Bottom distribution of a heating system is a method of organizing space heating in which pipes with coolant are located at floor level, hidden in a screed or laid in the basement. It is used both in private low-rise buildings and in multi-apartment buildings with central communications.
TM Ogint's assortment includes radiators and components that can be used when installing a heating network with bottom wiring. The products sold are of impeccable quality, have a long service life and are designed to operate in Russian conditions. The technical characteristics of heating devices and components comply with the requirements regulated by European standards.
Ogint bimetallic radiators are the best choice for systems with bottom wiring→
Combination of two-pipe and single-pipe options
In private two-story (or higher) houses, both two-pipe and single-pipe vertical risers can be used, along with horizontal single-pipe distribution to rooms with a variety of ways to connect heating devices.
Diagram of a single-pipe heating system for a 2-story house.
The temperature difference in room radiators in this case is calculated by the formula ∆T_р=∆T⁄P, where P is the number of heating devices connected in series (in this case P=3). A horizontal single-pipe main must carry P times more liquid than through horizontal pipes with a two-pipe distribution. This will require an increase in pump power for its forced circulation and high energy costs, but the hydraulic stability of the circuit will be high.
Advantages and disadvantages
Distributing risers from below means that the pipes through which liquid circulates through heating devices are located at the lowest point of the room: at floor level, under the floor, in basements and basements.
The heating scheme with bottom wiring has several disadvantages. Firstly, the closed water flow does not allow you to turn off one radiator or adjust its operation separately - this is only possible by turning off all devices and the entire pipeline.
This also explains the difficulties when eliminating a leak or repairing a radiator - you have to drain all the coolant. All these problems are solved using bypasses or bypass spare lines.
Single-pipe heating with bottom wiring - we do the system ourselves
A single-pipe heating system means that there is no separation of the coolant pipeline into a supply line and a return line: the liquid from the boiler moves along one ring, after which it returns back to the heating unit. When one-pipe heating systems with bottom wiring are created, the radiators are arranged in series, as shown in the photo. The coolant liquid enters them one by one: first - into the first battery, then into the second, then into the third, etc. As a result, the temperature of the coolant decreases gradually and in the very last device it is colder than at the initial stage.
In a two-pipe system, unlike a one-pipe design, there is both a supply and a return pipeline, which are connected to each other by heating devices similar to jumpers. In this case, the coolant entering each battery has the same temperature.
The principle of operation of the node
Understanding what an elevator is, it is worth noting the need for this complex to connect heating networks and private consumers with its help. The thermal unit is a module that performs the functions of pumping equipment. To see what an elevator is in a heating system, you need to go down into the basement of almost any apartment building. There, among the shut-off valves and pressure meters, you will be able to find the desired element of the heating system (the diagram is shown in the figure below).
When figuring out what an elevator is, it is worth determining its functionality based on the tasks it performs. These include the redistribution of pressure from inside the heating system, while dispensing coolant at an acceptable temperature. In fact, the volume of water doubles, moving along the lines from the boiler room. This effect is achieved in the presence of water in a separate sealed vessel.
The temperature of the coolant coming from the boiler room is usually in the range of 105-150 0 C. It is not possible to use it with this parameter in domestic conditions for safety reasons.
Regulatory documents regulate the limiting temperature value for the coolant, which should be no more than 95 0 C.
For reference. Currently, the issue of reducing the temperature of hot water from 60 0 C, provided for by SanPin, to 50 0 C, is being actively discussed, citing the need to save on resources. As experts note, the consumer will not notice such a minimal difference, and in order to ensure proper disinfection of water in pipes every day, it is recommended to increase it to 70 0 C. It is too early to judge how rational and thoughtful this initiative is. Changes to SanPin have not yet been made.
Returning to the topic of the heating system elevator, we note that it is he who provides the temperature in the system. Thanks to these actions, it is possible to reduce risks:
- With overheated batteries it is easy to get burned;
- Heating radiators are not always able to withstand long-term exposure to elevated coolant temperatures under pressure;
- The wiring of polymer or metal-plastic pipes does not provide for their use with such hot coolants.
Why is this particular node convenient?
Elevator unit in any apartment building
You can hear the opinion that it would be more convenient not to use a heating elevator with this operating principle, but to directly supply water at a lower temperature. However, this opinion is erroneous, because the diameters of the lines will have to be significantly increased to transfer the colder coolant.
