Sometimes residents of the private sector make a very serious mistake when they install autonomous heating with aluminum radiators and do not think about the fact that in such cases ordinary water is not suitable as a coolant.
In addition, such a liquid is not the only one of its kind - there are different options and you cannot do without it, because ordinary water with its salts and alkalis will destroy aluminum, and this, of course, will not suit you, so in any case you need look for a way out.
Aluminum radiators
We will now tell you about the different types of this drug, the conditions for its use, and also invite you to watch the video in this article.
Types and features of antifreeze
The heating system uses a special antifreeze that is safe for rubber parts and metal.
Antifreeze is classified according to the type of base:
- propylene glycol;
- ethylene glycol;
- solutions based on alcohol and glycerin.
The varieties differ from each other in physical and technical characteristics. When choosing one of them, you should take into account the features of the heating system and the conditions in which it operates. Special compounds are produced to fill the systems. Automotive antifreezes, such as antifreeze, are not suitable for heating. They contain a lot of toxic substances and negatively affect the rubber and metal elements of the highway; they last 1, maximum 2 years.
Propylene glycol
The main positive property of the propylene glycol composition is harmlessness. It is non-toxic and can be used in open heating systems and double-circuit boilers where water is heated for water supply. Even if propylene glycol leaks into water, significant harm to health will not occur.
Antifreeze based on propylene glycol is not toxic and decomposes faster in the environment
The technical properties of propylene glycol antifreeze are also good. They do not have an aggressive effect on the inner surface of the system elements.
There are also disadvantages:
- high viscosity, which is twice the viscosity of ethylene glycol;
- interaction with zinc: a reaction occurs with the formation of white insoluble flakes, the metal is destroyed;
- high price.
It is easy to distinguish propylene glycol coolant from ethylene glycol: the first is colored green and is often labeled ECO. Instead of propylene glycol antifreeze, you can purchase counterfeit glycerin.
Ethylene glycol
After use, ethylene glycol must be disposed of in a special way, since the substance is toxic.
Ethylene glycol compounds are highly toxic. This is their main drawback. The danger of ethylene glycol is indicated by the red or yellow color of the liquid. Thanks to the bright color, it is easier to detect coolant leaks. It may be harmful if it comes into contact with the lungs or skin. The lethal concentration when ingested is 2 mg per 1 kg of weight. In this regard, the disposal of this type of antifreeze poses a certain problem. For safety reasons, ethylene glycol coolant is used only in single-circuit systems where there is no risk of it entering the water supply circuit. The technical properties of ethylene glycol allow the use of liquids based on it at temperatures down to –65°C.
In some countries, ethylene glycol coolant is prohibited for use.
Solutions based on alcohol and glycerin
Glycerin compounds are diluted with alcohol to eliminate viscosity.
There is a mixed opinion regarding glycerin coolants. Some say that glycerin is the best household antifreeze for the heating system, others point out its many disadvantages:
- high viscosity of the substance, which accelerates equipment wear - to compensate for the high viscosity of glycerin, the composition is diluted with alcohol;
- higher density compared to other antifreezes;
- transformation into poison at temperatures above 90°C;
- risk of foaming;
- relatively low heat capacity;
- chemical interaction with rubber and plastic;
- after the water evaporates it becomes hard or jelly-like.
However, glycerin coolants have many positive properties:
- fire and explosion safety;
- environmental friendliness;
- chemical inertness to zinc;
- wide range of operating temperatures: from –30°C to 105°C;
- low cost;
- long service life - 10 years;
- do not expand when frozen.
Glycerin compositions are produced according to specifications, and this is another drawback, because manufacturers themselves set the standards.
Glycerin antifreeze is not produced in some countries.
You can also use solutions containing 40-55% ethyl alcohol as a coolant. They are environmentally friendly and crystallize at –30°C. However, their use is limited to hermetically sealed systems because they are highly volatile. The boiling point is 90°C, which is the minimum among all types of coolants.
