The topic of today's article is the density of roof insulation. The topic is relevant because the thermal characteristics of the roof itself depend on the density of the thermal insulation material. And the higher the density, the higher the thermal conductivity of the thermal insulation layer, as well as its price. Therefore, it is important to choose the right insulation. This will be discussed in the article using mineral wool as an example.
Density of mineral wool of different versions Source fasadec.ru
Manufacturer Rockwool
Danish rockwool insulation for roofing occupies a leading position in the Russian sales market. Today there are three directions of the company, but we will focus only on insulation for flat roofs.
Rockwool - roofing insulation
It consists of mineral wool slabs made of basalt rock. Area of application: multilayer structures. The task is thermal insulation of flat roofs.
It is also possible to use cement-free roofing screed material. However, not all products of this brand can effectively insulate a roof. After all, the range is represented by universal and special plates.
- Rockwool Roof Butts designates the bottom layer with the letter H, the top layer with the letter B, and the universal one has no letter designation.
- Rockwool Cut-to-falls Roof Slab and Rockwool Underlao Roof Slab are used as the bottom layer in a multilayer structure.
Advice
. In places where there is no required roof slope, Cut-to-falls Roof Slab is usually used.
All products of the above-mentioned company have good characteristics and long service life. They are easy to use during installation, thanks to zero coefficients of linear expansion and shrinkage.
Generalization on mineral wool
Since the main topic of the article is the density of roof insulation, it is necessary to indicate that the choice will depend on which roof will have to be insulated. If this is a pitched structure, then there is no point in using material with a density higher than 125 kg/m³. If the roof is flat, and even more so if it is planned to organize, for example, a recreation area on it, then mineral wool slabs should not have a density lower than 175 kg/m³.
Insulation of a flat roof with mineral wool slabs Source goldkryshi.ru
Roof insulation - how to choose the right one
Note! The roof accounts for up to 40% of all heat loss in a building!
This figure becomes more understandable if you take a “thermal” photo of a house with an uninsulated roof. On it, the “hottest” areas are painted red. And they fall precisely on the roof of the house.
photo of a house with an uninsulated roof
Technology of roof insulation with mineral wool
There are two types of roofs: pitched and flat. Insulation of a pitched roof is carried out using two technologies:
- between the rafters;
- above the rafters. In principle, it is a gable roof. Mineral wool is used very rarely for insulation, rather as an exception. It is mainly used for insulation with rigid boards, such as extruded polystyrene foam. The method is complex and financially expensive. With a large overhang that still needs to be properly closed.
A flat roof also has two methods of insulation: from above (from the outside) and from below (from the inside), although bottom insulation contradicts all the norms and rules of building science. But it still applies, and therefore will be discussed in detail.
Insulation between rafters
The insulation algorithm between the rafters is very simple:
- mats are cut to a width 2 cm greater than the distance between the rafters;
- insulation is installed between the rafters at random;
- the insulating layer is covered with a vapor barrier film (type B or C);
- Interior finishing is mounted on top of the film if the roof slope is attic.
The technology for attaching the film completely follows the instructions for attaching the membrane.
However, there are several nuances here.
1. When laying low-density glass wool, the insulation sags. The problem is solved like this:
- every meter, a temporary strip is attached to the rafters, which holds the wool between two beams;
- in this way the span is completely insulated;
- using twine and a stapler, secure the first window between the bottom of the roof and the first batten. At the same time, the twine is constantly stretched between the rafters, rising up each time by 5-10 cm;
- The first rail is removed and work continues higher.
You can see what cotton wool fixed in this way looks like in the photo.
2. If the width of the rafters is not enough for full thermal insulation, then the first layer 10 cm thick is attached, then the sheathing is filled, and the slabs of the second layer of insulation are inserted into it. Insulation of the attic roof is carried out using the same technology. The only exception: finishing work on top of the insulating layer.
Insulation above the rafters
The technology for insulating the roof from the inside with mineral wool above the rafters consists of the following operations:
- Flooring is laid on the rafters from boards 20 mm thick. For mineral wool, it may not be continuous, but with a gap between the boards of up to 5 cm;
- a vapor barrier film of type B or C is rolled out onto the flooring overlapping from top to bottom. In some places it is grabbed with a stapler, but the main fixation will be done with the sheathing beam;
- the first row of sheathing is filled with a beam width of 10 cm (sometimes they say: height). The pitch is equal to the width of the mats, but, ATTENTION, it is 2 cm narrower so that the insulation becomes out of place;
- the first layer of insulation is laid;
- the second one is placed perpendicular to the first lathing. Here you also need a beam 10 cm high. Sometimes you can find recommendations to use a beam 12 cm wide so as not to fill the counter-lattice. It is better to abandon this idea, since the ventilation processes of the space between the windproof membrane and the roof are disrupted;
- the second layer of insulation is laid. Here it is important to avoid contact of the connecting seams with the beam of the lower sheathing;
- The thermal insulation layer is covered with a windproof membrane. How to lay it and fix it, see the “Preparatory work” section;
- a counter-lattice is placed over the membrane. For these purposes, you can use a 30x30 mm square beam or 30x40 mm slats.