VIDEO: Elevator unit of the central heating main
In fact, a competent design of a thermal heating unit allows you to mix into the supply volume of water part of the return volume, which has already cooled down. Although some sources refer to the elevator unit of the heating system as outdated hydraulic equipment, it has proven its effectiveness in operation. More modern devices used instead of the elevator unit circuit are the following types:
- plate heat exchanger;
- mixer with three-way valve.
Elevator operation
Considering the elevator unit of the heating system, what it is and how it works, it is worth noting that the working design is similar to water pumps. However, operation does not require energy transfer from other systems. It shows its reliability under certain conditions.
From the outside, the base part of the device is similar in appearance to a hydraulic tee mounted on the return branch. However, through a standard tee, the coolant would painlessly penetrate into the return line without passing through the radiators. Such behavior would be meaningless.
Standard elevator layout
The classic diagram of the elevator unit of the heating system contains the following components:
- A prechamber, a supply pipe, at the end of which there is a nozzle of a certain diameter. The coolant enters it from the return.
- A diffuser is mounted in the outlet part. It transfers water to consumers.
Today there are units where the diameter of the nozzle is adjusted by an electric drive. This makes it possible to optimize the coolant temperature automatically.
The choice of a unit with an electric drive is based on the fact that it is possible to change the coolant mixing coefficient within 2-5, which is impossible in elevators where the nozzle diameter is not adjustable. Thus, a system with an adjustable nozzle allows significant savings on heating, which is possible in houses where central meters are installed.
How does a thermal unit circuit work?
In general, the operating principle can be described as follows:
- water moves along the line from the boiler room to the entrance to the nozzle;
- during passage along a small diameter, the speed of the working coolant increases significantly;
- an area with a slight vacuum is formed;
- due to the resulting vacuum, water is sucked from the return;
- turbulent flows in a homogeneous mass are sent to the outlet through the diffuser.
You can see everything in more detail on the working diagram.
For efficient operation of the system, which involves the circuit of the elevator unit of the heating system, it is necessary to ensure that the pressure between the supply and return is greater than the value of the calculated hydraulic resistance.
Disadvantages of the system
In addition to positive qualities, a thermal unit or thermal unit diagram has a certain drawback. They are as follows. The heating system elevator does not have the ability to adjust the output temperature mixture. In such a situation, you will need to measure the heated coolant from the main line or from the return pipeline. It will be possible to lower the temperature only by changing the dimensions of the nozzle, which is structurally impossible to do.
In some cases, elevators with electric drives save the day. Their design includes a mechanical drive. This unit is driven by an electric drive. In this way it is possible to vary the diameter of the nozzle. The basic element of this design is the throttle needle, which has a conical shape. It fits into the hole along the inner diameter of the structure. Moving over a certain distance, it manages to adjust the temperature of the mixture precisely by changing the diameter of the nozzle.
Both a manual drive in the form of a handle and a remote-started electric drive can be mounted on the shaft.
Thanks to such modernized solutions, the boiler room in the basement does not undergo significant, expensive re-equipment. It is enough to mount the regulator to get a modern heating unit.
Malfunctions
In most cases, breakdowns are caused by the following factors:
- equipment clogging;
- a gradual increase in the diameter of the nozzle during operation, as a result of which the temperature of the coolant is more difficult to control;
- clogged mud traps;
- breakdown of fittings;
- failure of regulators, etc.
It is not difficult to determine the breakdown of this device; it immediately affects the temperature of the coolant and its sharp drop. In case of minor deviations from the norm, most likely, we are talking about clogging or a slight increase in the diameter of the nozzle. If the difference is very significant (more than 5 degrees), then you need to carry out diagnostics and call a specialist for repairs.
The diameter of the nozzle increases either due to corrosion in contact with water, or as a result of involuntary drilling. Both ultimately lead to an imbalance in the system and must be corrected immediately.
You need to know that modern modernized systems can be operated with electricity consumption metering units. Without this device in the heating circuit, it is difficult to achieve an economical effect. Installing heat and hot water meters can significantly reduce utility bills.
VIDEO: How the unit works
Single-pipe forced circulation heating system: old advantages and new possibilities
Today there is a return of interest from the engineering community to such a heat supply tool as a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation in multi-storey and individual construction. In the early 90s, it was rejected by domestic heating engineers after three decades of uncontested and widespread predominance in buildings of any number of floors and purposes. Traditional, fundamentally uncontrollable single-pipe heating did not fit into the concept of energy-efficient housing, and in the last two decades it has been widely replaced by two-pipe heating. But modern single-pipe designs combine their traditional advantages (hydraulic stability, efficiency) with the ability to regulate heating devices, as in their two-pipe counterparts.
What is a one-pipe heating system and how does it differ from a two-pipe one?