Alcohol as a coolant.. (need advice)
I duplicate my earlier message here, now with the addition of the article: Ethylene glycol, which is part of antifreeze, when it enters the human body becomes “poison” (belongs to the third danger group) - a one-time “dose” of only 100 ml can be a lethal dose for an adult of this substance. Ethylene glycol vapors are also harmful to health. That is why antifreezes on this basis are recommended for use exclusively (!) in closed heating systems (with a closed expansion tank). If the system is open (an open expansion tank is used), the solution is to use antifreeze not based on ethylene glycol, but based on PROPYLENE GLYCOL
Article **Reefs and shoals of the sea Antifreeze**
“SHOULD OR NOT POUR antifreeze into the heating system?” - 99% of owners of individual houses ask this Hamlet question, but, like the unfortunate prince, they do not find an answer. We dare to say that there is no clear answer to this question. Antifreeze is a special coolant for liquid heating systems. There are many types of antifreeze. They are based on aqueous solutions of various substances: salts, alcohols, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, etc., to which additives are added that correct the physical properties of these solutions. Their main advantage is their low freezing point. In Russia, the most widely used antifreezes are based on an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol - NORT, DIXIS, Hot Blood. Concentrated solutions of them have a crystallization temperature of up to – 68 C. By changing the ratio of concentrate and water, you can obtain a liquid with a freezing point from – 10 ° to – 65 ° C. In addition, when cooling antifreeze, there is a gap between the temperature at which crystallization begins and the temperature at which the solution finally solidifies a significant temperature range within which both ice crystals and liquid are present. This state of the solution is called “sludge”. For example, with a 35% concentration of ethylene glycol in the solution, the antifreeze will be in a “sludge” state in the temperature range from – 20° to – 30° C, which eliminates the “rupture” of the system at these temperatures. Antifreeze contains a set of various additives - additives that should give it additional useful qualities - protect the metals included in the heating system from corrosion; dissolve and remove formed sediments and scale; prevent the destruction of seals - rubber, Teflon, paronite, sealants... The set of these additives determines the characteristics of a particular brand of antifreeze. The need for antifreeze in modern Russia is very high, because... cutting off electricity in populated areas for a long period of time and without warning is the corporate style of Anatoly Borisovich’s department. The losses of home owners from such shutdowns in winter can be calculated in amounts with many zeros. It would seem that there is a solution - fill in antifreeze and live in peace! But why then do all serious manufacturers of heating boilers not recommend using antifreeze in their products? Thus, the Slovak “PROTERM” warns: “...cast iron boilers are not designed to work with non-freezing liquids...the manufacturer is not responsible for problems caused by the use of antifreeze.” The German “VAILLANT” states categorically: “...the use of non-freezing liquids in wall-mounted boilers is unacceptable!” Less scrupulous manufacturers are more cunning. For example, they state that their products use gaskets made of paronite, which is compatible with many types of antifreeze, while keeping silent about the fact that the material of the seals is not the only problem when using antifreeze. Advertising brochures and articles, not to mention salespeople in stores, never inform customers about any restrictions on the use of antifreeze in boiler equipment. However, in the passports for the equipment of the manufacturing company, they always emphasize that the coolant is only water. (The passports, however, are carefully read after purchasing the boiler). However, we will forgive the sellers - they need to sell the goods. Our task is to provide our customers with objective information - “forewarned is forearmed.” What is the essence of the problems associated with the use of antifreeze in heating systems? First. Antifreeze is a substance whose physical properties differ significantly from the physical properties of water. This is the price paid for the low freezing temperature. The heat capacity of antifreeze is 15–20% less than that of water; viscosity is 2 – 3 times higher; volumetric expansion is greater by 40 - 60%, Moreover, these values change with changes in the concentration of the solution and are different for different manufacturers. The values of thermal conductivity, boiling point, and other physical characteristics also differ. In practice, this means that if you intend to use antifreeze in the heating system, you must make changes to the design of the heating system in advance, because all design calculations are based on the physical properties of water, not antifreeze. It will be necessary to increase the thermal power of the radiators by 40 - 50%, increase the volume of the expansion tank by 40 - 50%, increase the pressure of the circulation pump by 60%, change a number of other parameters of the heating system, including the boiler power. Obviously, the cost of the equipment will have to be adjusted. Second. Ethylene glycol-based antifreezes are quite critical to extreme operating conditions of heating systems, especially overheating. If the temperature of the water in the system, even at any one point, exceeds the critical value for a given brand of antifreeze, thermal decomposition of ethylene glycol and anti-corrosion additives will occur with the formation of acids and solid precipitation. If precipitation falls on the heating elements of the boiler, “carbon deposits” are formed, which leads to a deterioration in heat transfer in this area of the heating element, to the formation of new deposits and to further overheating of these areas. Acids formed as a result of the thermal decomposition of ethylene glycol begin to interact with the metals of the heating system, provoking their corrosion. Thermal decomposition of additives can lead to the loss of the protective properties of antifreeze in relation to the sealing material - rubber, paronite, etc. and cause leaks at connections. The use of pipelines with an internal zinc coating is prohibited. Finally, overheating of antifreeze causes it to “foam” i.e. increased foaming, which leads to airing of the system. From the above it is clear that the biggest danger for ethylene glycol antifreeze is overheating. This undesirable phenomenon can be eliminated only by carefully monitoring the operating modes of the boiler and heating system. Unfortunately, this is not always possible. It is clear why manufacturers of boiler equipment do not allow the use of antifreeze - it is impossible to correctly design a boiler without knowing the physical properties of the coolant. Third. Antifreezes have the property of increased permeability or fluidity. The more threaded connections, gaskets, and seals, the greater the likelihood of leaks. The tricky thing about antifreeze is that leaks often appear when the heating is turned off and the system has cooled down. Due to cooling, the volume of metal compounds decreases and, as a result, microchannels appear through which antifreeze begins to ooze. For this reason, all connections in the heating system must be accessible for inspection and repair. Under no circumstances should they be hidden under plaster, cladding or in a monolith. Antifreezes based on ethylene glycol are toxic, so they cannot be used to heat water in hot water systems, where if the heat exchangers are leaking, they can get into hot water distribution points, and their vapors should not penetrate into living spaces. Ignoring the listed features and properties of antifreeze when using them in heating systems can lead to a noticeable decrease in the efficiency of the system and a decrease in the service life of the equipment. Currently, new generation antifreezes are becoming increasingly widespread in Russia. These are propylene glycol antifreezes, well known in Europe since the late 90s of the last century. These antifreezes are based on an environmentally friendly substance - food-grade propylene glycol. These antifreezes are absolutely harmless and can be used in double-circuit heating systems and in refrigeration units in the food industry. Their thermal and hydraulic characteristics are similar to those of ethylene glycol antifreeze, but they are less aggressive to metals and materials of heating systems. It is characteristic that many leading manufacturers of heating boilers have already permitted the use of propylene glycol antifreeze in their boiler equipment. Despite the rather high price, propylene glycol antifreezes have a real prospect of firmly establishing themselves in the Russian market of antifreeze liquids. Currently, both types of antifreeze under different brands are already produced at several Russian enterprises.
