. Flooring is laid on top of it.
When using heating, the screed is affected not only by the physical effects of the mass of a person or furniture, but also by the forces arising from the thermal expansion of the material. It is necessary to select high-quality mixtures and pouring thickness. If you skimp on materials, this will lead to the formation of cracks, deformations or overheating of the heating elements.
To form a durable structure, the thickness of the finishing fill is made at least 3 cm. The counting is from the top edge of the heating pipe. For a private home, the layer thickness can reach 7 cm, in work premises up to 10 cm. If this parameter is impossible to achieve due to the individual characteristics of the room, it is permissible to use a self-leveling mixture or add a universal plasticizer to the solution. In this case, the layer is made 2.5 cm thick.
An important element of the screed is the seams to compensate for the thermal expansion of concrete. A damper tape made of foamed polyethylene is laid around the perimeter of the room or along the contour of the heated floor. It mirrors the behavior of the screed, protects floors from temperature changes, ensuring their integrity and safety. When concrete expands due to heating, the tape, on the contrary, contracts, relieving temperature stress. When the screed cools, foamed polyethylene fills the resulting space.
Choose single-layer or double-layer thermal insulation
First of all, you should consider the installation of a flat roof - insulation can be planned in two ways:
Single-layer thermal insulation system. The main distinguishing feature: the entire insulating layer is made of flat roof insulation of the same density. If it is planned to construct a roof that is in use, then a concrete screed is laid on top of the heat-insulating layer. This system is most often used when repairing old roofs or in the construction of garages, warehouses and industrial buildings. The two-layer thermal insulation system is designed differently. The top layer, 30-50 mm thick, is made of insulation of increased strength and density. It is designed to redistribute mechanical load. The lower one, with a thickness of 70 to 170 mm, performs the main heat-insulating function
This design allows you to significantly reduce the weight of the roof and, accordingly, reduce the load on the floors, which is very important when renovating old buildings. There are modern materials that combine the properties of both layers
These insulation materials have a hard top edge and a softer bottom edge. Installation of such slabs occurs very quickly and reduces the time and labor costs for installing the coating.
The two-layer system guarantees the absence of through seams in the thermal insulation layer
Fixation methods
Basically, four fastening methods are used to fix joists on a concrete floor. Therefore, if you do not know how to attach joists to a concrete floor, then after studying all these methods you will understand this issue.
Fixation with self-tapping screws
This method is considered simple, but it is not suitable for all cases.
- First you need to prepare the concrete surface. To do this, it is cleared of debris (it is allowed to use a vacuum cleaner). Then they repair cracks, chips and other defects with cement mortar or polyurethane foam.
- Next, in the logs (treated with antiseptics) you need to drill holes with a drill to install plastic dowels. Then you need to drill counter holes in the concrete using a hammer drill.
- Then the dowels are driven into the concrete with hammer blows, and then self-tapping screws are screwed into them with a screwdriver. Moreover, the head of the screw is driven into the hole 2-3 cm.
Fixation with anchors
- First, you also need to prepare the concrete floor (remove debris from it and repair all defects with mortar).
- After which it is necessary to make through holes in the timber (treated with antiseptics) with an electric drill.
- Next, you need to drill holes in the concrete opposite each hole with a hammer drill.
- Then the anchors are mounted on a concrete base and tightened with keys. The main thing here is not to overtighten the bolt, because this will cause the beam to bend. This is especially true for those places where there is a gap.
Before installing the anchors, trenches (small recesses) are made in the joists to hide the bolt heads.
Anchors need to be installed every 600-1000 mm. This distance is selected taking into account the partial immersion of the anchors in concrete (approximately 60 mm). Many people fix the beams to the concrete with 4-5 anchors ⌀ 10 mm.
Calculated heat losses
As mentioned earlier, it is impossible to build a perfectly warm house. Therefore, designers set the amount of calculated heat loss. It depends on many reasons.