A single-pipe heating system for a private house, like a two-pipe one. includes:
- a boiler that generates thermal energy, which can use different fuels and can be of a variety of designs;
- radiators that directly heat the premises of the house;
- a pipeline through which the coolant fluid circulates, ensuring the transfer of thermal energy from the boiler to the radiators;
- additional equipment that ensures circulation and efficient operation (expansion tank, shut-off and control valves, connecting elements, circulation pump (one or more), safety unit, etc.).
- Saving pipes and connecting elements;
- Less time and labor required for installation work;
- With open pipe routing, the main pipeline is less noticeable in the interior of the rooms.
But if you decide to use a single-pipe system when installing water heating in your home yourself, then you must also take into account its disadvantages:
- Less uniform heating of radiators - as you move away from the boiler, colder coolant will flow into the radiators;
- It may be difficult to regulate the temperature of individual radiators;
- It is more difficult to ensure good natural circulation of the coolant, especially with a long circuit length.
In order to ensure that the shortcomings of a single-pipe system do not affect the efficiency of its operation or at least minimize them, it is necessary to select the most suitable type.
What to choose?
Boiler room in a private house
When choosing the option of a two-pipe heating system, it is based on which boiler will be used to heat the house. If the unit is non-volatile (stove, solid fuel, gas or diesel boiler without automation that requires power), then the heating system must be appropriate - with natural circulation, horizontal layout, top wiring and an open expansion tank.
To increase the efficiency of its operation, it is possible to install a circulation pump, but if the power is turned off, the coolant will continue to move by gravity.
A energy-dependent boiler allows you to choose any option, but in practice, preference is given to a system with a membrane expansion tank, a circulation pump, a horizontal layout and bottom wiring. If the house has two or three floors of a small area, it is more convenient to use a vertical layout.
The procedure for installing single-pipe heating with your own hands
To install a one-pipe heating system with your own hands, prepare the following tools:
- pipe cutting knife;
- soldering iron for polypropylene pipes and fittings;
- key for assembling heating batteries;
- fum tape.
Scheme of a vertical single-pipe heating system with bottom wiring.
To install a single-pipe heating system in a private house with your own hands, you first need to install a boiler, which must be located at a certain depth, but placing it in the basement is highly not recommended. As a rule, a recess in the floor is prepared for installing a heating boiler. Preparing such a recess involves filling it with concrete and, at the request of the owners, decorating it with tiles.
After the boiler is installed, the chimney is installed. The connection between the boiler and the chimney is carried out using a corrugated metal pipe, when choosing which it is necessary to assemble the required diameter. After this, the main pipe is connected to the boiler for the main line. The diameter of this pipe is about 25 mm.
Only metal pipes can be connected to the boiler, since other materials are not able to withstand high heating temperatures. Adapters are prohibited. To stabilize the heat heating process, the expansion tank must be installed at a height of about 3 m. Thus, the expansion tank becomes the highest point of the heating system.
The next stage is the installation of radiators and pipes. In parallel with this, the installation of Mayevsky taps and valves is being carried out. Batteries are installed under window openings
It is important that there is free space between the battery and the window sill, sufficient for the circulation of hot air flows. Pipes are installed straight and without bends
The presence of bends will impede the normal circulation of the coolant and reduce the efficiency of the heating system. This is especially important for single-pipe systems.
The end of the pipes of the home heating system is attached to the reverse side of the heating boiler circuit. To prevent unnecessary and excess materials and impurities from entering the boiler, a special metal filter is installed on it.
When installing a heating system, it is necessary to carry out work on constructing a unit that will perform the function of filling the heating system with water; if necessary, water can be drained through it.
The single-pipe heating installation is complete. After completing all installation work, it is necessary to check the serviceability and correct operation of the boiler. To do this, the boiler is filled with water and turned on.