Is there an alternative to antifreeze? Yes, it exists. Firstly, this is the construction of heating systems with electrically independent boilers. Such boilers, both domestic and foreign, are well known. Their use, however, imposes certain restrictions on the design of the heating system. Secondly, the use of backup power sources. They come in battery and electric generator types. Battery sources consist of a car battery, a charger and a voltage converter. When the power supply stops, the device automatically turns on and ensures the heating system is operational for up to 8 - 10 hours of continuous operation. The duration of this period depends on the power of the electrical devices of the heating system, the battery capacity and can be increased by adding additional batteries. When the power supply is restored, the device automatically switches to battery charging mode. The cost of such devices starts from 100 USD. They do not require separate premises and qualified maintenance. Electric generator power supplies (mini-power plants), if fuel is available, provide unlimited operating time, but are much more expensive, require a separate room and are more difficult to operate. When deciding which coolant to choose, you need to imagine how likely a long (day or more) power outage is in your area. If such an event is unlikely (your house is located in a comfortable locality with a developed engineering infrastructure), it is better to fill the heating system with water and install a battery uninterruptible power supply. You will maintain the stability of the heating system parameters and extend the service life of the boiler equipment. If your cottage community is located in an “open field”, “hangs” on one cable and outages can last for days, it is better to fill it with antifreeze. At least the equipment in which you have invested more than one thousand dollars will not have to be scrapped. When pouring antifreeze, check whether it precipitates when mixed with water. If yes, then use distilled water. Never pour antifreeze into galvanized pipes. When interacting with zinc, the water-glycol mixture forms a heavy sediment, which can damage the heating system. It is not recommended to dilute antifreeze by more than 50% - this will lead to a deterioration in its anti-corrosion properties. Antifreeze ages, so it must be replaced at intervals specified by the manufacturer (4 - 5 years), flushing the system with special compounds. In conclusion, we can only repeat what was said at the very beginning: “there is no clear answer....” Each homeowner must decide for himself which coolant to use, carefully weighing the pros and cons. In fairness, it should be noted that during the entire period of active use of ethylene glycol antifreeze in Russia, no serious accidents of boiler equipment caused by antifreeze have been recorded. (Maybe the devil is not as scary as he is painted?) In any case, taking into account the physical properties of antifreeze and following the above recommendations for their operation will reduce the negative consequences of their use to an acceptable minimum
Advantages and disadvantages
Distilled water is also used as a coolant, but if during the winter period the owners may be absent from the house for a long time or the electricity is periodically turned off, the coolant in the radiators may freeze. In such cases, it is recommended to fill the system with antifreeze for heating.
Advantages:
- pipes will not burst due to the expansion of frozen water;
- no need to drain water from the system while you are away;
- antifreeze has a low freezing point - up to –65°C, and even at a lower temperature it does not turn into ice, but becomes jelly-like, expanding to a much lesser extent than water;
- when the temperature rises, the frozen coolant retains its properties;
- the composition contains additives that prevent the formation of scale and reaction with metals.
More careful sealing is required due to the increased fluidity of antifreeze
. Disadvantages:
- low-quality antifreezes destroy the elements of the heating system, as solid sediment falls in them, which damages fittings and devices;
- lower level of heat capacity compared to water (less by 15%), to compensate for this disadvantage, it is necessary to increase the circulation rate of the coolant by exactly the same amount;
- increased viscosity (30-50% higher compared to water) and higher density (5-10%), which makes it necessary to install more powerful pumping equipment;
- toxicity;
- sediment formation over time;
- high price;
- the need for careful sealing of connections due to increased fluidity (50% higher than water).