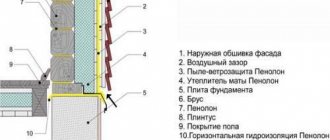
Insulating a flat roof from the outside
Insulation of flat roofs from the outside is carried out on the top floors of apartment buildings, private houses, and garages. The order of work is as follows:
- Type C vapor barrier film (2) is laid on reinforced concrete floors (indicated by number 1 in the diagram);
- mats of basalt wool grade P-175 (3) are laid on the film in two layers. The slabs of each row must be installed with a shift, according to the principle of brickwork. In this case, the seams of the top row should not coincide with the joints of the bottom;
- a two-layer flat slate screed (4) is mounted on top of the insulation;
- the entire structure is filled with bitumen-polymer insulating composition (5).
By the way, it’s simple, but very expensive. However, the appearance is worth the expense, as confirmed by the photo below.
How to choose the “right” insulation for a roof?
The most important from the point of view of subsequent operation are:
In addition, the type of roofing also influences the choice of insulation. As you know, roofs can be pitched or flat, usable or unusable. And each type needs its own insulation.
So, for example, for a pitched roof it is necessary to choose non-flammable insulation with a density of 25-45 kg/m3 (the value depends on the steepness of the slopes). If the attic is being insulated, it is recommended to choose non-flammable slab insulation with a density of at least 35 kg/m3.
But the correct choice of appropriate roofing insulation does not guarantee high-quality and durable thermal insulation of the roof. Installation errors and imaginary savings are what can nullify all your efforts.
The main reasons for poor-quality thermal insulation are the low professionalism of the craftsmen and the customer’s desire to save on materials.
Do you need THIS result?
If not, then learn from the mistakes of others!
result of improper installation of insulation
And for a flat roof in use, insulation with insufficient density is selected. The result is a violation of the integrity of the roofing pie even under minor loads.
Installers also make their “mite” by violating the insulation laying technology or ignoring problematic and hard-to-reach places - junctions with walls, ventilation ducts, dormer windows, etc.
Typical mistakes when installing roof insulation:
- The presence of depressions or cavities that allow cold air to pass through
- Inaccurate installation of insulation
- Incorrect insulation thickness
- Excessively tight installation (insulation too wide)
And also, remember that the thickness of the insulation should be selected on the basis of thermal calculations, and also correspond to the climatic region of construction and the selected thermal insulation material.
And, of course, trust the work only to professionals with sufficient work experience and good recommendations.
Only then will the roof of your house reliably protect you for many years!
Results
For roof insulation with mineral wool, soft glass wool and dense stone wool with a soft end are suitable. The materials are laid spaced between the rafters. The thermal insulation density must be at least 55 kg/m. cube, but you shouldn’t take too heavy wool, it will still put an additional load on the rafter system. For flat concrete roofs, heavy and dense stone wool is suitable. It is important to calculate the thickness of the thermal insulation; for this you can use an online calculator, it’s easier. In tandem with mineral wool, vapor and waterproofing are used, which prevent the entry and retention of moisture in the thermal insulation cake.
Choice of insulation
From all of the above, we can conclude that the best insulation for a roof is basalt slabs or glass wool.
Kawabanga! Determination of frost resistance of concrete
Rolled mineral wool URSA is the most popular insulation for roofing
If a fire occurs, the insulation should not ignite, produce smoke, and should also prevent the spread of fire. Mineral wool and fiberglass have these properties.
When choosing, you only need to pay attention to the manufacturer’s information, which indicates what maximum combustion temperature a particular material has.
For good sound insulation, choose a material that indicates the sound absorption index.
Ursa (URSA) mineral wool insulation for roofing has the highest index “A”. Namely ursa pureone, which was used during the reconstruction of the Bolshoi Theater.
Pay attention to weight
When choosing insulation for the roof, you need to take into account its weight. In this case, you can give preference to glass wool, since it has a lower mass compared to mineral wool.
When insulating an attic roof, the insulation is usually inserted between the rafters; in this case, mineral wool will slide under its own weight, and fiberglass with acrylic-latex binders will be well held in a given space.
Mineral wool or fiberglass used as insulation should not release harmful toxic substances, odors or dust into the space. Almost all insulation materials sold in Russia currently meet this requirement.
Basalt insulation Rockwool (Rockwool)
Rockwool basalt insulation
ROCKWOOL insulation is rigid slabs that are best used for insulating flat roofs.