Advantages and disadvantages
| Two-pipe heating | Single pipe heating | |
| Complexity of design and installation | Complex design and connection scheme. | Easier and simpler. Less time is spent on work. |
| It is easy to eliminate defects made at the design stage. | The difficulty is in calculating the thermal and hydraulic parameters of the network, as well as eliminating errors made during the development of the project. | |
| Restrictions on the number of floors of buildings | No. | No. |
| Contour length restrictions | There are no restrictions on the length of the contour. It is possible to insert additional batteries into an already assembled line. | The number of radiators on one riser is limited. |
| Material consumption | Double pipe flow. | Installing only one line allows you to save on the amount of pipe material. |
| Despite the increased consumption of pipe material, in general the costs are not much higher than an alternative single-pipe complex. The 2-pipe system uses smaller diameter pipes, which are much cheaper. | ||
| Automatic system balancing | Possibility of installing a thermostatic head on each radiator to maintain a constant temperature of the coolant. | Installation of a special bypass with a needle or three-way valve on each battery. |
| Compared to a thermostatic head, the cost of a bypass is at least 5 times higher. This negates all budget savings from installing single-pipe heating. | ||
| Possibility of radiator repair without stopping the entire heating system | All network elements operate independently of each other. Installation of ball valves at the inlet and outlet of each heating device allows for repair work to be carried out while the heating is running. | Since all elements of the system are interconnected, a malfunction of one of its sections leads to blocking of the entire circuit. |
| Uniform heating of heating devices | The flow of water into the radiators directly from the boiler ensures a uniform temperature throughout the entire circuit. | The passage of water sequentially through all the batteries leads to the fact that the maximum temperature is concentrated on the first radiator in the network, each subsequent one heats up less and less. This is the reason for the high heat loss coefficient. |
Summarize:
- firstly, a 2-pipe system is actually not much more expensive than a single-circuit system.
- secondly, it minimizes heat loss during operation.
- thirdly, the two-pipe concept allows significant savings in water and energy in the future.
Features of a single-pipe heating system
The single-pipe heating system has gained wide popularity in private construction due to the following advantages:
- Hydraulic stability - replacing the radiator, increasing sections, turning off individual circuits does not change the heat transfer of other elements of the system;
- Minimum number of pipes;
- A smaller amount of coolant in the system reduces its inertia and the time it takes to warm up the room;
- Aesthetic appearance, especially when installing a hidden highway;
- Easy installation;
- When using modern shut-off valves, precise control of the operating mode of the entire system and individual elements is possible;
- Serial connection of heating devices allows you to install water heated floors, install heated towel rails, etc.
- Inexpensive installation and operation.
The thermostat on the radiator assembly allows you to regulate the heating temperature of the battery
The main disadvantage of single-pipe heat supply is the imbalance of heating of devices along the length of the main line. The further the radiator is from the boiler, the less it heats up. Under the action of the pump, the radiators are heated more evenly, but cooling of the coolant is still observed, especially if the pipeline is of sufficient length. The negative effect of this phenomenon is reduced in two ways:
- They increase the number of sections of the last radiators, due to which their power and the amount of heat released into the room increase - uniform heating of the rooms is achieved;
- They rationally design the passage of the highway through the rooms - they start with bedrooms, children's and “cold” rooms (corner, with windows to the north), then go to the living room, kitchen, bathroom, toilet and end with utility rooms.
Installation recommendations
If the work of assembling the system will be carried out with his own hands, then the master will need a step-by-step description of the installation process.
It is important to follow these rules:
- it is required to equip 2 circuits: for hot and cold water;
- pipes must be laid with a slight slope directed towards the last radiator;
- both contours are laid parallel to each other;
- to prevent heat loss in the main riser, it is better to wrap it with an insulator;
- installation of a container to collect excess water is carried out at the highest point;
- the dimensions of the pipes and connecting parts must match;
- all parts of the system are made of the same material.
The sequence of work is as follows:
- Diverting the main riser from the boiler. An expansion tank is installed here.
- Dividing supply pipes.
- Simultaneous laying of a pipe through which cold liquid is supplied to the boiler.
- Fixing the pump.
- Attaching batteries or radiators.
Before refueling 2-pipe heating systems, you need to carefully inspect whether all connections are securely tightened.
Disadvantages of a single-pipe heating system
Along with the advantages, such a system has disadvantages:
1. Requirements for the diameters of the main pipeline.
2. In the first radiators, the coolant temperature is the highest, and in subsequent radiators it is lower and lower due to the constant admixture of coolant from the radiators passed through to the main flow.
3. From the second point it follows that the last radiators need to be made of a larger area than the first ones, otherwise they will be much colder.
4. And in general, with such a connection, you should not “plant” more than 10 radiators on one branch, since uniform heating will not work. Conclusion: “Leningrad women” “live” better in small houses.
I assume the single-pipe heating system is sufficiently lit. There are a couple more good radiator installation schemes that relate to two-pipe systems. This is a radial (collector) heating system and the Tichelman scheme. Read about them in the following articles.
single pipe heating system
2013-2017 Copyright Use of site materials is permitted with reference to vodotopim.ru
Features of connecting single-pipe heating in a two-story house
In two-story houses, natural air circulation, which is the rise of warm air to the 2nd floor and the flow of cooler air to the 1st floor, is especially pronounced and can create noticeable discomfort. To maintain approximately equal temperatures on different floors of the house, you need to carefully consider the order of connecting radiators and the number of sections in them.