Despite its disadvantages, antifreeze is used in heating systems because it practically does not freeze or expand, leading to damage to pipes and equipment.
Is it possible to pour alcohol into heating radiators?
Anyone who has their own heating system in a private house or cottage. Surely, sooner or later, you are faced with the question of what to replace the water with?
Water, for all its ideality, has two serious disadvantages.
It freezes at zero, and what’s even worse is that when it freezes, it expands. Broken pipes, radiators, boilers, pumps, taps, etc. When frozen, all this can be obtained in full.
There are exactly two possible solutions here. Buy ready-made and make it yourself.
The store offers a special liquid that does not freeze. Antifreeze based on ethylene glycol or polypropylene glycol. Its composition is identical to what you pour into the expansion tank of your car. Just slightly different additives.
This antifreeze has exactly two advantages.
• It really doesn't freeze or evaporate.
• It is easy to buy in the store.
It seems that what more could you ask for, this is the ideal solution, but, as always, the devil is in the details.
• It must be completely changed periodically.
• It corrodes the standard seals.
• It has lower heat capacity.
• It is more fluid when static and thicker when in motion than water.
• Those based on ethylene glycol are poisonous, and those based on polypropylene glycol are even more expensive.
The price of a more or less decent antifreeze based on ethylene glycol is 80 rubles/liter, and for those based on polypropylene glycol 120 rubles/liter.
The average volume of a heating system is 100 liters, a total of 5K-12K per coolant. In principle, it’s not particularly expensive. BUT.
It must be completely changed periodically.
Depending on the quality of the additives, every 3-5 years the entire coolant must be completely drained. It is advisable to flush the system. And fill in a new one. This is due to the fact that ethylene/polypropylene glycols are unstable. And without additives they decompose quite quickly. With the formation of insoluble precipitates in the form of flakes. Which happily settle on all sorts of narrowings. There is no point in being confident in the quality of additives. Therefore, 3-4 maximum 5 years and it is necessary to change. And if there is a defect, it may settle down in a couple of years.
It corrodes the standard seals
.
Glycols are quite aggressive, even though they contain additives, but still. Many standard seals in boilers and radiators can fail and leak over time. Therefore, by the way, many manufacturers prohibit using them as a coolant.
•It has lower heat capacity.
Standard ethylene/polypropylene glycol (for temperature -30) has a heat capacity of 3.3-3.5 kJ/kg*K (Water has a heat capacity of 4.18 kJ/kg*K)
That is, to put it simply, glycol needs to be pumped 25% more in volume. And that's not so bad.
It is more fluid when static and thicker when in motion than water.
I won’t write clever terms about kinematic viscosity and so on. I'll go straight to the conclusions. To work with any type of glycol, you may need the next pump in the model range.
That is, if you had a grudfoss 25-40 180 pump, then you will need to install a grudfoss 25-60 180.
If there was grudfoss 25-60 180 then you may need grudfoss 25-80 180, etc.
Yes, this is rude, and not a fact, but the probability is far from zero. And if replacing a conventional pump is not a problem, then nothing can be done with the one built into the boiler. And you will have to embed an additional one, and there are also problems there.
And the fact that it is more liquid (the surface tension film is weaker) can lead to the fact that joints that have never leaked will leak. And it will have to be redone.
Based on ethylene glycol, it is poisonous.
But this, IMHO, is not particularly important; polypropylene glycol manufacturers emphasize this fact more in order to compete with cheaper ethylene glycol. The system is closed and you do not have access to liquid vapor.
Well, basically everything. If all this suits you... then please.
This is a solution of ethyl alcohol, in the forty-degree version known as vodka. (Isopropyl alcohol can be used, but methyl alcohol cannot be used from the point of view of toxicity)
Its advantages are exactly the same as glycols.
• It is inexpensive. (about 35 r/l of finished coolant)
• It does not need to be changed, but only topped up if necessary.
• Does not corrode standard seals.
• Has a slightly higher heat capacity than water (in weak concentrations up to 40%).
• It is almost as fluid when static and almost as fluid when in motion as water.
• Not poisonous. (You can even drink it)
But it also has its drawbacks.
• Fire hazardous at concentrations above 40%. (therefore it is highly undesirable to do more than 39%)
• It evaporates before water.
• Freezing is not so simple.
Therefore it needs to be calculated.
Let's take Ryazan. Cold five days. This is -27 degrees C. This means the minimum for the system is -24 degrees. (Still, it’s a little warmer in the house, and even if it freezes, the alcohol mixture hardly expands and won’t break the pipes)
It turns out that I need it. 34% alcohol mixture. -23.6 gr.
The boiling point of such a mixture is 85 degrees.
