- June 6, 2020
- Construction
- Ruslan Pyatintsev
Proper insulation of the room helps reduce the cost of thermal energy and allows you to protect yourself from the consequences of sudden temperature changes. In order to achieve a constant temperature regime inside the house, it is necessary to determine which areas should be insulated, and most importantly, which insulation to choose. In most cases, people pay more attention to window insulation, trying to protect themselves from drafts, ignoring such an important part of the house as the ceiling.
Criteria for selecting insulation thickness
Before purchasing a material, the question often arises only as a last resort: what kind of insulation layer is needed for the ceiling of the house and what thickness will be optimal? The thermal insulation properties of the ceiling affect the temperature in the room no less than doorways, walls or floors. If you do not reliably insulate the entire house, heat will escape through the ceiling, since warm air always rises.
There are two ways to insulate the ceiling:
- Insulation from the inside. This is a more practical choice, but the insulation will take away a couple of tens of centimeters of ceiling height. The thickness will depend on the temperature difference and the insulation used, so for rooms with low ceilings you should choose the following method.
- Insulation from the attic or roof. For this type of insulation, it is better to call specialists so as not to damage communication channels and electrical wiring in niches and ceilings.
It also makes sense to separately note such an important area directly connected to the ceiling as the roof. With sufficient insulation thickness, the roof is guaranteed to provide reliable protection from wind, snow load, noise, cold and other natural factors. The roof should not only play a functional role, but also have a pleasant appearance.
When the roof is not insulated correctly, condensation accumulates under the covering, which causes metal corrosion, wear of wooden components and waterlogging of the insulation. Both of these technologies are suitable for thermal insulation of the ceiling in a private house, since each of them gives a good effect. The room retains heat, which means heating costs are reduced several times. These methods differ in installation technologies and the set of necessary materials.
The fact is that some materials are capable of strongly absorbing moisture, while others are not. To prevent condensation from forming, materials with high vapor-permeable properties are used to insulate the ceiling inside the building. Most often, vapor-tight materials are used as external insulation.
By minimizing the percentage of heat loss, the selected material should prevent the formation of processes associated with natural steam circulation occurring indoors. The insulation must be protected from moisture. The modern construction market provides several options. For example, expanded clay has a loose, light consistency. Its clay base does not burn at all, is not afraid of water and increases thermal insulation.
The main task is to choose the insulation itself. Here, first of all, you need to build on the type of room. The choice of material and how thick the insulation on the ceiling should be depends on this, because the thickness is different for different tasks.
Insulation from the attic
Almost all types of insulating materials are used to insulate the ceiling on the cold attic side. Bulk options, hard foam slabs, and soft cotton mats are in use.
Both industrial products and good old folk methods are used. The main advantages of the former include manufacturability. Their manufacturers have thought through and provided everything for prompt installation.
Folk remedies are much more difficult to install. It is not easy to collect them in the required volume and deliver them to the place of work, since this is most often done in buckets by hand. But they are much cheaper, better than industrial products, they coexist with wood and do not emit toxins harmful to us.
The installation of thermal insulation from the attic space requires periodic maintenance of the insulation system.
Bulk materials must be periodically loosened so that they dry better, the rest must be inspected and artificially dried, for example, with a hairdryer if necessary.
For inspection and maintenance, “paths” of two or three boards are constructed along the joists above the thermal insulation. If it is planned to pour the screed over heat-insulating boards and rigid mats, then the trajectory of the proposed path is laid out with a reinforcing mesh.
Use of mineral wool
The group of mineral wools includes glass wool, stone (i.e. basalt) wool and slag wool. Glass wool has been used less and less in recent years due to its ability to produce abundant dust with small glassy particles, which can be hazardous to health if inhaled.
Working with glass wool is only allowed in a respirator and goggles. In addition, the smallest glass fibers are harmful to the skin.
Therefore, personal protective equipment should include overalls made of thick fabric with strong elastic bands on the legs and sleeves, and gloves are also a must.
Slag wool is not used for insulating ceilings in low-rise buildings due to its toxicity. What remains is basalt, also known as stone wool, produced from volcanic rocks. It is safe to use and easy to install.
The technology for installing thermal insulation with basalt wool is determined by the type of floor:
- On reinforced concrete floors. First, the base is repaired and leveled, then a vapor barrier is laid with the edges extending onto the walls. Then the mats are rolled out and laid in 2 layers so that the butt seams of the lower tier overlap the middle of the upper mat, i.e. at a run.
- On wooden floors. The mats are laid in the space between the joists. Previously, a vapor barrier material is placed in each “cell” formed by the joists, extending onto the joists and around the perimeter of the walls.
The wool is cut before installation. Cut it so that the piece is at least 2 cm wider and longer than the actual size of the cell.
Before installing in place, the cotton piece is slightly compressed so that after it straightens out in its proper place and covers the entire space. This prevents the formation of cold bridges.
Thermal insulation with polystyrene foam boards
Slab insulation is used mainly on reinforced concrete floors. It is difficult to choose the size for laying in the space between the joists. You have to cut, waste time, and often material when cutting incorrectly, and in general it’s difficult to do everything without gaps, and these are ways for heat loss.
In arranging an insulation complex for reinforced concrete floors, two types of slab thermal insulation are used:
- Styrofoam. It is also non-extruded polystyrene foam. The material requires a mandatory vapor barrier layer before installation due to the fact that its structure contains channels that can absorb water.
- Extruded polystyrene. Most often it is Penoplex. Due to the almost waterproof surface, it is not necessary to lay a vapor barrier before laying it over living spaces, bedrooms, living rooms, and children's rooms.
Before installing slab thermal insulation on the side of the cold attic, the base must be repaired and leveled. The vapor barrier film is laid in the form of a pallet with sides curved onto the walls.