You can, of course, solve this issue more simply: block the connection between the floors of the house with a door on the flight of stairs. However, this can ruin the interior of the house, although such a DIY solution to the problem is quite common.
Scheme of one-pipe and two-pipe heating.
There is 2 options for uniform heat distribution throughout a two-story house, called forced ventilation. However, it cannot be taken seriously, because at the first power failure, the discomfort will return, and such a system will be quite expensive to install and operate.
In order for the temperatures on the floors of the house to be equal or at least become closer, on the 2nd floor, instead of heating radiators, you can install a water heated floor system made of metal-plastic pipes with a diameter of 20 mm.
It is almost impossible to solve the issue of equally comfortable heating of 2 floors, especially with your own hands, but a thoughtful layout of the house and installation of an autonomous heating system will allow you to reduce the difference in conditions. Moreover, a single-pipe heating system is best suited for heating a two-story building.
Types of heating systems
The heating system differs in the following components: the fuel used, the type of coolant, the type of circulation.
Let's take a closer look at each:
Fuel used
The following types of coolants are used: gas, solid fuel, liquid fuel, electricity and geothermal source. Installing heating in cottages for boilers that require burning liquid fuel is done very rarely. Often when other sources of fuel are unavailable and it costs a lot of money to bring them. Electric heating devices are easy to install and easy to use. However, the cost of the heat produced is more expensive than when burning solid fuel or gas.
Type of coolant
According to this criterion, coolants for heating buildings are: gas, water, steam, electric and air. In Russia, heating schemes using heat-conducting liquids are considered common. Then come gas and electric types. Steam is used only in industrial companies, and air heating installation is used in the southern regions.
Type of circulation
Heated water in a pipe system can move in two ways: natural and forced. The main advantage of the first type is its independence from the supplied electricity. In them, a heat-conducting liquid moves through pipes due to its ability to rise to the top when heated, and when it cools, it goes down. However, the lack of stability in operation, the need to use an increased diameter of pipes, the difficulty of adjusting the temperature and the use of batteries with a considerable volume inside, leads to their infrequent choice by users.
The movement of thermal fluid by a forced system occurs due to the action of electrically driven circulation pumps. This helps to greatly increase the comfort of use, reliability, and reduce the costs required for their operation.
General provisions
Excessive reinforcing items affect the quality of the heating system and cause its elements to wear out faster. Loose pipes and connections (without clamps or clamps) last much longer. This must be taken into account when connecting batteries to the system.
It is also necessary to take into account that the entire heating system must be made of the same material: polypropylene, metal (of the same brand).
Connecting a single-pipe heating system is suitable for small cottages and apartments.
This closed system (see diagram) will heat a room in which no more than 10 radiators can be placed. The remaining heating devices will not make sense (even a large surface area), since as the distance increases, cooled water will simply reach them through the pipes.
Single-pipe systems are simple both in design and installation. They are more cost-effective and low-cost.
Connecting a heating radiator to a two-pipe system Connecting aluminum radiators Connecting an electric boiler to a heating system Scheme and steps for connecting a gas heating boiler to a heating system
Principles of calculation
In order not to make mistakes when calculating heating, you need to first draw a diagram on paper. All components of the structure are indicated on it
It is important to understand how much fluid flows through all the nodes separately, at what speed it moves, how the operation of the entire system changes as a result of changes in the functionality of its individual elements
During the calculation, you should not miss the hydrodynamic resistance of water as it moves, which affects the pressure inside the system and pressure.
To carry out the procedure, special tables and formulas are used. Correct calculation will avoid problems with the functionality of the heating structure in the future. Date: September 25, 2022
Single-pipe heating scheme - what to consider
In one- and two-story houses it is possible to use both vertical and horizontal single-pipe heating systems.
At the same time, for overhead wiring you need an attic space, which is not always convenient. As a rule, the movement of coolant in the heating system is natural. In order to increase the circulation rate of the coolant, a pump is included in the system.
A simple one-pipe heating circuit: 1 - boiler; 2 - main riser; 3 - expansion pipe; 4 — return risers; 5 - upper wiring; 6 — air collector; 7 — expansion tank; 8 - circulation pump; 9 - return line.