Additionally, I will take into account that under pressure the liquid boils at a higher temperature. (You can use the following rule. For 1 atmosphere of pressure above atmospheric, the boiling point increases by 13%) Since on average a typical system is 2 excess atmospheres, then 85 * 1.26 = 107.1 g.
The automation of any boiler is set to a maximum temperature of 90 degrees.
107.1>90. This means that it also passes through boiling.
Total: 34% Not fire hazardous, will not freeze, will not boil. In principle, the 39% mixture gives similar results.
All that remains is to calculate how much alcohol is needed to obtain the required strength.
There is a formula to obtain the required amount of water.
X is the required number of liters of water per liter of alcohol.
N-initial alcohol concentration (typically 96%)
B-required alcohol concentration (in my case 34%)
It turns out 96/34-1 = 1.82 liters of water.
1 liter of alcohol + 1.82 liters of water = 2.82 liters of ready-made solution. 34%
But since very often the initial volume is not known, it is much easier to go not from calculations, but from the readings of an alcohol meter.
The algorithm is simple. You need to get a 34% solution.
1. Fill the system with water.
2. Drain 10 liters of water and pump in 10 liters of alcohol instead.
3. Let the system work for 10-30 minutes (you may have to add water), drain a little and measure with an alcohol meter.
4. If it turns out to be 20%, then roughly 10 liters / 20% we get 1% = 0.5 liters of alcohol. You need to add another 14% or 7 liters of alcohol.
5. Drain 7 liters from the system and fill in 7 liters of alcohol instead.
Yes, it’s rude, and not entirely correct, but quickly and effectively. Among the tools, one Chinese alcohol meter costs 100 rubles.
As a coolant, an alcohol solution is not ideal, and this is primarily due to the need for calculation.
You can’t just take and pour pure alcohol. And you can’t even use vodka, because it’s a fire hazard. Need less than 39 grams.
Temperatures of -25-28 are enough for most regions of Russia, even in dacha mode. And for home use as permanent residence it can be used anywhere.
Otherwise, it does not have all the disadvantages inherent in glycols.
When installing a heating system at home, you should not only choose the right pipes and radiators, but also pay attention to the coolant. Let's find out which coolant to choose for aluminum radiators, what conditions for using such liquids exist.
If the room space is more than 20 sq.m., then installation of an additional radiator is necessary.
Installation of aluminum radiators.
The most common coolant for a heating system is water, but it sometimes leads to numerous difficulties. This is not only corrosion, but also the formation of scale, the need for more frequent cleaning of the system. In addition, water freezes already at temperatures close to zero degrees, pipes and individual circuit elements can simply burst due to thermal expansion. Therefore, it is important not only to choose the right batteries, but also to use a non-freezing coolant. Among the advantages, it is necessary to note complete safety for humans. If the system leaks, there will be no harm to health, while antifreeze is poisonous.
As a coolant, you can use not only ordinary water, but also specially produced antifreeze. Such mixtures do not freeze even at low temperatures, without changing their qualities at all. Each variety has its own limits, this must be taken into account when choosing.
Antifreeze contains special additives that are inhibitors of corrosion and various mineral deposits.
Installation diagram of an aluminum radiator.
But when purchasing, you should choose exactly those compounds that are suitable specifically for aluminum heating radiators. But such coolants also have their drawbacks:
- heat capacity is fifteen percent lower than that of water;
- high viscosity, that is, a pump is required to ensure circulation in the system;
- when heated, strong expansion is observed;
- fluidity is 50 percent higher than that of water, that is, high demands are placed on sealed connections;
- ethylene glycol antifreezes are poisonous and can only be used for single-circuit boilers.
You can make your own radiator mixture. To do this you will need: distilled water and 40% ethyl alcohol.
To use antifreeze in a heating system, it is not always possible to fill in ready-made commercial mixtures. In this case, you can use a coolant that can be easily prepared with your own hands. you ask how is this possible? Everything is very simple, this coolant is a non-freezing mixture of distilled water and forty percent ethyl alcohol. Such antifreeze, prepared with your own hands for the heating system, has the following characteristics:
- the viscosity of the liquid is slightly higher than that of water, but much lower than that of commercial antifreeze;
- fluidity is less than antifreeze, which makes it possible to somewhat reduce the requirements for the tightness of circuit connections. Rubber seals are not damaged when using this particular liquid;
- Alcohol-based mixtures have another advantage, making them an excellent choice for metal radiators. The fact is that alcohol prevents the development of corrosion, and this is important for systems whose destruction can lead to a variety of troubles;
- in this case, it is recommended to use hard water for the heating system, which, together with alcohol, prevents the formation of scale on the internal surfaces. The sediment is formed in solid form; during preventive flushing it is very easily removed from the system;
- when the alcohol content in the mixture is 30 percent or more, it does not evaporate separately;
- The boiling point of the alcohol coolant is approximately equal to the value for ordinary water. That is, when the temperature rises to 85 degrees Celsius, it does not boil with the formation of large masses of steam;
- alcohol in the coolant composition reduces thermal expansion, that is, when freezing, heating pipes and other elements are not damaged.