The insulation of this brand has a clear classification:
Foam glass as roof insulation
This insulation, sometimes called cellular, foam or gas glass, is produced from crushed glass using high-temperature technologies.
However, despite the large list of advantages of foam glass, this material also has its own sins, which consist in its large mass and low mechanical strength to impact loads.
In addition, the price of foam glass is somewhat high compared to other materials used for thermal insulation.
Cellulose insulation for roofing (Ecowool)
Those additional ingredients that are present in ecowool are not harmful to human health and harm the environment. The material is 81% recycled paper, the remaining 19% is natural boron minerals.
The release of toxic substances is not observed, since ecowool at high temperatures decomposes into two components - carbon monoxide and water. In addition to this property, cellulose insulation has many other advantages:
- high thermal insulation qualities;
- increased sound insulation;
- hygroscopicity;
- biostability;
- manufacturability;
- possibility of reusable use.
The biostability of ecowool is ensured by processing the source material with special means that prevent the formation of mold and various fungi, as well as rodents and harmful insects in its structure.
The following brands of cellulose insulation have become very popular - Unisol (Ukraine), Ecowool (Canada) and Ecowool (Kazakhstan).
Foam concrete for roofing
The birth of foam concrete dates back to 1975, when a cellular material based on protein components was produced in Germany. The material is obtained from a mixture of cement, filler, water and special additives that make it possible to obtain a foamed mass.
In its structure, this insulation is more reminiscent of hardened concrete foam, but unlike it, it has incomparably light weight, since the sealed capsule cells are filled with air.
It is this property that makes it possible to use foam concrete for insulation of roof structures, without strengthening the rafter system, load-bearing walls and foundation. The advantages of such insulation include such properties as:
Foam concrete is applied using special installations, filling with its mass all hard-to-reach places, the smallest cracks, cracks and holes.
Expanded polystyrene
This insulation, commonly referred to as foam plastic, is superior to mineral wool products in many respects, as it is not afraid of moisture.
The main advantages of expanded polystyrene include:
Currently, it is not recommended to insulate roofs with polystyrene, especially soft roofs.
Polyurethane foam as roofing insulation
This type of insulation is a type of plastic and its structure can be semi-rigid or rigid. It is a frozen foam, which is 80-90% composed of tiny capsules filled with gas.
To insulate building structures, a rigid type of polyurethane is used, which can be produced directly on the construction site using special equipment.
The advantages of polyurethane foam are its following properties:
And of course, there is no material without flaws. Polyurethane also has them, which is expressed in the following points:
Expanded clay
The insulation material, called expanded clay, is ordinary clay, molded into granules and baked at high temperatures. Granules can have different sizes, and pores that form during clay sintering.
The result is a fairly light bulk material that is environmentally friendly and clean. The advantages of expanded clay rightly include:
Completely environmentally friendly material.
Good noise and thermal insulation obtained due to the smallest air pores in the granules.
Disadvantages include low resistance to humid environments. Requires high-quality waterproofing devices. Also, in order to obtain high-quality insulation, it is necessary to pour a sufficiently large layer of expanded clay.
Thermal insulation thickness
When choosing a material for thermal insulation, the question often arises of how to calculate the thickness of the insulation for the roof. For this, there are special formulas and building codes and regulations (SNiP II-3 -79), according to which thermal engineering calculations are made.
Kawabanga! Wear of asphalt concrete pavement
Knowing this coefficient and the thermal conductivity of the insulation, its optimal thickness can be easily calculated.
Which insulation is better for the roof - this question is decided by each individual, based on the technical characteristics of each material separately, and of course on the cost of the insulation.
It may be necessary to choose several types of insulation that will fully meet the requirements for the comfort of the attic space.
Currently, there are a lot of materials for thermal insulation on the building materials market and everyone can choose the price of insulation for the roof based on their financial capabilities.
Using mineral wool with different densities
Let's look at the density of mineral wool using a few examples. That is, we will designate for which structures, what class of insulation should be used.
For facade
Wall insulation with mineral wool is carried out in two ways:
- Under plaster . Here the insulation is installed, a reinforcing frame is laid on it, on which the plaster solution is applied. It turns out that the heat-insulating layer bears the weight of the plaster layer. And this is sometimes quite a significant load. Therefore, in this case it is recommended to use mineral wool with a density of 100 kg/m³.
- Ventilated facade . This is a frame structure made of wooden beams or metal profiles, which is attached to the wall of the house. Thermal insulation material is laid between the sheathing elements. It turns out that the latter does not bear any load. This means that material with a density of up to 100 kg/m³ can be used here.
Mineral wool inside a ventilated facade Source tn.ru
Insulation of walls from the inside
Here, in principle, the same option as for facade planes. Only instead of a ventilated facade, they use a sheathing that is attached to the wall. For this type of insulation, it is better to use mineral wool in rolls or mats with a density of 40-60 kg/m³.