Control and shut-off valves are needed to shut off the emergency area when performing preventive and repair work, redistribute the coolant flow, and replace a broken element. It's practical, fast and very convenient. Mandatory conditions, without which it will not be possible to make a correct one-pipe heating system: layout of system elements for a specific room, location of pipe junction, connection to a heating boiler; locations of the expansion tank, installation of radiators, shut-off valves and pumps; drain taps, etc.
Depending on the area of the house, various options for installing a heating system are selected. For private houses with an area of up to 150 m², it will be sufficient to install a heating system in which antifreeze or water circulates naturally. Due to the difference in coolant density in different sections of the batteries, such a system, the diagram of which is shown in IMAGE 2, will work in a balanced manner.
If the area of the house exceeds 150 m², then you need to use a forced circulation system. For this, a water pump of suitable power is installed.
In any case, radiators must be additionally equipped with taps (valves), the installation of which will make it possible to shut off the water supply at a specific section of the pipeline at the required time. This is necessary to isolate a certain area during repair work and maintain heating of other rooms. At the same time, the remaining rooms in the building will be heated as usual.
Significant advantages of beam distribution
The main task of the heating system is to replace the heat that the building loses due to differences between the internal and external air temperatures, as well as due to the varying degrees of thermal conductivity of the external walls. Its solution largely depends on a well-chosen layout of the pipes delivering the coolant to the devices.
In practice, you can connect all heating devices together using the following methods:
- tee connection;
- radial (collector) connection, when a separate pair of pipes is supplied to each heating device using a collector for direct and reverse supply of coolant.
The tee or perimeter type of pipe connection is cheaper. But due to the fact that the devices are connected to each other and connected by a pipeline to a single riser, the system will need to be completely disconnected and freed from coolant to repair a separate radiator or section. Or equip it with bypasses and shut-off valves, which will significantly increase the cost of organizing heating.
With traditional perimeter wiring, the entire pipeline is most often installed in an open way, less often in a hidden way. Radiant heating systems are mainly installed in walls or floors, because... a large number of pipes laid on top of structures negatively affects the interior.
Concealed installation is carried out by a system of underfloor heating pipes, which, in accordance with the technological specifics, is arranged according to a radial scheme. The radial pipeline to the heating devices is also laid in a hidden way in the floor screed, because this is better for technological and architectural reasons.
Assembling a pipeline using a radial scheme will cost significantly more than installing a system using a perimeter method. However, due to the specifics of such wiring, the heated coolant is supplied to all points simultaneously
A large number of pipes when using the beam method of pipeline assembly can ruin the interior. Therefore, all heating communications are laid in the floor or walls.
All connections remain on the surface, so there is virtually no risk of leakage under the screed. This cannot be done with a tee system, because If the connections wear out, you will have to break the walls and floor.
In order to reduce pipe consumption, pipelines assembled according to a radial scheme are laid not along the perimeter, but along the shortest paths - from the collector to the device
The main disadvantage of collector wiring is its high material consumption, which is due to its large length. For normal operation, technical devices are required, because These are purely coercive schemes. And the main advantage is that you can set different temperatures in each room, creating a comfortable microclimate in any room.
Each radiator or convector is connected independently, which is also convenient for carrying out maintenance work and replacing worn-out system elements without having to turn off the heating in the entire house or apartment.
Hidden installation allows you to significantly improve the visual appearance of any room, leaving only the heating radiators visible
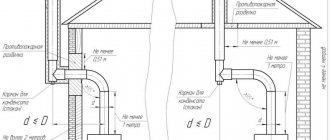
Limitations of a two-pipe heating scheme with lower wiring
Two-pipe heating systems with natural circulation of coolants and bottom wiring have serious limitations and therefore are rarely implemented. The fact is that almost all batteries in such a circuit are finite and require drains. And since the design solution also includes an open-type expansion tank communicating with the external environment, residents will have to bleed air every day.
Overhead lines looping supply lines practically eliminate this problem, but in the end the system turns out to be even more complex and cumbersome to implement.
Two-pipe heating with bottom wiring, in terms of the number of pipes required for installation, is not inferior to a design with an upper wiring option. If preference is given to the second method, then the main advantage of the lower location of the pipes is lost, which is the absence of the pipeline in sight.
Installation of overhead lines requires that risers are located in the room, starting from the floor to the ceiling. And in this case, the whole point of the lower wiring is lost.
Horizontal and vertical wiring types
The horizontal and vertical wiring options differ in the position of the main risers and pipelines, which are combined into a single heating system.
Vertical design means that radiators are connected to risers located vertically. Installation of such wiring is more expensive than horizontal wiring (read: “How a horizontal heating system works - types, differences in wiring”). Its advantage is that there are no air pockets. It is better to install a vertical system when arranging heat supply for multi-storey buildings. Connection to the riser is carried out floor by floor.