Lay the slabs freely. Placed in two layers with seams separated in the lower and upper tier. If Penoplex with a mounting chamfer is used, the seams do not need to be sealed; if polystyrene is used, then the seams are filled with sealant or mounting foam.
Screeding on slabs is most often carried out partially, only in the area where service paths are installed. It is either filled with a cement-sand mixture with a reinforcing mesh layer not exceeding 4 cm, or constructed from gypsum fiber sheets.
If the solution is poured, then waterproofing is laid over the insulation. Purely so that concrete milk does not seep into the insulation and affect its insulating qualities.
Ecowool insulation
Another popular insulation option is ecowool, made from natural cellulose. Its advantages include manufacturability of application (spraying) and treatment with fire retardants and antiseptics.
Arrangement with expanded clay gravel
The most famous backfill thermal insulation material is expanded clay. It is used both directly for insulation and to lighten insulating compounds and mixtures. Expanded clay is produced in the form of gravel ranging in size from 4 to 10 mm.
It is made from environmentally friendly, easily sintered clay. The material is affordable, non-flammable, moisture-resistant, lightweight, which greatly simplifies delivery and filling. They pour it either into the space between the joists, or directly onto the reinforced concrete floor.
Before filling the expanded clay, the base is covered with a vapor barrier film, the edges of which usually extend onto the walls. These peculiar sides should be 10-15 cm above the level of the gravel layer poured onto the ceiling.
It is not necessary to arrange maintenance paths on expanded clay. You can walk straight on the backfill. Periodically it needs to be turned with a rake so that all the artificial pebbles of the insulating layer can dry.
In addition to expanded clay, a wide range of folk fill-in insulation products are still used, attracting mainly owners of eco-houses as adherents of materials that are safe for themselves and the environment.
Bulk folk materials
Adherents of environmentally friendly construction methods have their own opinion, based on centuries of successful practice, regarding the options for thermal insulation of the ceiling.
They believe that it is correct and reasonable to insulate both the ceiling under a cold roof and the slopes only with clean natural materials.
In terms of insulating qualities, natural options are certainly inferior to industrially produced insulation materials.
But thermal insulation of natural origin is distinguished by:
- Environmental priorities. They do not pose a threat to the environment, do not emit or distribute harmful chemical components. Natural thermal insulators do not need to be disposed of in a special way; they can simply be burned or placed in a compost heap.
- Practicality. Eco-friendly insulation materials retained heat perfectly even in those days when the home was heated only by a stove. In addition, there was no such powerful heating equipment that current owners of private houses have.
- Economic advantages. You can prepare natural thermal insulation for pennies or even for free. Replacement as technical characteristics are lost can be carried out much more often than factory products.
- Symbiosis with natural building materials. Natural heat insulators work well alongside wood, clay, and soil backfill. At a stable temperature, they do not deteriorate from contact with stone.
- Safety for residents. In extremely rare cases, natural materials can cause an allergic reaction.
Most natural heat insulators, according to the installation method, belong to the backfill variety. They are freely distributed over the ceiling, periodically turned to dry and increase the thermal insulation properties. For maintenance, paths are made of a pair of boards laid on logs.
The following are still used as natural thermal insulation:
- Wood shavings and sawdust. An abundance of them remains after the construction of a wooden house; supplies can be replenished at sawmills and woodworking workshops. Cover with a layer of 15 - 30 cm.
- Straw. You can prepare it at the nearest farm that grows cereal crops. Lay in a layer of 25 cm.
- Moss. Excellent, practically non-rotting thermal insulation, used both inside and outside the building. The qualities inherent in nature allow moss to be used for ten years or more. The insulation layer can be relatively small, up to 10 cm.
- Dry leaves, hay. You can stock up on such thermal insulation absolutely free, but you will have to replace it almost every year due to the tendency to quickly become saturated with moisture. You can use not only foliage, but also pine needles. It is enough to insulate with a layer of up to 20 cm.
- Seaweed. This insulation option is not readily available in all regions of our country. True, residents of Primorye have them in sufficient quantities and can change them every year. The laying power is up to 20 cm. Significant advantages include the distribution of volatile iodine molecules that are useful for people.
If your area has a pond overgrown with reeds, this plant will also serve. Its stems are tied together with a rope or metal wire. Then the fagots fill the space between the ceiling beams and joists.
The above types of natural thermal insulation have a number of significant disadvantages that are not typical for factory products. Therefore, to improve consumer qualities, natural insulation materials must be carefully prepared before installation.
Disadvantages that should be minimized before use quite rightly include:
- Flammability and ability to support combustion perfectly . Treatment with fire retardants effectively combats this disadvantage. Instead, you can use clay or slag, a layer of which is covered with an insulating backfill on top.
- Reduction of heat-insulating thickness . Thermal insulating natural filling must be stirred frequently to avoid pressing; it must be dried to prevent wetting and the associated decrease in insulating properties.
- Incoherence . During the maintenance of the insulation and the device within the attic, drafts necessary for drying, some of the material can simply be carried outside. This means you need to constantly replenish the stock. This disadvantage can be overcome by baling.
- Tendency to rot . The ability to quickly and easily absorb moisture can lead to rot, especially if regular maintenance is neglected. Antiseptics used for wood treatment are suitable as a preventative measure.
- Attractiveness to rodents . Rats and mice live freely in dry and warm beds made of straw, moss, and hay; to repel them you will have to purchase specialized products from the SES.
There are two more popular types of folk thermal insulation: soil-vegetative layer and crumpled clay. They do not burn and do not attract mice.
They are not afraid of moisture and weathering drafts. But there is a serious drawback - considerable weight, due to which it is necessary to strengthen the overlap.