Comparative characteristics of foam concrete and other building materials
| Options | Ceramic brick | Ceramic block | Silicate brick | Gas block | Foam block |
| Dimensions, cm | 25/12/6,5 | 38/25/24 | 25/12/6,5 | 20/30/60 | 20/30/60 |
| Wall weight, kg/m2 | 1200 — 1800 | 600 — 800 | 1450 — 2000 | 100- 900 | 100 — 900 |
| Density, kg/m 3 | 1500 — 1750 | 700 — 900 | 1700 — 1950 | 300 — 1200 | 300 — 1200 |
| Water absorption,% | 12 | 12 — 14 | 16 | 20 | 14 |
| Thermal conductivity, W/M*k | 0,4 — 0,7 | 0,1 — 0,2 | 0,8 — 1,1 | 0,1 — 0,4 | 0,1 — 0,4 |
| Frost resistance, cycle | 25 | 50 | 25 | 35 | 35 |
| Ultimate compressive strength, MPa | 2,5 — 25 | — | 5 — 30 | 0,5 — 25 | 0,25 — 12,5 |
| Consumption, pcs./m 3 | 400 — 500 | 34 — 45 | 400 — 500 | 21 — 27 | 21 — 27 |
| Price, $/m 3 | 63 — 112 | 62 — 90 | 17 — 90 | 60 — 94 | 49 — 68 |
- What is the difference between aerated concrete or foam concrete - comparison of advantages and disadvantages
TechnoNIKOL is a reliable Russian brand
This is an exclusively Russian brand that has 53 factories in 7 countries. Among them are Germany and Great Britain, Italy and Lithuania. Official representative offices are located in 18 countries. The company's training centers are also located there. TechnoNIKOL has its own Research Centers for the development of new technologies for heat and sound insulation. The products of this concern are very popular due to competitive prices and are sold in 95 countries.
TechnoNIKOL general building thermal insulation based on stone wool
An inexpensive way to perform thermal insulation on any construction site is with materials based on stone wool with a universal purpose. At TechnoNIKOL such products are represented by the BAZALIT series. All brands can be mounted horizontally or vertically.
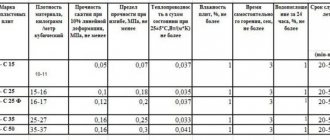
- BAZALIT L-30 - has a density of 25-35 kg/m3 and a thermal conductivity of 0.032 W/(m*K) at an outside temperature of 10 degrees. Well suited for a base layer followed by cover.
- BASALIT L-50 - denser slabs (36-50 kg/m3), designed for installation in any spatial position. Particularly good for the bottom layer when insulating floors and interfloor ceilings.
- BASALIT L-75 is the most dense material based on stone wool with an indicator of 51-75 kg/m3. Vapor permeability of 0.5 mg/(m.h.Pa) allows its use in the middle layer on walls with light masonry.
TechnoNIKOL stone wool for insulation of all types of roofs
For all types of roofing, the TechnoNIKOL company has developed a line of TECHNORUF insulation materials. The TECHNORUF N EXTRA brand is produced in the form of a basalt slab with a density of 90-110 kg/m3 and can withstand pressure up to 3000 kg per 1 m2. It is optimal for arranging a sloping roof. TECHNORUF N PROF is next in class and has a density of 110-130 kg/m3. With a deformation of 10%, it is capable of carrying a load of up to 4000 kg per square meter, which is also not bad for insulating a roof of complex shape.
TECHNORUF V PROF is designed for all types of flat roofs. It has a pronounced hydrophobic effect. It can act as the top durable layer in three-layer structures. Its density is 175-205 kg/m3, and its strength can withstand up to 8000 kg of pressure per m2. To quickly create a slope on a flat roof for precipitation, use TECHNOROOF WEDGE 4.2%, which automatically forms a slope contour. At the same time, cotton wool itself effectively combats cold retention and has a thermal conductivity index of 0.038 W/(m*K).
TechnoNIKOL TECHNORUF N EXTRA.
TechnoNIKOL stone wool for insulation of ventilated facades
For ventilated facades, the manufacturer offers a whole line of basalt wool from the TECHNOVENT series. TECHNOVENT EXTRA brand is quite suitable as a base layer or in combination with another insulator. Its breathability is 35 m*s*Pa.
There is another type of this material - this is TECHNOVENT N PROF, the air permeability of which is 80 m*s*Pa. The insulation is intended for use in industrial and civil construction during new construction and reconstruction of buildings and structures for various purposes as an inner layer with two-layer thermal insulation in curtain wall systems with an air gap.
TechnoNIKOL stone wool for insulating a wet facade
TECHNOFAS EXTRA insulation, designed to retain a thick layer of plaster, is well suited for wet facades. The density of the slab is 80-100 kg/m3, and the thickness is from 50 to 150 mm.