It is advisable to install a two-pipe horizontal heating system with a bottom pipe routing method:
- in buildings of great length, but low number of storeys;
- in residential premises that do not have walls;
- in panel-frame buildings.
When implementing a two-pipe design, heat is saved. Horizontal wiring is done mainly in one- and two-story buildings - you can also design a collector heating circuit.
Positive aspects of a two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring
Heating diagram for a private house.
Thanks to this design of the system, it becomes possible to regulate the temperature inside each individual room, without affecting any other elements that make up the heating system. Moreover, this configuration is also an excellent way to save on the purchase of a low-power pump, thanks to which the process of liquid circulation starts in the pipes. This happens because pressure losses in the pipes, when installing this type of heating, are reduced to a minimum, and sometimes, in warmer periods, completely disappear. The hydraulic resistance of a heating system with two pipes connected is also several times less than with a series one-pipe version. Therefore, inside the house with peace of mind it will be possible to install pipes of small diameters, which will significantly improve the appearance of the heated room, because large pipes and radiators located in the most prominent places in the room look very rude and unaesthetic.
The next important advantage is the ability to disconnect and replace one of the radiators, which for any reason has failed. After all, even if one component of the system breaks down, it continues to function normally. Whereas sequential heating systems completely fail in such situations. After all, with a two-pipe heat distribution, shut-off valves are installed on the supply pipe, right next to the radiators, which can be turned off if an urgent need arises.
Other undoubtedly positive features of a heating system with bottom wiring include:
- small heat losses, since the main line is routed through the basement or underground space;
- the ability to function in those rooms where only the lower floors are equipped;
- the fact that not a single element of the shut-off valves on the supply and return risers remains visible, since they are easy to install in the same basement.
The disadvantages of this type of wiring include the fact that low liquid pressure is constantly maintained in the supply risers, as a result of which the flow level of the coolant used is also reduced.
Moreover, with such an organization of the heating system, there remains a constant need to bleed air from the system manually. However, you can additionally organize an air pipe, but this will complicate an already complex system, making it also expensive.
Materials and components
Polymer pipes and fittings for them
The type and quantity of materials, components and equipment for a two-pipe heating system are determined at the design stage.
To install a two-pipe heating system, you must purchase:
- boiler
- radiators
- expansion tank
- pipes
- fitting
- sweeps
- air vents
- emergency valve
- circulation pump (optional)
Criterias of choice
The boiler is selected taking into account the availability and cost of fuel, the design power of the system, and the requirements for the level of automation. The most popular are gas and solid fuel boilers.
Types of radiators
Radiators on the market are made from:
- cast iron
- aluminum
- become
- copper
- combinations of steel (pipe) and aluminum (fins)
When choosing a radiator, pay attention to the technical characteristics, durability and reliability of the device, ease of installation, design, and connection principle. For example, due to the inertia of cast iron batteries, there is no point in installing thermostats on them to regulate the microclimate. Steel and bimetallic radiators are prone to corrosion, and they are best used as part of closed-type heating systems.
Polypropylene pipes
The following pipes are used to lay the pipeline:
- steel (from ordinary or alloyed stainless steel)
- copper
- polypropylene , reinforced with fiberglass or aluminum foil
- made of cross-linked polyethylene
- metal-plastic
When choosing, take into account durability, corrosion resistance, suitability for hidden installation (under screed), and cost. Installation of polymer pipes can be done independently, but laying a metal pipeline requires skill in working with a welding machine (for fastening steel elements) or a device for soldering copper. The fittings must match the pipes.
Connection methods
Radiators can be connected to pipes in different ways, depending on the installation location and the route of pipes in the room and, of course, the heating scheme:
When the connection method is selected (see diagram), you must:
- Wipe all joints and pipes with sandpaper and degrease them.
- Secure the radiator. This can be a temporary fixation or an installation one, depending on the complexity of the arrangement of the heating system pipes according to your scheme.
- We screw in the adapters, which, by turning, can be adjusted to the direction of the pipes to which the elements are connected. If, for example, they are located on the floor, then the adapter is screwed down with a thread; if the pipes go deep into the room, then the direction of the adapter changes. So the main thing is to look carefully at the layout of a single-pipe heating system.
- Adapters for pipes, preferably made of domestically produced polypropylene, as experts advise, are attached to the main pipe using a soldering iron.
- We install the tap on top and the plug on the bottom, as shown in the diagram, or vice versa.