Soil - the top layer of soil, enriched with waste products of representatives of flora and fauna, is mixed with any of the above-mentioned folk heat insulators for ease. It is simply scattered over the ceiling, like expanded clay.
Clay is diluted in a container with water to the consistency of sour cream, chopped straw or shavings are added to it and poured onto the ceiling in a layer of 10 - 15 cm. After the poured composition has hardened, the cracks are covered with softened clay.
Types of insulation
Thermal insulation materials are used both for insulating external enclosing structures and in multi-layer “pies” indoors or on the roof.
The thermal insulation layer, depending on the type and density of the products used, can be:
- single-layer – based on thermal insulation products of the same type and thickness;
- multilayer - based on two or more heat-insulating products of different densities and types;
- combined - based on multilayer thermal insulation products of the same type, made of layers of different densities, interconnected due to both chemical and physical adhesion.
In order to choose the right insulation for your home, you need to take into account several important criteria: environmental friendliness of the material, susceptibility of thermal insulation to fire, reaction to moisture.
Necessary materials
First of all, to insulate the ceiling and the space between the beams in the house from the inside and outside, we will use a layered structure. Each layer of our pie plays a strictly defined function. List of layers used:
- Vapor barrier layer
- A layer of waterproof, high-density thermal insulation
- Waterproofing layer
- Layer of main insulation
- Waterproofing layer
Vapor barrier layer
Glassine or plastic film can be used as such a layer. Its function is to prevent the penetration of water vapor from the living space into the ceiling.
A layer of waterproof, high-density thermal insulation
This layer consists of 50 mm thick foam plastic slabs. It is a reliable insulation material for the ceiling in a wooden house.
Polystyrene foam has a high water-repellent property and a very low thermal conductivity coefficient. It plays the role of the last line of defense against low temperatures.
Foam boards
Layer of main insulation
Mineral wool made from basalt fibers is used as the main protective layer. Thanks to the interweaving of basalt threads, this ceiling insulation retains a huge amount of air.
In addition, basalt fibers have a low thermal conductivity coefficient. All this prevents precious heat from evaporating. Mineral wool is produced in rolls or mats 50 mm thick.
Waterproofing layer
This is a layer of the same material as the vapor barrier layer. The difference lies in the function performed - to retain water in case of possible roof leaks.
Tools for getting the job done
To insulate the ceiling in a wooden house you will need the simplest set of tools:
- Wood hacksaw
- Knife
- Hammer
- Construction stapler (can be replaced with a hammer and small nails with a wide head)
As you can see, such a set can end up in the workshop of almost every home craftsman.
Important to remember! Insulating a wooden ceiling with mineral wool will require the use of a respirator, safety glasses and gloves. Dust from basalt fibers is hazardous to the respiratory tract and can cause irritation to the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes.
Work order
Installed vapor barrier
You are in the attic and all the necessary materials have already been raised there. Now let's look at how to properly insulate the ceiling. The first step is to attach the vapor barrier layer.
If you use polyethylene film (reinforced is recommended), then it is laid out over the entire area of the attic. The film should fit tightly to the beams and the space between the beams, and extend onto the walls with an overlap of at least 10 cm.
A stapler is used to fix it. If it is necessary to lay a new strip of vapor barrier, then make an overlap of at least 10 cm onto the adjacent strip.
After installing the vapor barrier, they begin laying the foam. This material, necessary for ceiling insulation, is usually produced in slabs measuring 1 m x 1 m. For installation, it is marked and cut with a knife so that the slab lies between the beams with force.
A gap of 1 cm is left between adjacent foam plates. Later it is filled with polyurethane foam. It will securely fasten the plates together and eliminate small cracks through which heat can escape.
Mineral wool is laid on top of the waterproofing. It is recommended to lay two layers. The second layer should overlap the joints of the first. The level of insulation should be equal to the height of the floor beams.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=790sgi2anTc
The main insulation is covered with a layer of waterproofing. If you plan to use the attic as a living space or storage, you can immediately lay a floorboard or cover the floor with plywood slabs.
Insulation from the outside is complete, you can begin insulating the ceiling from the inside. To do this, a board or beam with a width of at least 50 mm is attached to the ceiling to the ceiling plank.
Then, between the boards, waterproofing is installed on the ceiling and the insulation is attached to the ceiling (it is laid in the space between the boards). From above, everything is covered with a layer of vapor barrier and a finishing ceiling (plasterboard, plastic, fabric or PVC film).
Now you know how to insulate the ceiling of a wooden house. This ceiling will reliably protect you from the cold and will last at least 30 – 50 years.
Mineral wool
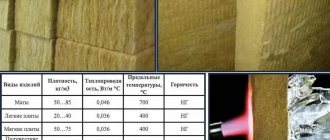
Mineral wool is one of the simplest and most popular insulation materials, and at the same time quite affordable. Before calculating how thick this type of insulation should be on the ceiling, you should take into account its disadvantages:
- May be dangerous for children and allergy sufferers.
- Rodents and parasites often appear, and fungus may appear.
- Highly resistant to fire, but easily absorbs moisture. Good waterproofing is required.
- To insulate the ceiling with this material, it is necessary to install an additional frame.
The average thickness of insulation on the ceiling in a private house is 0.5-1 cm. Usually a thickness of 2 cm is enough to insulate a house in cold northern latitudes. It is very important to take into account the wall material when choosing the thickness of the ceiling insulation. For example, if they are made of strong wooden boards 2 x 2 cm, then one half-centimeter layer of mineral wool will be enough. The generally accepted standard for the thickness of a factory-made mineral wool panel in Russia is two layers of 1 cm each.
Let's consider what the thickness of the insulation for the ceiling of a cold attic should be.