When a thin layer of plaster is planned, you can save money and choose TECHNOFAS EFFECT, which, with a smaller cross-section, has an increased density of 125-137 kg/m3, which will provide the required strength. TECHNOFAS DECOR is produced for insulating facades on balconies and loggias, therefore it has an increased tensile strength of 25 kPa.
TechnoNIKOL TECHNOFAS EXTRA.
Choosing foam concrete correctly - selection criteria
2. Price matters too. On average, for the D800 brand it is about $80 per cubic meter. If the material is much cheaper, you should think about it - this may affect the quality.
3. Carefully inspect the blocks - they should not be pure and bright white. Technology will not allow this. Normally, foam concrete should be greyish, slightly lighter or darker, and uneven coloring of the surface is not allowed.
An example of improperly organized storage of foam blocks; they are not covered with anything on top and it is already clear that they have absorbed moisture from the damp earth.
Advantages
The main advantages of mineral wool are:
- Low fire hazard, no harmful emissions.
- Ease of installation.
- Low density and low total weight of the insulation.
- Good sound insulation.
- Repels rodents.
- Resists mildew.
- Long service life.
- Independence of characteristics from temperature.
- Affordable price.
In addition to the advantages, it is necessary to note a number of disadvantages:
- Low strength.
- The need for waterproofing.
- Hygroscopicity of glass wool. Moisture absorption leads to a significant reduction in thermal insulation
- If the calculation and installation are incorrect, the mats fall out of the sheathing.
The disadvantages are offset by careful calculation and high-quality installation of insulation.
About the choice of insulation and types of roofing
Now let’s try to find out: which insulation is better for the roof? What should you know when purchasing? The insulation must be selected, first of all, according to the type of roof.
In principle, the roof can be:
- single slope;
- hip;
- flat;
- gable;
- tent
The most popular and practical is the gable roof.
What does it depend on?
The defining characteristics of roof insulation in residential and public buildings include:
- Thermal conductivity. The best insulation materials should have a minimum thermal conductivity to reduce the overall heat transfer coefficient. The lower density, as already noted, is due to porosity. In addition, according to the production technology, the pores should not be connected to each other, as this will lead to heat convection. A derivative of porosity is also the ability of a material to absorb sound.
- Moisture vapor permeability, which should also be minimal. Therefore, the ability of the heat insulator material to absorb water should also be minimal. The same applies to the ability to condensate.
- Installation features. The insulating material must be resistant to water and solvents, have high strength and not lose its insulating characteristics during the entire warranty period. This set of parameters is determined by the quality of the heat insulator production technology, and not by its density.
- Environmental characteristics. Thermal insulation material must be non-flammable and non-explosive. In the unlikely event of fire, combustion products should not present a toxic hazard.
Important: the density of insulation most of all depends on the density of the components, the production technology of the heat insulator and the degree of safety for the environment.
About the types of insulation
About the types of insulation
The most common insulation materials at the moment are:
- expanded clay;
- polyurethane foam;
- mineral wool;
- foam glass;
- Styrofoam;
- foam concrete;
- cellulose
Each of the materials has its own characteristics. Let's get to know them.
Expanded clay
Expanded clay is poured onto the outer part of the roof or covering slab. Then the material is compacted and fixed with concrete screed and roofing felt.
Note! This method of insulation can be resorted to only in cases where the load-bearing floor is designed to bear a lot of weight (and expanded clay together with a concrete screed weigh a lot).
Mineral wool
This material is rightfully considered one of the best; it is not flammable and does not absorb moisture. Mineral wool has excellent thermal and sound insulation parameters, as well as a good service life.
Foam glass
Foam glass is an environmentally friendly and versatile, however, quite expensive material
To make it, glass production waste and carbon are foamed. Foam glass is durable, moisture-resistant, not subject to deformation, does not burn and retains its thermal insulation properties for a long time.
But the material still has one drawback - poor adhesion. To improve it, use polymer cement adhesive during installation.
Expanded polystyrene
This material is installed from the inside - foam boards are placed in one layer on the pre-installed waterproofing, maintaining maximum sealing density. All joints are treated with mounting foam, which is covered with mounting tape.
Foam concrete
Note! You cannot insulate a roof with foam concrete yourself! The fact is that this procedure is carried out by specialists using a special portable unit.
The thickness of the material layer can vary from 3 to 15 cm, depending on specific conditions.
Polyurethane foam
Fire safety, low cost, excellent thermal insulation characteristics - these are the main qualities of polyurethane foam. It is applied from the inside using a special installation, and after this there are no gaps left.
Any roof can be insulated with polyurethane foam.
Cellulose
Ecowool - cellulose wool
The material is also coated with antiseptics for biological stability - that is, to protect against rodents. The result is an inexpensive, lightweight and environmentally friendly material with excellent thermal and sound insulation properties.