Circulation
The upward movement of the coolant is ensured by a special pump; the water moves downward independently, that is, without the help of any units under the weight of its own weight.
You don’t have to use a circulation pump, but you will have to install pipes with a larger diameter.
One-pipe system design options
The water heating main is necessarily equipped with an expansion tank that equalizes the pressure. It accepts excess coolant during expansion and returns it to the pipeline when cooling, preventing pressure surges. There are two fundamentally different types of expansion tanks - open and closed. The type of heating system will depend on which of them will be built into the main line.
Open heating system
An open heating system involves direct contact of the coolant with the atmosphere. Used for non-volatile or combined heating installations. An open expansion tank is a cylindrical or rectangular container, partially or completely open. At a certain level, a drain is performed to drain excess liquid into the street or into the sewer.
In the scheme of an open heating system with forced circulation, the expansion tank is included directly after the boiler, the outlet is arranged at the highest point of the line. The tank itself should be located above all connected devices, so the tank is often placed in the attic. In this case, it must be insulated at subzero temperatures.
Due to the contact of the coolant and air in the tank, the hot water is saturated with oxygen and its natural evaporation occurs. This implies the limitations and disadvantages of such a scheme:
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the coolant level in the tank and replenish it on time;
- It is necessary to observe pipeline slopes (5-7 degrees) so that the air released in the pipeline is vented into the expansion tank and the atmosphere;
- Antifreeze cannot be used instead of water, as it releases toxic substances when evaporated;
- The presence of oxygen in the coolant reduces the service life of heating devices with steel parts.
Attention! The absence of slopes when installing a pipeline for an open heating system will lead to airing of the line. However, open heating also has its advantages:
However, open heating also has its advantages:
- There is no need to monitor the pressure in the line;
- You can even replenish the coolant with a bucket, simply adding it to the expansion tank to the required level;
- Even if there are small leaks, the system will function properly - as long as there is a sufficient amount of water in the pipeline.
Scheme of an open type heating system with forced circulation
Closed heating system
The scheme of a closed heating system with forced circulation is currently the most widespread. It is a closed hydraulic line, completely closed from air access.
A closed water heating system involves the use of a membrane-type expansion tank. It is a sealed cylindrical metal case, the internal cavity of which is divided by a membrane. One part is filled with air, and the second part is squeezed out of the line with water, the volume of which increases when heated.
You can install a membrane expansion tank anywhere in the main line, but for ease of maintenance it is connected to the “return” - next to the boiler.
A feature of the closed circuit is the presence of slight excess pressure in the line. Therefore, a closed highway must contain a security group. This unit is installed on the pipeline leaving the boiler (supply) without shut-off valves. Contains a pressure gauge, an air vent and a safety valve for releasing water in emergency mode.
Important! A security group must be included in the closed system scheme
- The coolant under pressure warms up faster;
- The possibility of airing the heating main is virtually eliminated;
- Filling with antifreeze is possible, since the coolant does not evaporate and is not saturated with oxygen (relevant for buildings of periodic use);
- Ease of maintenance – all devices that ensure the operation, control and safety of the system are installed in one place;
- Using modern equipment, it is possible to make a closed heating system fully automated and integrate it with smart home programs.
Disadvantage: energy dependence. The solution is to purchase an autonomous generator.
Scheme of a closed type heating system with forced circulation
Selecting a heating boiler
Water heating using a single-circuit scheme involves running one pipe, and such a small load can be supported by any type of boiler - electric, gas, solid or liquid fuel, combined unit. Therefore, the choice of boiler most often depends on the availability of a particular type of fuel in a particular region.
Without gas supplied from a central gas pipeline, it will be easier and cheaper to heat a private house using solid fuel - wood, coal, pellets.
An electric heating boiler is a last resort, provided there is no gas or space to store a large volume of firewood or coal.
We are not yet considering geothermal boilers and solar power sources due to their rare use and high cost of acquisition and installation.
Having chosen a boiler, you need to decide on its thermal power. The standard calculation formula is that for 10 m2 of heated area you need to spend 1 kW of thermal energy. Then everything is simple: to calculate the total power of the boiler, you need to multiply the length and width of the building, divide the result by 10, multiply the new result by 1 kW.
Example: with house dimensions of 9 x 12 meters, the boiler’s thermal power is obtained as follows: ((12 x 9) / 10) x 1 kW = 10.8 kW. But these are not final figures: add up to a 20% reserve to our 10.8 kW, when the heating boiler at home is forced to operate for a long time at full power - at low temperatures or in an attached room, which was not previously included in power calculations. The end result is -12-14 kW.