If you have to choose between water and an alcohol mixture, many experts recommend giving preference to the second option (if the boiler design allows this). The proportions of this composition are calculated based on what temperature values are planned:
If for some reason the boiler is turned off, be sure to drain the hot water from the radiator, otherwise the pipes may burst.
- when the temperature drops to minus 10.6 degrees, the alcohol content should be 20.3 percent;
- when it drops to minus 23.6 degrees, the alcohol content is 33.8 percent;
- when freezing to minus 28.7 degrees, the alcohol content should be 39 percent;
- when reduced to minus 33.9 percent, the alcohol content is 46.3 percent.
When preparing coolant for aluminum radiators, the volume must be calculated based on the fact that one liter of 96% ethyl alcohol contains 960 ml of anhydrous alcohol. To obtain a 33% alcohol solution, you need to divide 96 by 33, which will give a volume of 2.9 liters. When adding 2.9 liters of water to one liter of alcohol, we obtain a 33% alcohol solution, which is an excellent coolant, poured into an aluminum radiator for the heating system. The resulting solution will not freeze even at temperatures down to minus 22.5 degrees.
When should you not use antifreeze? But it is not always possible to use such a convenient and effective coolant as antifreeze for a heating system. If you are still choosing what exactly to use, consider the following factors:
Calculation of the required radiator power.
- It is strictly forbidden to take antifreeze if ion (electrolysis) boilers are used. In them, heating is carried out by passing current through the entire volume of the boiler tank, and this is unacceptable for antifreeze. When designing a home heating system, make sure that it can be used with a certain type of coolant;
- Antifreeze cannot be used in an open system. But in this case, such a ban applies only to those mixtures that are produced on the basis of toxic ethylene glycol; the rest can be used in open circuits, if there is a manufacturer’s indication for this;
- You cannot reduce the temperature to more than minus 20 degrees. This can seriously reduce the characteristics of the additives included in the composition, that is, pockets of corrosion will appear inside the system and scale will appear;
- When making hermetic connections, it is not recommended to use linen winding, which is coated with ordinary oil paint on top. When using antifreeze in heating aluminum radiators, it is allowed to use linen winding only with sealants, since oil paint is easily corroded by antifreeze, and this leads to a complete loss of tightness;
- Antifreeze cannot be used when galvanized fittings and pipes are used for the heating circuit;
- When the boiler heats the coolant to a temperature above 70 degrees Celsius, antifreeze can no longer be used. This value is the limit for most of these mixtures, which have the highest thermal expansion at higher temperatures.
When choosing antifreeze for aluminum radiators, you need to remember some conditions for working with it. These rules are mandatory for use; they will make the operation of the circuit not only more efficient, but also safer:
- The heating system must be equipped with a more powerful circulation pump than is required for conventional water heating. If the length of the circuit is quite large, then it is necessary to install an external installation of the circulation pump;
- installation of a special expansion tank is required, that is, a capacious expansion tank, the volume of which will be approximately twice that required for a traditional water circuit;
- It is recommended to use large-volume aluminum radiators, as well as heating pipes;
- you cannot install automatic air vents; when using antifreeze in the system, you can only install manual taps, for example, Mayevsky;
- When making detachable connections, you can use sealing gaskets only made of paronite, chemically resistant rubber, or Teflon. Many experts advise using linen winding, which is sealed with a sealant that is resistant to ethylene glycol (if a coolant based on it is used);
- It is not recommended to dilute antifreeze with water, but if this is allowed by its composition, then you can only use purified, distilled water. Melt and rain water are absolutely not suitable for this;
- Before pouring antifreeze for aluminum radiators, it is necessary to carry out preparatory work. The entire circuit, including the boiler, should be flushed with water. The timing of replacement is regulated by antifreeze manufacturers, but experts recommend doing this once every two to three years; you cannot leave the coolant in the system for a longer period of time;
- After antifreeze is poured into the system, you should not immediately put a very large load on the boiler, that is, put it at a high temperature. In this case, it is recommended to increase the temperature gradually so that the coolant has time to warm up smoothly. Such a liquid has a lower heat capacity than water, so this condition must be strictly observed.
Special mention should be made about the water coolant. If in cold weather, for various reasons, the boiler is stopped for a long period, then it is necessary to drain all the hot water that may be there from the heating system in order to prevent rupture of the pipes.
Heating a home: how to choose a coolant for a radiator? When choosing antifreeze or any other coolant for a heating system, numerous factors must be taken into account. This must be done at the design stage of the entire heating system, since the water system is not suitable for the use of antifreeze.