The quality of insulation of this area of the house lies in the correct installation of thermal insulation of the roof and floor. When laying mineral wool, it is necessary to additionally use a vapor barrier and a windproof layer, otherwise even several thick layers of mineral wool will not help to effectively insulate the attic. Depending on climatic conditions, the thickness of attic insulation is usually used in the range of 5-20 cm.
But again, the thickness of the layer will greatly depend on the types of building materials in the structure of the building, so it is recommended that you carefully read the table below: “Coefficient of useful properties of building materials.”
Foam
Among the common foam insulation materials, materials based on polyurethane and polystyrene (penoizol) are most often used.
- Polyurethane foam is a relatively new and expensive insulation material, its structure resembles polystyrene foam. Moisture resistant, retains performance properties for more than 50 years, low thermal conductivity (0.02 W/mK). Disadvantages: high cost (from 20,000 rubles per 1m3), application requires special equipment.
- Penoizol. In fact, this is ordinary foam plastic, the main difference is a seamless monolithic coating.
The process of applying penoizol to a cold attic
Thermal conductivity is almost twice as high as that of polyurethane foam - 0.42 W/mK. It does not rot, does not bloom, rodents and other living creatures do not grow in it. It is airtight, so it should not be used to fill the wooden floor of the attic. Relatively high toxicity does not allow indoor use. Price from 2500 RUR per m3.
Folgoizol
Folgoizol, or folgopergamine, is a lightweight and highly elastic material for thermal insulation, which is a base made of dense fiberglass covered with aluminum foil.
To insulate ceilings, it is better to use foil insulation of the highest strength; this will extend its service life for decades. The layers of insulation fit tightly to each other, preventing cold from passing through the seams.
Folgoizol practically does not absorb water, but can withstand temperatures up to +125 °C. Dense material with good thermal conductivity. Taking into account such distinctive features, this insulation is well suited for thermal insulation of baths, steam rooms and saunas.
Before deciding how thick the insulation on a foil insulation ceiling should be, you should know the following:
- It is mainly used for thermal insulation of pipes, and it will not save you from frost. It is often used as additional insulation.
- Suitable for latitudes with mild climates.
- The average thickness of the ceiling insulation in this case can be about 1-2 cm.
Option No. 2 - installation of mineral wool from the inside
It can be done in two ways. The first of these is similar to gluing and plastering foam. The second option, no less common, is internal installation, carried out under a suspended sheathing, which is installed on concrete or wooden ceilings.
The frame for the sheathing can be made from wooden blocks or from two types - UD and CD profiles. Experts recommend using metal products, since they will not move in the event of a temperature change.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
- First of all, a horizontal line is struck along the perimeter of the room at the level of the future ceiling plane. The easiest way to do this is with a laser level, but if you don’t have one, you can use a hydraulic level, which is a long soft tube with graduated tips that operates using the communicating vessels method.
- Then, according to the applied markings, two UD profiles are fixed on two opposite, longer walls.
- Perpendicular to them, the location of CD profiles is marked on the ceiling, usually observing an installation step of about 50 centimeters.
- In accordance with the markings, the perforated suspensions are secured with dowels at intervals of one meter, their wings are bent downwards.
- Next, they begin to glue the mineral wool slabs to the ceiling. The insulation under the wings of the suspension is cut with a knife.
- To complete the work, CD profiles are inserted into the UD profiles and fastened to each other and to the hangers using self-tapping screws. Now you can begin covering the frame with plasterboard or other finishing material.
Styrofoam
Oddly enough, polystyrene foam does not require careful vapor and waterproofing. All this is because the foam itself is already very hygroscopic, and its vapor permeability is 0%.
The second advantage of this simple building material is its thermal insulation properties, the operation of which continues for many years. For example, glass wool does not have such properties, and foam plastic, on the contrary, unlike it, does not cake.
The third advantage of polystyrene foam, many experts consider its unpretentiousness. Insulating the ceiling with foam plastic will not take you much time.
The entire process takes from an hour to several days, depending on the complexity of the work and the territory in which the construction work is being carried out. With such fittings you will not need any professional skills or expensive tools. Even an incompetent or a beginner can cope with such work. Polystyrene foam, as a means of insulation, is more effective than other insulation materials if the installation of the thermal insulation layer is carried out with the same thickness of the material.
The last and important point of the advantages of polystyrene foam can be considered its price. If you purchase it, it will significantly help reduce costs.
Polystyrene foam consists of granules enriched with gas, which are dissolved in a polymer mixture. Thanks to this composition, it has incredibly low density, minimal weight, and high sound and heat insulation properties.
As a ceiling insulation, polystyrene foam is significantly inferior to others: it is noticeably more expensive than mineral wool, it is very brittle and will crumble during installation, and is easily flammable.
How thick should this type of insulation be on the ceiling?
Insulating the ceiling and external frame with foam plastic can significantly reduce heat loss. A 20-centimeter layer of insulation on the ceiling of a house is distinguished by such high heat retention that even a reinforced concrete ceiling several meters thick does not have.
For work, they usually purchase foam plastic no thicker than 3 cm; for insulating walls in a room, a layer 5 cm thick, one to one in size, is suitable. To insulate a cold attic with polystyrene foam, it is necessary to lay the layers as closely as possible to each other. The average thickness of the material layer is 10 cm. To insulate the ceiling of a room, you can use half that thickness.
What thickness should be for a cold attic ceiling with this type of insulation?
To insulate the attic, the sheets are laid in several layers with offset seams at the joints to minimize the possibility of drafts. Usually a standard layer of 10 cm is sufficient.
How to insulate a ceiling with mineral wool without installing a frame
In cases where it is necessary to insulate the ceiling from the inside without a significant loss of height, mineral wool sheets are attached directly to the ceiling using glue, adhesive putty, dowels with long rods and plastic caps in the form of umbrellas. For insulation with a thickness of 50 mm, dowel-nails 10 x 120 mm will do.
