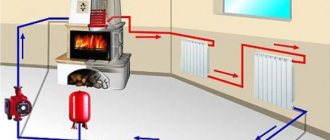
Such a pump is used as part of a heating system to ensure forced circulation of the coolant. The device runs on electricity and consumes little energy - from 60 to 100 watts, which is comparable to a regular household light bulb.
Unfortunately, if the power supply to a private home is interrupted from time to time, then the operation of the pump will be inconsistent, which will lead to disruption of the movement of fluid through the pipes. Before installing the pump, it is recommended to think in advance about how to make the water circulation in the circuit constant.
Application cases
A heating system equipped with a pump for forced pumping of coolant is appropriate in cases where the liquid cannot overcome hydraulic resistance and therefore does not rise up through the pipes. In heating systems with natural circulation of water, the slope and diameter of the pipes must be strictly observed, and the slightest mistake will damage the entire complex.
This limits the use of the system to compact rooms: after all, the larger the heated area, the longer the circuit, and, accordingly, the weaker the water flow. Even when using a powerful boiler, the coolant pressure rarely exceeds 0.6 MPa. And changing the pipe wiring to improve fluid flow will be expensive.
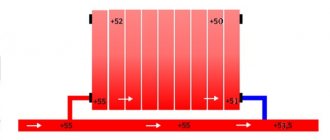
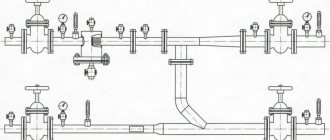
Connection diagrams for heating devices
Rice. 16. Some diagrams for connecting heating devices
Rice. 17. Wiring for radiators of the heating system
Rice. 18. Wiring diagram for a cast iron radiator
Rice. 19. Installation diagram of cast iron radiators
Advantages
A system equipped with a circulation pump does not have these disadvantages. It is perfect for heating rooms ranging from 200 to 800 m2. Its advantages include:
- no requirements for the configuration of the heating circuit - for coolant circulation there is no need to create narrow places in the pipeline, install pipes at an angle and use other technical techniques;
- rapid acceleration of the liquid - circulation of heated water in the circuit begins immediately after turning on the pump. As a result, the rooms of a private house warm up to the desired temperature in just a few minutes;
- high efficiency - thanks to the rapid circulation of the coolant, heat losses are reduced. The problem is solved when one of the rooms warms up more than the others. Due to this, fuel is consumed more economically;
- reliability of operation - the simple design of the pump eliminates the occurrence of accidental breakdowns.
It is worth noting that difficulties can only arise during power outages, but they are not difficult to deal with: if the house has an electric generator, the heating system can operate continuously.
If you plan to equip a system with natural circulation with a pump, its design remains virtually unchanged.
All you need to do is install the pump itself, and also move the expansion tank from the water supply circuit to the circuit through which it returns to the boiler.
Features of installing a pump in a system with natural coolant circulation
In order to ensure the operation of the heating during a power outage, it is necessary to create a minimum hydraulic resistance in all sections of the circuit.
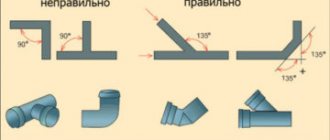
The normal movement of the thermal agent is hampered by any turns and height differences in the pipeline, the resistance of shut-off equipment and a decrease in the cross-section of the pipeline.
Therefore, when installing the circulation pump, the following requirements are observed:
- the insertion is performed without opening the main circuit, in parallel to it. The required pipeline diameter must be at least 32 mm, and the cross-section of the pipes for connecting the pump must be a quarter smaller;
- Shut-off valves are installed before and after the pump so that if the equipment malfunctions, it can be dismantled without the need to discharge the coolant;
- In the area between the pump taps, a ball valve is mounted, which is closed during the forced supply of coolant. Otherwise, it will circulate in a small circle between the pump insertion points.
A check valve installed instead of a ball valve will help automate the switching process in the absence of electricity.
The so-called bypass will be closed until the pump turns off and the pressure in front of the valve does not exceed the force of the operating spring.
The disadvantage of spring check valves is the additional resistance to fluid flow, so the best solution would be to install a ball-type device.