Climatic features of the construction site
The methodology is described in SP 23-101-2004 (“Design of thermal protection of buildings”). The minimum temperature of the coldest five-day period, the average temperature for the heating season and its duration, the average seasonal wind speed and its preferred direction, the humidity conditions of the construction area, and the intensity of solar radiation during the heating period are taken into account.
We insulate taking into account heat loss
So, for example, for the Moscow region, the minimum temperature of the coldest five-day period is taken to be -28°C, the average temperature of the heating season is -3.1°C, the duration of the heating season is 214 days, the wind speed in the coldest period is 4.9 m/s, the rest of the time - 3.8 m/s, humidity zone - 2 (normal).
Architecture of the building
This refers to space-planning solutions, glass area, number of storeys, whether there are unheated basements and attics, and the location of interior spaces. Heat loss in the corner room is higher than in the room in the middle. If we take an apartment building as an example, then apartments in the outer entrances with two or more external walls “freeze” more than those that are protected from the street cold by neighbors. All these factors influence the amount of heat loss.
To determine the permissible heat loss through the ceiling above an unheated basement, the proximity to the wall is taken into account. That is, the entire floor area is divided into zones 2 m wide. For each of them, standard heat transfer resistance values are provided. In this case, the first zone in the corners (double hatching in the diagram) is taken into account twice.
Scheme of dividing the floor surface into calculation zones. Illustration from the reference book by E. G. Malyavina “Heat loss of a building”
Thermal resistance for different zones has the following values: I - R=2.1 W/(m°C); II - R=4.3 W/(m°C); III - R=8.6 W/(m°C); IV - R=14.2 W/(m°C). The total resistance to heat transfer is summed up.
Geodesy
In addition to the climatic conditions of the area, the type of soil and groundwater level at the construction site are important for calculating heat loss through the floor along the ground.
Structure of enclosing structures
Building structures are heterogeneous in their structure: they consist of different materials with different thermal resistance. Heat loss is calculated taking into account the thermal characteristics and thickness of all materials present in the structure, including air gaps, interior and exterior finishing materials and through fasteners.
Building structures are heterogeneous in their structure
If you don’t want to go into such thermal details, you can, to simplify things, use either heat loss calculators on websites dedicated to construction issues, or calculate them using average values derived for a standard design. For example, for the Moscow region, the thermal resistance of attic floors or an uninsulated basement is taken to be 4.12 (recommended) or 3.3 (permissible). That is, the floor structure, including insulation, must have heat transfer resistance within these parameters.
Knowledge of heat loss allows you to build a comfortable house for living, optimizing the choice of structural, insulation and finishing materials. This information will help you select heating equipment, as well as reduce the costs of subsequent operation (heating).
Floor with joists on a concrete base
One of the oldest methods of insulating the floor in a private house is a floor on joists. Only earlier they did it without insulation, but today insulation is laid between the joists. This increases energy efficiency - heat loss is reduced and heating costs are reduced. The disadvantage of such a floor is that it “eats up” quite a lot of space, and secondly, creaking is possible. It’s not even like that - it’s rarely possible to make a floor using joists without squeaking. The advantage of this method of insulating a concrete floor is that it is relatively inexpensive and installation does not take very much time.
Insulation of concrete floors using joists
Insulation scheme by logs
If the base is uneven, pour a layer of sand to level it, tamp it down, and level it. Logs are installed on the sand. Instead of sand, fiberboard cut into pieces of varying thickness is used. The sections are impregnated with a protective compound, dried and used to level the logs.
Logs are dry timber or boards of sufficient thickness. They are placed around the room at a certain step and the flooring is laid on them. The pitch of the lag and the thickness of the flooring are interrelated. The thicker the flooring material, the less often you can install logs and vice versa. The main criterion is the load-bearing capacity of the structure. The floor should not sag under load. In this design, it is more convenient to choose a lag pitch that matches the width of the insulation. And the thickness of the flooring is determined based on this parameter. This way the insulation will be installed with a minimum amount of waste.