Kawabanga! Foam concrete blocks - characteristics of their advantages, disadvantages, selection criteria and tips for use
Steam and waterproofing
Polyethylene is unreliable and breaks easily.
Roof insulation with mineral wool is impossible without hydro- and vapor barrier. Roll materials are used for this. Polypropylene film reinforced with fiberglass mesh is laid as a vapor barrier. It is important that the vapor barrier is strong, since it is laid stretched and holds the weight of the insulation. Regular polyethylene cannot be used.
A three-layer polypropylene membrane is used as waterproofing, it is also called a diffusion membrane. This material does not allow water to pass through at all, but allows steam to pass through in one direction, so it is important to lay it on the correct side. One side is fleecy and the other is smooth. The rough surface must be laid against the insulation. The manufacturer's logo is printed on the smooth side. The material also has pores that are visible visually. An important condition when insulating a rafter roof is to create a ventilated gap between the diffusion membrane and the finish.
Properties of fiberglass and foam concrete
Fiberglass insulation has almost the same characteristics as mineral wool. These two materials have only two important differences:
- water absorption of mineral wool is much greater than that of ordinary wool;
- low resistance to high temperatures.
Scheme of roof insulation with foam concrete.
The positive aspects of using materials include:
- lightness of the material;
- low sound absorption.
Calculation of mineral wool thickness for roofing
The thickness of mineral wool for roof insulation is calculated based on the region in which the house is located. It all depends on climatic conditions. The calculation can be done using an online calculator - this is the easiest way. Many mineral wool manufacturers provide this opportunity on their Internet resources. Don't worry, the calculations are accurate.
In addition, you can independently calculate the thickness of the thermal insulation, but you will have to take into account many factors:
- standard coefficient for your climate zone;
- thickness of the enclosing structure - separately for each layer, including non-ventilated air gaps;
- lambda of thermal conductivity of the material of each layer of the enclosing structure.
To begin with, the actual thermal resistance of the enclosing structure is calculated. To do this, its thickness in meters is divided by the lambda of the thermal conductivity of the material. If the structure is multilayer, then the operation is performed for each layer separately, and the results are summed up. Then you need to calculate the difference between the actual and nominal thermal resistance of the roof. The difference is the heat loss that needs to be compensated by insulation. Therefore, to find out the thickness of the thermal insulation, you need to multiply its lambda thermal conductivity by the difference between the actual and nominal thermal resistance of the roof. Please note that the result will be in meters. You need to add at least 10% to the resulting figure.
Modern non-volatile heating boilers operate in autonomous mode, so they can be used even far from civilization.
A useful article about AGV gas heating boilers is here.
Criteria for choosing insulation for the attic
High-quality insulation makes the attic suitable for year-round use
When choosing a heat insulator, you need to pay attention to the performance characteristics of the materials, including comparing:
- noise insulation properties;
- ease of installation;
- moisture resistance;
- resistance to biological degradation;
- lifetime;
- efficiency;
- environmental friendliness;
- fire safety.
But the main quality by which insulation material is evaluated is its thermal conductivity coefficient, on which the ability to retain heat in a room depends
.
From the point of view of ease of installation and use of insulation, preference should be given to universal materials. If the same thermal insulator can be used for walls, roof and floor, the insulation of all structures will last the same period.
Sound insulation properties are a particularly important parameter if the roofing is made of metal (seam roofing, metal tiles, corrugated sheets). Gusts of wind, rain and hail make such a roof “sound”, and staying in the attic will cause discomfort.
Slab insulation from a well-known manufacturer
Since the roof frame is usually made of wood, it is advisable to use insulation that is fire resistant and flame retardant. Otherwise, an accidental fire will cause the entire attic and roof to quickly become engulfed in fire.
What does the indicator affect?
An ordinary house loses up to 35% of energy through the ceiling and floors in winter, but also receives the same amount in summer.
The effect of density on product properties varies from one insulating material to another, and this is true even within the same group of different inorganic insulating materials (mineral wool, glass wool, basalt wool, etc.). Therefore, it is inappropriate to compare different materials based only on their density.
Reference. The defining thermophysical characteristic of insulation is its thermal conductivity.
For example, in the case of mineral wool, the quality of thermal insulation depends on the fiberization process adopted and the structure of the sheets or rolls. Thus, during the production of basalt wool, a significant proportion of crushed particles is formed. They no longer have a fibrous structure, but increase the mass of the insulation. As a result, the thermal or acoustic properties of the final product are degraded.
The effectiveness of roof insulation no longer depends on the density of the product, but on the value of its thermal resistance (or R). Thermal resistance is the ability of insulation to resist the transfer of energy in the form of heat, and is therefore a more important factor when choosing an insulating material: the higher the R-value, the more effective the insulation.