Advice: When installing a sheet on the ceiling, it is recommended to use dowel-nails with a plastic rod, but before purchasing all the fasteners, take 5-10 pieces of each and try it on the first slab. The fact is that plastic rods are either fragile or too soft. The first ones break, and the second ones are difficult to hammer in and do not expand the dowel tip well; metal ones are better, but choose stainless steel nails. Procedure: Preparatory work, cleaning the ceiling surface from the old coating, sealing unevenness and cracks with cement mortar. Apply a primer with a brush or spray gun and let it dry.
Make two layers. Using a notched trowel, apply adhesive putty to one side of the slab with a layer of 5-8 mm. Attach the slab to the ceiling and press. It’s good if you have an assistant who will fix the slab in the center and then along the edges. After installing the slabs, wall profiles for the suspended ceiling are attached; a vapor barrier can be omitted if there is ventilation between the ceilings.
Dowel-nail, 2. Mineral wool, 3.
Concrete ceiling. The work can be made easier if you apply glue like liquid nails to the surface of the slab. There are many manufacturers of mineral wool and it is difficult to single out one in particular, and it is not worth it. Quality is visible to the touch: if it is dense, then more material was spent on its production . Also pay attention to the composition: fiberglass, slag (the cheapest), or basalt mineral wool, the most popular today. It is recommended for insulation both from the inside and outside; glass wool is best used outside; mineral wool from slag is used for insulation of communications: pipelines, sewers. Thermal qualities are determined by the value of thermal conductivity or thermal resistance R. Basalt wool is a non-flammable material, it can be placed in the passage chimney box, from which sandwich chimneys for sauna stoves are made.
Expanded clay
Now let’s look at how thick the insulation on an expanded clay ceiling should be. This is the most wear-resistant material of all of the above, and at the same time environmentally friendly and inexpensive. It is characterized by high resistance to fire and good water absorption.
If you use expanded clay as ceiling insulation, the thickness should be maximum: 10 cm and above. To create a dense insulating layer, it is better to use a mixture of several types of expanded clay to insulate the ceiling. A 20-centimeter layer insulates heat better than a half-meter thick wooden wall.
Quite often it is used in baths. What thickness should the ceiling insulation be in this case? It all depends on the insulating layer.
The ceiling is first lined with waterproofing material, and then a layer of expanded clay is poured. The thickness of the ceiling insulation in a bathhouse made of blocks in this case will be about 25 cm. Waterproofing material is laid on top of it, just like on mineral wool.
Let's consider what the thickness of the insulation for the ceiling of a cold attic should be.
For the walls of attic structures, it is better to lay expanded clay in large blocks of 20-40 cm. Expanded clay particles are very light, so they will not significantly increase the load and are well suited for insulating roofs and attics. The downside is that for the most effective insulation of the ceiling, the thickness of the roof insulation must be at least half a meter.
Thermal insulation made of extruded polystyrene foam
Scheme of ceiling insulation with extruded polystyrene foam.
Most often, polyplex products are used to insulate a home. The material consists of polystyrene granules combined with a special agent. Polyplex has many cells filled with air, ensuring its low mass.
The material is environmentally friendly and is used for thermal insulation of residential walls. Excellent soundproofing qualities allow you to use polyplex for finishing the ceiling of a house. The material does not deform, withstands significant loads, and has a long service life.
Polyplex is used to insulate ceilings in low-rise buildings. It is not mounted on a wooden base, since the material does not allow air to pass through and can contribute to the appearance of mold. Polyplex slabs are laid on a vapor barrier layer and used as insulation for a concrete ceiling. A roll 1 m wide and 50 m long has a thickness of 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10 mm. They use a product with a thickness of 15, 20, 30 mm with a roll length of 15 m. In the form of mats, polyplex allows you to obtain a greater thickness of materials - up to 45 mm with a standard size of 1x2 m.
Mats are used to insulate metal and brick surfaces.
The latest generation polyplex is of high quality and belongs to fire safety group B2. The service life is 25 years, it is elastic, resistant to deformation, absorbs noise, reducing its level by 20 dB.
Extruded polyplex slabs are used for thermal insulation of walls and ceilings of residential premises, and the thickness of the insulation is 20 mm with standard dimensions of 600x2500 mm. The material thickness includes all intermediate dimensions between 10 mm and 200 mm, in multiples of 10.
Ecowool
As the name suggests, this is a more environmentally friendly material than mineral wool. It is most often used for walls, but is also suitable for ceilings as a healthier alternative. Since this type of cotton insulation consists of small crumbly particles, it is possible to carry out both “dry” and “wet” installation.
The “dry” option is simpler. Essentially, you just need to pour the insulation into the space between the beams. For the “wet” method, cotton wool is mixed with an adhesive base and sprayed under air pressure through a special pneumatic tube.
Ecowool prevents the appearance of mold and mildew. It is difficult to ignite due to fireproof impregnation, but even if it does catch fire, it emits a minimum of harmless smoke. It does not retain moisture. Ecowool does not lose its beneficial properties for many years.
How thick should this type of insulation be on the ceiling?
The size of the ecowool layer is not particularly important, since it is compressed to a minimum thickness of a few millimeters and will not load the attic floor. Thanks to the ability to lay wool in one layer, you can save a lot, but due to these features, there are no specific standards for the ecowool layer, and you will have to calculate the thickness of the insulation yourself.
So, let's consider what the thickness of the insulation for the ceiling of a cold attic should be if it is made of ecowool?