"Dry" and "wet" pumps
There are two main types of pumps: “dry” and “wet”. The first are designed so that the rotor does not interact with the coolant. They have a high efficiency of 80%, but are quite noisy and prone to breakdowns. One of the most common malfunctions of “dry” pumps is damage to the sealing rings, which results in the leakage of the device.
In systems equipped with a “wet” pump, this problem is eliminated. They are easier to operate and do not require careful maintenance. On the other hand, a “wet” pump has an efficiency of less than 50%, and since there must always be water inside it, you have to carefully monitor the horizontal position of the shaft. For use in heating a private home, a “wet” pump is convenient because it is practically silent. The rotor speed switching mechanism is stepless.
Given their low power, wet pumps are suitable for short pipelines. “Dry” ones, on the contrary, are better used for heating large areas. In addition, the latter are rarely installed in private homes due to noise during operation, and if there are plans to install them, then this is done in a pre-prepared place with sound insulation.
Manufacturer's choice
In this important matter, it is still worth paying attention to those companies that have been operating in this market for a long time and have a strong reputation. Experts advise paying attention to brands such as WILO , DAB , Pedrollo and others. As a rule, fully automated assembly takes place at manufacturing plants, which guarantees product quality. Many models have an electronically commutated motor and a built-in power regulator that monitors the water circulation in the system and the ambient temperature. It can be used to make additional adjustments. In addition, it should be noted that many modern pumps are connected to the automation of the heating boiler, which avoids unnecessary losses.
Power determination
When choosing a pump, you need to consider factors such as:
- power of heating radiators;
- coolant movement speed;
- total pipeline length;
- flow section of pipelines;
- boiler power.
Each of these parameters is easy to calculate if you know at least one of them. So, based on the power of the radiators, you can set the boiler power and water consumption. Having determined the water flow, it will not be difficult to find the diameter of the pipes. It is necessary to determine in advance the speed of movement of the coolant in the system circuit: optimally - 1.5 m/sec. Knowing the required circulation speed, pipe diameter and other parameters, it will be possible to calculate the pressure force and power of the pump.
Calculations
To more accurately determine the pump power, you can use the rule of 1 kW of power per 1 liter of pumped water. Thus, a 25 kW pump can circulate a maximum of 25 liters of coolant.
Sometimes a simplified selection scheme is used, based on the area of the heated room:
- to heat buildings with an area of up to 250 m2, buy a pump with a capacity of 3.5 cubic meters of water per hour and a pressure force of 0.4 atmospheres;
- from 250 to 350 m2 - with a capacity of 4.5 cubic meters per hour and a pressure force of 0.6 atmospheres;
- from 350 m2 - with a capacity of 11 cubic meters per hour and a pressure force of 0.8 atmospheres.
Despite the high performance characteristics of some models, the pumps are not suitable for driving water through a system with artificial circulation in buildings with a total area of more than 800 m2.
European calculation method
When choosing equipment, you can use another method - standard housing improvement projects developed in the European Union. So, per 1 m2 of space there should be a pump power of 97 Watt, provided that the air temperature outside is 25C° (minus), or 101 Watt if the temperature drops to 30C° (minus).
This norm applies to buildings with a height of three floors or more. When arranging a private house up to two floors high, the pump power per 1 m2 of area should be 173 Watts at street temperatures up to 25C° below zero and 177 Watts – below 25C°.
Main classification
There are quite a few types of pumps, but the main difference is which rotor is used:
- wet;
- dry.
In “wet” mode, the rotor is separated from the stator by a special stainless steel glass. The shaft can be either metal or ceramic. The flowing liquid not only lubricates the parts, but also cools the engine.
Pumps with a “dry” rotor are used mainly for large volumes of water; some models are installed inside pipelines. Pump costs are calculated using the formula: Q=N/(t2-t1), where N is the power of the boiler or dispenser, and t2-t1 is the temperature of the water at the outlet and inlet. According to European standards, per 1 sq. m of house area requires 100 W; in Russia this figure must be looked at by region.
Carrying out installation work
Heating systems equipped with a pump can be either single-pipe or double-pipe. Any scheme involves installing the device on a pipe through which the cooled coolant is returned to the boiler. This is explained by the fact that the rubber cuffs and seals of the pump, when heated by hot water, change their consumer properties and quickly wear out. In the return circuit, the water is cooled and does not harm the equipment.