Regulatory requirements for mechanical, rather than thermophysical, characteristics of thermal insulation are regulated by SNiP 3.04.01-87. Since the weight of the heat insulator determines the total loads on the roof , increased attention should be paid to measures to reduce the magnitude of such loads. Such measures include:
Sealing joints with cement or concrete of the minimum required density (but not lower than M150.- Treatment of potential joints with asphalt concrete, the layer of which must be at least 100 mm with a compressive/shear strength of at least 80 kPa.
- The wood of the sheathing must be of quality not lower than grade III.
It is prohibited to lay high-humidity heat insulation, the density of which is artificially increased.
Basic properties of insulation for pitched roofs
In the past, sawdust and straw were used for insulation. Nowadays there is a wide variety of insulation materials on the market. If you add manufacturers to the list, then there will be a huge variety of names
But every development has its place, so it’s important to learn how to choose the material wisely
To do this, pay attention to the following characteristics:
Give preference to options designed for a period of at least 25 years.
Preparatory work
The preparatory work for roof insulation has a peculiarity - it basically comes down to laying a one-sided vapor barrier membrane of type A or AM (builders call it “waterproofing”). The need for this type of work (vapor barrier) is shown in the material “Installing a vapor barrier with your own hands.”
Before laying the windproof membrane, it is necessary to ensure the integrity of the wooden roof structures (if they begin to rot, replace them), and then treat them with antiseptics and fire retardants.
In the process of fixing the membrane, several rules should be followed:
- There must be a ventilation gap between the membrane and the roofing finish. According to SNiP no less than 6 cm, in practice 4-5 cm;
- should be laid on the rafters, and not on the sheathing under the roof;
- air movement must be free over the entire surface of the roof slope. If ventilation is conditionally limited, i.e. exists for each gap between the rafters or slats (boards) separately, then in winter ice will certainly appear in certain places. This can be easily verified by those who have carried out thermal insulation work on their own;
- between the rafters the membrane should sag by about 1 cm. If pulled tightly, it can break under the influence of temperature fluctuations, like electrical wires during severe frost;
- secured with a stapler. The staples must be taped;
- laid with an overlap (15-20 cm);
- the seams are sealed with construction tape;
- If a finished roof is being insulated, the membrane can be installed using two technologies:
- with a smooth sheet at the bottom of the rafters, after which insulation is carried out in stages along a two-layer sheathing, where the first row is packed horizontally, the second, along the first, vertically;
- along the rafters, but going inside the rafter system. In this case, the insulation is laid between the rafters, using the technology of insulation from the inside without a finished roof.
Laying a windproof membrane when insulating a finished roof.
Thermal insulation technology for pitched roofs
Thermal insulation of a pitched roof
So, how to properly insulate a pitched roof:
As you can see, insulating a pitched roof is not the most difficult process, so it’s possible to do it with your own hands even for a person far from the construction industry.
Construction of a pitched roof with insulation
Insulation of a gable roof
There are two possible situations here:
- The roof is already covered with roofing material.
- Not covered yet.
Let's start with the second case, because it is simpler.
Laying waterproofing on rafters
If polyurethane foam is chosen as the thermal insulation material, then all work from the inside of the attic is reduced to applying foam to the pitched plane of the roof structure. The main task is the uniformity of the applied material.
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that ecowool is installed using wet and dry technology. The first is when water is added to the material
In the case of insulation of pitched roofs, dry technology is used.
Filling ecowool into the space between two films
Polyurethane foam for roof insulation
I would like to dwell on one more insulation material, which today is often used for thermal insulation of roofing structures. It is applied by spraying in the form of foam, which polymerizes into a durable mass under the influence of air. A seamless surface is formed on the surface of the processed parts and assemblies, one hundred percent sealed.
It should be noted that the density of polyurethane foam varies over a very wide range: 8-100 kg/m³. So which one is intended for which building structures?
- From 8 to 20 kg/m³ - this is the material that is used for internal insulation and sound insulation. This is an open-cell mass with low mechanical protection that absorbs moisture well.
- 20-25 kg/m³ . Here the situation is this: 50% of the cells are closed, 50% are open. This type of polyurethane foam is used for both external and internal insulation. A mandatory requirement is protection from precipitation.
- Density from 30 to 35 . All pores are closed, which reduces water absorption to a minimum. But such material does not tolerate mechanical loads. Although it is recommended to use it for thermal insulation of foundations for backfilling with soil.
Insulation of the foundation with polyurethane foam Source ppu-perm-master.ru
- 40-45. A material of this density can be used to insulate deep foundation structures.
- 60-70 kg/m³ . Polyurethane foam of this density can be laid under screeds. That is, the density of the material allows it to withstand significant loads. If we talk about the insulation of flat roofs, especially those in use, then this option can be considered ideal.
- 100-110 kg per 1 m³ . This is the most optimal option when the task is to insulate building structures subject to significant mechanical loads.