In this case, a 25 cm layer will be enough for full functionality. Since under these conditions the insulation dries out and evaporates over time, the layer should be increased by 25 percent of the total thickness. Over the course of a month, the insulation will slowly harden until it turns into one large monolithic surface.
Installation process
Having decided on the material for thermal insulation, the question arises: how to properly insulate the attic floor? If we talk about mineral wool, what density should it have and what layer of insulation will be best?
Selecting the layer and density of mineral wool
It is better to do insulation with mineral wool in two layers
In short, the larger the layer of mineral wool, the better. However, you need to remember that mineral wool has its own coefficient of thermal conductivity. The lower this coefficient, the higher the thermal insulation properties, and, therefore, it is possible to lay a smaller layer of wool or have greater insulation efficiency. Mineral wool with a thickness of 15-20 centimeters is often used, however, to ensure increased thermal insulation, a 30-centimeter layer of insulation can be used. It is also worth noting that with equal insulation thickness, two layers of mineral wool are always better than one.
You also need to pay attention to the density of mineral wool, because it varies: from 30 kg/m3 to 220 kg/m3. Thermal insulation properties practically do not depend on density
Denser insulation is used for facades and floors under screed. Mineral wool with a density of 35 kg/m3 is also suitable for attic flooring, since the insulation will be located on a horizontal, non-loaded surface.
Vapor barrier
Since mineral wool tends to absorb moisture, you need to start insulation by laying a vapor barrier material.
Vapor barrier - the first layer of insulation
Important! It is best to lay a layer of vapor barrier under the wooden beams, because otherwise they will be very susceptible to rotting. However, if it is impossible to install a vapor barrier film under the beams, they need to be impregnated with solutions that protect against rot and mold.. The best option is to lay a continuous layer of vapor barrier, but due to the size of the attic this is not always possible, so all joints need to be taped with special tape to ensure tightness
The edges of the vapor barrier must be raised above the level of the future insulation and glued with the same tape
The best option is to lay a continuous layer of vapor barrier, but due to the size of the attic this is not always possible, so all joints must be taped with special tape to ensure tightness. The edges of the vapor barrier must be raised above the level of the future insulation and taped with the same tape.
Thermal insulation
When working with heat-insulating materials, you need to wear special clothing
Next comes the installation of insulation. It must be laid so as to completely fill the entire space between the wooden beams. If we are talking about mineral wool, then it does not need to be pressed or squeezed. It should completely cover the space between the beams, leaving no cracks or gaps. It would also be a good idea to cover the floor beams themselves with heat-insulating material, because they can serve as a kind of cold bridges.
When laying mineral wool, it is very important to protect yourself, and especially your respiratory tract, from insulation fibers. Therefore, you need to use a respirator, as well as gloves, goggles and long sleeves.
Waterproofing
We complete the insulation of the attic floor with waterproofing and subfloor installation
Due to the property of mineral wool to absorb moisture, waterproofing must be laid over the layer of mineral wool. This is also necessary if a concrete screed will be poured over the insulation.
If the attic is constantly used, a subfloor can be made on top of such a heat-insulating “pie”. Its role can be a concrete screed or OSB slabs. If the attic is practically not used, then you can simply lay boards on top of the existing beams. Then, if necessary, go up to the attic, moving around it will not create difficulties.
As you can see, insulating the attic floor is an accessible task, even for those who have never done it. You need to decide on the material for thermal insulation, although most often it is mineral wool.
When installing a heat-insulating “pie”, it is important to remember the need for vapor barrier and waterproofing. This will allow you to achieve high results in insulating the attic floor
Rules for calculating the thickness of ceiling insulation
In order to accurately calculate the thickness of the insulation, it is necessary to determine the heat transfer resistance coefficient of all ceiling materials. It depends on the heating period degree-day (DHD) indicators, which can be calculated independently using the formula presented below.
Tables and other values for calculation can be found in SP 50.13330.2012 or use the one presented below.
“Values of heat transfer resistance in rooms”
It is not at all necessary to carry out these calculations. It is enough just to use a ready-made table.
“Thermal resistance for major cities of Russia (R)”
Advantages and choice of slab thickness
Mineral wool has the following advantages:
- light weight; elasticity; fire resistance; low price; long service life.
The thickness of mineral wool is an important parameter when choosing a material. This indicator depends on the ceiling covering. It also takes into account which method will be chosen to insulate the ceiling with mineral wool.
So, for concrete floors, choose wool with a thickness of at least 10 cm. If there is a heated attic space, insulation with a thickness of 8 cm is used. A pitched type of roof requires the installation of mineral wool 30 cm thick.
Calculation example
Let’s say the house is located in the city of Anadyr with the required room temperature of 20 °C. Then, according to the table “Thermal resistance for large cities of Russia”, in the column “For coatings”, the average R value will be 6.4 m2⋅°C/W (rounded 6.39 to 6.4).
When calculating the thermal resistance of a structure, it is necessary to add up the indicators of each layer: R = R1 + R2 + R3, etc. The thickness of the insulation depends on the building material and its size: the lower the thermal resistance of the ceiling, the larger the insulation layer should be.
The ceiling is made of cement-based aerated concrete, 0.8 m thick. Mineral wool is used as insulation. According to SP 50.13330.2012, thermal conductivity (λ) of reinforced concrete = 0.38 W/(m⋅°C). Based on the above data, the formula for the thermal resistance of the ceiling will look like this:
- Rп = 0.8 / 0.38 = 2.1;
- Ry = R - Rп = 6, 4 - 2.1 = 4.3.
When the coefficient of thermal resistance of the insulation layer (Ry) for a ceiling made of a given material has become known, it remains to calculate the thickness of the layer of this insulation (p), in this case mineral wool. To do this, it is necessary to calculate the thermal conductivity coefficient of mineral wool (k). Different manufacturers will have different thermal conductivity.