How to insulate floors in a private house: comparison of materials
What to put on the logs
You can lay boards or any sheet material on the logs. Sheet material is usually laid in two layers. The sheets are laid with seams spaced apart to avoid cross-shaped joints. Moreover, the sheets of the second layer are laid so that the seams also do not coincide. The first and second layers are connected using screws and/or glue. The choice of method depends on the type of sheet material selected.
This is what insulation of a concrete floor looks like using joists
In regions where boards are inexpensive, you can do a combination - lay boards on the joists, sheet material on them, and then the finishing floor covering on it. Is it possible to lay the topcoat on boards? If the surface meets the requirements for the base of a particular material, then it is possible. But, if they do not want to have a plank floor, they prefer to lay sheet material on top of the boards. Most often this is plywood. It provides a more stable base that is less prone to warping than planks.
Find out the cost of thermal insulation for your specific premises
We will call you back at a time convenient for you
PROPERTIES OF POLYURETHANE FOAM, SO NECESSARY WHEN INSULATING A WAREHOUSE
The only drawback of polyurethane foam is its exposure to ultraviolet rays. However, this problem can be solved by simply painting the thermal insulation with any paint that will protect the surface.
Naturally, it is impossible to create the necessary microclimate in the warehouse only by thermal insulation of the room. Therefore, in combination with insulation, it is necessary to take care of high-quality, well-designed ventilation. This complex will help make your warehouse an ideal place to store any goods.
Most modern private entrepreneurs, as well as various firms, enterprises and factories, have warehouses at their disposal. As a rule, finished products, goods for sale, consumables, raw materials and much more are stored in warehouses.
Whatever is contained in these structures, if the warehouse is not properly insulated, during the cold winter or hot summer periods of the year the contents of the warehouse risk becoming unusable or losing their original characteristics.
Insulating a garage with your own hands
Most garages are built of brick or foam block. Therefore, the question often arises of how to insulate a brick garage rather than a metal one.
The work is divided into several stages:
- walls;
- floor;
- gates;
- ceiling.
Walls
Do-it-yourself insulation of a garage means, first of all, wall cladding. Most of the heat is lost through them. So how to insulate the walls in a brick garage?
Pasting walls with foam sheets
This is the answer to the question of how to insulate a garage cheaply.
- The walls are cleaned of old plaster and paint. All irregularities are covered with cement-sand mortar.
- After drying, the walls are impregnated with soil or an antiseptic to destroy mold and mildew.
- Then 100 mm thick foam sheets are glued on. To do this, use a notched trowel and special glue.
- After 24 hours, a plaster mesh is attached to the foam. To do this, add a little solution and press the stack into it.
- Then the surface is plastered and puttied. You can use both ready-made facade plaster in bags and cement-sand mortar M150. It is better not to waste energy on mixing the solution yourself, but to buy ready-made dry mixtures.
Installation of insulation on the frame
A more expensive, but effective and reliable way to insulate garage walls:
- The surface of the walls is cleaned, all bulges are removed. Potholes and cracks are expanded and sealed with cement-sand mortar.
- An antiseptic or deep penetration primer is applied to the walls with a roller. This way mold and mildew are destroyed.
- After drying, the walls are sheathed with plastic film or membrane vapor barrier.
- Using a laser level, two horizontal guides are installed. One goes along the floor, the other under the ceiling. For this, a wooden beam 100×50 mm or a metal profile is used. They are attached to the wall using anchors or self-tapping dowels.
- Vertical guides are installed in increments of 600-800 mm. Absolute precision is not needed here. Therefore, for installation you can use a regular level or plumb line. Vertical guides are made of 100×50 mm timber or metal profile. They are attached to the wall in the same way as horizontal guides.
- Sheets of insulation are inserted between the bars. If polystyrene foam is used, it is attached with glue. Then additional fastening of the sheets is provided using plastic dowels in the shape of a mushroom. The consumption rate per sheet is 5-6 pieces. The seams are sealed with polyurethane foam.
If dense basalt mineral wool is used, then glue is not required. Simply secure with plastic dowels. The seams between the sheets are sealed using pieces of mineral wool.