So, let’s summarize and decide which of the above options is suitable for insulating roof structures. Optimally, it is polyurethane foam with a density of 40 to 60 kg/m³.
Vapor barrier materials
The most popular vapor barrier material is a special film that protects wood and insulation from the effects of steam, which turns into condensation as a result of temperature changes. The negative impact of moisture on the elements of the roofing structure need not be mentioned once again - suffice it to say that it significantly reduces the service life of the roof and the effectiveness of the thermal insulation material.
The vapor barrier membrane is attached to the roof or ceiling before thermal insulation materials are laid. In rooms where heating is installed, a vapor barrier should be installed only under the finishing layer. To protect structures that are constantly exposed to temperature contrast, a vapor barrier layer must be placed on both sides. The exception is concrete floors, which do not require such protection.
To create a vapor barrier layer, a film with different characteristics can be used. The simplest option is a film made of non-woven material, but a much more effective option is a foil membrane. The latter option, as its name implies, has a thin layer of foil on one side, which prevents heat from escaping beyond the structure. The roof vapor barrier installed from the inside of the house is connected with special tape, ensuring a tight connection.
Which mineral wool is better to insulate a roof?
The current GOST 52953-2008 assumes the following classification of mineral wool:
Glass - made from raw materials such as sand, etibor, limestone and soda. When heated to a temperature of 1400 °C, the components of the material are transformed into a single fiber with the following characteristics:
- Thermal conductivity from 0.04 to 0.045 W/m*K.
- Resistant to fire (glass wool does not even smolder).
- Resistance to chemically active substances.
- High levels of noise absorption (you will not hear the sound of raindrops falling on the roof).
- High strength.
- Resistance to temperature changes.
The disadvantages of glass mineral wool include the fragility of its fibers. In addition, such fibers can injure human skin, and ordinary clothing does not protect against the penetration of tiny glass wool fibers. The disadvantages of glass wool include low heat resistance. The operating temperature of the material ranges from −60°C to +450°C.
Stone - made from rocks. Elements of volcanic origin are melted at temperatures above 1500 °C. Advantages of stone wool:
- Thermal conductivity is in the range of 0.036-0.045 W/m*K.
- Wide operating temperature range: from −190 °C to +700 °C.
- Stone mineral wool can be used to insulate the roofs of buildings in the far north.
- The moisture-repellent characteristics of stone wool are due to the lack of hygroscopicity.
- Stone wool is an environmentally friendly and chemically neutral material for roof insulation.
- The fibers of this material are not sharp. You can work with stone wool with unprotected hands without any consequences in the form of irritation.
The disadvantage of mineral wool is the presence of phenol-formaldehyde resins in its composition, which contribute to the release of phenol. This process can take place when mineral wool is heated to temperatures above 700 °C.
Slag . Compared to other types of mineral wool, slag roof insulation has worse characteristics. Today, such material is practically absent from the building materials market. The main advantage of slag mineral wool is its low cost. Experts do not recommend using it for roof insulation, so in this article we will not consider its properties.
Insulating the attic floor
Of course, the easiest way will be to install thermal insulation during the construction of the building - this will simplify the design and some of the nuances of the work. In most cases, it will not be possible to follow this advice - lack of finances or time may well interfere, so the ceiling remains without insulation. As a rule, this state of affairs persists until the first frost, and the owners have to quickly lay thermal insulation.
Before insulating the attic floor, you need to carry out a number of preparatory work, which is especially important when using bulk thermal insulation materials. There are two insulation technologies - traditional and modern.
The traditional method of floor insulation is implemented as follows:
- The first step is to treat the boards attached to the ceiling with clay or lime mortar - such treatment will ensure the structure is airtight while maintaining normal ventilation;
- When the mixture hardens, you can proceed directly to insulation work - pouring bulk materials into the space between the floor beams onto pre-treated boards.
Today, a more modern method of floor insulation is used much more often:
- First of all, a vapor barrier membrane is laid on the floor and beams with a 20-cm overlap, which will not only protect the insulating material, but will also complement its thermal insulation properties, reducing the amount of heat escaping from the building through the ceiling;
- To ensure a tight seal, the membrane in the overlap areas must be sealed using construction tape;
- The next step is laying the selected insulation (mineral wool, ecowool, expanded clay or one of the bulk materials) using the appropriate technology;
- To ensure that the floor beams do not have cold bridges, it is necessary to ensure that the insulation passes over them;
- Above the insulation, in compliance with the already known rules, another layer of vapor barrier film is laid, which is attached to the beams with counter-battens;
- All that remains is to lay a covering of boards or fairly strong plywood over the finished thermal insulation structure.
Sometimes, instead of insulating the floor from the attic side, thermal insulation is installed inside the building itself. This design is also quite effective in insulation, but requires additional finishing.