Let's take as an example the minimum coefficient - 0.045 W/m*k, according to the table above.
p = Ry ⋅ k = 4.3 ⋅ 0.045 = 0.19 m.
Accordingly, with such input data, the thickness of the insulation on the ceiling in the house will be 19 cm. Below are examples of calculations for the attic.
How to calculate the thickness of thermal insulation
We will show the determination of the thickness of the insulating layer using examples. Let's take as a basis the formula for calculating thermal resistance (in previous sections we already used it to compare the efficiency of different materials):
- R – heat transfer resistance of the insulating “pie”, m²•°C/W;
- δ – insulation thickness, m;
- λ – coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material, W/(m•°C).
The essence of the calculation: using the standard thermal resistance specified for your region of residence, calculate the thickness of the insulation, knowing the characteristic λ. The R value is determined according to the scheme given in the regulatory documents; a map with indicators for the Russian Federation is shown in the photo.
Similar maps can be found in regulatory documents of other CIS countries
Example 1. It is necessary to calculate the insulation of a summer house with an attic located in the Moscow region. We find the characteristics R for Moscow, choose the indicator 4.7 m²•°C/W (for coatings), take the coefficient λ of basalt wool equal to 0.05 W/(m•°C) and calculate the thickness: δ = 4.7 x 0.05 = 0.235 m ≈ 240 mm .
Example 2. We determine the thickness of the insulating layer of Penoplex for a concrete floor, location - Cherepovets. The algorithm is like this:
- We find on the Internet or reference literature the thermal conductivity of reinforced concrete λ = 2.04 W/(m•°C) and find out the thermal stability of a standard 220 mm floor slab: R = 0.22 / 2.04 = 0.1 m²•°C/W.
- Using the schematic map, we find the standard value of R for Cherepovets, take the overlap indicator - 4.26 m²•°C/W (the figure is highlighted in green).
- We subtract the found plate resistance from the required heat transfer value: 4.26 - 0.1 = 4.16 m²•°C/W.
- We calculate the thickness of polystyrene foam insulation λ = 0.037 W/(m•°C): δ = 4.16 x 0.037 = 0.154 m ≈ 160 mm.
Comment. The algorithm does not take into account the heat resistance of interior finishing and attic floors, so it gives the result with a small margin. If we take away the resistance of the flooring boards and plasterboard ceiling lining, the thickness of the EPS will decrease to 135 mm.
conclusions
To calculate the thickness of the ceiling insulation as accurately as possible, it is necessary to take into account many more factors that were omitted in this example: humidity, functionality of the ceiling, wall and roof material. Before making your own calculations, be sure to study the current SNiP and the Code of Practice for Thermal Protection of Buildings, since many of the values given in the tables above may change.
You can spend a huge amount of time trying to independently answer the question of what layer of insulation is needed for the ceiling of the house. It will be much easier to use online calculators, which are available on most construction company websites and sites selling building materials.
Now, knowing all the main indicators and formulas, you can easily calculate and choose the thickness of insulation for the ceiling that is most suitable in your particular case. It is better to take into account the calculation results with a reserve in order to protect yourself from abnormal frosts and weather changes. But remember that everything depends primarily on the right choice of insulation.
Preparatory part
Before you insulate the floors in the attic of your home, you need to be well prepared.
This includes:
- selection of wool and related materials;
- calculation of the required amount of material;
Selection of mineral wool
Stone or mineral wool is the name of a whole direction, in which there are dozens of different models. Based on the name, this includes all soft insulation materials made from rocks; the most famous option is basalt wool.
A number of sources include glass wool and slag wool here. In the first case, glass is used as the basis, and slag wool is made from blast furnace slag (a by-product of blast furnace production).
All materials are good, but which one is better is a moot point. I’ll say right away that if you take material from a well-promoted brand, there is not much difference in quality.
Mineral wool on any base is suitable for a cold attic
It is much more important to choose the type of material.
There are 2 types of such insulation:
- Soft mats that are sold rolled into rolls.
- Dense slabs.
Theoretically, insulating the ceiling from the cold attic side can be done using both options, but from experience, it is better to give preference to dense slabs.
The price of the slabs is slightly higher, but this material does not shrink over time, plus, when wet, some models of slabs can be dried without loss of volume and quality.
As for soft mats, here you are buying a “pig in a poke”; well-known manufacturers make good products, but it is not a fact that you will not buy a fake.
Such mats are inexpensive, but in an attic they lose volume in a couple of years.
It is better to insulate the ceiling of a cold attic using slabs
Related materials
This is the case with related materials. Any cotton wool is afraid of moisture; to protect it, a vapor barrier membrane is needed.
It is a fabric that allows steam to pass through only in one direction; neither steam nor moisture passes through from the other side.
Vapor barrier allows steam and moisture to pass through only in one direction
Material calculation
To calculate the amount of wool, you need the area of the attic and the thickness of the insulation:
- With the area of the attic floor, everything is simple - the length is multiplied by the width. Plus 5% for shrinkage and trimming.
- The thickness of the material depends on the climate zone. In central Russia, to insulate an attic floor with mineral wool, the thickness of the slabs is 100 mm, the mats are taken 150 mm. Accordingly, the further north, the thicker the layer.
It is advisable to do insulation of the attic floor with mineral wool in several layers
Selection of mineral wool
Among materials for insulation, mineral wool is in increasingly growing demand. This is no coincidence. Let's start with the fact that this is an environmentally friendly material, safe for the environment and humans. Mineral wool has a high heat retention class, absorbs sounds well, is not afraid of rotting, open fire, and is not interesting to rodents and insects. Increased elasticity and dimensional stability predetermine easy installation without fasteners. Mineral wool does not break, crumble, or slide over time, providing reliable thermal protection for up to 50 years.