If the temperature in the cold season in the general circuit does not fall below five degrees Celsius, then it is best to prefer a type of coolant such as water, but all salt compounds must be removed from its composition as much as possible. When the temperature in the house is expected to drop to sub-zero levels, only antifreeze can be used, since the water will simply freeze under such conditions. To avoid freezing, you can completely drain all water from the heating system, but there is one serious drawback. The fact is that the radiators will fill with air, and this will lead to corrosion in the presence of high humidity.
There is another way to avoid freezing by using water as a coolant, but for this it is necessary to build in special electric heating elements, which will be controlled using temperature sensors or an installed remote control. This option allows you to maintain the temperature level in the system above 5 degrees Celsius, but the cost of the heating circuit increases many times, that is, it is cheaper to immediately install a system designed for antifreeze. When choosing the required antifreeze for the circuit, you should pay attention to the following characteristics:
- extremely low temperature that can be maintained by the coolant;
- the composition of the liquid, its purpose, that is, for which system it is intended;
- purpose of antifreeze. Is the coolant intended to work in aluminum radiators, how does it interact with plastic pipes, rubber, steel elements, etc.;
- length of time for using antifreeze;
- coolant safety. You should pay attention to how safe the liquid is for humans if it is necessary to drain it after its service life has ended).
But the color of antifreeze for radiators does not matter at all, it simply shows what brand the liquid belongs to.
The choice of coolant when installing a heating system is a fairly important part of the operation of the entire circuit. The efficiency of home heating, its safety, and service life depend on the right purchase. Today, for aluminum radiators, which are becoming increasingly popular, several types of coolants can be used. This is ordinary water, antifreeze based on various components and a special mixture of water and ethyl alcohol. The choice of coolant largely depends on what conditions of use of the system are observed, since it is not always possible to fill it.
Features of using antifreeze in the heating system
When replacing antifreeze, the old liquid is completely drained from the heating system
. Since glycol compounds are unsafe, precautions must be taken when using them. In addition, there are certain features of using antifreeze in the heating system:
- Glycol coolant should not be poured into an open system where the liquid in the expansion tank is in contact with the atmosphere, because toxic substances may be released into the air. This is only allowed when using propylene glycol coolant if there is confidence in its quality.
- When purchasing coolant from another manufacturer in order to add it to the system, you need to check for compatibility with the old antifreeze, because the additives can neutralize each other, which leads to the disappearance of the anti-corrosion properties. If it is not known which coolant was used previously, the liquid must be completely drained.
- To work in a system with antifreeze, you will need a pump 60% more powerful than for water.
- Radiators must be selected with a higher degree of heat transfer, for example aluminum or bimetallic. In addition, it is advisable to choose a model with a large internal diameter and volume.
- The system does not work with automatic air vents, so Mayevsky taps are installed.
- The system must be equipped with an accurate temperature controller, since exceeding certain limits leads to the disintegration of the coolant. The reaction is accompanied by precipitation, which subsequently causes the formation of soot, corrosion, acid, foam and airing of the system.
Only with proper operation and compliance with all recommendations for the selection of equipment will the use of antifreeze in the heating system be beneficial.
Antifreeze based on ethyl alcohol
A solution of alcohol and water is used in a concentration of 40-55%. The freezing point of this composition is -30 ˚С. The substance is safe and environmentally friendly. This type of mixture is recommended for use only in closed-circuit systems where there is forced circulation of liquid. Alcohol is a volatile material that evaporates easily and its concentration decreases over time in an open system. It is not recommended to use ethyl alcohol solution at high temperatures, since its boiling point is 90 °C.
Pouring coolant into the heating system with your own hands
After draining the antifreeze, the system is washed with clean water.
Antifreeze for heating ages over time, its heat capacity and anti-corrosion properties decrease, so it is changed periodically. The average frequency is 5 years. Before adding coolant, it is necessary to drain the old antifreeze from the system.
Work order:
- Be sure to warm up the heating boiler, regardless of the ambient temperature.
- Open the batteries and switch the system to gravity mode.
- Disconnect the boiler and other system devices from the power supply.
- Prepare buckets and basins for draining the old coolant.
- Using a shut-off valve, the pump is disconnected, since without coolant it instantly fails. The old antifreeze will remain inside, but its volume will be small, so it will not affect the operation of the system.
- Open the valve and fill the containers. It is preferable to drain the system through a filling valve located near the boiler, at the lowest point. If a drain hole is not provided, connect one end of the hose to the drain hole of the battery or to the Mayevsky tap, and insert the other end into the container.
- After draining the coolant, the system is washed with clean water or solutions specially designed for this purpose.
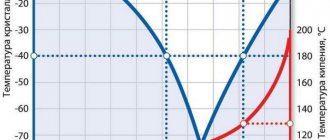
- In accordance with the manufacturer's instructions, the liquid is diluted according to the required freezing point. The freezing temperature has a nonlinear dependence on the amount of water poured in - when diluting 20 liters of antifreeze with a freezing point of –65°C with 50% water, the freezing temperature will be –20°C, and not –32.5°C, as one might assume.