If you are designing a system with forced circulation from scratch, it is better to immediately buy pipes of small diameter in order to save money. This will not affect the quality of heating in any way, but will make the operation of the equipment cheaper.
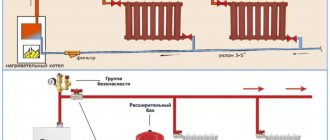
Expansion tank
An important element of the circuit is the expansion tank. It is connected to the return circuit and serves as a reference point: here the pressure force changes its sign - in the circuit up to the tank it is pumped, pushing water through the pipes, and after that it is rarefied, so that the pump sucks in the liquid. You need to remember the rule: when the pump is turned on, the hydrostatic pressure at any point in the suction zone must remain high - then the water circulation will not be disrupted.
An expansion tank is also needed to compensate for the lack of space in a closed system when the coolant expands - water turns into steam and increases its volume. If it were not for the tank, then when the water overheated it would be released. In addition, to avoid overheating and other problems, it is recommended to install only modern automated boilers.
Pump installation
It is better to install the pump at home in a horizontal position: this way the equipment will produce less noise.
The pump is fastened to threaded connections; shut-off valves are inserted into the circuit - one valve on a straight section of the pipe, one on the outlet directly in front of the pump, and one more on the outlet behind it. This is necessary in order to cut off the pump from the coolant if necessary.
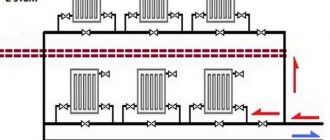
Bottom or top wiring?
A device with bottom wiring is mounted so that the inlet and outlet pipelines are installed below the radiators. The system provides a slight slope to combat air locks. For the same purpose, the structure is equipped with Mayevsky cranes. A certain advantage that lower wiring provides is the introduction of heating into operation in stages, as floors are erected. Which can be very important in individual construction.
Designs with bottom wiring involve placing the boiler and lines below the level of the radiators, which allows gradual commissioning of the heating system
Upper wiring involves placing the supply pipeline above the heating appliances. Most often it is mounted in the attic or in the inter-ceiling space. The coolant rises upward and from there is distributed throughout the rooms. In this case, the return pipeline is always installed below the radiator. An expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the structure, which performs its functions and is responsible for eliminating the possibility of air pockets. The system is not suitable for buildings with flat roofs.
The basic principles of designing heating wiring with diagrams are presented in the following material:
Where to put
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but on the supply or return pipeline it doesn’t matter. Modern units are made from materials that can withstand temperatures up to 100-115°C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, so considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you feel safer, put it in the return line.
Can be installed in the return or direct pipeline after/before the boiler up to the first branch
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system; it makes absolutely no difference whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch. What matters is the correct installation, in terms of strapping, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point regarding the installation location. If the heating system has two separate branches - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floor - it makes sense to install a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule remains on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal conditions in each part of the house independently of the other, and also in two-story houses to save on heating. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of movement of the coolant is set much lower, and this allows you to burn less fuel, without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump; systems with natural circulation work, but in this mode they have lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is installed into it. This gives high heating efficiency and reliability. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems is different.
All heating systems with heated floors are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
Forced circulation
Since a forced circulation heating system without a pump is inoperative, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They can jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a mesh dirt filter must be placed in front of the unit.
Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also advisable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps and remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
Natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not working. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed the entire time the pumping is running. In this mode, the system operates as forced.
Installation diagram of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When the electricity goes out or the unit fails, the valve on the jumper is opened, the valve leading to the pump is closed, and the system operates as a gravity system.
Installation features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require rework: it is necessary to rotate the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating which direction the coolant should flow. This is how you turn the unit so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, just when selecting a model, make sure that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (pressure created) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
Turnkey heating connection in country houses
Turnkey heating connection in country houses is the most convenient option - you don’t have to delve into the intricacies of designing, installing and launching the system - everything will be done by professionals. Another advantage of connecting heating on a turnkey basis is the guarantee that is provided for the work of the craftsmen.
Note that in the absence of experience, when connecting a heating system yourself, more materials are wasted, because certain areas have to be redone, and the materials themselves are not used optimally.
If you want to order a turnkey heating connection, just fill out the form and our specialists will quickly and with a quality guarantee arrange the heating of your home.