These characteristics are fully inherent in insulation based on Izover Profi mineral wool. It consists of long slabs in rolls, which are equally suitable for the entire house - ceiling, walls, flat (in frame structures) and pitched roofs (attics), balconies, interior partitions, ceilings above the basement. The improved thermal conductivity coefficient (0.037) will save up to 67% on heating costs when compared with uninsulated spaces. As is known, ordinary mineral wool suffers even when slightly wet - drops of water displace air from the fibers and are difficult to weather, which can lead to a decrease in thermal insulation properties over time. Thanks to the special AquaProtect technology, Izover Profi repels water well and dries much faster due to optimal vapor permeability.
Insulation with mineral wool
Buy at isover market
A nice bonus is savings on transportation and storage due to the increased compression ratio in the packaging - it can be easily loaded into a passenger car, taking up 3 times less space compared to conventional basalt slabs (35 sq. m Isover Pro versus 6 sq. m of ordinary mineral wool, The same amount can be placed on the roof rack if you load an Isover module from several packages there, compressed with high-strength film at the factory). We will consider insulation technology in detail below.
How to calculate the thermal insulation of an attic floor?
Chief editor of the Stroyday.ru project. Engineer.
Open loopholes for warm air are a completely independent problem that can be solved by installing valves, gate valves and heat exchangers on ventilation ducts, carefully sealing all cracks or leaks at the joints of structures, in places where utility lines are installed, etc.
Through, let's say, the upper part of the house, up to half of all generated thermal energy can leak out absolutely uselessly! Something needs to be done!
But heat leakage through solid enclosing structures is a completely different story. It is impossible to completely eliminate heat exchange, that is, the transfer of heat from heated air to building structures. This means that we need to strive to ensure that these fences (walls, floors, and, in our case, ceilings) “are able to resist” the transfer of heat through themselves, so that with minimal costs it is possible to maintain the optimal temperature for people in the premises, at any weather outside. That is, so that the heating system is able, without working “to wear out”, and spending a reasonable amount of energy, to replenish these inevitable heat losses, reduced to the possible minimum.
The phrase “knew how to resist,” used a little higher, could not even be put in quotation marks. The ability of a building envelope to prevent heat transfer is called heat transfer resistance. This is one of the main thermal characteristics in construction.
Chief editor of the Stroyday.ru project. Engineer.
This value is subject to certain physical laws, and is measured in rather cumbersome units: m²×℃/W . The larger this value, the less heat is lost through such a structure, the more effective its thermal insulation is considered.
How to find such thermal resistance of a specific obstacle? This is not difficult: you need to know the thickness of this barrier (in meters), and also have information about what material it is made of.
In reference books, you can easily find indicators of the thermal conductivity coefficient - a tabular value calculated for most materials used in construction. Usually this coefficient is denoted in the documentation by the letter λ , and is measured in W / (m ×℃) . Very often, the value of the coefficient is indicated, among other things, in passports or other accompanying documents of building materials.
So, if the quantities are known, you can substitute them into the formula.
Rt = h / λ
Rt is the desired heat transfer resistance.
h is the thickness of the enclosing structure (in meters!).
λ is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material from which this partition is made.
For example, what is the thermal resistance of a solid wooden wall made of 40 mm boards? The thermal conductivity coefficient of natural wood with normal humidity is approximately 0.15 W/(m×℃).
Rt = 0.04 / 0.15 ≈ 0.267 m²×℃/W
Let's be honest, not very big.
But, as a rule, fences are not made single-layer, but are a combination of several materials. And if these layers are tightly adjacent to one another, then their resistance indicators are summed up. One of these layers is usually insulation, which, due to its very low thermal conductivity coefficient, can provide considerable thermal resistance even at relatively small thicknesses.
Well, what heat transfer resistance can be considered sufficient?
Don’t worry – everything has already been calculated by experts for us. For various building structures (floors, coverings, walls) and for all climatic regions of Russia, so-called normalized values have been derived. And in accordance with the current rules, a house can be considered well insulated if the normalized resistance has been achieved.
This parameter can certainly be clarified with any local design or construction organization. It’s even easier to use the proposed map-scheme. It shows three values for each region.
Map indicating the values of the normalized heat transfer resistance of building structures.
Not all cities, of course, fit on this map. But finding the required value with a sufficient degree of accuracy should not be difficult. You can use interpolation if your place of residence is located somewhere between two specified points.
The three resistance values are specifically shown in different colors with explanations at the bottom of the card. In the context of this article, we are interested in the meaning of “for overlap” - blue numbers.
If you have a clear idea of the design of the ceiling between the living room and the cold attic, or if an existing ceiling is being insulated, then it is quite possible to independently calculate which layer and which thermal insulation material will make the structure truly insulated.
Chief editor of the Stroyday.ru project. Engineer.
And it’s even easier - don’t look for values of thermal conductivity coefficients in reference books, and don’t create a formula for a set of layers - but just use our online calculator. Everything is already taken into account in advance.
Several explanations on working with the program will be posted below.
Calculator for calculating the thickness of attic floor insulation
Main nuances of the procedure
- The wood rots, therefore, the steam rising from the house must pass freely. If you install a vapor barrier or use a material that does not “breathe,” the tree may soon collapse.
- Insulation with foil should be laid with it (foil) down to protect the wood from moisture.
You can see examples of correct and incorrect installation in the image below.
But here is a universal scheme - insulating the attic floor using any of the materials.
Video - thermal insulation of attic floors
As a result, we note that the thermal insulation of the attic floor will be most effective if the attic itself is reliably protected from moisture penetration from the outside. In other words, you also need to properly arrange the roof. Good luck with your work!