- Clean the dirt filter.
- Using a pump connected to the injection hole, the system is filled with fresh composition.
- During operation, it is necessary to bleed air, monitoring the pressure using the pressure gauge.
To dilute the coolant, use only distilled water that does not contain calcium and magnesium salts, otherwise a precipitate will form. As a last resort, you should check the reaction by separately mixing tap water with a small amount of antifreeze in the required proportions. It is imperative to combine the composition with water in a separate container to ensure uniform mixing. You cannot pour antifreeze first and then water into the system. This leads to uneven heating of radiators, failure of pumping equipment, and foaming. If, unknowingly, the system was filled in this way, the pump is turned on at minimum power and the air is gradually released. Mixing will occur after some time, but there is no guarantee that it will be uniform.
If ethylene glycol coolant is poured into the system, the containers used in the process should be disposed of and the pump should be washed with hot water and detergent.
Ethylene glycol in antifreeze
For home use, mixtures based on ethylene glycol are used. This is a toxic substance that, if it comes into contact with the skin, causes chemical damage and poisoning. The freezing point is - 30 ˚С, at a concentration of 45%. When the amount of ethylene glycol is 65%, the freezing point reaches – 65 ˚С. You can choose the most optimal composition option on the website, depending on your individual characteristics and final goals.
Disadvantage : sensitivity to overheating. A short-term rise in temperature above the stated limit leads to the fact that the solution decomposes into acids and a precipitate that is insoluble in water forms. The sediment can form carbon deposits, which reduce the efficiency of the heat exchanger, causing re-overheating and sludge formation. Acids enter into a chemical reaction with the metal elements of the system - forming local foci of corrosion, which ultimately lead to the destruction of the circuit.
It is necessary to carefully monitor the temperature of the heat exchanger where ethylene glycol-based coolant is used.
Propylene glycol
Propylene glycol is one of the types of glycol used as a coolant. It is less dangerous for the human body. The composition of such antifreeze must include additional additives that help maintain the integrity of the metal used in the system. Additives are used that prevent oxidation and reduce foaming.
Such compositions can be used in double-circuit boilers, since in the event of a leak their release into the water does not harm a person.
The disadvantage is the high cost. A composition based on propylene glycol is 2-2.5 times more expensive than a similar substance created on the basis of ethylene glycol.
Manufacturers of coolants
It is necessary to buy liquid in trusted stores so as not to damage your heating system.
Antifreeze consists of 30-65% glycol, 30-50% distilled water, 3-4% additives that prevent foaming, metal corrosion, and sedimentation. The market offers a wide range of antifreezes designed for the heating system of a country house. They are made mainly from imported raw materials and are sold at approximately the same price. If a product is too cheap, you should doubt its quality. You can check the composition using soda. Since counterfeit antifreezes are mostly acidic, you can mix a pinch of soda with a small amount of coolant. If hissing is observed and foam forms, the product is of poor quality; if no reaction occurs, the antifreeze is good.
The best antifreezes are the following:
- Dixis-65. Coolant with the best crystallization performance. This antifreeze is suitable for gas and electric heating boilers, systems with elements made of cast iron, copper, plastic, aluminum, and brass. Ambient temperature from –65°C to +95°C. Can be used to heat houses in the Far North. When used in milder climatic conditions, the coolant can be diluted 1:1 with water. Advantages: service life - at least 5 years, fire safety.
- Warm Eco house. Propylene glycol coolant with a crystallization temperature of –31°C. Service life – 5 years or more. The boiling point is 106°C, and destruction occurs only at +170°C. It is compatible with sealants and does not expand.
- Thermagent-65. Antifreeze of domestic production, made from German raw materials. Can be used in systems with rubber gaskets and sealant. Retains properties for up to 10 years and has a low freezing point. Can be used in ambient temperatures down to –65°C.
Antifreeze is a coolant that has a lower expansion coefficient compared to water. This property is of primary importance. In other physical and technical parameters, water is superior to antifreeze. The use of antifreeze must be competent. Then the service life of the system will increase.
Types of coolants and differences between them
There are several main liquids used as coolants:
- water;
- antifreeze, based on ethyl alcohol;
- ethylene glycol based antifreeze;
- based on propylene glycol.
Water is a cheap liquid that is safe for the environment. In case of accidental leaks, such coolant does not cause harm to humans. Restore the previous volume of liquid by simply adding water to the expansion tank.
Disadvantages of water as a coolant:
- During operation, scale forms, which reduces heat transfer, resulting in increased energy consumption;
- if the heater is turned off and the pressure in the system decreases at sub-zero temperatures, it freezes, expands and renders the entire heating system unusable;
- it is necessary to replace it at least once a year, unlike antifreeze, which can last more than 5 years.
Antifreeze has a low freezing point. It maintains the system circuit even when the heater is turned off. Antifreeze is a solution consisting of water and glycol with the addition of additives.